Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acute Fia2
Uploaded by
Andrei MurariuCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acute Fia2
Uploaded by
Andrei MurariuCopyright:
Available Formats
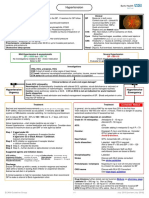
Emergency Department NUH
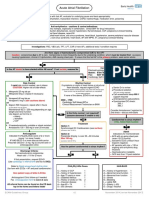
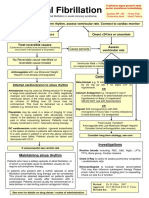
Acute Atrial Fibrillation
For all patients with fast AF, evaluate for underlying cause and treat appropriately:
Infection, hyperthyroidism, dehydration, myocardial infarction, COPD, haemorrhage, medication error, poisoning
Anti-arrhythmics – cautions & contra-indications:
All may be negatively inotropic, especially in combination. Check BNF for drug interactions
Amiodarone: Sino-atrial block and conduction disturbances, severe hypotension, thyroid disease, CCF, pregnancy & breast-feeding.
Flecainide: Atrial flutter, CCF, structural heart disease, recent MI
B-blockers: asthma / COPD, uncontrolled heart failure, sick sinus syndrome, heart block, hypotension, severe peripheral vascular disease
Ca channel blockers: heart failure, hypotension, sick sinus syndrome, heart block, AF with WPW, VT, pregnancy & breast-feeding
Digoxin: heart block, WPW, VT
Investigations: FBC, VBG (all), TFT, LFT, CXR (if new AF), additional tests if condition requires
Are there signs of haemodynamic compromise DUE to the AF?
Caution: compromise due to AF is rare. Compromise is more frequently due to the underlying condition, which must be treated first: eg sepsis
causing hypotension, chronic LV dysfunction, AMI causing chest pain. If unsure that the fast AF is the primary problem, seek senior advice
No Yes
Contacts
Is the AF known to have started within 48 hours? If not certain, assume No
Electrophysiology SpR at Barts (24/7):
Mobile: 07810 878 450
Fax: 0207 600 3069
No Yes Cardiology SpR: bleep 148 (in hours)
Rate Control Rhythm Control Synchronised DC Cardioversion
If rapid rate control needed, use iv doses If symptoms or signs of heart failure or structural
CAUTION: Higher risk of side-effects heart disease, request urgent ECHO Senior Dr to review
(CAUTION: dilated cardiomyopathy may have few clinical signs. Procedural sedation
1. Metoprolol 25 mg tds po Rate control may be preferred if significant co-morbidities
(RSI not usually required)
Metoprolol 5mg iv (repeat if necessary) or frail elderly patient)
Call anaesthetist bleep 095 if
OR support required
If none of the above, ECHO is not required
2. Verapamil 40 mg tds po Anteroposterior pad positions
Verapamil 5 mg iv (see cautions above) 0900 – 1700: Synchronised DC shock:
OR Cardiology SpR bleep 148 or 200 J
3. Digoxin 500 mcg po/iv, repeat after 4 hours Clinical Measurement Technician on 8039 360 J
(a third dose may be given)
Maintenance 62.5 – 250 mcg depending on age, Consider Amiodarone if resistant to
weight and renal function 2nd shock – discuss with Barts
Use digoxin as first line in: Is the Echo normal / not required?
No
elderly (assume abnormal if unable to do)
immobile Yes Cardioverted to sinus rhythm?
