Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy Notes - Lecture 1
Uploaded by
ellie0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesOriginal Title
anatomy notes - lecture 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesAnatomy Notes - Lecture 1
Uploaded by
ellieCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
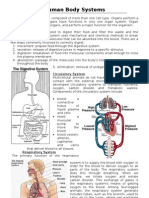
BODY SYSTEMS AND MAJOR ORGANS
BIOL122 – ANATOMY AND TISSUE STRUCTURE
LECTURE ONE
Learning Objectives
Outline the eleven body systems.
Describe their major organs and functions.
Describe some of the interrelationships between them.
Six Levels of Organisation
Chemical > Cellular > Tissue > Organ > System > Organismal
Organs interact to maintain homeostasis in an ever-changing environment in an organism.
The Body Systems:
1. Integumentary.
2. Skeletal.
3. Muscular.
4. Cardiovascular.
5. Lymphatic and immune.
6. Endocrine.
7. Nervous.
8. Respiratory.
9. Digestive.
10. Urinary.
11. Reproductive.
System Components Function Interrelationships with Systems
Integumentary Skin. Protection. E.g. water barrier, microbes & Waste elimination is not primary system for this,
Hair. sun. primary system is kidneys!
Nails. Temperature regulation. E.g. sweat.
Sweat glands. Waste elimination.
Oil glands. Helps make vitamin D.
Detects sensation – hot, cold, touch, pain.
Skeletal Bones. Support and protection. Blood cells produced interact with the cardiovascular
Joints. Muscle attachments. system.
Cartilages. Houses cells that produce blood cells.
(bone marrow)
Stores minerals and lipids.
Muscular Skeletal muscle. Enables movement. Interacts with the integumentary system e.g. the
Stabilises body position (posture) generation of heat, reacts by sweating.
Generates heat. Interacts with nervous system to maintain posture.
Cardiovascular Blood. Transport of substances e.g. gases, Interacts with respiratory system to regulate gases.
Heart. (cardiac smooth muscle nutrients, waste, hormones. Interacts with urinary system as excretes waste for
under involuntary control) Regulation. regulation and water content.
Blood vessels. Temperature regulation. Interacts with endocrine system as transports
Water content regulation. hormones.
Defence against disease. (WBCs)
Repair of tissues.
Lymphatic and Lymphatic fluid. Returns proteins and fluid to blood. Lymphatic fluid formed from tissue fluid moving from
Immune Lymphatic vessels & lymph nodes. Carries lipids from GI tract to blood. blood into tissue. Arterial end of capillary – high blood
Bone marrow (WBC formed), Protects against disease and cancer. pressure, fluid move out of blood into tissue and vice
spleen (WBC maturation), thymus, (lymph full of WBC) versa at venous end due to lower pressure in capillary. Not
tonsils. all fluid can be reabsorbed into capillary – goes onto form
lymph.
Endocrine Hormone producing glands. Co-ordinates body functions. Pituitary - growth hormone.
E.g. hypothalamus, pituitary, thymus, Releases hormones from glands to have Vasopressin - water regulation Oxytocin - maternal
thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, effect on target organs. bonding & lactation.
ovaries and testes. Thyroid gland - thyroxin
Pancreas - insulin & glucagon
Adrenal gland – adrenaline & cortisol (stress hormones)
Testes – testosterone.
Ovary – oestrogen progesterone
Nervous Brain. Generate nerve impulses to regulate body CNS & PNS
Spinal cord. activities. Interacts with all body systems to generate reaction.
Nerves. Detects stimuli and responds to them. Interacts with muscles and glands. (skeletal and
Special sense organs. E.g. eyes, Initiates muscles contraction or gland endocrine)
ears. secretion. Thermoreceptors = body temp.
Baroreceptors = blood pressure.
