Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antibiotic Chart-Infectious Disease Bug Drug Table-2019
Uploaded by
Duy LuuCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antibiotic Chart-Infectious Disease Bug Drug Table-2019
Uploaded by
Duy LuuCopyright:
Available Formats
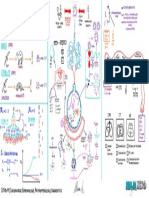
Infectious Disease Bug-Drug Table –© 2019 Dr.
Jessica Louie
PEK = Proteus, E.coli, Klebsiella, HN = Haemophilus, Neisseria
CAPES = Citrobacter, Acinetobacter, Providencia, Enterobacter, Serratia
(MRSE 70-80%)
MSSE (20-30%)
Frequency (hr)
CAPES (AmpC)
Common dose
Grp A & B Strep)
Pseudomonas
Strep viridans
Mouth anaerobes = Peptostreptococcus, Fusobacterium, Prevotella
Enterococcus
Staph aureus
(similar cov. Of
pneumoniae
(respiratory)
Static/Cidal
Time/Conc.
Renal/Liver
Atypicals = Mycoplasma, Chlamydia, Legionella
anaerobe
Staph epi
B. fragilis
Max/day
Others: Pneumocystis carinii (PCP), Toxoplasma, Giardia, Trichomonas, etc.
(faecalis,
faecium)
Atypical
Mouth
Italicized: usual activity is cidal, but italic is static for that specific organism
MRSA
Route
Other
Strep
DLR: dapto & linezolid resistant, MR: methicillin resistant
PEK
CSF
HN
VRE: vanco resistant enterococcus, U: urine
GPC: gram positive coverage, GN: gram negative coverage
DOC: Meningococci, Clostridium, Treponema, R Yes Cidal T IV, PO,
Natural-PCN Penicillin Pen VK Acinetomyces . S. pneumo S. pyogenes, IM (IM-
+/- BL + DOC ++ +/- ++ - Borrelia, Leptospira syph, RF) 250-500 6-8
Omnipen-N, DOC: Listeria, Proteus R Yes Cidal T
Ampicillin
Amino-PCN Polycillin-N Extended Coverage: G (-) bacilli IV, PO 250-500 6 14
Amoxicillin Amoxil +/- BL + + DOC +/- PE +/- ++ - EC, Proteus, H. inf, PO 250-875 8-12 -
Ampicillin/Sulbactam Unasyn R Yes Cidal T IV, IM 6 12
1.5-3
PCN + Beta- Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Augmentin + + + ++ +/- ++ ++ ++ PO 250 -875/125 8-12 -
lactamase Less active vs Pen G against G (+) Anti-
Oxacillin, Nafcillin Bactocill L Yes Cidal T
Inhibitor staphylococcal
Dicloxacillin Dynapen DOC - + R=ox IV, IM 1-2gm 4-6
Piperacillin/Tazobactam Zosyn ++ Extended gram(-) R Yes Cidal T 2.25-
Ticarcillin/Clavulanate Timentin + ++ + Ticar (-) ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ Very good vs. anaerobes IV 4.5gm 6
Surgical px (except colorectal), cellulitis, R NO Cidal T
1s t Cefazolin (1st) Ancef, Kefzol DOC soft-tiss infxn, post-op
(MIC 2-4) + + ++ +/- ++ IV 0.5-2gm 6-8 12
Zinacef, Gains gram(-) but less gram(+) activity. R NO Cidal T
2nd Cefuroxime (2nd) Kefurox + ++ ++ ++ DOC ++ Use for RTI IV 0.75-1.5 8 9
Surg px (colorectal), abd infxn, DM foot ulcers, R NO Cidal T
Cefoxitin (2nd) Mefoxin
2nd Cefox may have act. Vs. Mycobacterium
Cefotetan (2nd) Cefotan
+ - ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ chelonae, abscessus, fortiuitum IV 1-2gm 6-8 12
Cefotaxime, Excellent vs Strep DOC CAP, CTX+Flagyl=Erta R Yes Cidal T IV
Claforan
+ DOC oral anaerobes, meningitis d/t enterics, L IV, IM 1-2gm 8-12 12
3rd Ceftriaxone Rocephin
MIC 2-8 (no DOC DOC Neisseria, nosoc. Pneumonia, sepsis, UTI 1-2gm 24 (tri ) 4
(IM in ED)
Ceftizoxime( 3rd) Cefizox
(high) ceftiz) ++ (septic) (CAP) ++ ++ Ceftri + Amp may have synergy vs. E. faecalis R IV 1-2gm 8-12
Not reliable against gram(+) R Yes Cidal T
Ceftazidime (3rd) Fortaz, Tazidime,
3rd Meningitis d/t G (-) enterics, pneumonia, IV 1gm 6-8 16
Monobactam Aztreonam Tazicef, Azactam
++ ++ ++ ++ sepsis, febrile neutropenia IV, IM 1-2 6-12 8
+ Cefotax + Ceftaz, some BL resist. R Yes Cidal T
4th Cefepime (4th) Maxipime 2gm IV q8hr for GN (1gm IV q6hr can work)
MIC 4-8 ++ ++ ++ ++ + ++ ++ IV 1-2gm 8-12 6
1st/only BL vs. MRSA, <50 Yes Cidal T 600mg
5 th
Ceftaroline (5th) Teflaro - (poss No Prevotella, Bacteroides 31-50: 400
+++ ++ ++ ++ Faecalis) ++ ++ ++ + IV 15-30: 300 12
(almo Imi: better vs. gram(+), Enterococcus, Acineto, <20 Yes Cidal* T
Primaxin, I:
Faecalis st as Mycobacteria, Nocardia, higher MIC for (-) D<50 I/M I: 500mg I: 6 4g/d,
