Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Marking Scheme - Revision For UT 1 WS
Uploaded by
SiyaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Marking Scheme - Revision For UT 1 WS
Uploaded by
SiyaCopyright:
Available Formats
NPS International School
Marking Scheme
1 (a) 40 cm3 1
(b) Let w be the bond energy of the O-H bond
ΔH = [(390×12) + (498×3)] – [(946×2) + 12w]
2
1 mark 1 mark
-1286 = [4680 + 1494] – [1892 + 12w]
-1286 = 6174 – 1892 – 12w
12w = 5568
w = 464 kJ/mole 1
(c)
Energy
uncatalysed
Ea
E’a catalysed
4NH3 + 3O2
ΔH
2N2 + 6H2O
Progress of Reaction
2 exothermic profiles, 1 with a lower activation energy 1
Ea and E’a correctly labelled 1
Reactants and products written at the correct levels 1
ΔH correctly labelled 1
(d) The catalyst provides an alternative energy pathway with a lower the activation 1
energy for the reaction to occur.
More reactant particles have energy greater than or equal to the activation 1
energy. This results in a higher frequency of effective collisions.
Therefore, the rate of reaction increases. 1
NPSI/ Version1.0/23-24/Chem./10IG/03 Page No:1
NPS International School
2 (a) Number of moles of acid in experiment 1 = 0.01 X 1 = 0.01
Number of moles of acid in experiment 2 = 0.02 X 0.5 = 0.01 1
Number of moles of acid in experiment 3 = 0.05 X 0.3 = 0.015
(b) CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
Number of moles of calcium carbonate in experiment 1 = 1.6/100 = 0.016
Number of moles of calcium carbonate in experiment 2 = 1.1/100 = 0.011 1
(c) Using the mole ratio from the equation, hydrochloric acid is the limiting agent.
Expt 1: 0.01 × 24 000 × 0.5 = 120 cm3 of carbon dioxide
Expt 2: 0.01 × 24 000 × 0.5 = 120 cm3 of carbon dioxide 1
Expt 3: 0.015 × 24 000 × 0.5 = 180 cm3 of carbon dioxide
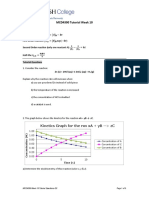
(d)
1 mark for each labelled graph 2
(e) Lumps of calcium carbonate have a smaller surface area of contact. 1
Thus, there is a lower frequency of collisions between reacting particles, leading
to a lower frequency of effective collisions between them. 1
Hence a lower speed of reaction. 1
NPSI/ Version1.0/23-24/Chem./10IG/03 Page No:2
NPS International School
3 (a) Stopwatch, 1
Deliver tube 1
Gas syringe/measuring cylinder 1
(b)
1 mark for each curve 2
(c) Hydrochloric acid has a higher concentration of hydrogen ions than ethanoic 1
acid.
This results in a higher frequency of collisions between reacting particles,
which in turn increases the frequency of effective collisions between them. 1
Hence, the rate of reaction is higher when hydrochloric acid is used. 1
(d) Increasing the temperature of the reaction mixture will increase the rate of 1
reaction.
The particles will have more kinetic energy and will move faster. 1
There are now more particles with energy that are greater than or equal to
activation energy. 1
This will increase the frequency of collisions between reacting particles which
in turn, will increase the frequency of effective collisions. 1
(e) 0.5 mol/dm3 of H2A 1
NPSI/ Version1.0/23-24/Chem./10IG/03 Page No:3
You might also like
- IBO 2020 - Theory Exam 1Document65 pagesIBO 2020 - Theory Exam 1ConorNo ratings yet
- AcsDocument21 pagesAcsalNo ratings yet
- CQI 9 4th EditionDocument1 pageCQI 9 4th Editionmirosek100% (1)
- Practice Worksheet of Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesPractice Worksheet of Chemical Bondingch khakanNo ratings yet
- Chem Student Book 2 AnswersDocument68 pagesChem Student Book 2 AnswersMeeran Hassan96% (25)
- Halogenoalkanes AnswersDocument64 pagesHalogenoalkanes AnswersSpider Gamer22No ratings yet
- IAL Chemistry SB2 Answers Topic11Document7 pagesIAL Chemistry SB2 Answers Topic11salmaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Online: Reaction Order and Rate LawsDocument14 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Online: Reaction Order and Rate LawsirfanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Matriculation Note SK025 by Vinarti MahmudDocument47 pagesChemistry Matriculation Note SK025 by Vinarti MahmudNurun NajwaNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme - Rate of Reaction WSDocument2 pagesMarking Scheme - Rate of Reaction WSSiyaNo ratings yet
- Mid Term General Chem II Fall 2001Document6 pagesMid Term General Chem II Fall 2001dr.ibrahimsalemvpNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme - Energy Changes WSDocument2 pagesMarking Scheme - Energy Changes WSSiyaNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Paper 1 Set 2 Marking GuideDocument7 pagesA Level Chemistry Paper 1 Set 2 Marking Guidessentume peterNo ratings yet