Osmoreceptors = concentration of body fluids
Chemoreceptors = chemicals in the body
Respiratory Lungs and air passages. Gaseous exchange. interacts with cardiovascular system as oxygenates
Pharynx (throat), larynx. (voice Regulates acid-base balance of body blood.
box) fluids. (important role in regulating body
Trachea, bronchioles, alveoli. pH)
Enables sound production when air passes
through vocal cords.
Digestive Organs of the GI tract: Physical and chemical breakdown of Pancreas interacts with endocrine system as secretes
Mouth. food. hormones e.g. insulin to break down glucose.
Pharynx. Absorbs nutrients.
Oesophagus. Eliminates solid waste.
Stomach.
Small and large intestines.
Accessory organs:
Salivary glands.
Gall bladder.
Liver.
Pancreas.
Urinary Kidneys. Produce, store, eliminate urine. Interacts with brain to release ADH to make us
Ureters. Eliminates metabolic wastes. conserve water.
Bladder. Regulates volume and chemical Kidneys produce erythropoietin which acts on red bone
Urethra. composition of the blood. marrow to produce RBC.
Helps to maintain the acid-base balance of
the body fluids.
Regulates production of red blood cells.
Reproductive Female: Gametes production. Sexually dimorphic – different in makes and females.
Ovaries. Hormone release – regulate reproduction
Uterus. and associated body changes during
Fallopian tubes. puberty
Vagina.
Male:
Testes.
Epididymis.
Vas deferens.
Penis.
You might also like
- Chapter 1 AnaPhy Notes - ReviewerDocument6 pagesChapter 1 AnaPhy Notes - ReviewerDanielle LeighNo ratings yet
- Human Body SystemsDocument4 pagesHuman Body Systemsoiu7hjjs100% (15)
- Body Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveDocument3 pagesBody Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveMicaela DNo ratings yet
- Grade 8Document5 pagesGrade 8Geneva Faye Lirazan MendozaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 1Document28 pagesOverview of Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 1Vincent Dajao CimafrancaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory ReviewerDocument8 pagesRespiratory ReviewerBLAIRY ZYNo ratings yet
- Organ SystemDocument2 pagesOrgan SystemCristina RamirezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology (Abridged) PDFDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology (Abridged) PDFJust IsaacNo ratings yet
- Human BodyDocument3 pagesHuman Bodyjavier andres martinez100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Typhoid FeverDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Typhoid FeverCharise Ligores67% (6)
- P7 Irama Biologis Tubuh Dan Shift Kerja2Document34 pagesP7 Irama Biologis Tubuh Dan Shift Kerja2Yudha Adi KusumaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyAnonymous 2k0o6az6lNo ratings yet
- Bioscience 1 NotesDocument21 pagesBioscience 1 NotesLulu0% (1)
- System Structure Purpose Interaction With Other SystemDocument1 pageSystem Structure Purpose Interaction With Other SystemLianne LagromaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Ch1 To Ch6Document30 pagesReviewer - Ch1 To Ch6cpagente01No ratings yet
- Anatomy AssessmentDocument7 pagesAnatomy AssessmentTrevannie EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Importance of Studying Anatomy and Physiology. Relate It With Your Daily ActivitiesDocument6 pagesDiscuss The Importance of Studying Anatomy and Physiology. Relate It With Your Daily ActivitiesJamaica SimanganNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesEssentials of Anatomy and PhysiologyAlexandrea ModillasNo ratings yet
- HESI Review 2020Document25 pagesHESI Review 2020Hannah BlasurcaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology NotesHimiko JacksonNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Notes Human Body Cells TissuesDocument21 pagesAnaPhy Notes Human Body Cells TissuesRON PEARL ANGELIE CADORNANo ratings yet