Imi/Mero/Dori Merrem, good Mer: better vs. Acineto, Pseudomonas
Carbapenem Doribax (no as No D M: 500mg M: 6 50mg
++ ++ ++ faecium) ++ ++ DOC ++ ++ ++ Dori: slightly better vs. Pseud ALL good 4 ESBL IV D: 500mg D: 6 /kg/d
Flagyl)
Similar to Ceftri + Flagyl <20 UK Cidal T
Ertapenem Invanz
+/- ++ ++ ++ ++
+/-
++ ++ No Pseudo, Acinetobacter, Enterococcus IV, IM 1gm 24 1
CPES
Vancocin, Coryne; C.diff (PO), R Yes Cidal T IV, PO,
Glycopeptide Vancomycin Lyphocin ++MR ++ ++ ++ ++ GPC Surgical ppx w/prosthetics; Endocarditis Thecal 500-1000 6-48
++MR hVISA, VISA 50, NO Cidal C
Lipoglycopeptide Telavancin Vibativ
/DLR ++ ++ ++ ++ GPC 30 IV 10mg/kg 24
H (in- Coryne, Listeria, M ct, Legionella, Cdiff, L Yes Static T 600
Oxazolone Linezolid Zyvox
++MR ++ ++ ++ ++VRE GPC C. perfringens, Oral 4 MRSA infxn IV, PO F=1 po 12
vitro)
Quinupristin/ ++VRE Static T
Streptogramin Syncercid
Dalfopristin ++MR ++ ++ ++ Faecium GPC Static vs. faecium L Yes IV 7.5mg/kg 8-12
Lipopeptide Daptomycin Cubicin ++MR + ++ ++VRE GPC No activity in lung b/c surfactant in lungs breaks it down <30 Yes Cidal C IV 4-6mg/kg 24
IV: 1.5mg/kg 8 5mg/k
Cidal IV, Inh,
Polymixin Polymixin B & E Colistin Inh: 75mg 12 150mg
HEK CAE ++ Last line for Pseudomonas R Yes Thecal Inthec 10mg 24 20mg
Norfloxacin (1s t) Noroxin + + + Quinolones: Mycobacteria coverage R UK Cidal C PO 400-800 12
Best FQ vs. Pseudomonas, anthrax Mix UK Cidal C PO 250-750 12 PO
Ciprofloxacin (2nd) Cipro
+/- +/- urine +++ + +++ +++ ++ H.influ, M. cat, Legionella, N. gonor. IV 200-400 8-12 80%
Quinolone
Levofloxacin (3rd) Levaquin +/- +/- ++ ++ urine ++ +++ ++ ++ ++ More respiratory/atypicals R UK Cidal C IV, PO 500-750 24 1:1
Moxifloxacin (3rd) Avelox Better vs. S. pneumo, Stenotrophomonas L UK Cidal C
+/- +/- +++ +++ urine ++ +++ ++ ++ ++ ++ IV, PO 400 24
Gentamicin/ Garamycin/ Amikacin: mycobacteria R NO Cidal C
AMG IV,
Tobramycin/Amikacin Nebcin/Amikin syn syn syn syn syn ++ HPEK ++ ++ Streptomycin: M. avium Thecal 2mg/kg 8-24
Erythromycin Erythrocin + + + + L NO Static T IV, PO 250-500 6-12
H. influ, H.pylori, Myco. Avium, M. catarrhalis
Macrolide Clarithromycin/ Biaxin,
H (Azith), A>C>E intracellular>extracellular
(Az=N <30 NO Static T
Azithromycin Zithromax STD (Az preferred): C. trach, N. gonor, PO 250-500
+/-MR +/-MR +/- R + ) + ++ U. urealyticum L IV, PO 250-500 24
Tetracycline - + + +R + + H.pylori, Protozoa (Plasmodium), Rickettsia R NO Static T PO 250-50 6
Minocycline Minocin + + +R + + + + Burkholderia cefaciae, Rickettsia R NO Static T IV, PO 100-200 12
Tetracycline
DOC walk pneumo M.,Chlamydia pneumo., L NO Static T
Doxycycline Vibramycin
++MR ++MR +/- R + + +/- R +/- R + ++ Rickettsia; Oral 4 MRSA infxn IV, PO 100 12-24
+HNE No cov of PPP (Proteus, Providencia, L NO Static T
Glycylcycline Tigecycline Tygacil +/- LD
++MR ++ ++ ++ ++VRE +EK K CAES ++ ++ ++ Pseudomonas), in-vitro C.diff. IV 50 12 100
+MR *May need D-test – resistance-induced L NO Static T PO 150-450 6-8
Streptogramin Clindamycin Cleocin Peptococci, Propionibac, Actin, C. perfringens
(D) +/-R ++ ++ ++ +R C, strep IV 100-900 6-12
Prevotella, Peptococcus, Peptostreptococcus, <10 Yes Cidal C
Other Metronidazole Flagyl
H.pylori, C.diff, Trichomonas vaginalis, Giardia
++ GN DOC lamblia, Entamoeba histolytica IV, PO 500 6-8
PCP (DOC), Toxoplasma gondii, Salmonella <30 Yes Static C 80/400-
Trimethoprim/
Sulfonamide Bactrim (hole in Shigella, Strenotrophomonas maltophilia 160/800
Sulfamethoxazole ++MR ++ +/- ++ UTI cov) ++ ++ ++ (DOC); Oral 4 MRSA infxn, uncomplic’d UTI IV, PO ~10mg/kg/d 12
Furadantin, Saprophyticus, DOC for UTI (Cystitis) R NO Cidal C
Other Nitrofurantoin (urine) Macrobid ++U ++U ++U EK U +/-U Not vs. Proteus, anaerobic, parasitic PO 100 12
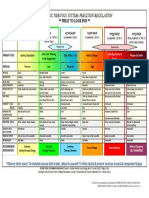
Infectious Disease Bug-Drug Table –© 2019 Dr. Jessica Louie Adverse Effects
Drugs NOT cleared Renally Renal Dose Adjust Nephrotoxic Drug Hepatotoxic Drugs Hypersensitivity Bone Marrow Suppression Photosensitivity Teeth/Bone Development