- Shailendra KR.: Physical ChemistryDocument13 pagesShailendra KR.: Physical ChemistryAli SaabNo ratings yet
- 4 Skema Pemarkahan Rate of ReactionDocument47 pages4 Skema Pemarkahan Rate of ReactionJun QiangNo ratings yet
- Mock MCQ Time-TrialDocument11 pagesMock MCQ Time-Trial2022 BALAKRISHNAN ADHITHINo ratings yet
- ENGGEN 140 2023 S1 - Mock Test 2 SolutionsDocument24 pagesENGGEN 140 2023 S1 - Mock Test 2 SolutionsKingstanIINo ratings yet
- MCQs For Class XII ChemistryDocument29 pagesMCQs For Class XII Chemistryjkc collegeNo ratings yet
- MCD4390 Week 10 Tutorial QuestionsDocument5 pagesMCD4390 Week 10 Tutorial QuestionsGabbar100% (1)
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2019 Chemistry Set 5Document7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2019 Chemistry Set 5NitilNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics 119 Ques!!!Document27 pagesChemical Kinetics 119 Ques!!!elifnazNo ratings yet
- Expected Questions For Board Examination 2013Document34 pagesExpected Questions For Board Examination 2013Harsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- CBQ ChemDocument35 pagesCBQ ChemIniya RajasekharNo ratings yet
- Chem. Assig.Document8 pagesChem. Assig.aryan asliaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 - Polarography and Voltammetry - 481Document10 pagesTutorial 9 - Polarography and Voltammetry - 481HassanNo ratings yet
- 3 (N) (Special Mock Exam 37)Document6 pages3 (N) (Special Mock Exam 37)Vinaigrette HeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Answers PDFDocument126 pagesChemistry Answers PDFNurafiqah FarhaniNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Handout - Studentcopy - 2023Document12 pagesTopic 6 Handout - Studentcopy - 2023钱俊翰No ratings yet
- 2017 Y5 T4 Chem Focus - KineticsDocument4 pages2017 Y5 T4 Chem Focus - KineticsxmxmxmxmxmNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-Manual CH1002Document18 pagesTutorial-Manual CH1002Gift Chulu100% (2)
- GZB - Xii - WS-8 - Chemistry - Chemical Kinetics - OctoberDocument3 pagesGZB - Xii - WS-8 - Chemistry - Chemical Kinetics - OctoberSaman PanwarNo ratings yet
- 2020 ACJC H2 Paper 3 AnswersDocument23 pages2020 ACJC H2 Paper 3 AnswersbeverlyyyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Capsule 30Document32 pagesChemistry Capsule 30Rohith SNo ratings yet
- Year 12 Chemistry Learning Cycle 1 AssessmentDocument11 pagesYear 12 Chemistry Learning Cycle 1 AssessmentjimNo ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry SL IaDocument12 pagesIb Chemistry SL Iaapi-613949102No ratings yet
- Shalini Memorial School: SC O LDocument2 pagesShalini Memorial School: SC O LPŕį Ņćę ĂãťîfNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelTrung Hoàng HuyNo ratings yet
- Cape CHM 2006 MsDocument4 pagesCape CHM 2006 MsChavi RamloganNo ratings yet
- 2023 JC2 H1 Chem BT MCQ MSDocument7 pages2023 JC2 H1 Chem BT MCQ MSemman tzhNo ratings yet
- PT-1 Chemistry (SET-A) 2023-24Document4 pagesPT-1 Chemistry (SET-A) 2023-24Manraj SinghNo ratings yet
- EquationDocument9 pagesEquationHoang Uyen Vy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Q: 2 Attempt Any Three of The Following Question (12) : InstructionsDocument2 pagesQ: 2 Attempt Any Three of The Following Question (12) : InstructionsSmruthi SuvarnaNo ratings yet
- 9701 Nos Ps 5Document5 pages9701 Nos Ps 5Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY XI MsDocument4 pagesCHEMISTRY XI MsAKASH KUMAR X ANo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences P2 Feb-March 2017 EngDocument20 pagesPhysical Sciences P2 Feb-March 2017 EngmzolisimanxusaNo ratings yet
- Physical Test - Q - 05.07.2021Document3 pagesPhysical Test - Q - 05.07.2021joydeep17590No ratings yet
- (Ii) Mustcalculated in (I) (1) A (S) To Na (G) + Gaseous Ions To Solid Nah BecauseDocument67 pages(Ii) Mustcalculated in (I) (1) A (S) To Na (G) + Gaseous Ions To Solid Nah BecauseG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- HSSC I Send Up Key ChemistryDocument5 pagesHSSC I Send Up Key Chemistrymymegaacc111No ratings yet
- XII - Revision Sheet - 2 - ChemistryDocument3 pagesXII - Revision Sheet - 2 - ChemistryVipin VNo ratings yet
- Question On Chemical Kinetics-MA 2022Document12 pagesQuestion On Chemical Kinetics-MA 2022Sangay ChodenNo ratings yet
- JH PC Chemical Kinetics DPP 22 To 34Document18 pagesJH PC Chemical Kinetics DPP 22 To 34The IndianNo ratings yet
