Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fibre To Fabric Class 6 Notes.
Uploaded by
amritha mishra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesThe document discusses the process of transforming fibres into fabric, from the origins of different fibres to the manufacturing stages. There are natural fibres from plants and animals, as well as semi-synthetic and synthetic fibres. Natural fibres include cotton, jute, flax and wool, and are obtained directly from plants and animals. These fibres are then spun into yarns which are woven or knitted into fabrics. The properties and uses of different fibres like cotton and jute are also outlined. Fabric production involves processes like ginning, spinning, weaving and knitting using equipment like looms.
Original Description:
Original Title
fibre to fabric class 6 notes.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the process of transforming fibres into fabric, from the origins of different fibres to the manufacturing stages. There are natural fibres from plants and animals, as well as semi-synthetic and synthetic fibres. Natural fibres include cotton, jute, flax and wool, and are obtained directly from plants and animals. These fibres are then spun into yarns which are woven or knitted into fabrics. The properties and uses of different fibres like cotton and jute are also outlined. Fabric production involves processes like ginning, spinning, weaving and knitting using equipment like looms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesFibre To Fabric Class 6 Notes.
Uploaded by
amritha mishraThe document discusses the process of transforming fibres into fabric, from the origins of different fibres to the manufacturing stages. There are natural fibres from plants and animals, as well as semi-synthetic and synthetic fibres. Natural fibres include cotton, jute, flax and wool, and are obtained directly from plants and animals. These fibres are then spun into yarns which are woven or knitted into fabrics. The properties and uses of different fibres like cotton and jute are also outlined. Fabric production involves processes like ginning, spinning, weaving and knitting using equipment like looms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
FIBRE TO FABRIC
Important points.
1. We use fabrics as a shield to protect ourselves from different weather
conditions.
2. Clothes can also be a symbol of beauty and status.
3. Our purpose and the properties of a fabric determine which type of fabric
can be used.
4. There are threads like structures in the fabric. These threads are also
called yarn. So, fabric is made up of yarn.
5. The end of the yarn is separated into thin strands. These thinner strands
are called fibres.
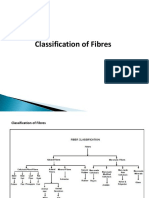
6. Fibres are classified into 3 categories based on their origin. They are
(i) Natural fibres
(ii) Semi-synthetic fibres
(iii) Synthetic fibres (or) artificial fibres
7. Natural fibres:- the fibres which are obtained from natural sources like
plants and animals are called natural fibres. It is again classified into two
types. They are
(i) Plant fibres
(ii) Animal fibres.
8. Plant fibres:- The fibres which are obtained from plants are called plant
fibres. They contain cellulose. Eg:- cotton, jute, flax, hemp, coir, corn
fibre.
9. Animal fibres:- The fibres which are obtained from animals are called
animal fibres. They contain protein. Eg:- silk, wool
10.Natural fibres are biodegradable. (means decompose in soil after some
days by the action of bacteria)
11.Semi-synthetic fibres:- For these fibres, the raw material is from plants
but during the process of fibres some chemicals are added.
Eg:- Rayon, cellulose acetate, cellulose nitrate.
12.Semi synthetic fibres are bio degradable.
13.Rayon is also known as artificial silk (or) regenerated fibre.
14.Synthetic fibre:- The fibres which are obtained from petro-chemicals are
called synthetic fibres. Eg:- Nylon, polyester, orlon, acrylic etc.,
15.Synthetic fibres are non biodegradable.
16.Acrylic is also called fake fur (or) artificial wool.
17.Natural fibres are expensive, not durable but they give us comfort.
18.Synthetic fibres are durable, affordable but do not give comfort.
19.Identifying a fibre:-
Take a fibre and show it to a flame using a tong.
If it burns with paper burning smell but they do not shrink or melt, then it
is a plant fibre.
If it burns with burning hair smell and shrinks but do not melt, it is an
animal fibre.
If the fibre melts and gives a smell similar to burning plastics, then it is a
synthetic fibre.
20.Cotton is obtained from cotton fruits. Cotton fruit is of the size of lemon.
After maturing,
The fruit burst open and the seeds covered with cotton fibres can be seen.
21.Cotton plants grow well in black soil and warm climate.
22.The process of separation of seeds from cotton balls is called ginning.
The obtained cotton after ginning is called lint.
23.The process of making yarn from fibres is called spinning.
24.For spinning, takli or charka is used.