CCF
If No, follow Rate Control
OR Treatment
4. If haemodynamically unstable or shock resistant: Option 1:
Amiodarone 150 – 300 mg iv over 20 minutes Yes
Synchronised DC Cardioversion (see red box)
(success rate 70-90%)
Admit
Anticoagulate Option 2: Indications for monitored bed:
Indicated if CHA2DS2VASc score of 2 or more Flecainide 2mg/kg iv over 30 – 60 minutes ACS with on-going chest pain
(score 1 or more if male) Max 150 mg (even if ECG normal)
IF HAS-BLED 3 or more discuss with senior (success rate 40-70%) Ischaemic ECG (unless 6 hour
Prescribe tinzaparin 175 units / kg sc od until seen troponin negative)
in anticoagulation clinic AF persists with rate > 130 or
Has the patient cardioverted to sinus rhythm? ongoing anti-arrhythmic drug
infusions
Discharge Criteria:
Haemodynamic instability
No haemodynamic compromise
No Yes GCS less than 15 post sedation
Heart rate < 110 for 2 hours
If first presentation, request ECHO
(request on EPR ‘CV Echocardiogram – indicate outpatient test)
Cardiology OPD referral form sent
(fax with ECGs – AF and post cardioversion) CHA2DS2VASc Score HAS-BLED
Give patient copy of letter & ECGs
Anticoagulant Clinic follow-up if needed: C = history of CCF 1 H = history of hypertension 1
Email H = history of hypertension 1 A = Abnormal renal function 1
NUH_DVTANTICOAGNURSES1@bartshealth.nhs.uk A = Age 75 years or more 2 A = Abnormal liver function 1
including: D = Diabetes Mellitus 1 S = Stroke 1
Patient initials, DOB, hospital number, home and S = History of stroke or TIA 2 B = Bleeding 1
mobile numbers V = Vascular disease 1 L = Labile INR 1
A = Age 65 – 74 1 E = Elderly (> 65) 1
Advise patient to attend Forrest Ward, 1st floor, S = Sex (female) 1 D = Drugs / Alcohol 1
zone 9, 10.30 next working day
ECAM Guidelines Group v3 July 2015 [review July 2017]
Emergency Department
Acute Atrial Fibrillation
Lead Author
Consultant Emergency Medicine
Co-Authors / Collaborators
Consultant Cardiologists
Anticoagulation Nurses
Reference Documents
Management of Atrial Fibrillation, NICE CG180, June 2014
British National Formulary
ECAM Guidelines Group v3 July 2015 [review July 2017]
You might also like
- The Ehra Book of Intervntional Electrophysiology - OxfordDocument321 pagesThe Ehra Book of Intervntional Electrophysiology - Oxfordmorris njageNo ratings yet
- ACLS MneumonicsDocument4 pagesACLS MneumonicsnaranothNo ratings yet
- Handbook of AnesthesiologyDocument176 pagesHandbook of AnesthesiologyarmelzahfauziNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingFrom EverandOrthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingNo ratings yet
- Advanced EKG RefresherDocument181 pagesAdvanced EKG RefresherIoana Antonesi100% (3)
- ACLS Megacode Testing ScenariosDocument12 pagesACLS Megacode Testing Scenariosealm10100% (2)
- Acute FiaDocument2 pagesAcute FiaAndrei MurariuNo ratings yet
- Algorithm 1: Initial Evaluation and Management: Symptoms of Possible ACSDocument6 pagesAlgorithm 1: Initial Evaluation and Management: Symptoms of Possible ACSNenyNo ratings yet
- Prescribing in Chest PainDocument4 pagesPrescribing in Chest PainYY_1992No ratings yet
- Section 2artfibDocument2 pagesSection 2artfibIain Tarrant-MurphyNo ratings yet
- DS Male SurgicalDocument6 pagesDS Male SurgicalErryl Justine AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- ACLS Simplify AlgorithmDocument6 pagesACLS Simplify AlgorithmKristine Monforte Coma UritaNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndromes - HandoutDocument4 pagesAcute Coronary Syndromes - Handoutapi-641524095No ratings yet
- Primary Care Guidelines VertigoDocument1 pagePrimary Care Guidelines VertigoSyahidatul Kautsar NajibNo ratings yet
- Management of ArrhythmiasDocument4 pagesManagement of ArrhythmiasAray Al-AfiqahNo ratings yet
- ENT Vertigo FINAL v0.41Document1 pageENT Vertigo FINAL v0.41Farmasi BhamadaNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612Document1 pageAlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612YassarNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation - Student ResidencyDocument6 pagesAtrial Fibrillation - Student Residencyapi-404356063No ratings yet
- Notes On Cardiac ArrestDocument2 pagesNotes On Cardiac ArrestChris KingNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromesDocument7 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromesOwen J. WieseNo ratings yet
