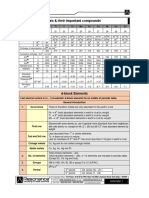
OCTAHEDRAL
VOID (OV) Simple Cubic Body Centered Cubic Face Centered Cubic Hexagonal Closed Packed Density
Unit Cell (S.C.C.) Unit Cell (B.C.C.) Unit Cell (F.C.C.) Unit Cell (H.C.C.)
Surrounded by 6 spheres
Z× M
C.N. = 6
d=
TETRAHEDRAL N A × a3
Present on edge centre and body
body centre of FCC unit
VOID (TV)
Surrounded by 4 spheres
C.N. = 4
Coordination No. Packging Efficiency
Lattic Corners Corners + Body Corners + All Corners + Face Centers (C.N.) (P.E.)
Present on body diagonal line at a points Center Face Center + 3 atoms in middle layers
a 3 It is no. of nearest 4
distance of
4
from corner of FCC
1 1 1 1 1 1 Z× π r3
unit Effective Number 8× 8 = 1 8 × 8 + 1 = 2 8× 8 + 6× 2 = 3 12 × 6 + 2 × 2 + 3 = 6 Neighbours of a PE = 3 × 100
of atoms (Z) lattice point a3
CRYSTALLINE & AMORPHOUS Packing Efficiency 52% 68% 74% 74%
(PE)
SOLID
STRUCTURE OF VARIOUS IONIC CRYSTALS
Coordination No. 6 8 12 12
CRYSTALLINE AMORPHOUS Crystal Lattice C.N. Number of Formula Eg
Structure Points Units per unit cell
• Have a long range • Do not have ordered
Rock salt Cl-,-CCP LiCl, KCl
order of particles structure or have a very 6:6 4
NaCl type Na+ -OV RbCl, AgCl
short order
• Anisotropic • Isotropic Zinc-Blende ZnS, Bes,
S2--CCP 4
• True solids • Pseudo solids Zns type
4:4
CuCl, CuI
Zn2+-Alternate TV
• Sharp melting point • Diffused melting point
• NaCl, Quartz, ZnS • Glass, Rubber, etc. CsCl type Cl--Corners 8:8 1 CsBr, CsI,
(BCC type) Cs+-Body centre CsCN
Molecular Covalent/Network
Fluorite type Ca2+-CCP SrF2, BaF2,
(CaF2) 8:4 4 SrCl2
Ionic Solid Metallic Solids F-all TV
Anti-Fluorite O2--CCP K2O, Li2O,
type (Na2O) 4:8 4
Li+-all TV K2S
CRYSTAL LATTICE / SPACE
LATTICE
A regular 3-D arrangement of constituent
MAGNETIC & ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES
particles. DEFECTS IN CRYSTALS
UNIT CELL
STOICHIOMETRIC
Smallest repeating DEFECTS NON STOICHIOMETRIC MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
unit which repeats DEFECT • Paramagnetic- Weakly attracted by magnetic field. eg. O2, Cu2+ etc.
itself over and over
again to generate IN NON-IONIC IN IONIC • Diamagnetic- Weakly repelled by magnetic field. H2O, NaCl, etc.
entire crystal SOLIDS SOLIDS • Ferromagnetic- permanent magnetism even in absence of magnetic
fields eg. Fe, Ni, CO, CrO2, etc.
Vacancy Interstitial Schottky Frenkel Metal excess Metal deficiency • Ferrimagnetic- Magnetic moment is smaller than that of
Defects Defects Defects Defects Defect Defects ferromagnetic substances. eg.
Types of Crystal Lattice/ • Equal no. of • Smaller ion is • It may arise either • Antiferromagnetic- Zero magnetic moment due to equal no. of anti-
• Some of the • Some particles dislocated from parallel eg. domains. eg. MnO, etc.
14 Bravis Lattices lattice sites occupy an
cations and
anions are it's normal site
due to anionic • Occurs due to cationic
are vacant interstial site vacancies or due to vacancy and presence
missing to an interstitial
sites presence of extra of a cation having
Cubic a=b=c α = β = γ = 90° cations at interstitial higher charge.
• Decrease in • increase in • Decrease in
• no change density Sites
ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES
Tetragonal a = b ≠c α = β = γ = 90° density density density • Appearance in oxides
• Generate F-centres • Conductors- Valence bond is partially filled or it overlaps with higher
Orthorhombic a ≠b ≠c α = β = γ = 90° of d-block metals.
which are responsible energy unoccupied conduction bond.
Monoclinic a ≠b ≠c α = γ = β ≠ 90° for colour in crystal
• Insulators- Large energy gap between valance and conduction bond.
Hexagonal a=b≠c α = β = 90° γ = 120° O 2- • Semi-conductors- Small energy gap between valance and conduction
bond.
Rhombohedral a=b=c α = β = γ ≠ 90° • p-type semiconductor (by doping e- deficient impurities
e- Fe3+
Triclinic a ≠b ≠ c α ≠ β ≠ γ ≠ 90° • n-type semiconductor (by doping e- rich impurities
Fe3+