Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adobe Scan 06 Feb 2023
Uploaded by
Rudraksh BairagiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adobe Scan 06 Feb 2023
Uploaded by
Rudraksh BairagiCopyright:
Available Formats
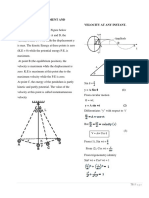
acipe ofsuperposition ofw a v e s
h u t when two or more waves overlap in medium the
a resultant displacement of aparticle is the
calic sum of the displacement due to each wave
t . bethedisplacementofthe particles due todifferent wavesofthe particlethem
themet dinplacement is pven by
Y-Y.0-Y r.9-Y,(r.9....
otas ta.0010130 SMS 1695at5
XPHYSICS WAVES
Interferenee of wavees
Consider to harmonie progressive wave on a stretched string both with same
frequency and same angular wave number kthey only differ in the
amplitude. A, angular
initial phase by p the
equation are
YA sin (kx - t )
*Asin (kx-t P)
When the two waves
superimpose by the principle of superposition we have the net
displacement
Y Y+Y
A sin (kx- ot) sin
+
(kx- at+
9)
2A sin ot+kx-ot+
By sinA+sinB - 2sincos
=Y-2Acos sin kx-t + )
quation ( i s also a harmonic travelling waves w i t h same frequency and wavelength and initial phase
angle
But its amplitude is a function of phase
angle p
A'-2Acos
g=0ie, the two waves are in face
A-2Acos0 A=2A
In this case the amplitudes are added and hence the
condition is called constructive interference.
fg= 180 ( ) ie, the two waves are out of face r first harmonic
A=0
d harmo
The amplitudes gets subtracted hence it is called
destructive interference
Standing waves and normal modes
Consider a wave uavelling along the we x-axis
Y,-Asiolkox F ot)
And a reflected waves from an open boundary of the
sanae anplitude and wavelength in theve direction
x-as Y, A sinkox + at)
By the principle of superposition K acme
Y-Yi+Y 1C
=A sin (kx- t ) +A sin (kx + ot)
the Be
=A [sin (kx -ut)+ sin (kx + wt)
ALL:0761-4064225 (3.00 TO 2.30 PM) SMS: 78799854295
You might also like
- Pertemuan II Gelombang Dan Optik 2013Document42 pagesPertemuan II Gelombang Dan Optik 2013Yunia TriashariNo ratings yet
- Wave Motion Sound WaveDocument69 pagesWave Motion Sound WaveRizwanbhatNo ratings yet
- Final Lecture11Document48 pagesFinal Lecture11ViralBipinchandraRathodNo ratings yet
- Protein Structure Determination '16Document34 pagesProtein Structure Determination '16Brandon ArceNo ratings yet
- Physics TextbookDocument544 pagesPhysics TextbookHannah Coker100% (1)
- Mechanical WavesDocument23 pagesMechanical WavesAgus SetyawanNo ratings yet
- Geophysics Lec4Document19 pagesGeophysics Lec4R P SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Wave MIC_Part-2_29-11-2023Document72 pagesWave MIC_Part-2_29-11-2023Krish RawatNo ratings yet
- 5 Metodos de Discretizacao 05Document79 pages5 Metodos de Discretizacao 05Jefferson FelipeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document22 pagesChapter 15Rynardt VogelNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2022 PDF DownloadDocument16 pagesJEE Main 2022 PDF DownloadHh HhNo ratings yet
- Physics Ch4 NotesDocument22 pagesPhysics Ch4 NotesAli GorganiNo ratings yet
- Text Sections 16.2 - 16.5 - Sinusoidal Waves - Energy and Power in Sinusoidal WavesDocument7 pagesText Sections 16.2 - 16.5 - Sinusoidal Waves - Energy and Power in Sinusoidal WavesÐânĩĕl JøŚĕ CäŚŧrø ÂrïźăNo ratings yet
- Hecht - Chapter 2Document44 pagesHecht - Chapter 2JunHyoung KimNo ratings yet
- Prelimexam Jan 2018 Thur FriDocument14 pagesPrelimexam Jan 2018 Thur FriAyushNo ratings yet
- Guided Revision: Section-I Single Correct Answer Type 9 Q. (3 M (-1) )Document25 pagesGuided Revision: Section-I Single Correct Answer Type 9 Q. (3 M (-1) )royalNo ratings yet
- WAVES STUDYDocument22 pagesWAVES STUDYFathima IshahathNo ratings yet
- PH6 (Ondes Progressives)Document8 pagesPH6 (Ondes Progressives)chihebNo ratings yet
