Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Microbiology
Uploaded by
Rose Kasidi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views5 pagesmicrobiology
Original Title
1. INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY - Copy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentmicrobiology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views5 pagesIntroduction To Microbiology
Uploaded by
Rose Kasidimicrobiology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
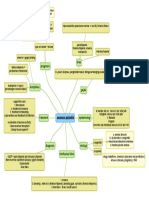
INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY
Definition
Micro – small, Bio – Life, Logy – Study
Microbiology is the study of living organism/micro organism (bacteria,
fungi, algae, protozoan and viruses) of microscopic size.
It is concerned with their morphology, structure, reproduction,
metabolism and classification.
History and evolution
- Lecretius (98 -55 BC) and Girolamo Fracastro (1478 - 1553) suggested
that a disease was caused by an invisible living creature.
- Robert Hooke (1635 - 1703) – Coined the word “cell”
- Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann – Described the cell theory
(A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of an organism)
1. The spontaneous generation (Abiogenesis)
Was stated by Aristotle in 346 BC, that living organisms could develop from non
living or decomposing matter.
Theory was supported by John Needham (1748)
- He boiled mutton broth and then tightly stoppered the flasks.
- Cloud was formed in the flask
- He concluded that the cloud was microorganisms
2. Biogenesis
Living organisms could develop from other
organisms.
A. Francesco Redi and the fly experiment (1629 - 1697)
B.Lazaro Spallanzani C. Louis Pasteur (1822 - 1895)
(1729 - 1799): The heating His experiment ended the spontaneous generation.
challenge
He opposed Needham’s
work.
The germ theory of disease: Bacteria are the
cause of disease in human, plant and animal.
The germ theory of fermentation:
Pasteurization ( heating milk at 62.8 0C for 30
min).
Protection against infection (Immunity): Principle of immunization
attenuated vaccines (older cultures of bacterium Pasteur applied this principle for
are on virulent bacteriums of same disease e.g.,
Chicken cholera)
prevention of Anthrax
D. Antony Van Leeuwenhoek
“Father of microscopy” The first person to observe and describe microorganisms.
E. Robert Koch (1843 - 1910)
Koch’s postulate: A specific microorganism can always found in association with a given disease
(Bacillus anthracis is a causative agent of Anthrax).
Staining: He discovered staining (Adding a dye to a microorganism to become visible).
F. Joseph Lister
He described Sepsis (surgical infections) using phenolic solution on wound to kills pathogens.
G. Alexander Flemmings
He is called as “father of antibiotics”. Penicillium notatum (Fungi) that produce antibiotic
Penicillin.
H. Fraun Hesse
Used agar as a solidifying agent
I. Richard J. Petri
Invented a petri plate
J. Edward Jenner
He described the concept of vaccination through a process called Variolation (An individual
affected by cow pox will not get small pox).
You might also like
- Microbiology Discovery TimelineDocument4 pagesMicrobiology Discovery TimelineRica Mae Agasen SalazarNo ratings yet
- The History and Scope of MicrobiologyDocument59 pagesThe History and Scope of MicrobiologyKrittika ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- HistoryofmicrobiologyDocument19 pagesHistoryofmicrobiologyPeak LevelNo ratings yet
- Micro 1 History of MicroDocument4 pagesMicro 1 History of MicroJewel Heart AbuboNo ratings yet
- The History and Scope of Microbiology: Prof. Khaled H. Abu-Elteen Hashemite UniversityDocument61 pagesThe History and Scope of Microbiology: Prof. Khaled H. Abu-Elteen Hashemite UniversityPaulo GanNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Its HistoryDocument61 pagesMicrobiology and Its Historylaiba tanveerNo ratings yet
- The History and Scope of Microbiology: Prof. Khaled H. Abu-Elteen Hashemite UniversityDocument61 pagesThe History and Scope of Microbiology: Prof. Khaled H. Abu-Elteen Hashemite UniversityOdurNo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument78 pagesHistorySubrat PandeyNo ratings yet
- Microbiology History and ScopeDocument49 pagesMicrobiology History and ScopeDelem SaviñonNo ratings yet
- BacteriologyDocument149 pagesBacteriologyDeynielle Keith B. TiwagNo ratings yet
- Introductory Microbiology: A Guide to the Microscopic WorldDocument24 pagesIntroductory Microbiology: A Guide to the Microscopic WorldSambeet BeheraNo ratings yet
