Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Noun Clause
Uploaded by
Minh Thuận Hoàng ThịOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Noun Clause
Uploaded by
Minh Thuận Hoàng ThịCopyright:
Available Formats
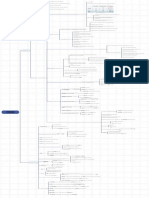
Noun clause is a dependent clause which f unctions as a noun or
noun phrase.
e.g: T hat he is not the best choice goes without saying.
It can be subject, object, or complement. Derived f rom statements ➔ that-clauses
Two types of e.g: She believed (that) everything would be f ine.
Definition
nominal
e.g: I didn’t know how she got there all by herself .
clauses
e.g: T he question is what we can do to solve the problem.
Derived f rom questions ➔ wh-clauses
(What can we do to solve the problem?)
Beginning with T HAT , a question word, or IF/
WHET HER
e.g: We had a talk about who should be invited. Noun clauses af ter PREPOSIT IONS
e.g: Do you know whether/if there’s a good f ilm on
Used with embedded Yes/No questions
e.g: It wasn’t possible that he could be mistaken. (with IT ) Position tonight?
e.g: I’m disappointed that I didn’t get the job. (af ter an IF is pref erred when the noun clause is the object of the
In dif f erent structures e.g: I don’t know if I can do anything to help.
adjective) verb.
e.g: I heard the rumor that the prof essor had been
e.g: It is debatable whether it’s necessary to tell her all
kidnapped. (af ter a noun) T alking about choices or alternatives
about this.
WHETHER and IF
T he verb tense in the independent clause determines Noun clause as subject e.g: Whether we will pass this course remains to be seen.
the verb tense in the dependent noun clause.
e.g: T he question is whether we
e.g: T he president AGREES that solar power IS the Af ter BE (noun clause as subject complement) should risk everything again this
answer to the energy crisis. Sequence of Tenses time.
e.g: T he president AGREED that solar power WAS the
NOUN CLAUSE
e.g: We need to discriminate between whether she really needs
answer to the energy crisis. WHET HER is used in other positions Af ter a preposition
the
money or is just being greedy.
T he question whether to wait another year will be discussed
Af ter a noun
today.
Bef ore a to-Inf initive e.g: I can’t decide whether to go or not.
Immediately bef ore OR NOT e.g: We have to decide whether or not we are going.
e.g: We regret that you did not f ind our product
satisf actory.
Inf ormally af ter common reporting verbs e.g: He thought (that) ...., she said (that) ....
NOT af ter some verbs (email, reply, shout, etc. e.g: She shout that she was okay.
Leaving out THAT in that- noun clause Af ter adjectives e.g: I'm glad (that) he's okay.
Noun clauses as object NOT af ter nouns e.g: I didn't believe his claims that he was ill.
e.g: We told the driver we were in a hurry.
e.g: T hat he was lying was obvious.
NOT in that-clauses as S or SC
e.g: T he problem was that he was lying.
e.g: We explain to the driver that we were in a hurry.
It was assumed that the stock market would
continue to rise.
