Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pollution Sewage
Uploaded by
Aungphone MaeooOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pollution Sewage
Uploaded by
Aungphone MaeooCopyright:
Available Formats
Pollution (Sewage) ①
(a) What is sewage? (4)
(a) Describe regulations controlling sewage discharge (4)
(b) Sketch biological sewage treatment plant (6)
(c) Describe above plant (6)
4/2002
Sewage means:
Drainage and wastes from toilets, but not including wash water from
basins, and wash tubs.
All drainage from medical premises, including wash water from basins
and wash tubs.
Drainage from spaces containing living animals.
Untreated sewage contains oxygen absorbing bacteria, which could
deprive fish, and living plants. Untreated sewage may also spread of disease
such typhoid, dysentery and poliomyclitics... etc.
Regulation
Annex IV of the MARPOL 73/78 (IMO) is international regulation for the
prevention of pollution by sewage from ships. This regulation is effective for all
ships 200 GRT and above with minimum 10 person of crew.
According to the regulation, the ship must have approved type sewage
treatment plant and holding tank with sufficient capacity.
Distance in NM from nearest land
Type of sewage
0 NM 4 NM 12 NM
Sewage treated by
approved No visible floating solids or discoloration
Sewage treatment plant
Sewage comminuted and
disinfected with approved Prohibited
equipment
Untreated sewage Prohibited
Moderate rate,
Sewage held in holding ship en-route at
Prohibited
tanks not less than 4
knots.
Restricted 30/06/2023 17:42:06
Pollution (Sewage) ②
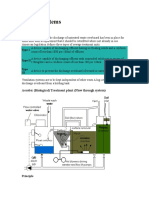
The System shown has four compartments. Incoming sewage
passes through a coarse screen into the primary collection tank where it
remains until displaced by overflow into the aeration section. A connection
is provided so that the primary collection tank can be pumped out.
In the aeration tank, waste is retained for about 24 hours being
thoroughly mixed and aerated by the aerators located at the bottom of the
tank. The aerobic bacteria and micro organisms break down the organic
wastes into mainly carbon dioxide, water and inert organic material and
produce new bacteria cells and organisms. CO2 is emitted via the vent
system.
Rotary blower supplied air provided oxygen for bacteria and micro
organisms. After prolonged aeration, the mixed liquor is displaced into the
settlement tank where biological floc is formed.
Settling compartment is designed to precipitate all solids to the
bottom of the hopper as activated sludge which is then returned by air lift
back to the aeration tank where it is mixed with the incoming raw sewage.
Clean effluent from the top of the settling tank is collected in the last
compartment for disinfection and discharge overboard. Disinfection is
achieved by treating the clean effluent with a solution of calcium or sodium
hypochlorite; this is usually carried out in a tank or compartment on the
end of the sewage treatment unit. In some plants this disinfection is
carried out by ultra-violet radiation.
The discharge of the resulting harmless effluent is controlled by float
switch connected to the discharge pump.
Restricted 30/06/2023 17:42:06
Pollution (Sewage) ③
Restricted 30/06/2023 17:42:06
You might also like
- Trickling Filter PDFDocument7 pagesTrickling Filter PDFAini ZahraNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment PlantDocument11 pagesSewage Treatment Plantjaffna86% (7)
- Lecture 9 - Water PollutionDocument42 pagesLecture 9 - Water PollutionCiara Crew100% (1)
- Microbiology of Trickling FilterDocument20 pagesMicrobiology of Trickling Filtermansikakani100% (3)
- SewageDocument31 pagesSewagemaneeshNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsDocument45 pagesLecture 6 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsHamza RiazNo ratings yet
- Ee2 Module 4 KtuDocument49 pagesEe2 Module 4 Ktusharin vargheseNo ratings yet
- Effluent Treatment PlantDocument67 pagesEffluent Treatment PlantSWATHI ACHARNo ratings yet
- Sludge TreatmentDocument9 pagesSludge Treatmentrollrams100% (1)
- 109.03 SEO Blower & Diffusers Biological TreatmentDocument52 pages109.03 SEO Blower & Diffusers Biological TreatmentibrahimNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment PlantDocument32 pagesSewage Treatment Plantjamroze496114100% (2)
- Sweage Treatment Plant (STP)Document57 pagesSweage Treatment Plant (STP)pra311288No ratings yet
- Water Treatment & MethodsDocument39 pagesWater Treatment & MethodsHaydar TaşNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report v.1Document4 pagesNarrative Report v.1Crisyl Lipawen100% (1)