Hepatic CL: All renally cleared • Vancomycin • Imipenem, Meropenem, Doripenem (minor • Class: Penicillin & Cephalosporins • (see hematologic below…) – • Class: Quinolones… • Class: Tetracycline (caution <8 y/o)
• Oxacillin medications EXCEPT • Televancin increase AST/ALT) • Ertapenem IM – hypersen to amide ↓ plts (thrombocytopenia) d/t halogenation at C8 – inhibition of bone & teeth
• Ceftriaxone Cefepime • Colistin • Class: Quinolones (rare ↑ LFTs, fulminant • Vancomycin: rash/anaphylaxis • Penicillinase-R PCNs (Nafcillin, (spar>lome>cipro=oflox=nor>levo> discoloration – most common
• Linezolid • Aminoglycosides failure) • Metronidazole: urticarial, flushing, Oxacillin) – high dose, long duration gati=moxi=0) w/TCN, less w/Doxy
• Synercid (but UH adjusts Cefepime Other Renal Problems: • Erythromycin (inc. LFTs) erythematous rash • Linezolid • Class: Tetracyclines (more common
• Moxifloxacin < 30) • Quinolones – crystalluria, interstitial nephritis • Telithromycin Cross-sen w/PCN: 5-15% ceph, 50% • Bactrim w/TCN, NOT allx rxn!)
• Erythromycin • Tetracyclines – AFR, azotemia, renal damage • Clindamycin (inc. LFTs) carbapenems, 1-2% aztreonam • Quinolones • Doxycycline
• Azithromycin reported (renal dose adjust all except doxy) • Tetracyclines • Tigecycyline
• Doxycycline • Metronidazole – urethral burning, cystitis, • Synercid (hyperbilirubinemia up to 25%, • Bactrim
• Tigecycline polyuria, incontinence, urine discoloration reversible LFT incr.) Cartilage Toxicity Arthralgia/Myalgia/Myopathy/Tendons Infusion-Related
• Clindamycin • Bactrim – caution in renal insuff, keep hydrated • Linezolid (incr. LFTs) • Class: Quinolones • Class: Quinolones – BBW for tendon • Nafcillin (thrombophlebitis)
• Ciprofloxacin – mixed renal/hepatic CL to prevent crystalluria • Nitrofurantoin ( Alk Phos, AST/ALT, hepatitis) (animal data) rupture/tendonitis (athletes, pt • Cephalothin – 1s t gen IV CEPH (thrombophlebitis)
CSF Penetration Drugs BacterioSTATIC Drugs Concentration-Dependent Drugs w/corticosteroid use, pt >60 yr) • Cephalosporins
(everything else CIDAL) (everything else Time-dependent) Cardiac (QT prolongation) • Synercid • Carbapenems (inflam, inject site rxn, pruritis/rash)
• Pencillin • Imipenem/Meropenem • Linezolid • Televancin o May be up to 40% in debilitated pt w/ • Vancomycin/Telavancin: Red-Man Syndrome (d/t rapid infusion or large dose) –
• Telavancin comorbidities,
• Ampicillin/Amoxicillin • Vancomycin • Synercid • Daptomycin prevent w/prolong infusion time, dilute conc, pre-med Benadryl
• Quinolones: o May require analgesics for pain control
• Unasyn/Augmentin • Linezolid • Erythromycin, Clarithromycin, • Norfloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin, Moxifloxacin • Gemifloxacin rash (incr. in female<40, postmeno w/HRT, tx duration >7days)
levo, gati, moxi, gemi o Extend dose q8 to q12
• Oxacillin • Synercid Azithromycin • Aminoglycosides • Tetracyclines: rare skin conditions/allergies (anaphylaxis, urticarial, pruritus,
• Macrolides • Daptomycin – CK elevations (2.8%) – monitor
• Piperacillin/Tazobactam (Zosyn) • Daptomycin • Tetracycline, Minocycline, Doxycycline • Metronidazole exfoliative dermatitis, rashes)
• Telithromycin (ketolide) weekly
• Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone, Ceftizoxime • Colistin • Tigecycline • Bactrim • Tigecycline: injection site rxn (8.2%)
o Dapto targets cell membranes, statins also • Synercid: thrombophlebitis, rash, infusion site rxn
• Ceftazidime, Aztreonam • Metronidazole • Nitrofurantoin
target cell membranes – both have • Bactrim: generalized skin eruption (maculopapular rash/urtiaria), Steven
• Cefepime • Bactrim myopathy SE Johnson’s Syndrome (SJS), Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)
• Ceftaroline
Routes of Administration • Nitrofurantoin: macular, urticarial rashes
Intrathecal: IM: Cephalosporin Options: Abx in Pregnancy CI in Children Electrolyte Imbalances