You might also like
- Star Trek The Next Generation RPG Last Unicorn Games PDFDocument320 pagesStar Trek The Next Generation RPG Last Unicorn Games PDFNicolas Morin50% (2)
- Solo Improv GamesDocument1 pageSolo Improv GamesEduardo Garcia Rajo100% (3)
- Differences Alif Hamza Wasly QataiDocument2 pagesDifferences Alif Hamza Wasly QataiGnei Zahara AhamathNo ratings yet
- Grammar Glossary PDFDocument11 pagesGrammar Glossary PDFPecky27No ratings yet
- CASE STUDY-1 and 2 - WORDDocument7 pagesCASE STUDY-1 and 2 - WORDAbdul Khaliq Choudhary100% (1)
- Pronouns & QuantifiersDocument1 pagePronouns & QuantifiersMinh Thuận Hoàng ThịNo ratings yet
- Clean White Minimalist Mindmap BrainstormDocument1 pageClean White Minimalist Mindmap BrainstormNhậtNo ratings yet
- Portfolio of EnglishDocument52 pagesPortfolio of EnglishJoséantonio SeverinoNo ratings yet
- Exo GrammDocument27 pagesExo Grammamandine3remyNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses IpadDocument4 pagesRelative Clauses IpaddanigheoNo ratings yet
- ARTICLESDocument1 pageARTICLESNguyễn Thị Hoài ThuNo ratings yet
- 英語從句整理筆記Document4 pages英語從句整理筆記shuyutoma.ee09No ratings yet
- Learn & Talk I: Chapter 7 WorkDocument12 pagesLearn & Talk I: Chapter 7 WorkChobz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Adverbs or AdjectivesDocument1 pageAdverbs or Adjectivesevamairl31No ratings yet
- Noun ClausesDocument1 pageNoun ClausesPhương ThảoNo ratings yet
- t3 e 658 Know Your Grammar ks34 Foldable Fact Sheet - Ver - 3Document2 pagest3 e 658 Know Your Grammar ks34 Foldable Fact Sheet - Ver - 3RoxanneNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Week 1, Day 1 ResourcesDocument8 pages1.1 Week 1, Day 1 ResourcessdfsdfNo ratings yet
- Mapa MentalDocument1 pageMapa MentalIsa PeñaNo ratings yet
- SENTENCES MergedDocument4 pagesSENTENCES MergedHuỳnh Võ Bích HuânNo ratings yet
- Present SimpleDocument1 pagePresent SimpleGabriel Escobar QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Differences Alif Hamza Wasly QataiDocument2 pagesDifferences Alif Hamza Wasly QataiGnei Zahara AhamathNo ratings yet
- English Fundamentals 1 - Qs PDFDocument4 pagesEnglish Fundamentals 1 - Qs PDFKhát Vọng100% (1)
- Learn & Talk I: Chapter 7 WorkDocument12 pagesLearn & Talk I: Chapter 7 WorkChobz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- LessonPlan G11 LFocus U9-11Document7 pagesLessonPlan G11 LFocus U9-11Thu HiềnNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Syntax Lecture 3Document22 pagesFoundations of Syntax Lecture 37doboz1csardabanNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses: "Teachers Who Love Teaching Teach Children To Love Learning"Document25 pagesRelative Clauses: "Teachers Who Love Teaching Teach Children To Love Learning"haNo ratings yet
- Learn & Talk I: Chapter 7 Work Lesson 63 Revision SevenDocument14 pagesLearn & Talk I: Chapter 7 Work Lesson 63 Revision SevenChobz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 1803indonesian GrammerDocument7 pages1803indonesian GrammerFiona ChauNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Appositive & Infinitive PhrasesDocument6 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - Appositive & Infinitive PhrasesAmy100% (3)
- Nama: Puspa Nuraini Putri Absen: 19 Kelas: Xi Ips 2 Rangkuman Materi Bahasa Inggris LMDocument10 pagesNama: Puspa Nuraini Putri Absen: 19 Kelas: Xi Ips 2 Rangkuman Materi Bahasa Inggris LMpuspa nurainiNo ratings yet
- Let's Go 2and 3Document11 pagesLet's Go 2and 3Sina MosaviNo ratings yet