25.Cotton fibres are soft, absorb water, porous and take time to dry.
26.Cotton is used for filling mattresses, quits or pillows, making clothes.
27.Jute is also called golden fibre.
28.Jute fibre is harder, stronger, coarse and rough.
29.Jute is a bast fibre or stem fibre.
30.Alluvial soil is suitable for growing jute and it is cultivated during the
rainy season.
31.In India, jute is mainly grown in west Bengal, bihar and assam.
32.Jute fibre is obtained from the stem of the jute plant. Jute plant grow upto
a height of 2-3 meters. They are harvested at flowering stage.
33.After harvesting, plants are soaked in water for 2-3 weeks. The plants get
rotten and easy to peel. Then the fibres are separated, dried to make jute
yarn.
34.The process of soaking the jute plant in water and peeling the fibre is
called `retting’.
35.From Red sorrel (gongura) plant, jute is obtained.
36.Wool is obtained from the fleece of sheep or goat. It is also obtained from
the hair of rabbits, yak and camels.
37.Silk fibre is drawn from the cocoon of silk worm.
38.Hemp and flax are also plant fibres.
39.Linen fibre is obtained from flax plant.
40.Weaving and knitting are used for making different kinds of fabric.
41.Two sets of yarn are arranged together to make fabric is called weaving.
42.The length wise yarn of a fabric is called warp whereas breadth wise yarn
is called weft.
43.Weaving is done on looms. The looms that are worked by man power are
called hand looms.
44.Power looms are run by machines.
45.Calico is a type of fabric used in book binding.
46.Warangal is famous for carpet industry.
47.In knitting, a single yarn is used to make a piece of fabric.
You might also like
- Piping Spool Fabrication ProcedureDocument14 pagesPiping Spool Fabrication ProcedureMiky Andrean100% (6)
- CSWIP 3.1 Welding Inspection NotesDocument102 pagesCSWIP 3.1 Welding Inspection NotesMohamad Junid Bin Omar91% (32)
- Plant and Animal FibresDocument12 pagesPlant and Animal Fibresvenka07No ratings yet
- Engleski TTF Skripta 1 SemestarDocument6 pagesEngleski TTF Skripta 1 SemestarAndrea VekarićNo ratings yet
- 10 Mittleider Grow BOX GardensDocument213 pages10 Mittleider Grow BOX GardensAnonymous NSvApyJZn100% (7)
- Fundamentals of MasstransferandkineticshydrogenationDocument14 pagesFundamentals of MasstransferandkineticshydrogenationRamandhaPrasetyaAdibrataNo ratings yet
- Science 3Document8 pagesScience 3Cris CNo ratings yet
- Fibre To FabricDocument2 pagesFibre To FabricmailtomicaiahNo ratings yet
- 7th Chemistry DLP Study Package FinalDocument101 pages7th Chemistry DLP Study Package FinalAdityaNo ratings yet
- CBSE CLASS 7 Fibre To Fabric PDFDocument17 pagesCBSE CLASS 7 Fibre To Fabric PDFManoj JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Types of Fibres - Class 6, Fibre To FabricDocument5 pagesTypes of Fibres - Class 6, Fibre To FabricPriyaNo ratings yet
- Fibre To Fabric (G6) : Handout I. Short Answer QuestionsDocument4 pagesFibre To Fabric (G6) : Handout I. Short Answer Questionsdon shiphrahNo ratings yet
- Fibre To Fabric Notes 1Document3 pagesFibre To Fabric Notes 1Mohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- FibreDocument5 pagesFibreamp1279No ratings yet
- Scheme of The EvaluationDocument6 pagesScheme of The EvaluationSabihanaz InamdarNo ratings yet
- c3 Fibre To Fabric NotesDocument5 pagesc3 Fibre To Fabric NotesNAVNEETA AGARWALNo ratings yet
- RB VVWWL MC TP6 D VX 7 F4 e VDocument2 pagesRB VVWWL MC TP6 D VX 7 F4 e VRamyNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Fibre To Fabric Sample QuestionsDocument3 pagesGrade 6 Fibre To Fabric Sample Questionsmohamedaahil12318No ratings yet
- Fibre To Fabric: Chapter: - 3Document4 pagesFibre To Fabric: Chapter: - 3santhu BNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Revision NotesDocument3 pagesClass 6 Science Chapter 3 Revision NotesNandini JhaNo ratings yet
- Fibres To FabricDocument23 pagesFibres To FabricPallavi Luthra KapoorNo ratings yet
- FIBRE (Power Point)Document54 pagesFIBRE (Power Point)MonirHossainNo ratings yet