• Vancomycin • Penicillin Gen. IV PO Category B Category C • Quinolones: previously CI in kids <16 • Ticarcillin (high Na load)
• Aminoglycosides • Unasyn • B-lactams • Vancomycin (IV) but evidence say that CF kids use • Penicillin VK (high K load)
1st Cefazolin Cephalexin (Keflex) 250-500mg Q6h
• Colistin • Oxacillin Cephradine • Marolides • Telavancin (CI – limb/digit malform) FQ as DOC w/o complications • Cipro/gatifloxacin (glucose
• Ceftriaxone Cefadroxil • Clindamycin • Linezolid • Tetracyclines: caution < 8yrs d/t bone disturbance, avoid
Inhalation: • Synercid • Telithromycin formation & teeth discoloration w/glyburide)
• Aztreonam 2nd Cefuroxime Cefuroxime
• Colistin • Ertapenem Cefoxitin Cefaclor • Daptomycin • Quinolones (avoid d/t possible cartilage toxicity)
IV ONLY: PO ONLY: Cefotetan Cefprozil • Vancomycin (Oral) • Colistin
• Piperacillin/Tazobactam (Zoysn) • Amoxicillin 3rd Cefotaxime Cefixime • Metronidazole • Bactrim (avoid 1st & 3rd trimesters)
Ceftriaxone Cefpodoxime 100-200 mg Q12h (avoid 1s t trimester) Category D
• Imipenem, Meropenem, Doripenem • Augmentin
Ceftazidime Cefdinir • Nitrofurantoin • Aminoglycosides
• Telavancin • Norfloxacin
Ceftibuten (at term 38-42 weeks) • Tetracyclines
• Synercid • Clarithromycin
4th Cefepime - & <1 month old • Tigecycline
• Daptomycin • Tetracycline
infants • Voriconazole
• Aminoglycosides • Nitrofurantoin 5th Ceftaroline -
• Tigecycline Hematologic Lung
Spectrum of Activity Increased bleeding • Bactrim: dose related (limit to 15mg/kg) • Nitrofurantoin:
Mycobacteria Parasites Others • Ticarcillin / Cefotetan o Agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, o Interstitial lung dz
• Amikacin • Toxoplasma: • Spirochetes: (Treponema, Borrelia, Leptospira) • Interferences w/coagulation tests: Telavancin hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia o Pulmonary edema
• Clarithryomycin/Azithromycin (M. avium) o Bactrim o Peniicillin (DOC) (does NOT interfere w/coag tho) • Nitrofurantoin o Pulmonary fibrosis (rare)
• Giardia: o Doxycycline • Quinolones: rare-anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia o Anemia, hemolytic anemia, eosinophilia, Lupus
o Metronidazole • Rickettsia: • Linezolid: neutropenia • Minocycline: drug-induced lupus
• Entamoeba: o Tetracycline, Minocycline, Doxycycline (DOC) o Thrombocytopenia • Metronidazole reported
o Metronidazole • Plasmodium (Protozoa): o Anemia o Reversible neutropenia (rare) Taste Disturbances (metallic)
• Trichomonas o Tetracycline o Leucopenia / Pancytopenia • Telavancin
o Metronidazole • Pneumocystis: opportunistic infxn in immunocompromised o ↑risk w/ duration of Rx (2wk or longer), concomitant meds • Clarithromycin
o Use of Vit B6 may ↓ risk of developing toxicity • Metronidazole
• Chlamydia trachomatis: “MD Questions” pts
o Bactrim (DOC) o Monitor CBC weekly
o Macrolides
o Doxycycline CNS Adverse Effects
o Quinolones Seizures Peripheral Neuropathy Ototoxicity
Drug-Interactions • Penicillin G Neuromuscular blockade (CI in myasthenia gravis): • Vancomycin: Cp>50-80 mg/L
1A2: 3A4: 3A4: 3A4: • Imipenem (NTE 4gm/day), Mero/Dori also but • Aminoglycosides • Aminoglycosides (25% incidence, irreversible)
• Quinolones inhibit it • Macrolides inhibit it: • Telithromycin strong inhibitor of it • Synercid inhibits it not as significant as Imi • Colistin o Auditory: Amikacin
o Dec. CL of concomitant agent: Ery ~ Cla, no Azith (ketolide, like macrolide) o CCB (amlodipine) increased • Quinolones (rare) Peripheral neuropathy: o Vestibular: Strep, Gentamycin
Theophylline, Caffeine, Warfarin • ↑ levels of: Drug Effect/Rec amlodipine toxicity • Metronidazole • Colistin (perioral paresthesias, tingling sensation in fingers) o Both: Tobramycin
o Enox>>cipro, grepa>>>levo, nor, o CBZ o Statins: ↑myopathy • Bactrim • Linezolid • Erythromycin
Simvastatin ↑ cmax 5.3-8.9x
oflox, spar, trova>gati, moxi o Cimetidine suspend statin o Calcineurin inhibitors • Nitrofurantoin (long-term use and/or renal insufficiency) • Minocycline: vertigo reported (extreme dizziness)