- Annex IV - Explained & Sewage Treatment-1Document8 pagesAnnex IV - Explained & Sewage Treatment-1Gaurav ShresthNo ratings yet
- Sedimentation PresentationDocument30 pagesSedimentation PresentationShepherd Nhanga100% (3)
- MARPOL ANNEX 4 ExplainedDocument10 pagesMARPOL ANNEX 4 ExplainedORLANDONo ratings yet
- Sewage Systems: RegulationsDocument4 pagesSewage Systems: RegulationsrajaNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment PlantDocument9 pagesSewage Treatment PlantMeghanath AdkonkarNo ratings yet
- Mep STPDocument5 pagesMep STPAnakin SkywalkerNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment PlantsDocument8 pagesSewage Treatment PlantsJefferson SmithNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument5 pagesThesisJaphet Del Rosario AlveroNo ratings yet
- CED308 Module 6Document83 pagesCED308 Module 6Nitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment Plant On Ships ExplainedDocument6 pagesSewage Treatment Plant On Ships ExplainedGiorgi KandelakiNo ratings yet
- Annex Iv PresentasiDocument9 pagesAnnex Iv PresentasiDanial Farid NaufalNo ratings yet
- Excreta & Sewage Disposal LectDocument79 pagesExcreta & Sewage Disposal LectKathy YoungNo ratings yet
- Marpol Annex IVDocument14 pagesMarpol Annex IVdroad2078No ratings yet
- Saadiyat Sewage Treatment Plant, UAE-Abu Dhabi: A Case StudyDocument4 pagesSaadiyat Sewage Treatment Plant, UAE-Abu Dhabi: A Case StudyLexNo ratings yet
- Google 16Document12 pagesGoogle 16Win AlcaideNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment PlantDocument6 pagesSewage Treatment PlantvijayNo ratings yet
- Main UASB ReactorDocument23 pagesMain UASB ReactorsasisNo ratings yet
- Maren Vi Final CoverageDocument28 pagesMaren Vi Final CoverageJoshua CandagananNo ratings yet
- Activated SludgeDocument26 pagesActivated SludgeNoshaba NoreenNo ratings yet
- Tet Unit 3 NotesDocument25 pagesTet Unit 3 NotesnesamaniconstructionsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7.2Document20 pagesChapter 7.2Aakash MandalNo ratings yet
- Modern Sewage TreatmentDocument2 pagesModern Sewage TreatmentZothan Puia100% (1)
- Sewage Treatment Plant: Q. State The Procedure For Discharging Sewage Into The SeaDocument5 pagesSewage Treatment Plant: Q. State The Procedure For Discharging Sewage Into The SeaMohammad Jahid AlamNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment+PlantDocument16 pagesSewage Treatment+PlantSteven TanNo ratings yet
- Sreethan Pcpi 1Document12 pagesSreethan Pcpi 1sreethan reddyNo ratings yet
- 9.6.2023 - Shorthand Notes On Sewage Sludge Treatment and DisposalDocument17 pages9.6.2023 - Shorthand Notes On Sewage Sludge Treatment and DisposalLucas AgumbaNo ratings yet
- CONTENTS+ CertificateDocument15 pagesCONTENTS+ CertificateMeena SinghNo ratings yet
- Why Ballast Water Management?Document7 pagesWhy Ballast Water Management?Goran JurisicNo ratings yet
- Group Presentation Wastewater TreatmentDocument25 pagesGroup Presentation Wastewater TreatmentKushalKallychurnNo ratings yet
- Astewater Reatment Lant DesignDocument2 pagesAstewater Reatment Lant Designas3ateNo ratings yet
- SjshdbsDocument21 pagesSjshdbsCarenNo ratings yet
- Sewage System Onboard ShipsDocument11 pagesSewage System Onboard ShipsRohit KakadeNo ratings yet
- 7 - Water Waste Treatment and Disposal For Building PremisesDocument4 pages7 - Water Waste Treatment and Disposal For Building PremisesEugene MicarandayoNo ratings yet
- Excreta and Sewage DisposalDocument51 pagesExcreta and Sewage DisposalMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment PlantDocument18 pagesSewage Treatment PlantJohn Paul BarretoNo ratings yet
- Lecture-06: Sludge Treatment and Disposal: Ce 333: Environmental Engineering IiDocument6 pagesLecture-06: Sludge Treatment and Disposal: Ce 333: Environmental Engineering IiMirza Md. Nazmus SakibNo ratings yet
- Ballast Water Management Onboard ShipDocument10 pagesBallast Water Management Onboard ShipAnmol SatyamNo ratings yet
- Espiritu, Charlene M.: The Objective of Preliminary Treatment Is Only The Removal of Coarse SolidsDocument5 pagesEspiritu, Charlene M.: The Objective of Preliminary Treatment Is Only The Removal of Coarse SolidsCharleneMendozaEspirituNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment Plant: MD - ShamsuzzamanDocument11 pagesSewage Treatment Plant: MD - Shamsuzzamanapi-3701567100% (3)
- Glossary of Water Supply and SewageDocument16 pagesGlossary of Water Supply and SewageEyuel KokebNo ratings yet
- HYDRANAUTICS - Technical Service BulletinDocument50 pagesHYDRANAUTICS - Technical Service Bulletindpahomi1No ratings yet
- Sewage-Treatment 2Document32 pagesSewage-Treatment 2muyisco EmmaNo ratings yet
- Sewagetreatment1 130927055820 Phpapp01Document56 pagesSewagetreatment1 130927055820 Phpapp01Divakar MauryaNo ratings yet
- 109.05 SEO DisinfAection Uv Sterilizer & FlowmeterDocument97 pages109.05 SEO DisinfAection Uv Sterilizer & FlowmeteribrahimNo ratings yet
- Trickling Filter Trickling FiltersDocument5 pagesTrickling Filter Trickling Filterssneha raphelNo ratings yet
- Process DescriptionDocument4 pagesProcess DescriptionPuspalata JenaNo ratings yet
- Water Remote Sensing: Advancements in Computer Vision Techniques for Water Remote SensingFrom EverandWater Remote Sensing: Advancements in Computer Vision Techniques for Water Remote SensingNo ratings yet
- Panel Discussion: The New Face (Environment) Duration: Maximum of 15-20 MinutesDocument5 pagesPanel Discussion: The New Face (Environment) Duration: Maximum of 15-20 MinutesQuize Manriquez FernandezNo ratings yet
- The Environmental Analyses and The Link Between Economic Growth and Greenhouse Gases Emissions of GhanaDocument15 pagesThe Environmental Analyses and The Link Between Economic Growth and Greenhouse Gases Emissions of GhanaFadulous WayneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Green Technology For Environmental SustainabilityDocument2 pagesChapter 4: Green Technology For Environmental SustainabilitytaufiqNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Sustainable DevelopmentDocument5 pagesLiterature Review Sustainable DevelopmentJade NelsonNo ratings yet
- Electronic Waste ManagementDocument18 pagesElectronic Waste ManagementSwetha MaheshNo ratings yet
- WACS Villaba, LeyteDocument11 pagesWACS Villaba, Leyteroderick biazonNo ratings yet
- Play, Radio, Environment, Nature, Greenpeace, EnvironmentalDocument4 pagesPlay, Radio, Environment, Nature, Greenpeace, EnvironmentalAlinaNo ratings yet
- Sustainability: ForestsDocument4 pagesSustainability: ForestsAriana MuñozNo ratings yet
- SupwDocument13 pagesSupwviswanathbpNo ratings yet
- Global Climate ChangeDocument12 pagesGlobal Climate ChangeCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- First Periodical MAPEH 9Document4 pagesFirst Periodical MAPEH 9Gladys GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Republic Act 8749 Salient FeaturesDocument15 pagesDokumen - Tips - Republic Act 8749 Salient FeaturesMisael AquinoNo ratings yet
- Health 6 Learners GuideDocument12 pagesHealth 6 Learners Guidemilaflor zalsosNo ratings yet
- Pollution PPT 090720025050 Phpapp02Document19 pagesPollution PPT 090720025050 Phpapp02sukhvir UppalNo ratings yet
- 500 Profs of Environmental-Supervosoir-list-China-University-of-Geosciences-China-2Document64 pages500 Profs of Environmental-Supervosoir-list-China-University-of-Geosciences-China-2muhammadNo ratings yet
- Disposal of Trade WastewaterDocument3 pagesDisposal of Trade WastewaterCarloNo ratings yet
- Ecm446 - Group 6 - Ceec224c3 - Assignment ProjectDocument13 pagesEcm446 - Group 6 - Ceec224c3 - Assignment Project2022855516No ratings yet
- HW3 - 12217038 - Raden Keanu Paranindhia BenedettoDocument4 pagesHW3 - 12217038 - Raden Keanu Paranindhia BenedettoKeanu ParanindhiaNo ratings yet
- Acs Spring 2020 Expo 3281335 - 2Document1 pageAcs Spring 2020 Expo 3281335 - 2Amm ÃrNo ratings yet
- Environmental Management Systems Auditor / Lead Auditor Training Course General EnvironmentDocument26 pagesEnvironmental Management Systems Auditor / Lead Auditor Training Course General EnvironmentRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Pink and Blue Environment Future Modern Presentation - 20230920 - 192808 - 0000Document12 pagesPink and Blue Environment Future Modern Presentation - 20230920 - 192808 - 0000Rei B.XNo ratings yet
- Please Upload The Question Paper Together With Your Answers: Mid-Term Test SolutionDocument7 pagesPlease Upload The Question Paper Together With Your Answers: Mid-Term Test Solutionsui sui mangNo ratings yet
- Grammar Labsheet #1 10th 2016Document2 pagesGrammar Labsheet #1 10th 2016Ricardo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Kaliza Tressy Meghan Sustainability Brief 1Document4 pagesKaliza Tressy Meghan Sustainability Brief 1KALIZA TRESSY MEGHANNo ratings yet
- Swot Greenhouse FarmingDocument22 pagesSwot Greenhouse FarmingVrinda GoyalNo ratings yet
- Evs Question Paper SetDocument2 pagesEvs Question Paper SetPrakrutiShahNo ratings yet
- Green House Gases and The Role of CompostingDocument3 pagesGreen House Gases and The Role of CompostingDewa Putu Adhi Nugraha AnomNo ratings yet
- Test 3Document5 pagesTest 3Ngọc HồNo ratings yet
- BibliographyDocument12 pagesBibliographyapi-284874590No ratings yet