- Textile Raw Materials-IIDocument2 pagesTextile Raw Materials-IIMOJAHID HASAN Fall 19100% (1)
- Properties Natural FibresDocument46 pagesProperties Natural FibresanishaNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 3 Fibre To FabricDocument5 pagesScience Chapter 3 Fibre To Fabricsaangee.inNo ratings yet
- SUNI - Classification and Types of Clothing FibersDocument32 pagesSUNI - Classification and Types of Clothing FibersJoseph MontainNo ratings yet
- Classification of FibresDocument12 pagesClassification of FibresARYAN RATHORENo ratings yet
- Bijendra Public School: Class - 6 Subject - SCIENCE Chapter - 3 Fibre To FabricDocument4 pagesBijendra Public School: Class - 6 Subject - SCIENCE Chapter - 3 Fibre To Fabricsmitha_gururaj100% (1)
- Class 6 Chemistry Fibre To FabricDocument9 pagesClass 6 Chemistry Fibre To FabricSachin SharmaNo ratings yet
- L3Fibre To FabricDocument2 pagesL3Fibre To FabricSHAHANA RIZVI TGTNo ratings yet
- Types of FibersDocument7 pagesTypes of FibersAbubakar JavedNo ratings yet
- Fibre To FabricDocument68 pagesFibre To Fabricprincess clubNo ratings yet
- Fibre To Fabric NotesDocument7 pagesFibre To Fabric NotesMidhun Bhuvanesh.B 7ANo ratings yet
- Chemistry Work Sheet-Grade 7 (Animal Fibre)Document3 pagesChemistry Work Sheet-Grade 7 (Animal Fibre)Diya PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Class - VI Fibre To FabricDocument24 pagesChapter - 3 Class - VI Fibre To Fabricamit lakraNo ratings yet
- TextileDocument13 pagesTextileZahid zamiNo ratings yet
- Fibre To FabricDocument10 pagesFibre To FabricNayanika VermaNo ratings yet
- Training Report On Textile Wet ProcessingDocument38 pagesTraining Report On Textile Wet ProcessingMunazza SohailNo ratings yet
- 79 1 ET V1 S1 - Unit - 1 PDFDocument14 pages79 1 ET V1 S1 - Unit - 1 PDFvandana upadhyayNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 6 - Chapter 03Document11 pagesExp SC 6 - Chapter 03megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- What Are Natural FibersDocument2 pagesWhat Are Natural FibersCathy BiasettiNo ratings yet
- Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Fibre To FabricDocument7 pagesSolutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Fibre To FabricRajendra PatelNo ratings yet
- Relations Between Fiber Structure and PropertiesDocument7 pagesRelations Between Fiber Structure and PropertiesChikam BuraNo ratings yet
- Importance of Fibers in Textiles: Kavitha RajanDocument44 pagesImportance of Fibers in Textiles: Kavitha RajankavineshpraneetaNo ratings yet
- Types of Fibers Written ReportDocument7 pagesTypes of Fibers Written ReportMikee Betinol DomalaonNo ratings yet
- Ls No 3 Fibre To Fabric.Document7 pagesLs No 3 Fibre To Fabric.drjri100% (1)
- Fiber To FabricDocument6 pagesFiber To FabricPinki NegiNo ratings yet
- Textile Industry - 01 LectureDocument40 pagesTextile Industry - 01 Lectureisabelism100% (1)
- 321 e Lesson 22Document13 pages321 e Lesson 22mahmudtexNo ratings yet
- 7 Fiber To FabricDocument14 pages7 Fiber To FabricRuchika Bhasin AbrolNo ratings yet
- CGTPaper IIDocument130 pagesCGTPaper IIMd. Humayun KabirNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Fibre To FabricDocument23 pagesPresentation On Fibre To Fabricjoydeepparamanik07No ratings yet
- Study On Textile FibersDocument9 pagesStudy On Textile FibersAbid hasanNo ratings yet
- MAKALAH TEKSTIL 1 Softfile BingDocument10 pagesMAKALAH TEKSTIL 1 Softfile BingHuswatun HasanaNo ratings yet
- Mid Term TEX 111Document8 pagesMid Term TEX 111Mainur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Kehe 105Document16 pagesKehe 105Saisab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Fibre To Fabric NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - Fibre To Fabric NotesBhure VedikaNo ratings yet
- Abrics and AW Aterials: VerviewDocument12 pagesAbrics and AW Aterials: VerviewCristina CostacheNo ratings yet
- Science Assignment 2 Class VIIDocument2 pagesScience Assignment 2 Class VIIsanjeetsksNo ratings yet