- SMBB3273 Short NoteDocument14 pagesSMBB3273 Short NoteWafiNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY 10 REVIEWER - 3rd QuarterDocument10 pagesBIOLOGY 10 REVIEWER - 3rd QuarterGeromme TudNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument19 pagesAnaphy ReviewerGian Paolo P. CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- Human Being Are Complex Multicellular OrganismsDocument9 pagesHuman Being Are Complex Multicellular OrganismsWilliam WongNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument38 pagesHuman Anatomy & PhysiologyDeva ChiruNo ratings yet
- Physiology Study Guide - Exam #1Document38 pagesPhysiology Study Guide - Exam #1Kamille TucaNo ratings yet
- Bernadette Gonzales. ScienceDocument4 pagesBernadette Gonzales. ScienceBernadette GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Assignment Topic 1Document3 pagesAssignment Topic 1Charlyn CasabalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Organ System Overview: Atoms Cell Tissue OrganDocument8 pagesAnatomy Organ System Overview: Atoms Cell Tissue OrganBea PrestoNo ratings yet
- IntroHomeostasis-1Document28 pagesIntroHomeostasis-1Zainudin HayatiNo ratings yet
- Control CoordinationDocument7 pagesControl CoordinationShaurya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Functions of Different Organ SystemsDocument4 pagesFunctions of Different Organ Systemsleeannhernandez0414No ratings yet
- The Human Body: Gross /macroscopic AnatomyDocument8 pagesThe Human Body: Gross /macroscopic AnatomyMuhamad Hafiz Bin Mohd BakriNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 ReviewerDocument7 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Reviewerain't your saintessNo ratings yet
- Ass Midterm PDFDocument2 pagesAss Midterm PDFSyra May PadlanNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY REV Chapt 1Document8 pagesANAPHY REV Chapt 1crptzxraffNo ratings yet
- Physiology 1 IntroductionDocument101 pagesPhysiology 1 IntroductionBrian KipchumbaNo ratings yet
- Differentiation: Similar in Structure Different Tissues Different Organs Different SystemsDocument13 pagesDifferentiation: Similar in Structure Different Tissues Different Organs Different SystemsShivani HiteshNo ratings yet
- Sistem Kontrol Saraf Dan Endokrin: Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraDocument26 pagesSistem Kontrol Saraf Dan Endokrin: Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraLoshseniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Human BodyDocument13 pagesIntroduction To The Human BodyDeroNo ratings yet
- The Human Body OrientationDocument6 pagesThe Human Body OrientationHenry BuñagNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: Cross-Talking Among Organ Systems Prof - Dr. Nesrin Kartal ÖzerDocument35 pagesHomeostasis: Cross-Talking Among Organ Systems Prof - Dr. Nesrin Kartal ÖzerErdem AltunNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination NotesDocument21 pagesControl and Coordination NotesShivraj singhNo ratings yet
- Bioplasma Field: Compiled by Campbell M GoldDocument3 pagesBioplasma Field: Compiled by Campbell M GoldNorland IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesEndocrine SystemSheinny RodriguezNo ratings yet
- NOTES ReportingsDocument16 pagesNOTES Reportings2240739No ratings yet
- Lecture (Unit-I)Document59 pagesLecture (Unit-I)Misbah Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument2 pagesAnaphy ReviewerNarena BoniteNo ratings yet
- Organ System 1Document15 pagesOrgan System 1LeoNo ratings yet
- PAP Review KEY - Unit 7 CBA 2016-2017Document5 pagesPAP Review KEY - Unit 7 CBA 2016-2017Tom PunnenNo ratings yet
- Physiology and Pathophysiology IntroductionDocument39 pagesPhysiology and Pathophysiology Introductionbasmala.a.zahranNo ratings yet
- How Animals SurviveDocument35 pagesHow Animals SurvivedhonaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE KeypointsDocument5 pagesSCIENCE KeypointsSadidah MalawiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 PEED 101Document12 pagesLecture 2 PEED 101morireNo ratings yet