o Cipro>levo>moxi o Cyclosporine Midazolam ↑cmax 2-6x (tacrolimus, cyclosporine) • Metronidazole (numb/paresthesias)
o Digoxin USE CAUTION ↑ levels, ↑toxicity Other Random Notes
o Phenytoin Digoxin ↑cmax 73%, - Metronidazole also • All drugs against Enterococcus are D-test • CAPES – Cefepime DOC b/c induce beta • Erythromycin – looks like human-
o Ritonavir monitor dig closely causes toxicity bacterioSTATIC, cidal effects are • Used for Clindamycin lactamase and will break down less motilin so has motilin-effect
o Tacrolimus Metoprolol ↑cmax 38%, w/calcineurin gained with synergy with AMG • When put disk of clinda on plate, usu stable cephalosporins • Tigecycline
o Theophylline inhibitors • VRE mostly d/t Faecium see zone of inhibition as circle – • Usually see CAPES in hospital o Indicated for CAP, SSTI
caution in HF pts
o Statins • S. epidermidis usu. methicillin- but when add Macrolide disk pneumonia – thus, prefer to use o NO bacteremia – lipophilic
o Valproic acid resistant (thus grouped with nearby to Clinda disk – may see Cefepime b/c do not want to wipe and doesn’t distribute into
Theophylline ↑ GI effects,
o Warfarin MRSA) “D” zone of inhibition (missing out gut flora with Zosyn blood well
admin 1 hr apart
Levels of macrolides ↓’d with rifampin • ESBL: resistance of beta-lactams, part of circle) – if see D in this test • When resistance to Pseudomonas, • Oral MRSA infxn agents:
Food: Bile Acid Sequestrants: tetrayclines • Probenacid: MAO inhibitor: Linezolid is a reversible, o usu found in E.coli, Klebsiella – it is considered induced usually resistance to all drugs for o Bactrim
• Tetracycline decr. Absorption w/food • Cholestyramine, colestipol o Carbapenem: incr. serum conc. & nonselective MAO inhibitor o Carbapenem DOC – Ertapenem resistance and DO NOT want to Pseudomonas – pumps efflux out all o Clindamycin
• Nitrofurantoin delayed absorption • May bind TCN and ↓ absorption extend Carbapenem T1/2 o SSRIs + MAOI (Linezolid) → better b/c less broad use Clindamycin for that infxn. the medications – o Doxycycline
Tetracyclines: Oral contraceptives: tetracyclines o Nitrofurantion: ↓ CL of Serotonin Syndrome (avoid use • Colistin is last line use for Pseudomonas o Linezolid
• Separate dose by >2 hrs from: - Efficacy may be reduced, Advise back up nitrofurantoin and ↑ levels w/ w/in 14 days of Linezolid) Pattern of Activity Antibiotics Goal of Therapy PK/PD Parameter Specifics
o Milk Warfarin possible ↑’d ADR o Serotonin syndrome: mild-severe Type I Aminoglycosides Maximize conc. Peak/MIC AMG: Peak/MIC > 10,
o Antacids • Tetracyclines: • Multivalent Cations: Quinolones - Cognitive: HA, agitation, Conc.-dependent killing Ketolides (telithromycin) (or 24hrs-AUC/MIC) AUC24 70-100 (> = toxicity)
o Iron supplements o May cause potentiation of • Digoxin: Macrolides affect biliary CL mental confusion, Moderate-Prolonged persistent Metronidazole
Anticonvulsants: warfarin induced anticoaguln • Sulfonylureas: Bactrim, causes hallucinations, coma effects Amphotericin B
Tetracyclines o Closely monitor INR hypoglycemia through PPB - Autonomic: sweating, Type II Beta-lactams Max duration of T > MIC Beta-Lactams:
• Barbiturates, CBZ, phenytoin • Tigecycline displacement hyperthermia, HTN, Time-dependent killing Macrolides exposure T > MIC > 40-50%
tachycardia, N/V Minimal persistent effects Oxazolidinones (Linezolid) >100% for more severe infxns
• ↑ hepatic metabolism of o Monitor INR • MTX: Bactrim
- Somatic: myoclonus (muscle Flucytosine
TCN…leads to↓ serum levels o NOT Cyp interaction o TMP causes additive inhibition of
twitching), hyperreflexia, Type III Azithromycin Max amt of drug 24hr- AUC/MIC Vancomycin:
Bactrim: • Bactrim DHF reductase and Time-dependent killing Clindamycin Maximize T > MIC
• (Fos)phenytoin: ↓ CL by inhibition o Potentiate effect,↑ bleeding via o SMX may ↑ MTX thru PPB tremor
Moderate-Prolonged persistent Daptomycin AUC24/MIC > 400