- History and Scope: Medical Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument43 pagesHistory and Scope: Medical Microbiology and ParasitologyPVallNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microbiology: Dr. Rose Elaine D. TanDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Microbiology: Dr. Rose Elaine D. TanqurratainiNo ratings yet
- Micropara History FiguresDocument3 pagesMicropara History FiguresAUDREY ARQUERONo ratings yet
- Clinical Bacteriology Lecture (W01)Document3 pagesClinical Bacteriology Lecture (W01)nicholehernandez05No ratings yet
- Micro Intro HistDocument2 pagesMicro Intro HistGounder KirthikaNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument6 pagesMicrobiologyMillence MyrNo ratings yet
- Local Media1727840620295339042Document3 pagesLocal Media1727840620295339042Jheza HuillerNo ratings yet
- Introduction Scope and Historical Development of Veterinary Microbiology Lecture NotesDocument11 pagesIntroduction Scope and Historical Development of Veterinary Microbiology Lecture Noteskaran kamboj0% (1)
- Microbiology and Parasitology (Lec) : Ancient Idea of MicroorganismsDocument6 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology (Lec) : Ancient Idea of MicroorganismsBANGTAN BORAHAENo ratings yet
- Mc3lec PrelimsDocument4 pagesMc3lec PrelimsCATHRYN MAE GAYLANNo ratings yet
- Clinical Bacteriology Lecture (W01)Document3 pagesClinical Bacteriology Lecture (W01)nicholehernandez05No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledDanica AbarquezNo ratings yet
- Microch 1 Notes NCCDocument43 pagesMicroch 1 Notes NCCStefania DiiorioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microbiology: Dr. Rose Elaine D. TanDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Microbiology: Dr. Rose Elaine D. Tandhainey100% (1)
- 2-History-of-Microbiology (Autosaved)Document31 pages2-History-of-Microbiology (Autosaved)ANIME SOLO100% (1)
- Medical Microbiology IntroductionDocument21 pagesMedical Microbiology IntroductionGemechu TesfaNo ratings yet
- History of MicrobiologyDocument3 pagesHistory of MicrobiologyKenneth ToNo ratings yet
- Introduction HistoryDocument50 pagesIntroduction HistoryBurhan MubasharNo ratings yet
- History of MicrobiologyDocument63 pagesHistory of MicrobiologyErdem AltunNo ratings yet
- History of MicrobiologyDocument22 pagesHistory of MicrobiologyMuhammad Abu Huraira100% (1)
- Lec 1A Prelim HX Micro HS3Document20 pagesLec 1A Prelim HX Micro HS3Nadja JamilahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument1 pageIntroduction To MicrobiologyDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lect-1-Microbiology For Medical StudentsDocument61 pagesLect-1-Microbiology For Medical StudentsMaria AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1.Introduction MOVDocument113 pages1.Introduction MOVHeny PatelNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1Document19 pagesLECTURE 1qaisnaser003No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (1) .PPTX Micro-ParaDocument36 pagesChapter 1 (1) .PPTX Micro-ParaLorelie AsisNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document19 pagesUnit 3Shruti ThakurNo ratings yet
- History of Microbiology: Key DiscoveriesDocument6 pagesHistory of Microbiology: Key DiscoveriesPapoo YarNo ratings yet
- MC3 Notes 01B History of MIcrobiologyDocument7 pagesMC3 Notes 01B History of MIcrobiologyKuronuma SawakoNo ratings yet
- 1 Microbiology+Document33 pages1 Microbiology+Prateek VijayavargiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 History of MicrobiologyDocument5 pagesLesson 1 History of MicrobiologyJoaqin CastroNo ratings yet
- Principles of MicrobiologyDocument35 pagesPrinciples of Microbiologyibtesam ayeshaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 MBP Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesWEEK 1 MBP Lecture Notesthe someoneNo ratings yet
- Microbiology NotebookDocument115 pagesMicrobiology NotebookNikoh Anthony EwayanNo ratings yet
- Golden Age Discoveries Led to Germ Theory and AntibioticsDocument3 pagesGolden Age Discoveries Led to Germ Theory and AntibioticsBecca TayNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction to Pharmaceutical MicrobiologyDocument27 pages1 - Introduction to Pharmaceutical MicrobiologyKaela Beatrice Sy LatoNo ratings yet
- General Veterinary MicrobiologyDocument73 pagesGeneral Veterinary MicrobiologySanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 - Microbiology IntroductionDocument3 pages1 - Microbiology IntroductionUltima PhaseNo ratings yet
