Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 5
Uploaded by
Salwa Sikander0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageVectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction, and can be positive or negative. They represent physical quantities like velocity, acceleration, and displacement, while scalars only have magnitude and are always positive, like distance, speed, and mass. Vectors can be added and resolved into perpendicular components, with the x-component equaling the magnitude multiplied by the cosine of the angle and the y-component equaling the sine. The magnitude of a vector is calculated using Pythagorean theorem, and its angle is found with tangent inverse. Systems in equilibrium have their vector components summing to zero in both the x and y directions.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentVectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction, and can be positive or negative. They represent physical quantities like velocity, acceleration, and displacement, while scalars only have magnitude and are always positive, like distance, speed, and mass. Vectors can be added and resolved into perpendicular components, with the x-component equaling the magnitude multiplied by the cosine of the angle and the y-component equaling the sine. The magnitude of a vector is calculated using Pythagorean theorem, and its angle is found with tangent inverse. Systems in equilibrium have their vector components summing to zero in both the x and y directions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageUnit 5
Uploaded by
Salwa SikanderVectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction, and can be positive or negative. They represent physical quantities like velocity, acceleration, and displacement, while scalars only have magnitude and are always positive, like distance, speed, and mass. Vectors can be added and resolved into perpendicular components, with the x-component equaling the magnitude multiplied by the cosine of the angle and the y-component equaling the sine. The magnitude of a vector is calculated using Pythagorean theorem, and its angle is found with tangent inverse. Systems in equilibrium have their vector components summing to zero in both the x and y directions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
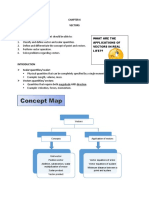
Unit 5
Introduction to Vectors
• The Definition of mathematical Vector
Vectors are quantities described by both magnitude and
direction
Vector represent:
• Scalar and Vector quantities
Scalar only magnitude and it’s always positive
Examples distance, speed, mass temperature etc.
Vectors magnitude and direction and it can be positive or
negative.
Examples: velocity, acceleration, displacement, weight etc.
• Additional of vectors and vector quantities
• Resolution of a vector into two components at right angles
X components 𝑭𝒙 = 𝑭 𝐜𝐨𝐬 𝜽
Y components 𝑭𝒚 = 𝑭 𝐬𝐢𝐧 𝜽
𝒙
Magnitude of a vector (𝒚) = √𝒙𝟐 + 𝒚𝟐
𝒚
To find the angle: 𝜽 = 𝐭𝐚𝐧−𝟏 ( )
𝒙
• Equilibrium
∑ 𝒇𝒙 = 𝟎 ∑ 𝒇𝒚 = 𝟎
You might also like
- Applied Physics LectureDocument16 pagesApplied Physics LectureKashif AliNo ratings yet
- 3 Chapter 2 Vectors PDFDocument24 pages3 Chapter 2 Vectors PDFملهم العبدالسلامةNo ratings yet
- 1 VectorsDocument25 pages1 VectorsAyham SmadiNo ratings yet
- Vector AlgebraDocument21 pagesVector AlgebraMaxNo ratings yet
- 02) Cartesian and Polar Form of A VectorDocument32 pages02) Cartesian and Polar Form of A VectorLamia Fateha meemNo ratings yet
- Scalars, Vectors and Components of VectorsDocument24 pagesScalars, Vectors and Components of VectorsAlyannah HermioneNo ratings yet
- Vector and ScalarDocument51 pagesVector and ScalarMusic LastNo ratings yet
- Mechanics: Vectors and ScalarsDocument31 pagesMechanics: Vectors and ScalarsEmmanuel SandramNo ratings yet
- Mathematical MethodDocument11 pagesMathematical MethodPrathmeshNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics LecturesDocument18 pagesApplied Physics LecturesKashif AliNo ratings yet
- Vector L1Document17 pagesVector L1amad khanNo ratings yet
- Notes - VectorsDocument14 pagesNotes - VectorsmichaeldelennboschNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 1 - DR Nader Shehata - Review On Vectors and ScalarsDocument41 pagesLecture - 1 - DR Nader Shehata - Review On Vectors and ScalarsLeadership IncNo ratings yet
- VectorDocument15 pagesVectorVeronica De LeonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 VectorsDocument37 pagesLesson 1 VectorsKenji BaguaNo ratings yet
- 2 Slides Vector Calculus 1 v1 Narration 2 No InkDocument21 pages2 Slides Vector Calculus 1 v1 Narration 2 No Inkd. r. o. a.No ratings yet
- EMF Theory by Sangeen PanezaiDocument100 pagesEMF Theory by Sangeen PanezaiSangeen Panezai0% (1)