of phenytoin metab by TMP ↓ vit K. in gut displacement → ↑MTX toxicity Tyr-containing foods: With Linezolid ↑↑ effects Fluoroquinolones FQ: AUC24/MIC >125 Gram negative
Metronidazole: o Also, displacement warfarin from o MTX = methotrexate BP (avoid these foods) – aged cheese, Streptogramins (Synercid) >30 Gram positive
• Incr. elim of Metro with PPB, and stereo-selective ↑ of meats, soy sauce, beer, red wine, sausage Tetracyclines
Barb/Phenytoin serum levels of S warfarin Pseudoephedrine: Linezolid, ↑ BP Vancomycin
• Decr. CL of phenytoin w/potential enantiomer Disulfuram rxn: Metronidazole
for toxicity • Metronidazole: Inhibits Warfarin,↑ INR (hypersensitivity to alcohol rxn) © 2019 Find Your Script; www.FindYourScript.com
You might also like
- Non Taccostare Allurna Giuseppe Verdi - A MinorDocument5 pagesNon Taccostare Allurna Giuseppe Verdi - A MinorMohammadNo ratings yet
- Son Tentacion - HeridaDocument12 pagesSon Tentacion - HeridaMauricio AguilarNo ratings yet
- Departments of Neurology, James J. Peters Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Bronx, NY, and Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, NYDocument1 pageDepartments of Neurology, James J. Peters Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Bronx, NY, and Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, NYyuliNo ratings yet
- Respiratory ExaminationDocument1 pageRespiratory ExaminationFANo ratings yet
- 13PLAN planMAUGDocument1 page13PLAN planMAUGEvanrey EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Chiquito Team Band - Lejos de TiDocument8 pagesChiquito Team Band - Lejos de TiMercedes Terrón EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Ave - Verum - Corpus - Mozart A-DurDocument3 pagesAve - Verum - Corpus - Mozart A-DurNatalia KarolakNo ratings yet
- Dilbert Aguilar - Mix Leo DanDocument7 pagesDilbert Aguilar - Mix Leo Danmaximo torres huancaNo ratings yet
- Humming Choir From Madama Butterfly - PucciniDocument2 pagesHumming Choir From Madama Butterfly - PucciniIgnasi SoleNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument20 pagesIlovepdf MergedIgnasi SoleNo ratings yet
- 12 - Surge Propera - Michael NavarrusDocument3 pages12 - Surge Propera - Michael NavarrusVíctor CruzNo ratings yet
- Angels We Have Heard on High Sheet MusicDocument7 pagesAngels We Have Heard on High Sheet MusicVanessa KaiserNo ratings yet
- Sullaria The Letter DuetDocument3 pagesSullaria The Letter DuetGiovanniFernandoMolinaOrtiz100% (2)
- Famplanenglishd 28533Document2 pagesFamplanenglishd 28533Sawera ChNo ratings yet
- NJTRailSystemMap Aug2022Document1 pageNJTRailSystemMap Aug2022novusenggNo ratings yet
- Rafaga - VeteDocument10 pagesRafaga - VeteMauricio AguilarNo ratings yet
- Its All Coming Back To Me Now Meat Loaf Marion RavenDocument10 pagesIts All Coming Back To Me Now Meat Loaf Marion RavenTim MorsbachNo ratings yet
- ARREBATAO - Trumpet in BB 1Document2 pagesARREBATAO - Trumpet in BB 1Juan Carlos Perez UribeNo ratings yet
- نموذج حصر حديد تسليح القواعد المنفصلةDocument3 pagesنموذج حصر حديد تسليح القواعد المنفصلةasemelsawy70No ratings yet
- MICROCharts PDFDocument19 pagesMICROCharts PDFvf6jxyb65dNo ratings yet
- Prepping MatrixDocument1 pagePrepping MatrixDiego Bruna EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Physical Exam (HEENTDocument1 pagePhysical Exam (HEENTJohnny BeeNo ratings yet
- The Little Negro - Claude DebussyDocument2 pagesThe Little Negro - Claude DebussyRaúl M-ANo ratings yet
- Joe Arroyo - La RebelionDocument7 pagesJoe Arroyo - La RebelionMauricio AguilarNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus - Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnostics - Key AtfDocument1 pageCoronavirus - Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnostics - Key AtfJuan Manuel Tapia AlzateNo ratings yet
- Nizam e Hazm Kay AmraazDocument3 pagesNizam e Hazm Kay AmraazMuhammad Javed AslamNo ratings yet
- P3 2 Storey Res 7 20 23Document1 pageP3 2 Storey Res 7 20 23Jehrome CruzNo ratings yet
- Heat LoadDocument41 pagesHeat LoadpanyamnrNo ratings yet