- 038 AnaphylaxisDocument5 pages038 AnaphylaxisabbuahmedibbuNo ratings yet
- ACS Algorithm 2016 PDFDocument1 pageACS Algorithm 2016 PDFrabin1994No ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation TDDocument6 pagesAtrial Fibrillation TDapi-594366475No ratings yet
- Periarestne AritmijeDocument10 pagesPeriarestne AritmijeMustafa ŠabićNo ratings yet
- TachycardiaDocument7 pagesTachycardiaArvind SahniNo ratings yet
- Cardio ACLS PDFDocument9 pagesCardio ACLS PDFfrankies fpNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guideline: Fibrinolytic Checklist Fibrinolytic ChecklistDocument4 pagesClinical Guideline: Fibrinolytic Checklist Fibrinolytic ChecklistRoi LevinzonNo ratings yet
- Algoritma Ambulance - PHCDocument11 pagesAlgoritma Ambulance - PHCYassarNo ratings yet
- Common Emergency Drugs 2019Document6 pagesCommon Emergency Drugs 2019Sohair Areez MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Current Clinical Strategies: Handbook of AnesthesiologyDocument180 pagesCurrent Clinical Strategies: Handbook of AnesthesiologydramaganaNo ratings yet
- PRN Medications: Indications & UseDocument23 pagesPRN Medications: Indications & Usedis_is_me100% (1)
- Management of Acute Coronary Syndrome / NSTEMI: Purpose of The GuidelineDocument7 pagesManagement of Acute Coronary Syndrome / NSTEMI: Purpose of The GuidelineSahera Nurhidayah NasutionNo ratings yet
- Care Plan:, Wrong, Wrong, Wrong, WrongDocument8 pagesCare Plan:, Wrong, Wrong, Wrong, Wronglovelylife theNo ratings yet
- Uro Gyn NotesDocument13 pagesUro Gyn NotesSheema ShNo ratings yet
- Acls Algorithms 2012Document12 pagesAcls Algorithms 2012Prashanth KumarNo ratings yet
- FlashcardsforStep2Part2 PDFDocument12 pagesFlashcardsforStep2Part2 PDFLoyla RoseNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias: Clinical DiagnosisDocument4 pagesArrhythmias: Clinical DiagnosispaveethrahNo ratings yet
- Dvanced Cardiac Life SupportDocument72 pagesDvanced Cardiac Life Supportolivia100% (1)
- Nclex Pharm ReviewDocument10 pagesNclex Pharm ReviewRuiqi YangNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain Cardiac Pre-Hospital ProtocolDocument1 pageChest Pain Cardiac Pre-Hospital Protocoleca nivlaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentmahNo ratings yet
- Neonatalseizureclinicalguideline PDFDocument15 pagesNeonatalseizureclinicalguideline PDFNURUL NADIA BINTI MOHD NAZIR / UPMNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument5 pagesAcute Coronary Syndromecotten joeNo ratings yet
- Chest PainDocument5 pagesChest PainAndrei MurariuNo ratings yet
- 2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Tachycardia AlgorithmDocument1 page2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Tachycardia AlgorithmRyggie ComelonNo ratings yet
- Algo Bradycardia DikonversiDocument5 pagesAlgo Bradycardia DikonversiDaniel SitungkirNo ratings yet
- 7698alorithm SeizureDocument3 pages7698alorithm Seizureboromeus abyasa daniswara100% (1)
- On Call ComplaintsDocument3 pagesOn Call ComplaintsrashaNo ratings yet
- Agitated PatientDocument2 pagesAgitated PatientCassandra GeldenhuysNo ratings yet
- ACLS-Pediatric Wide Complex Tachycardia: Sample Medical GuidelinesDocument2 pagesACLS-Pediatric Wide Complex Tachycardia: Sample Medical GuidelinesFebrialitaFatoniNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life SupportDocument37 pagesAdvanced Cardiac Life SupportRoy Acosta GumbanNo ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms Adult 2010 Revised May 31 2011Document12 pagesACLS Algorithms Adult 2010 Revised May 31 2011arturschander3614No ratings yet
- Treatment Algorithm For Autonomic Dysreflexia (Hypertensive Crisis) in Spinal Cord InjuryDocument1 pageTreatment Algorithm For Autonomic Dysreflexia (Hypertensive Crisis) in Spinal Cord InjuryHAYME THARRISNo ratings yet
- Paytonctrujillo - Er Drugs Nursing PharmacologyDocument9 pagesPaytonctrujillo - Er Drugs Nursing PharmacologyTricia Kaye IblanNo ratings yet
- 50 Emergency DrugsDocument70 pages50 Emergency DrugsderizNo ratings yet