- Noun ClauseDocument10 pagesNoun ClauseSokhifao LaiaNo ratings yet
- EappDocument2 pagesEappRUS SELLNo ratings yet
- English Lecture SheetsDocument63 pagesEnglish Lecture Sheetstipu1sultan_1100% (2)
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument1 pageGerund or InfinitiveRegi ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Learn & Talk I: Chapter 10 Holidays Lesson 87 April Fool's DayDocument12 pagesLearn & Talk I: Chapter 10 Holidays Lesson 87 April Fool's DayChobz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- English File 3rd - Pre-Inter TB 106Document1 pageEnglish File 3rd - Pre-Inter TB 106Liliana LardoneNo ratings yet
- の Nominalizer Japanese Grammar LessonDocument2 pagesの Nominalizer Japanese Grammar LessonJenel GasparNo ratings yet
- Postmodifier Adverbial Clause of Place: Where Roman Soldiers With Their Families After They From The ArmyDocument2 pagesPostmodifier Adverbial Clause of Place: Where Roman Soldiers With Their Families After They From The Armyvalentina antonia silva galvezNo ratings yet
- The Wonders of Grammar-2 PDFDocument2 pagesThe Wonders of Grammar-2 PDFAhmad SalmanNo ratings yet
- Part of Speech Powerpoint Presentation: By: Sheeraz Ahmed Memon Lecturer in EnglishDocument17 pagesPart of Speech Powerpoint Presentation: By: Sheeraz Ahmed Memon Lecturer in EnglishMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Learn & Talk I: Chapter 7 Work Lesson 54 Job HuntingDocument12 pagesLearn & Talk I: Chapter 7 Work Lesson 54 Job HuntingChobz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 03 Basic Sent ConfigDocument5 pages03 Basic Sent ConfigSimina MladinNo ratings yet
- Learn & Talk I: Chapter 7 Work Lesson 57 Asking For A LeaveDocument12 pagesLearn & Talk I: Chapter 7 Work Lesson 57 Asking For A Leavegleeters cosmeticsNo ratings yet
- Level Five1Document6 pagesLevel Five1Sina MosaviNo ratings yet
- Parts of A SentenceDocument33 pagesParts of A SentenceTherese NicoleNo ratings yet
- Word Classes (Noun To Verb)Document8 pagesWord Classes (Noun To Verb)floz fowneNo ratings yet
- That That That ( ) : Regrets Regrets ThinksDocument9 pagesThat That That ( ) : Regrets Regrets ThinksMiguel de LlanzaNo ratings yet
- ClausesDocument3 pagesClausesSamina ShamimNo ratings yet
- ClausesDocument3 pagesClausesSamina ShamimNo ratings yet
- English Lecture SheetsDocument63 pagesEnglish Lecture SheetsMiryam SarahNo ratings yet
- Adverbial ClausesDocument1 pageAdverbial ClausesMinh Thuận Hoàng ThịNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgCo1H7pruty7C TOVePYaFyvbZezbTfCAwy Uq DACNLz9fvmY6VmFuJa6U5q2dUO0qRbtLtGjc4p8hYUxohP7bPJNaX3x0niIH1XOtub XrAwdLn4OIDT05pehA G53pDYcmApGwaiz9CDocument10 pagesACFrOgCo1H7pruty7C TOVePYaFyvbZezbTfCAwy Uq DACNLz9fvmY6VmFuJa6U5q2dUO0qRbtLtGjc4p8hYUxohP7bPJNaX3x0niIH1XOtub XrAwdLn4OIDT05pehA G53pDYcmApGwaiz9CHiba YoucefiNo ratings yet
- Egyptian Grammar Glossary PDFDocument11 pagesEgyptian Grammar Glossary PDFPecky27No ratings yet
- Mind Map Skill 16-18Document3 pagesMind Map Skill 16-18Winahyu Cahyani WPNo ratings yet
- Words ReしAted To PしAces Of Entertainment: 2. WhatdotDocument1 pageWords ReしAted To PしAces Of Entertainment: 2. WhatdotJOSE RAMON HERNANDEZ HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Honoring: of I of I ThoDocument11 pagesHonoring: of I of I ThoMing dbNo ratings yet
- Handout For Technical English I IT ISCIM 19Document69 pagesHandout For Technical English I IT ISCIM 19EfraimeNo ratings yet