- Physics 2: ASSIGNEMENT 1: Total Marks 40 (Assignment One 20 and Assignment Two 20)Document2 pagesPhysics 2: ASSIGNEMENT 1: Total Marks 40 (Assignment One 20 and Assignment Two 20)humbleNo ratings yet
- Transverse WavesDocument27 pagesTransverse WavesDivya GovindarajNo ratings yet
- ENM206 Well Completions & Subsea Systems: The Offshore Environment and Offshore LoadingDocument23 pagesENM206 Well Completions & Subsea Systems: The Offshore Environment and Offshore Loadingipali4christ_5308248No ratings yet
- Offshore Wave Modelling & Pipeline LoadingDocument23 pagesOffshore Wave Modelling & Pipeline Loadingipali4christ_5308248No ratings yet
- Unit 2: Oscilations and Waves: RestoringDocument27 pagesUnit 2: Oscilations and Waves: RestoringDandy H HerkoNo ratings yet
- Notes ChemistryDocument18 pagesNotes ChemistryVibha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Wave_Motion_Short_Notes65dd7338188cf00018e54b2bDocument2 pagesWave_Motion_Short_Notes65dd7338188cf00018e54b2bDevansh BansalNo ratings yet
- CPH O2022 EnglishDocument16 pagesCPH O2022 EnglishHieu Phung Cong100% (2)
- Waves 1Document22 pagesWaves 12023MEB023 RUPANJANBHATTACHARYYANo ratings yet
- Propagation of Light Waves: 7.1 WavefrontsDocument4 pagesPropagation of Light Waves: 7.1 WavefrontsNiaNo ratings yet
- List of Formulae (Waves)Document1 pageList of Formulae (Waves)jeffNo ratings yet
- SAT Waves Teacher's GuideDocument7 pagesSAT Waves Teacher's GuideAmulya SreeNo ratings yet
- Traveling WavesDocument5 pagesTraveling WavesJoe SmithNo ratings yet
- Interference DiffractionDocument44 pagesInterference DiffractionMansi NegiNo ratings yet
- Physics WavesDocument10 pagesPhysics WavesJerry GJNo ratings yet
- Waves on a String ExplainedDocument27 pagesWaves on a String ExplainedBijimol BinuNo ratings yet
- Wave Motion and Sound-1 PDFDocument26 pagesWave Motion and Sound-1 PDFPriyanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Wave Motion Shyam PDFDocument84 pagesWave Motion Shyam PDFohyeah142008No ratings yet
- Chapter3 1 OscillationDocument32 pagesChapter3 1 Oscillation杨俊熙(Stanley)No ratings yet
- PHY11101 - Mechanical WavesDocument3 pagesPHY11101 - Mechanical WavesMD. SHAEKH ZAHAB CHOWDHURYNo ratings yet
- PHY 102: Waves & QuantaDocument15 pagesPHY 102: Waves & QuantaIik IkhsanNo ratings yet
- Four Fundamental Forces of NatureDocument3 pagesFour Fundamental Forces of NatureRaneemNo ratings yet
- 49waves No AnsDocument6 pages49waves No Ans黄心怡No ratings yet
- Wopho Problems PDFDocument17 pagesWopho Problems PDFIonel ChiosaNo ratings yet
- HSSRPTR - Plus One Chapter-15-FullDocument22 pagesHSSRPTR - Plus One Chapter-15-FullSPARTANo ratings yet
- Wave Motion on a StringDocument17 pagesWave Motion on a StringAnkit JhaNo ratings yet
- Unit I Quantum Mechanics-1Document23 pagesUnit I Quantum Mechanics-1uttamshetty27No ratings yet
- Wave and OscillationDocument25 pagesWave and OscillationEfty's InnovationNo ratings yet
- Wave On A String TheoryDocument20 pagesWave On A String TheoryrgNo ratings yet
- Eng Vibration Handout 3Document4 pagesEng Vibration Handout 3Je SolarteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14-OscillationsDocument23 pagesChapter 14-Oscillationszeus292122No ratings yet
- Grade Xii Book IIDocument137 pagesGrade Xii Book IIEdwinNo ratings yet
- Waves: Chapter - 00Document24 pagesWaves: Chapter - 00Raichal P BijuNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic WavesMạnh HiếuNo ratings yet
- Wopho ProblemsDocument17 pagesWopho Problemshantarto5844100% (1)
- DPP 2 Waves on StringDocument3 pagesDPP 2 Waves on Stringupanshupandit3No ratings yet
- On The: FloatingDocument57 pagesOn The: FloatingCarlos JoseNo ratings yet
- Oscillations PDFDocument10 pagesOscillations PDFmanas nikhilNo ratings yet
- AP10005 - PhysI - Chap16 (Physic 1)Document25 pagesAP10005 - PhysI - Chap16 (Physic 1)白卡持有人No ratings yet
- Travelling Wave 1Document25 pagesTravelling Wave 1Zal FaarizNo ratings yet