- Crucifixus AriaDocument13 pagesCrucifixus AriaMaria Jesus RuizNo ratings yet
- Missa Brevis: 4. SanctusDocument9 pagesMissa Brevis: 4. Sanctuslanamusica-1No ratings yet
- Спектр АБ активности антибиотиковDocument1 pageСпектр АБ активности антибиотиковbrounalisaNo ratings yet
- AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: PRECISION REGULATION WHAT TO LOOK FOR Babette RothschildDocument1 pageAUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: PRECISION REGULATION WHAT TO LOOK FOR Babette Rothschildest54No ratings yet
- Sistema NervosoDocument1 pageSistema NervosoPerisson Dantas100% (2)
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology) 03 Heparin - KeyDocument1 pageCardiovascular Pharmacology) 03 Heparin - Keyhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Notes AtherosclerosisDocument1 pageNotes AtherosclerosisElizabeth de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- REPALLEDocument1 pageREPALLEkishore.pd3dNo ratings yet
- (Free Scores - Com) - Christmas Medley Piano 27395 PDFDocument4 pages(Free Scores - Com) - Christmas Medley Piano 27395 PDFLuis AntonioNo ratings yet
- AmenoDocument11 pagesAmenoDavid Apraez LeytonNo ratings yet
- In PaceDocument3 pagesIn Pacemeylota2No ratings yet
- Enfermera - Gran OrquestaDocument10 pagesEnfermera - Gran Orquestacarlos santanderNo ratings yet
- Saxofone Alto-Partitura e PartesDocument9 pagesSaxofone Alto-Partitura e PartesEmily GregoryNo ratings yet
- Cadenza: To W.A. Mozart's "Andante Cantabile" (Violin Concerto 4)Document1 pageCadenza: To W.A. Mozart's "Andante Cantabile" (Violin Concerto 4)程子恒No ratings yet
- Result of Compaction Test: Lab Geoteknik (Formulir)Document1 pageResult of Compaction Test: Lab Geoteknik (Formulir)eka krisnantoNo ratings yet
- Ave Verum EbDocument2 pagesAve Verum EbDiego AranaNo ratings yet
- Arvo Part - Cantate Domino Canticum NovumDocument9 pagesArvo Part - Cantate Domino Canticum NovumKollár Boglárka100% (3)
- Village People - YmcaDocument3 pagesVillage People - YmcaalexNo ratings yet
- Arr. Jayme Amatnecks JR.: Tum Tum ... AhDocument8 pagesArr. Jayme Amatnecks JR.: Tum Tum ... AhvvkiuikNo ratings yet
- Henry:Bewaker:Wizard BladmuziekDocument3 pagesHenry:Bewaker:Wizard BladmuziekKoen BothNo ratings yet
- PDF Hoja de Registro Anestesico Gava CompressDocument2 pagesPDF Hoja de Registro Anestesico Gava CompressEDITH NATHALY CUMBAJIN PANELUISANo ratings yet
- 079254C 1g00u01 Iso CSW 1g00civ005 0001 - 0Document1 page079254C 1g00u01 Iso CSW 1g00civ005 0001 - 0Mahmoud HassanNo ratings yet
- 079254C 1g00u01 Iso CSW 1g00civ007 0001 - 0Document1 page079254C 1g00u01 Iso CSW 1g00civ007 0001 - 0Mahmoud HassanNo ratings yet
- Quando Ele Vem-Partitura e PartesDocument68 pagesQuando Ele Vem-Partitura e PartesAbner BarcellosNo ratings yet
- Fear No Danger To EnsueDocument5 pagesFear No Danger To EnsueAkosua PomaaNo ratings yet
- スケール練習 (Trombone)Document1 pageスケール練習 (Trombone)RenapsonNo ratings yet
- Requiem 11. Sanctus - MozartDocument4 pagesRequiem 11. Sanctus - MozartFran AnelloNo ratings yet
- Send Us Lord To Every Nation-1Document11 pagesSend Us Lord To Every Nation-1Melinda MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Selamat Hari Natal ScoreDocument6 pagesSelamat Hari Natal ScoreHengky SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Agonist Anti-Cholinergic Agents Neuromuscular Blocking Agents (Nmba)Document1 pageCholinergic Agonist Anti-Cholinergic Agents Neuromuscular Blocking Agents (Nmba)Johnny BNo ratings yet
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 3: MathFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 3: MathRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 4: MathFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 4: MathRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Chronic Bone Pathologies - Draw It To Know ItDocument1 pageChronic Bone Pathologies - Draw It To Know ItDuy LuuNo ratings yet