- 03.historical Development of MicrobiologyDocument27 pages03.historical Development of MicrobiologyBSNo ratings yet
- Microbiology DiscoveryDocument8 pagesMicrobiology DiscoveryMadhav KiranNo ratings yet
- STM 211 NoteDocument42 pagesSTM 211 NoteAkinpelu Joy100% (5)
- Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Microbiologymomo connorNo ratings yet
- Pendahuluan - Dunia MikrobaDocument14 pagesPendahuluan - Dunia MikrobaPatrick MarungNo ratings yet
- M1 Review On Basic MicrobiologyDocument15 pagesM1 Review On Basic MicrobiologyPedrosa NardNo ratings yet
- History of Microbiology 16th CENTURYDocument3 pagesHistory of Microbiology 16th CENTURYMeangel QuillaoNo ratings yet
- LECTUREACT1Document3 pagesLECTUREACT1Mariah Zeth PulveraNo ratings yet
- Intro To MicroDocument27 pagesIntro To MicroMarvin SimbulanNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Microbiology for NursesFrom EverandAn Introduction to Microbiology for NursesN. A. SimmonsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Hand Hygiene PPT 2020Document24 pagesHand Hygiene PPT 2020bevzie datuNo ratings yet
- Patient Case Study: Malaria Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument6 pagesPatient Case Study: Malaria Diagnosis and TreatmenthafizhamzaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2666765722001661 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S2666765722001661 MainJoshua HammedNo ratings yet
- Record pneumococcal vaccinationDocument1 pageRecord pneumococcal vaccinationalfredtan6288No ratings yet
- HIV Patients Opportunistic InfectionsDocument53 pagesHIV Patients Opportunistic InfectionsAbebe TilahunNo ratings yet
- Saran prasarana kepatuhan pada anemia aplastikDocument1 pageSaran prasarana kepatuhan pada anemia aplastikAlika Nigandiva41No ratings yet
- Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever HandoutDocument3 pagesEbola Hemorrhagic Fever Handoutapi-283376958No ratings yet
- Biology Investagotary ProjectDocument17 pagesBiology Investagotary ProjectSumanthNo ratings yet
- Global Handwashing DayDocument3 pagesGlobal Handwashing DayLav ZurcNo ratings yet
- Bryan (Encap)Document2 pagesBryan (Encap)bryan ramosNo ratings yet
- Emerging Infections - Implications For Dental CareDocument3 pagesEmerging Infections - Implications For Dental CareSergio Losada AmayaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of PotatoDocument8 pagesDiseases of PotatoAkash RoyNo ratings yet
- S4C Human Health and DiseaseDocument6 pagesS4C Human Health and Diseasejiya singhNo ratings yet
- Vaccinations For Infants and Children, Age 0-10 Years: Vaccine Is Your Child Up To Date?Document1 pageVaccinations For Infants and Children, Age 0-10 Years: Vaccine Is Your Child Up To Date?mailraffiqNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Infections GuideDocument91 pagesNervous System Infections GuideBea Bianca CruzNo ratings yet
- Medical Mycology CourseDocument3 pagesMedical Mycology CourseOdurNo ratings yet
- Karakteristik Pasien Transfusi Darah Dengan Inkompatibilitas Crossmatch Di UTD RSUP DR M Djamil PadangDocument5 pagesKarakteristik Pasien Transfusi Darah Dengan Inkompatibilitas Crossmatch Di UTD RSUP DR M Djamil PadangAesthetic GirlNo ratings yet
- Pro MetricDocument196 pagesPro MetricAuliani RidhaNo ratings yet
- Standard Price List: Products PackageDocument2 pagesStandard Price List: Products PackageYuli NugrohoNo ratings yet
- MAPEH Test Results for Grade 8Document3 pagesMAPEH Test Results for Grade 8Antis VergelNo ratings yet
- CholeraDocument4 pagesCholeraJoanne Kaye TaylorNo ratings yet
- Oral Tuberculosis: Negin Hekmatjoo (1702169) Armin Hekmatjoo (1702183)Document12 pagesOral Tuberculosis: Negin Hekmatjoo (1702169) Armin Hekmatjoo (1702183)Negin HekmatjooNo ratings yet
- NURS FPX 6212 Assessment 1 Quality and Safety Gap AnalysisDocument5 pagesNURS FPX 6212 Assessment 1 Quality and Safety Gap Analysisfarwaamjad771No ratings yet
- Health Problems Sopa de LetrasDocument1 pageHealth Problems Sopa de LetrasJason RojasNo ratings yet
- PICAREDocument2 pagesPICAREagus susantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter15 StreptococciDocument66 pagesChapter15 StreptococciNursheda Abangon AzisNo ratings yet
- Aujeszky's Disease OverviewDocument23 pagesAujeszky's Disease OverviewSyikin Zolkefly100% (1)
- SD Bioline Salmonella Typhi Igg Igm FastDocument1 pageSD Bioline Salmonella Typhi Igg Igm FastLabor KaruniaNo ratings yet
- Para Midterm ExamDocument10 pagesPara Midterm ExamKlenn Orteza100% (1)
- Needle Stick InjuriesDocument1 pageNeedle Stick InjuriesAgnes BNo ratings yet