- Graphite India Specialty Division ProfileDocument13 pagesGraphite India Specialty Division ProfileMADDI MADHAV.No ratings yet
- Hous1998 O9801042Document52 pagesHous1998 O9801042John Barry Leonard JrNo ratings yet
- Aw60 40le Zip in PDFDocument10 pagesAw60 40le Zip in PDFJosé Monteiro100% (2)
- Turbojet Engine With T-S DiagramDocument10 pagesTurbojet Engine With T-S Diagramprakash tyagiNo ratings yet
- Hoisting & Rigging Handbook - AEDC PDFDocument341 pagesHoisting & Rigging Handbook - AEDC PDFLim100% (1)
- Disabled Systems: Customer Name Reference Product Series NoDocument17 pagesDisabled Systems: Customer Name Reference Product Series NoАлександр КачеишвилиNo ratings yet
- Perkins KENR6223-02Document48 pagesPerkins KENR6223-02Jacques Van NiekerkNo ratings yet
- Austria's Largest Pumped Storage Power Plant Kopswerk IIDocument4 pagesAustria's Largest Pumped Storage Power Plant Kopswerk IIjoaoaugusto79No ratings yet
- API PLAN 62 - Installation of Steam Traps in Steam QuenchDocument3 pagesAPI PLAN 62 - Installation of Steam Traps in Steam Quenchrmehta26No ratings yet
- Colchester Alpha Brochure 2021Document7 pagesColchester Alpha Brochure 2021KhalilullahNo ratings yet
- R1150RT Elec DiagramDocument3 pagesR1150RT Elec DiagramJuan Garcia100% (2)
- Scooptram ST2D: Underground Diesel Loader With 3.6 Tonne Load CapacityDocument5 pagesScooptram ST2D: Underground Diesel Loader With 3.6 Tonne Load CapacityJohel Bautista HernandezNo ratings yet
- CC2500-1 Engine BeltDocument2 pagesCC2500-1 Engine BeltRyan LabradorNo ratings yet
- Overhauling For Maag Gear Box (CPU Version) of Tube MillDocument60 pagesOverhauling For Maag Gear Box (CPU Version) of Tube MillMahmoud Mohammad100% (6)
- Blademodeler: Ansys, Inc. Proprietary © 2009 Ansys, Inc. All Rights Reserved. April 30, 2009 Inventory #002693Document19 pagesBlademodeler: Ansys, Inc. Proprietary © 2009 Ansys, Inc. All Rights Reserved. April 30, 2009 Inventory #002693Ssheshan PugazhendhiNo ratings yet
- Welding Metallurgy: Sindo KouDocument15 pagesWelding Metallurgy: Sindo Kouyuvraj mohiteNo ratings yet
- Project Report On ATV Prototype BAJA SAE INDIADocument60 pagesProject Report On ATV Prototype BAJA SAE INDIAsanket50% (6)
- (20837429 - Polish Maritime Research) Design and Strength Calculations of The Tripod Support Structure For Offshore Power PlantDocument11 pages(20837429 - Polish Maritime Research) Design and Strength Calculations of The Tripod Support Structure For Offshore Power PlantLuthfi Rasyid100% (1)
- Composites Data SheetDocument2 pagesComposites Data Sheetvlade naumovskiNo ratings yet
- Bending The RulesDocument2 pagesBending The RuleskikiuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16: Drying - Grain Drying, Types of Drying, Types of Dryers, Importance of DryingDocument10 pagesChapter 16: Drying - Grain Drying, Types of Drying, Types of Dryers, Importance of Drying9567592146No ratings yet
- Assignment Shaft DesignDocument4 pagesAssignment Shaft DesignHasham Mehmood100% (1)
- Detailing of Reinforcment in Concrete Structures: 8.1 ScopeDocument34 pagesDetailing of Reinforcment in Concrete Structures: 8.1 ScopeARIFUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Hose Truck IntercoolerDocument25 pagesHose Truck IntercoolerCassie ZengNo ratings yet
- Design of Gas Induction Reactors PDFDocument32 pagesDesign of Gas Induction Reactors PDFRavindra V. LakhapatiNo ratings yet
- Tier 3Document11 pagesTier 3arun kurlanNo ratings yet
- Esl IntensifierDocument44 pagesEsl IntensifierdguyNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Small Volume ProverDocument48 pagesService Manual Small Volume ProverdrejasNo ratings yet
- Manual de Taller GX390 PDFDocument196 pagesManual de Taller GX390 PDFEDDU CAMPOS SANDOVAL100% (3)
- ME 323-A2M (PROPERTIES AND CHARACTERICTICS OF OF MATERIALS) Tadeo, Clarisse F.Document2 pagesME 323-A2M (PROPERTIES AND CHARACTERICTICS OF OF MATERIALS) Tadeo, Clarisse F.Tadeo, Clarisse F.No ratings yet