- Physiology Exam 1 Module 1Document79 pagesPhysiology Exam 1 Module 1Derrick ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Integrated Function Organ - Kel 2Document20 pagesIntegrated Function Organ - Kel 2Rashif AnbiaNo ratings yet
- AnaPhysio AbridgedDocument30 pagesAnaPhysio AbridgedJust IsaacNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chapter 7 NotesDocument7 pagesClass 10 Chapter 7 NotesIra LaratteNo ratings yet
- (Trans) Continuation Body SystemsDocument2 pages(Trans) Continuation Body SystemsJane NadalNo ratings yet
- CH 1 HomeostasisDocument67 pagesCH 1 Homeostasis360GamingNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - HormonesDocument24 pagesLesson 4 - HormonesKristie CorpusNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiologybobadillamarie156No ratings yet
- Body System Graphic Organizer With Answers 1pxx04bDocument3 pagesBody System Graphic Organizer With Answers 1pxx04bAthia ZamanNo ratings yet
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineFrom EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNo ratings yet
- Effect of Tart Cherry Juice (Prunus Cerasus) On Melatonin LevelsDocument9 pagesEffect of Tart Cherry Juice (Prunus Cerasus) On Melatonin LevelsYoottapol ChantapakdepongNo ratings yet
- The GITDocument5 pagesThe GITantoonieNo ratings yet
- Insect Internal MorphologyDocument64 pagesInsect Internal MorphologyharoldNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Organization and General Plan of TheDocument64 pagesChapter 1 Organization and General Plan of TheLoverna Abella0% (1)
- Lesson 4 - ConsciousnessDocument37 pagesLesson 4 - ConsciousnessDIMALANTA ANGELICANo ratings yet
- Freudian Dream Theory Today: Summary of The TheoryDocument2 pagesFreudian Dream Theory Today: Summary of The TheoryTim HeisNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris "Speech of Nursing About Anemia"Document5 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris "Speech of Nursing About Anemia"SeptyariNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument21 pagesThe Respiratory Systemhanatabbal19No ratings yet
- A7 Structural Organization in Animals MinDocument1 pageA7 Structural Organization in Animals MinDME MPonlineNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank HistoryDocument1 pageBlood Bank HistoryShawn PerezNo ratings yet
- Host Defense MechanismDocument35 pagesHost Defense MechanismEdgar DumagpiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Urine & Body Fluid Analysis 5th Edition 2023 ALGRAWANYDocument461 pagesFundamentals of Urine & Body Fluid Analysis 5th Edition 2023 ALGRAWANYDr-Issam IrakNo ratings yet
- Pranayam Chart by Inspirational YogaDocument2 pagesPranayam Chart by Inspirational YogaBishnudeo TantubaiNo ratings yet
- BLOOD COMPOSITION - Google FormsDocument3 pagesBLOOD COMPOSITION - Google FormsRonald Deck YamiNo ratings yet
- Biology - Human Transport NotesDocument4 pagesBiology - Human Transport Notesacsbr4science133% (3)
- VPB 111Document3 pagesVPB 111Dr-Ashok KeerNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 5 Activity 2Document3 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 5 Activity 2lucisNo ratings yet
- NCP BMDocument1 pageNCP BMSourabh MehraNo ratings yet
- Toxic Responses of Immune SystemDocument37 pagesToxic Responses of Immune Systemmaryem khalidNo ratings yet
- Outline and Evaluate Infradian And/or Ultradian Rhythms (16 Marks)Document2 pagesOutline and Evaluate Infradian And/or Ultradian Rhythms (16 Marks)HumaNo ratings yet
- SleepDocument28 pagesSleepapi-534716659No ratings yet
- Sleep Hygiene: Maintain A Regular Sleep ScheduleDocument3 pagesSleep Hygiene: Maintain A Regular Sleep ScheduleGen FelicianoNo ratings yet
- 7221 Detailed Content OutlineDocument53 pages7221 Detailed Content Outlineapi-258892726No ratings yet
- Controles BioradDocument2 pagesControles BioradDeqsa Corporativo0% (1)
- تقنيات تحاليل الدم 1Document6 pagesتقنيات تحاليل الدم 1hanan modaNo ratings yet