- ForcesDocument30 pagesForcesMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- MAI Lecture 02 Vectors and MatricesDocument38 pagesMAI Lecture 02 Vectors and MatricesYeabsiraNo ratings yet
- CH 1 FinalDocument31 pagesCH 1 FinalaliNo ratings yet
- 1 CL305 Vectors TensorsDocument49 pages1 CL305 Vectors Tensorsshivurkolli07No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 VectorDocument14 pagesChapter 6 VectorEmir Emir SyaminNo ratings yet
- Motion in PlaneDocument15 pagesMotion in PlaneKajol HNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 Mechanics: Rahadian N, S.Si. M.Si. VectorsDocument36 pagesPhysics 1 Mechanics: Rahadian N, S.Si. M.Si. VectorsDimas Asmoro AjiNo ratings yet
- Vector 1Document26 pagesVector 1A.HNo ratings yet
- Scalars and VectorsDocument13 pagesScalars and VectorsRahim QureshiNo ratings yet
- CH # 2 Vectors and EquilibriumDocument14 pagesCH # 2 Vectors and EquilibriumMehak MuradaniNo ratings yet
- Vectors: Physics TutorialDocument22 pagesVectors: Physics TutorialWahyu Yesa100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Mechanics (BS 19-23) : Chap-3 (Vectors)Document37 pagesFundamentals of Mechanics (BS 19-23) : Chap-3 (Vectors)Sajjad TahirNo ratings yet
- 1 VectorsDocument63 pages1 VectorsShafay SheikhNo ratings yet
- 01 CESTAT30 Statics of Rigid Bodies Principles Fundamentals of Statics Part2Document67 pages01 CESTAT30 Statics of Rigid Bodies Principles Fundamentals of Statics Part2kawawa.narestrictNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document28 pagesChapter 3Muhammad TehreemNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Scalars & VectorsDocument3 pages1.4 Scalars & VectorsAmira FarahinNo ratings yet
- Unit07 CompleteDocument26 pagesUnit07 CompleteSRMUBARIK GamingNo ratings yet
- Chapter+3 VectorsDocument36 pagesChapter+3 VectorsRazan AlmuairfiNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document24 pagesChap 1Tuấn Nghĩa NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Nota Fizik AtolDocument62 pagesNota Fizik AtolKhairun HusnaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Phys100Document20 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Phys100Ahven EmbestroNo ratings yet
- Lec 2-Vectors, Components, Operation On Vectors, Unit VectorsDocument23 pagesLec 2-Vectors, Components, Operation On Vectors, Unit VectorsColeen AmadoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1: Mathematical Physics: ContainsDocument29 pagesCHAPTER 1: Mathematical Physics: ContainsMukit Hasan JimNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid Bodies: Esci 123 - Engineering Mechanics 1Document24 pagesStatics of Rigid Bodies: Esci 123 - Engineering Mechanics 1Jeslyn MonteNo ratings yet
- Vecto R: Nur Islami, PHDDocument34 pagesVecto R: Nur Islami, PHDfitri dwi hartatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 VectorsDocument20 pagesChapter 3 Vectorsa.a.ab14442No ratings yet
- Lecture # 3 (Vectors, Lines and Planes)Document34 pagesLecture # 3 (Vectors, Lines and Planes)Rakhmeen GulNo ratings yet
- Vector PDFDocument34 pagesVector PDFNur RamadhantiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document57 pagesChapter 3KhaledNo ratings yet
- Vectors: Intensive Course P.L. Chathurika SilvaDocument11 pagesVectors: Intensive Course P.L. Chathurika SilvaMuhammed IfkazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Motion in A PlaneDocument30 pagesChapter 4 - Motion in A PlaneHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument39 pagesVectorsAli AsaadNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument18 pagesPHYSICSjannnlateo04No ratings yet
- CH 3Document57 pagesCH 3Nasr alzorikeNo ratings yet
- SCI 2 - Physics For Engineers. Lesson 1Document57 pagesSCI 2 - Physics For Engineers. Lesson 1fortxtonly80No ratings yet
- Dcee 27a Lect 1Document39 pagesDcee 27a Lect 1Geraldine TimpocNo ratings yet
- AP1201 - CH - 1 - PPT - 01 - VectorsV2013Document16 pagesAP1201 - CH - 1 - PPT - 01 - VectorsV2013Anson ChanNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Vectors: Key Concepts, Equations, and Problem Solving StrategiesDocument6 pagesMeasurement and Vectors: Key Concepts, Equations, and Problem Solving StrategiesKim SeungminNo ratings yet
- Vectors: An Introduction To Vector QuantitiesDocument13 pagesVectors: An Introduction To Vector QuantitiesggmmnmcncnnmNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Physical Quantities: Scalar and Vector QuantitiesDocument18 pagesTopic 2: Physical Quantities: Scalar and Vector QuantitiesAzmi NasriNo ratings yet
- Mathematics For Machine LearningDocument100 pagesMathematics For Machine LearningUmaphani MorthaNo ratings yet
- Vectors PowerPointDocument22 pagesVectors PowerPointChanelle SilveraNo ratings yet