- Biology of Sleep & Wakefulness - Draw It To Know ItDocument1 pageBiology of Sleep & Wakefulness - Draw It To Know ItDuy LuuNo ratings yet
- Blood Groups - ABO & RH - Draw It To Know ItDocument1 pageBlood Groups - ABO & RH - Draw It To Know ItDuy LuuNo ratings yet
- Calculation FormulasDocument8 pagesCalculation FormulasDuy LuuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 - WarfarinDocument24 pagesChapter 21 - WarfarinDuy LuuNo ratings yet
- Gendec - 2022-02-04T121135.640Document1 pageGendec - 2022-02-04T121135.640Robinson llanos ceraNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Virology: Understanding Viruses and Their StructureDocument27 pagesIntroduction to Virology: Understanding Viruses and Their StructureEsmond Mbulo100% (1)
- COVID 19 Vaccination A Guide For AdultsDocument12 pagesCOVID 19 Vaccination A Guide For AdultsMUHAMMAD AQEEL AKHTAR BIN MOHD HAIDRES MoeNo ratings yet
- Eabf1374 FullDocument12 pagesEabf1374 FullNiatazya Mumtaz SagitaNo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument8 pagesDengue FeverJay MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Derma BriefDocument7 pagesDerma BriefjeharatNo ratings yet
- Bacte Midterm Di TaposDocument9 pagesBacte Midterm Di TaposAL-HUSSEIN NAWABNo ratings yet
- Principles of Antimicrobial ChemotherapyDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Antimicrobial ChemotherapySteven miles PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Version Nueva Covid FluDocument2 pagesVersion Nueva Covid FluAdams QuintanillaNo ratings yet
- Afp For MbbsDocument65 pagesAfp For MbbsShyam Sundar SNo ratings yet
- Sa CelulitisDocument19 pagesSa CelulitisJulio Ramos EliasNo ratings yet
- VPD RashchrtDocument2 pagesVPD RashchrtMarco Ramos JacobNo ratings yet
- D. Prevent Transmission of Infectious MicroorganismsDocument22 pagesD. Prevent Transmission of Infectious MicroorganismsL1NEDS DNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR On New FilariaDocument50 pagesSEMINAR On New FilariaArun JvNo ratings yet
- Public Health Emergency Management (PHEM) : GuidelineDocument186 pagesPublic Health Emergency Management (PHEM) : GuidelineToni Tesfay75% (4)
- English 5 Q3 Week 4 PDFDocument4 pagesEnglish 5 Q3 Week 4 PDFGlayza EsponillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesDrug Study - AmoxicillinVANESSA PAULA ALGADORNo ratings yet
- Partial Genome Characterization of Novel ParapoxviDocument4 pagesPartial Genome Characterization of Novel Parapoxviali zohaibNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Infections 1Document62 pagesRespiratory Infections 1Eduardo Valdez RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Intensive Review For Mockboards (All Subjects)Document27 pagesIntensive Review For Mockboards (All Subjects)Shairah Joy Julgado DedalNo ratings yet
- Malaria Entomology and Vector Control Guide For ParticipantsDocument190 pagesMalaria Entomology and Vector Control Guide For ParticipantsZamboanga del Norte PHONo ratings yet
- Darmstadt 1994Document15 pagesDarmstadt 1994rismahNo ratings yet
- Herpes Simplex Buttock Infection Linked to Genital HerpesDocument20 pagesHerpes Simplex Buttock Infection Linked to Genital HerpesElsa MayoraNo ratings yet
- Ear 1, 2Document9 pagesEar 1, 2Nnbbh HggyyNo ratings yet
- Herpes Zoster PDFDocument19 pagesHerpes Zoster PDFNicolás LaverdeNo ratings yet
- EXO Notes - Parasitology - Intro To paraDocument12 pagesEXO Notes - Parasitology - Intro To paraEdmarie GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Jean Aitchison Presentation English A LevelDocument16 pagesJean Aitchison Presentation English A Levelclarissa.fayeNo ratings yet
- Animal HusbandryDocument21 pagesAnimal HusbandryKshiteeja DushingNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S209379112300063X MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S209379112300063X Mainshoshanasingh52No ratings yet
- Infection Control and Standard Safety MeasuresDocument25 pagesInfection Control and Standard Safety MeasuresManisha Thakur100% (1)