- NCP DS NCM114 RleDocument12 pagesNCP DS NCM114 RleAllysa Kyle AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Hematologic SystemDocument19 pagesPharmacology Hematologic SystemCurtney PedriaNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandAtrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Priapism (Painful Erection), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPriapism (Painful Erection), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument2 pagesAsthmaAndrei MurariuNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Hypertensive Emergency Hypertensive UrgencyDocument2 pagesHypertension: Hypertensive Emergency Hypertensive UrgencyAndrei MurariuNo ratings yet
- Chest PainDocument5 pagesChest PainAndrei MurariuNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapeutic Management of Patients With Pregnancy-Related Pelvic Girdle PainDocument24 pagesPhysiotherapeutic Management of Patients With Pregnancy-Related Pelvic Girdle PainAndrei MurariuNo ratings yet
- F4AECCF9 - PBL Week 4 KidneyDocument13 pagesF4AECCF9 - PBL Week 4 KidneyKahfi AzzumardiNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation TypedDocument8 pagesDefibrillation TypedValarmathiNo ratings yet
- Pericarditis: Assessment and Diagnostic FindingsDocument3 pagesPericarditis: Assessment and Diagnostic FindingsJANIEZA ANGEL RA�ISES BALTAZARNo ratings yet
- Nephritic SyndromeDocument23 pagesNephritic SyndromeLateefah TalalNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome: Akynbay MoldirDocument8 pagesNephrotic Syndrome: Akynbay MoldirMoldir AkynbayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyChristopher bruncanoNo ratings yet
- Physiology-Summary NotesDocument201 pagesPhysiology-Summary NotesReem NasserNo ratings yet
- Brunner and Suddarth's Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing 12th Ed. (Dragged) 4Document1 pageBrunner and Suddarth's Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing 12th Ed. (Dragged) 4jamie carpioNo ratings yet
- Saudi License Exam (SLE) 3rd Edt. UQUDocument445 pagesSaudi License Exam (SLE) 3rd Edt. UQUkingmedic98% (41)
- Paediatric CardiologyDocument15 pagesPaediatric CardiologyAaron Nameer Abrar RahmanNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana Hiperosmolar Hiperglicemic State (SHH)Document16 pagesTatalaksana Hiperosmolar Hiperglicemic State (SHH)Vidya VidyutNo ratings yet
- (First Author) 2013 American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1Document5 pages(First Author) 2013 American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1Mahesh T MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular Disease in PregnancyDocument57 pagesCardio Vascular Disease in PregnancySanthosh.S.U0% (1)
- Basic ECG For Refresher Course 2014Document116 pagesBasic ECG For Refresher Course 2014Winz DolleteNo ratings yet
- Pathology+101 Complete)Document147 pagesPathology+101 Complete)Goh Kah Yong100% (2)
- Study of Hemotologicalprofile and Serum Iron Indices in Chronic Kidney Disease in Tertiary Care CentreDocument5 pagesStudy of Hemotologicalprofile and Serum Iron Indices in Chronic Kidney Disease in Tertiary Care CentreIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- List of Diseases Imo 2019 Cardio-RespiratoryDocument2 pagesList of Diseases Imo 2019 Cardio-RespiratoryDimas Adjie Yuda MahendraNo ratings yet
- Final Sheet MotalityDocument69 pagesFinal Sheet MotalityAshima GabgotraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 BLS Introduction To Chain of SurvivalDocument23 pagesLecture 1 BLS Introduction To Chain of Survivaldonibung 007No ratings yet
- Bifascular and Trifascular BlockDocument4 pagesBifascular and Trifascular Blockahmed ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Broad Complex TachycardiaDocument63 pagesBroad Complex Tachycardiadragon66No ratings yet
- Know About Pediatric Cardiac SurgeryDocument8 pagesKnow About Pediatric Cardiac SurgeryAshish DolasNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Tachycardia in The Ischemic HeartDocument57 pagesVentricular Tachycardia in The Ischemic Heartusfcards100% (3)
- CV DrugsDocument6 pagesCV DrugssaharamichaelNo ratings yet
- Dysrhythmia Advance Content Outline A1 - 2020.1.2Document3 pagesDysrhythmia Advance Content Outline A1 - 2020.1.2Kimberly Whiteside50% (2)
- Nephrology 7E 2016 PDFDocument2,710 pagesNephrology 7E 2016 PDFĐàoTrườngGiangNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 2 - CICU - LITREV - PENANGANAN ARRHYTHMOGENIC RIGHT VENTRICULARDocument14 pagesKelompok 2 - CICU - LITREV - PENANGANAN ARRHYTHMOGENIC RIGHT VENTRICULARasep idoyNo ratings yet