- Clauses 1Document7 pagesClauses 1Rishi ChaprodNo ratings yet
- Protected Cultivation of Grapes 1623232731Document40 pagesProtected Cultivation of Grapes 1623232731Karan Bir Singh GillNo ratings yet
- 4 Insurance Sales Incentive Program Ideas That WorkDocument3 pages4 Insurance Sales Incentive Program Ideas That Workgeorge akamaNo ratings yet
- LM5 RIOL Lite DatasheetDocument12 pagesLM5 RIOL Lite DatasheetStilux VoltNo ratings yet
- 100 Days CalDocument9 pages100 Days CalinforumdocsNo ratings yet
- Sample Size Determination and Confidence Interval Derivation For Exponential DistributionDocument6 pagesSample Size Determination and Confidence Interval Derivation For Exponential DistributionIsmael NeuNo ratings yet
- SP 01 en Power Supply PS 303 ProDocument1 pageSP 01 en Power Supply PS 303 ProRemi de CaesNo ratings yet
- Exam Preparation Chartered Member Solutions 20080403Document36 pagesExam Preparation Chartered Member Solutions 20080403Jordy NgNo ratings yet
- Digital Finance and FinTech, Current Research and Future Research DirectionsDocument44 pagesDigital Finance and FinTech, Current Research and Future Research DirectionsShambachew Omer HussenNo ratings yet
- Aeci Mining Explosives Product Catalogue Surface Bulk Emulsions 2019 OctoberDocument14 pagesAeci Mining Explosives Product Catalogue Surface Bulk Emulsions 2019 OctoberMohamed Badian Traore0% (1)
- Bài Kt 2 Biên Dịch 1-LiêmDocument10 pagesBài Kt 2 Biên Dịch 1-LiêmNguyen Loan100% (1)
- Ayaz Ahmed SoomroDocument9 pagesAyaz Ahmed SoomroNoman RathoreNo ratings yet
- English Grammar ExerciseDocument4 pagesEnglish Grammar Exerciseanca_2402No ratings yet
- Tomahawk Missile and Weapon SystemDocument2 pagesTomahawk Missile and Weapon Systemjoma11No ratings yet
- Michael Buble - HomeDocument5 pagesMichael Buble - Homepurbaalam0702No ratings yet
- Brand ImageDocument2 pagesBrand Imagedollys59No ratings yet
- Radiation Monitoring InstrumentsDocument107 pagesRadiation Monitoring InstrumentsCristina ȚărnăNo ratings yet
- Stand Hip Thrust InstructionDocument14 pagesStand Hip Thrust InstructionddelgadoNo ratings yet
- Union Feb. 10, 2016Document16 pagesUnion Feb. 10, 2016Your News. When You Want It.No ratings yet
- NewJaisa Corporate ProfileDocument14 pagesNewJaisa Corporate ProfileCRAZY ಕನ್ನಡಿಗNo ratings yet
- Knowledge RepresentationDocument14 pagesKnowledge RepresentationGonibala LandyNo ratings yet
- WASA Wastewater and Potable Water Design Requirements PDFDocument233 pagesWASA Wastewater and Potable Water Design Requirements PDFYassin AlkadyNo ratings yet
- US Army Medical Course MD0363100 Electrosurgical Apparatus PDFDocument36 pagesUS Army Medical Course MD0363100 Electrosurgical Apparatus PDFpeterwolf67No ratings yet
- GaugesDocument33 pagesGaugesUsman ansarNo ratings yet
- !legendary Gangster Princesses and Legendary Mafia PrincesDocument160 pages!legendary Gangster Princesses and Legendary Mafia PrincesChina Patente VillegasNo ratings yet
- Inspection and Test Record For L.V. Cable: Record No.: - Page - ofDocument1 pageInspection and Test Record For L.V. Cable: Record No.: - Page - ofSchwihdi ZakNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarterly Exam in Mathematics 4Document9 pages3rd Quarterly Exam in Mathematics 4Jaycer De MesaNo ratings yet
- Listed Below Are Nine Technical Accounting Terms Used in ThisDocument1 pageListed Below Are Nine Technical Accounting Terms Used in Thistrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet