Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture05 (1) Microelectronic
Uploaded by
Gaith Al EliwiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture05 (1) Microelectronic
Uploaded by
Gaith Al EliwiCopyright:
Available Formats
Electronics
Bluest Lan, PhD
16.03.2023
Materials
• Solid-state materials: conductor, semiconductor, insulator
• Conductivity: conductor > semiconductor > insulator
• Resistivity: conductor < semiconductor < insulator
Resistivity
L Length
R=ρ
A
Cross-sectional area
Lecture 05: Physical Operation of Diodes: The pn Junctions 2
Semiconductor
Intrinsic semiconductor (single-element semiconductor):
• A material that behaves as an insulator at absolute zero temperature (0 Kelvin)
and becomes a semiconductor at higher temperatures
• Group IV element in the periodic table, such as silicon (S) and germanium (Ge)
Extrinsic semiconductor (compound semiconductor):
• A material that has been intentionally doped with impurities to increase its
electrical conductivity
• Elements from groups III and V or groups II and VI
Lecture 05: Physical Operation of Diodes: The pn Junctions 3
Intrinsic Semiconductor
T↑
n = p = ni
np = ni2
n: Concentration of free electrons
p: Concentration of holes
ni: number of free electrons and holes in a unit volume (cm3) of intrinsic silicon at a given temperature
Lecture 05: Physical Operation of Diodes: The pn Junctions 4
Intrinsic Carrier Concentration
• From semiconductor physics: ni = BT 3/2e −Eg/2kT
• B is a material-dependent parameter that is 7.3 × 1015 cm−3 K−3/2 for silicon
• T is the temperature in K
• Eg is a material parameter known as the bandgap energy (minimum energy
required to break a covalent bond) that is 1.12 electron volt (eV) for silicon
• k is Boltzmann’s constant (8.62 × 10−5 eV/K)
Lecture 05: Physical Operation of Diodes: The pn Junctions 5
Doped Semiconductors
pn = ni2
n type
ND NA
p ≈ NA ≫ ni
n ≈ ND ≫ ni
p type
ni2 ni2
p≈ n≈
ND NA
Lecture 05: Physical Operation of Diodes: The pn Junctions 6
Drift Current
μp: Hole mobility
Drift velocity vp−drift = μpE μn: Electron mobility
vn−drift = − μnE + q: Magnitude of electron charge
-
Current density
Ip + -
Jp = = qpvp−drift
A
I L
Jn = n = − qnvn−drift R=ρ
A A
1
J = Jp + Jn = q(pμp + nμn)E → J = E/ρ ρ=
q(pμp + nμn)
Lecture 05: Physical Operation of Diodes: The pn Junctions 7
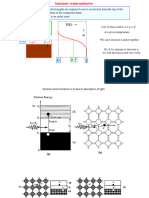
Physical Structure
+ -
Lecture 05: Physical Operation of Diodes: The pn Junctions 8
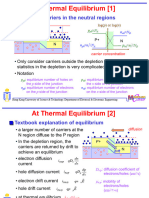
The pn Junction
Di usion current
Drift current
- + + -
Barrier voltage
Reverse bias Forward bias
Lecture 05: Physical Operation of Diodes: The pn Junctions 9
Zender Diode
rz ≈ 20 Ω
VZ = VZ0 + IZrz
Lecture 05: Physical Operation of Diodes: The pn Junctions 10
ff
References
• Sedra, Smith, Microelectronic Circuits 8e. Oxford University Press.
Lecture 05: Physical Operation of Diodes: The pn Junctions 11
You might also like
- Electrical Sciences EEE F111Document64 pagesElectrical Sciences EEE F111Kriti TambareNo ratings yet
- Lec 5Document19 pagesLec 5api-3721075No ratings yet
- Linear Network Theory: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionFrom EverandLinear Network Theory: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionNo ratings yet
- Lect 03 Semiconductors - Part 02Document99 pagesLect 03 Semiconductors - Part 02Malvin NdumeNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Diode: I-V Characteristics: Sung June KimDocument42 pagesPN Junction Diode: I-V Characteristics: Sung June KimasadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15Document20 pagesLecture 15Yavuz KaplanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Sciences EEE F111Document64 pagesElectrical Sciences EEE F111Kriti TambareNo ratings yet
- Electrical Sciences EEE F111Document64 pagesElectrical Sciences EEE F111KAUSTUBHNo ratings yet
- Week1 - Diode Semiconductor1Document42 pagesWeek1 - Diode Semiconductor1ALEN chiaNo ratings yet
- Charge Densities and Mass Action LawDocument36 pagesCharge Densities and Mass Action Lawgirishkumardarisi254No ratings yet
- Updated DiodeDocument21 pagesUpdated DiodeツadhritNo ratings yet
- Lecture89 - Diode and Its Applications - LDocument21 pagesLecture89 - Diode and Its Applications - Lridhamsharma2512No ratings yet
- Diode and Its Applications - LDocument22 pagesDiode and Its Applications - LDipankar PradhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture89 - 12284 - Diode and Its Applications - L 1Document22 pagesLecture89 - 12284 - Diode and Its Applications - L 1basuslathia01No ratings yet
- Chap - 03 - PN JunctionDocument44 pagesChap - 03 - PN JunctionnguyenhuyenthoainguylanNo ratings yet
- Radio Protection ChallengesDocument31 pagesRadio Protection ChallengesJackssonNo ratings yet
- Lec07 SSMDDocument11 pagesLec07 SSMDTayyaba SaharNo ratings yet
- ELEN0037 Microelectronic IC Design: Prof. Dr. Michael KraftDocument46 pagesELEN0037 Microelectronic IC Design: Prof. Dr. Michael KraftDominiqueNo ratings yet
- LEC 1 - Electronic Circuits AnalysisDocument17 pagesLEC 1 - Electronic Circuits Analysisgubaomar28No ratings yet
- Lec 20 21 22 EDDocument26 pagesLec 20 21 22 EDSATYAM KUMARNo ratings yet
- DiodesDocument73 pagesDiodeswinijon961No ratings yet
- Eeng350 02 PDFDocument47 pagesEeng350 02 PDFHasan JomaaNo ratings yet
- Lecture89 12284 Diode and Its Applications LDocument21 pagesLecture89 12284 Diode and Its Applications LtheinformationloopofficialNo ratings yet
- Lab4 F15 Si DiodeDocument15 pagesLab4 F15 Si DiodeJohn MarkNo ratings yet
- Extrinsic SemiconductorsDocument14 pagesExtrinsic SemiconductorsMaxi GarzonNo ratings yet
- Lect 03 Semiconductors - Part 02Document104 pagesLect 03 Semiconductors - Part 02ziademadaldeNo ratings yet
- Electronics Chapter 1, 2, 3 & 4.Document165 pagesElectronics Chapter 1, 2, 3 & 4.Mohamed EmadNo ratings yet
- PN DiodeDocument110 pagesPN DiodePranav NagarajiNo ratings yet
- 2 PN JunctionDocument70 pages2 PN JunctionJorge RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Elektronika Analog I Pertemuan 2Document75 pagesElektronika Analog I Pertemuan 2M. Rifki Izzul HaqNo ratings yet
- Class 2Document42 pagesClass 2EduardNo ratings yet
- Analog & Digital Electronics: Course No: PH-218 Lecture 2: PN JunctionDocument15 pagesAnalog & Digital Electronics: Course No: PH-218 Lecture 2: PN JunctionRahulMondolNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - 2: Outline - Basic Semiconductor Physics (Cont'd) - PN Junction DiodesDocument27 pagesLecture 1 - 2: Outline - Basic Semiconductor Physics (Cont'd) - PN Junction DiodesNgọc Linh Nguyễn ThịNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits & Electron Devices - EC 147201 Devices - EC 147201Document21 pagesElectric Circuits & Electron Devices - EC 147201 Devices - EC 147201Divya PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of MicroelectronicsDocument42 pagesFundamentals of MicroelectronicspishtiwanNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document18 pagesLec 3api-3721075No ratings yet
- Diode Operation: 97.398, Physical Electronics, Lecture 8Document21 pagesDiode Operation: 97.398, Physical Electronics, Lecture 8PULKITJOSHINo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Diode Circuits: ObjectiveDocument55 pagesChapter 1-Diode Circuits: ObjectiveRuben KandulnaNo ratings yet
- 02 PN JunctionDocument22 pages02 PN JunctioniramNo ratings yet
- 370 Notes PDFDocument19 pages370 Notes PDFRyanNo ratings yet
- Electronics Chapter 1, 2Document104 pagesElectronics Chapter 1, 2Rayan AbdelrahimNo ratings yet
- Class 24: Outline: Hour 1: Inductance & LR Circuits Hour 2: Energy in InductorsDocument37 pagesClass 24: Outline: Hour 1: Inductance & LR Circuits Hour 2: Energy in Inductorsakirank1No ratings yet
- Curs MIT PN Junction Diode 2009 Lec14Document17 pagesCurs MIT PN Junction Diode 2009 Lec14euNo ratings yet
- 3-1 Introduction and PN JunctionDocument16 pages3-1 Introduction and PN JunctionEric JaegerNo ratings yet
- CI-04 Feb2010Document2 pagesCI-04 Feb2010Javeed AhamedNo ratings yet
- Physics of Semiconductor DevicesDocument19 pagesPhysics of Semiconductor DevicesgautamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Basic Physics of SemiconductorsDocument41 pagesChapter 2-Basic Physics of SemiconductorsAmged TahaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 - The PN Junction Diode (II) : 6.012 - Microelectronic Devices and Circuits - Fall 2005 Lecture 16-1Document18 pagesLecture 16 - The PN Junction Diode (II) : 6.012 - Microelectronic Devices and Circuits - Fall 2005 Lecture 16-1Kulanthaivelu RamaswamyNo ratings yet
- Light Emitting Diode (LED) PrinciplesDocument18 pagesLight Emitting Diode (LED) PrinciplesSrinivas MishraNo ratings yet
- Principles of Semiconductor Devices-L20Document29 pagesPrinciples of Semiconductor Devices-L20LIAKMANNo ratings yet
- Cavity Resonator PDFDocument20 pagesCavity Resonator PDFkhanafzaal2576No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Engineering PDFDocument22 pagesBasic Electronics Engineering PDFAbhishekNo ratings yet
- 05 Derivation of The Ideal PN Junction Diode EquationDocument16 pages05 Derivation of The Ideal PN Junction Diode EquationhujohnnethaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of MicroelectronicsDocument394 pagesFundamentals of Microelectronicsomidsf100% (2)
- 2 HaftaDocument41 pages2 HaftaM. AymazNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electronics: An Introduction To Electronic Components and A Study of Circuits Containing Such DevicesDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Electronics: An Introduction To Electronic Components and A Study of Circuits Containing Such Devicesزكرياء بنحيرتNo ratings yet
- Class 15: Outline: Hour 1: Magnetic Force Expt. 6: Magnetic ForceDocument33 pagesClass 15: Outline: Hour 1: Magnetic Force Expt. 6: Magnetic Forceakirank1No ratings yet