- Textiles, for Commercial, Industrial, and Domestic Arts Schools: Also Adapted to Those Engaged in Wholesale and Retail Dry Goods, Wool, Cotton, and Dressmaker's TradesFrom EverandTextiles, for Commercial, Industrial, and Domestic Arts Schools: Also Adapted to Those Engaged in Wholesale and Retail Dry Goods, Wool, Cotton, and Dressmaker's TradesNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Thread Guide: Everything You Need to Know to Choose the Perfect Thread for Every ProjectFrom EverandThe Ultimate Thread Guide: Everything You Need to Know to Choose the Perfect Thread for Every ProjectRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Grotanol 3025 ZSDB - P - ALL ENDocument12 pagesGrotanol 3025 ZSDB - P - ALL ENAbdurahman MuizuddinNo ratings yet
- Nucleon Number ReferenceDocument6 pagesNucleon Number ReferenceNazihah NordinNo ratings yet
- F-Block ElementsDocument8 pagesF-Block ElementsSai Sasivardhan GampaNo ratings yet
- Fatima Laureano-Maravilla - Unit 3 - Photosynthesis ch8Document6 pagesFatima Laureano-Maravilla - Unit 3 - Photosynthesis ch8api-542684299No ratings yet
- API 20 Series Supply Chain Management Standards: Rick FairclothDocument11 pagesAPI 20 Series Supply Chain Management Standards: Rick FairclothNoel FrancisNo ratings yet
- BOQ Suryadev ChennaiDocument2 pagesBOQ Suryadev Chennaimkpasha55mpNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole AssyDocument2 pagesMetronidazole AssysaiNo ratings yet
- Herbs and Herbal Constituents Active Against Snake BiteDocument14 pagesHerbs and Herbal Constituents Active Against Snake BiteSundara Veer Raju MEDNo ratings yet
- Meaning of The Water CycleDocument3 pagesMeaning of The Water CycleCARLOS CIFUENTESNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology ReviewDocument64 pagesPharmacology ReviewRichard BakerNo ratings yet
- University of The East: Professor, NME 513 1-MEDocument3 pagesUniversity of The East: Professor, NME 513 1-MEAriel GamboaNo ratings yet
- PT - Medikon Prima Laboratories: MirsaDocument2 pagesPT - Medikon Prima Laboratories: MirsaMirsa Tyesha YusufNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document34 pagesCH 1Rana Hassan Tariq100% (1)
- Resource Management Strategy of Limestone by Evolution of Nil Waste ProcessDocument3 pagesResource Management Strategy of Limestone by Evolution of Nil Waste ProcessravibelavadiNo ratings yet
- Prob Set Heat and MassDocument15 pagesProb Set Heat and MassCheng PasionNo ratings yet
- NATSCI2 Gen and Inorganic Chemistry Course SyllabusDocument10 pagesNATSCI2 Gen and Inorganic Chemistry Course SyllabusAnonymousGodiswithyouNo ratings yet
- Types of Culture Media Used in MicrobiologyDocument3 pagesTypes of Culture Media Used in MicrobiologyAzriel BeronNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3: Operation Involving Particulate MatterDocument25 pagesLecture 3: Operation Involving Particulate MatterTaytoNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee 2007 P.2Document24 pagesIit Jee 2007 P.2Kainshk GuptaNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument4 pagesDaftar PustakaEva SuroyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SpectrophotometryDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Spectrophotometryiryasti2yudistiaNo ratings yet
- Pressurized Dosage FormsDocument85 pagesPressurized Dosage FormsHuma Hameed Dogar100% (1)
- AQUAPONICSDocument9 pagesAQUAPONICSExequiel ZoletaNo ratings yet
- SCERT Kerala State Syllabus 9th Standard Chemistry Textbooks English Medium Part 2Document64 pagesSCERT Kerala State Syllabus 9th Standard Chemistry Textbooks English Medium Part 2Huda FavasNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Color Reactions of Intact Protein (Casein)Document3 pagesIsolation and Color Reactions of Intact Protein (Casein)Gica Ira ÜNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology 5.12, Spring 2005: Problem Set #4Document9 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology 5.12, Spring 2005: Problem Set #4Minh TieuNo ratings yet