- Xi Chem Hy Answer KeyDocument4 pagesXi Chem Hy Answer Keymeditationmanifestation4No ratings yet
- 2013 RI H2 Chem P1 QP PDFDocument23 pages2013 RI H2 Chem P1 QP PDFsaffronNo ratings yet
- Test 52 - Chemical Kinetics - Top of PyramidDocument6 pagesTest 52 - Chemical Kinetics - Top of PyramidJay PatelNo ratings yet
- EBS 336 - Tests 2 - Q&A - 2018 PDFDocument4 pagesEBS 336 - Tests 2 - Q&A - 2018 PDFNurul Ain JabitNo ratings yet
- XII ChemistryDocument6 pagesXII ChemistrySaraswati maharanaNo ratings yet
- Pearson Textbook SolutionsDocument142 pagesPearson Textbook SolutionskermitspewNo ratings yet
- 1assignment On Rates of Reaction and Energy ChangesDocument6 pages1assignment On Rates of Reaction and Energy ChangesShehryar IftikharNo ratings yet
- 3A (BPS Paper 2 2016 Ans)Document4 pages3A (BPS Paper 2 2016 Ans)Vinaigrette HeNo ratings yet
- Class-12 Chemistry ElectroDocument4 pagesClass-12 Chemistry ElectroHemant ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt-18-19 XII Che Study-Package-5 SET-2 Chapter-3 PDFDocument44 pagesCLS Aipmt-18-19 XII Che Study-Package-5 SET-2 Chapter-3 PDFSarang0% (1)
- C8 Book AnswersDocument10 pagesC8 Book AnswersMo KhNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Polycarbonate and ABSDocument5 pagesDifference Between Polycarbonate and ABSNeelakandan DNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 5 PracticalDocument5 pagesBiology Paper 5 Practicalpro.is.only.me.cause.i.am.vrindaNo ratings yet
- Pretiox: Titanium DioxideDocument11 pagesPretiox: Titanium DioxideAbhinav TayadeNo ratings yet
- King Fahd University of Petrolum and Minirals: Mechanical Engineering Departmant ME203 - 8 HW8Document8 pagesKing Fahd University of Petrolum and Minirals: Mechanical Engineering Departmant ME203 - 8 HW8Mohammed AlbazzazNo ratings yet
- Theory Worksheet: Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument4 pagesTheory Worksheet: Acids, Bases and Saltsخانزاده بلال احمدخان لودہیNo ratings yet
- Trial Number ZeroDocument12 pagesTrial Number ZeroLeandro DijonNo ratings yet
- Visão Explodida NG1-2 Código 536850000Document4 pagesVisão Explodida NG1-2 Código 536850000miguel maninattNo ratings yet
- Astm A 529Document3 pagesAstm A 529nfidan.ctjvNo ratings yet
- 2020 05 Geogard-ECT TDS d15Document4 pages2020 05 Geogard-ECT TDS d15Andrianna VoutsinouNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Defect Chemistry and Defect Equilibria: 1) Concentration of Intrinsic DefectsDocument7 pagesUnit 4: Defect Chemistry and Defect Equilibria: 1) Concentration of Intrinsic DefectsTejinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Uses of Some Group 3A and 5A ElementsDocument5 pagesUses of Some Group 3A and 5A ElementsRahmot BadmosNo ratings yet
- TDS BLR 896 EN ScreenDocument1 pageTDS BLR 896 EN ScreenLuis Angel MendozaNo ratings yet
- EnzomologyDocument26 pagesEnzomologyToga Brandon100% (1)
- Manufacturing ReportDocument22 pagesManufacturing ReportR Sailesh ae18b011No ratings yet
- Catalysis Letters 10.1007s10562-012-0829-xDocument8 pagesCatalysis Letters 10.1007s10562-012-0829-xyokeshNo ratings yet
- EII Lots EmpiricalFormula PDFDocument7 pagesEII Lots EmpiricalFormula PDFMohammadNo ratings yet
- Week 1 and 2 Summative TestDocument4 pagesWeek 1 and 2 Summative TestJulie Anne Portal - OdascoNo ratings yet
- Questionsheet 1: Homeostasis A2.3Document9 pagesQuestionsheet 1: Homeostasis A2.3Kajana Sivarasa ShenthanNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Tutorial 2Document22 pagesNatural Gas Tutorial 2Sylvester TetteyNo ratings yet
- Alkyd ResinDocument7 pagesAlkyd ResinAmr Abdelmegid abdelsalam husseinNo ratings yet
- Redox Reaction _ Practice Sheet __ JEE ChallengersDocument5 pagesRedox Reaction _ Practice Sheet __ JEE ChallengersCalming MusicNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Controlled ReleaseDocument46 pagesMechanisms of Controlled Releaselaurik1315No ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Report PLCDocument10 pagesInorganic Chemistry Report PLCPablo LópezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry EavporationDocument20 pagesChemistry EavporationSouvik JEE 2024No ratings yet
- Review Problems From Diff BooksDocument9 pagesReview Problems From Diff BooksHannah AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Distillation Column Design and SimulationDocument29 pagesDistillation Column Design and Simulationhinman714No ratings yet
- 2nd Lab ReportDocument13 pages2nd Lab Reportali hasan100% (1)