- EEE 205 / ECE 202 Electronic Devices and Circuits I Spring 2012Document26 pagesEEE 205 / ECE 202 Electronic Devices and Circuits I Spring 2012nehal hasnain refathNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH 6 Animal Tissues Class 9th ScienceDocument11 pagesNotes of CH 6 Animal Tissues Class 9th ScienceSingh JNo ratings yet
- FREE EthnicKnittingBookPattern HeadbandDocument4 pagesFREE EthnicKnittingBookPattern HeadbandriyuuhiNo ratings yet
- ThinkSmart Hub SpecDocument5 pagesThinkSmart Hub SpecJose LopezNo ratings yet
- CMC en Muros de Estabilización (Paper Congreso) )Document10 pagesCMC en Muros de Estabilización (Paper Congreso) )Agustín CuadradoNo ratings yet
- Mrs - Sanjana Jadhav: Mobile No-9422400137Document3 pagesMrs - Sanjana Jadhav: Mobile No-9422400137Sanjana JadhavNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment of Ship Platform ColissionDocument6 pagesRisk Assessment of Ship Platform Colission123habib123fikriNo ratings yet
- SmartPRO 5000U Plus ManualDocument10 pagesSmartPRO 5000U Plus ManualMugiranezaNo ratings yet
- Third Periodic TestDocument4 pagesThird Periodic TestCrizelda AmarentoNo ratings yet
- M2-Exam 2Document13 pagesM2-Exam 2youngturtlevibesNo ratings yet
- Understand Concept of Multi-Rate Signal Processing: (Autonomous College Affiliated To University of Mumbai)Document2 pagesUnderstand Concept of Multi-Rate Signal Processing: (Autonomous College Affiliated To University of Mumbai)nicO neeNo ratings yet
- Asmi-52: 2/4-Wire SHDSL ModemDocument4 pagesAsmi-52: 2/4-Wire SHDSL ModemManuel FreireNo ratings yet
- OP25 Windows 10 Virtual Machine Setup Guide July 10, 2022Document30 pagesOP25 Windows 10 Virtual Machine Setup Guide July 10, 2022ValerioNo ratings yet
- Neraca energiATK-2Document29 pagesNeraca energiATK-2MauliyaLailaNo ratings yet
- Cylindicator Sensor Design GuideDocument2 pagesCylindicator Sensor Design GuideTavo VergaraNo ratings yet
- Labour Productivity ChartDocument635 pagesLabour Productivity ChartFrederick AgliamNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Teknis Genset Dan AtsDocument2 pagesSpesifikasi Teknis Genset Dan AtsRamadan yusuf afifNo ratings yet
- Digital Image ProcessingDocument156 pagesDigital Image ProcessingAnushka BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Sony HCD Zx30avDocument80 pagesSony HCD Zx30avrrobles8777No ratings yet
- Test For CarbohydratesDocument15 pagesTest For CarbohydratesKevin SangNo ratings yet
- Flight MechanicsDocument3 pagesFlight MechanicsQwer QwerNo ratings yet
- Parson Merton CritiqueDocument9 pagesParson Merton CritiqueVishnu VarmaNo ratings yet
- Phase Diagrams: By: Cherides P. MarianoDocument25 pagesPhase Diagrams: By: Cherides P. MarianoWild RiftNo ratings yet
- C & Embedded QuestionsDocument109 pagesC & Embedded QuestionskalkikaliNo ratings yet
- Sam W Hoke Torch PatentDocument5 pagesSam W Hoke Torch PatentRichard.nlNo ratings yet
- NTSE Stage - 1 Mock Test - 3Document16 pagesNTSE Stage - 1 Mock Test - 3Apex Institute100% (1)
- Grade 11 SEM: Markscheme Examiners ReportDocument29 pagesGrade 11 SEM: Markscheme Examiners ReportDr. Love TrivediNo ratings yet
- 3 772Document61 pages3 772D MNCNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD - Modify ToolbarDocument18 pagesAutoCAD - Modify ToolbarMarcusNo ratings yet
- Mcknight - Proposed Mastering Eq PDFDocument3 pagesMcknight - Proposed Mastering Eq PDFIordan Dan FfnNo ratings yet
- Mahesh - Informatica DeveloperDocument5 pagesMahesh - Informatica DeveloperMadhav GarikapatiNo ratings yet