Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AC Vs DC
Uploaded by
Satish PatelOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AC Vs DC
Uploaded by
Satish PatelCopyright:
Available Formats
AC vs DC
Description of the Experiment
Observing the magnetic effect of current due to AC and DC using a bulb with soft filament and a bar magnet.
Introduction:
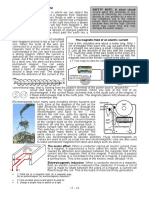
The laws of electromagnetism state that electric charges and magnetic fields
are closely intertwined, with the movement of charged particles generating a
surrounding magnetic field. One example of this is current-carrying wires; as N S
currents are the movement of electrons, which are negatively charged
particles, their movement throughout the wire generates a magnetic field
around the wire. If a strong magnet is brought near the current carrying wire,
it will either gets attracted or repulsed depending up on the polarity of the
magnet and the direction of current flowing through it.
In this experiment, we will demonstrate the magnetic effect of current due to AC and
DC using a bulb with soft filament and a bar magnet.
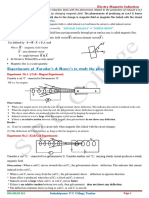
Activity: Observation:
Observe that
1. Connect the soft filament bulb to the DC power supply. 1. When DC power is given, filaments get attracted(or
2. Bring the bar magnet near the bulb. repulsed) in one direction.
3. Repeat the same by connecting the bulb to the AC 2. When AC power is given, filaments get attracted
power supply. and repulsed periodically executing a periodic motion.
4. Observe the motion of the filament in both the cases.
Questions: Homework:
Think and Answer: Answer the following questions.
1. Suppose the filament is attracted when DC power is
given and North pole of the magnet was towards the 1. Compare and contrast Biot-Savart law in magnetostatics
filament. If we change the polarity of the magnet, what with Coulomb’s law in electrostatics.
will happen. 2. If a current is passed through a spring, does the spring
2. If we change the direction of the DC then what will stretch or compress? Explain.
happen after changing the polarity of the magnet, then 3. Two concentric, coplanar circular loops of different
what will happen diameters carry steady currents in the same direction. Do
3. When AC power is given, the motion of the filament is the loops attract or repel each other? Explain.
to and fro. Explain. 4. Suppose three infinitely long parallel wires are arranged in
such a way that when looking at the cross section, they are
Points to ponder: at the corners of an equilateral triangle. Can currents
1. A magnet at rest produces magnetic field around it while an be arranged (combination of flowing in or out of the page) so
electric charge at rest produces an electric field around it. that all three wires
2. A current carrying conductor has a magnetic field and not an (a) attract, and (b) repel each other? Explain.
electric field around it.
3. An electric field can not be produced without a charge
whereas a magnetic field can be produced without a magnet.
4. No poles are produced in a coil carrying current but such a
coil shows north and south polarity.
5. All oscillating or accelerated charge produces
electromagnetic waves in addition to electric and magnetic
fields.
Explore:
A long copper rod of radius a has an off-center cylindrical
hole through its entire length, as shown in Figure. The
conductor carries a current I which is directed out of the
page and is uniformly distributed throughout the cross
section. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic
field at the point P.
You might also like
- PHYSICSDocument7 pagesPHYSICSMohamed Mounir MYP3No ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETISM EXPLAINEDDocument12 pagesELECTROMAGNETISM EXPLAINEDMuneer Kaleri75% (4)
- ElectromagnetismDocument26 pagesElectromagnetismMuhammad AimanNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Induction and Faradays Law in General Physics 2Document43 pagesMagnetic Induction and Faradays Law in General Physics 2Heidi QuiranteNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solution Cbse Class 10 Sci Chap 13Document11 pagesNcert Solution Cbse Class 10 Sci Chap 13Aaryan KumarNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction NOtesDocument76 pagesElectromagnetic Induction NOtesashunaik409No ratings yet
- State Whether The Following Statements Are True or FalseDocument11 pagesState Whether The Following Statements Are True or Falsearohi90% (1)
- Physics Module 11 Homework SolutionsDocument5 pagesPhysics Module 11 Homework SolutionsHanin MoatazNo ratings yet
- edited_magnetic_effectsDocument72 pagesedited_magnetic_effectsq-tipNo ratings yet
- 3 Force On A Current Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic FieldDocument5 pages3 Force On A Current Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic FieldJesstal NiniNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism Short NotesDocument10 pagesElectromagnetism Short Notespadhaai karoNo ratings yet
- Teja.P Group5 EPT 01 FMGTPDocument4 pagesTeja.P Group5 EPT 01 FMGTPTeja pNo ratings yet
- EEC 125 Note UpdatedDocument23 pagesEEC 125 Note UpdatedElijah EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Emi Physics Deep RoyDocument21 pagesEmi Physics Deep Roysubhashdas197301No ratings yet
- ElectromagnetismDocument45 pagesElectromagnetismNtirnyuy LeenaNo ratings yet
- Gen Physics q4Document26 pagesGen Physics q4solimanmichikoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductonDocument12 pagesElectromagnetic InductonAishwarya TripathiNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument85 pagesPhysics NotesJfoxx Samuel0% (1)
- CLASS-10 Subject: ScienceDocument62 pagesCLASS-10 Subject: ScienceZeonNo ratings yet
- EMI Practice Problem - Set ADocument8 pagesEMI Practice Problem - Set AAG Sir PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic InductionMonica SreeNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: What We Have Already LearntDocument14 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: What We Have Already LearntAnonymous pZp8uyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Magnetic Effects NotesDocument12 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Magnetic Effects NotesAkshithNo ratings yet
- 17.14 Electromagnetism: SAFETY NOTE: A Short CircuitDocument1 page17.14 Electromagnetism: SAFETY NOTE: A Short CircuitSuresh SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current 2020-21Document6 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current 2020-21Rgpadma NathanNo ratings yet
- Module 2.lesson1Document6 pagesModule 2.lesson1Jerald AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction Physics ProjectDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Induction Physics ProjectDcryptRNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism: Sonny P. de Leon MT1Document58 pagesElectricity and Magnetism: Sonny P. de Leon MT1iMer22100% (1)
- Current Can Produce Magnetism.: What Is The Source of Magnetism?Document7 pagesCurrent Can Produce Magnetism.: What Is The Source of Magnetism?Herleiy Jyne SmithNo ratings yet
- Magnetic FieldDocument44 pagesMagnetic FieldAbdulfatai AbdulrasheedNo ratings yet
- z1 ElectromagneticInduction1Document7 pagesz1 ElectromagneticInduction1Gan PentonNo ratings yet
- Currents V2.2 Priya With Cover Page and HW IndexDocument12 pagesCurrents V2.2 Priya With Cover Page and HW Index2010sujithrasujithraNo ratings yet
- Pajunar J Jonna P. - Assignment 2Document4 pagesPajunar J Jonna P. - Assignment 2Jonna PajunarNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocument13 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Currentanjupal100% (4)
- Project FileDocument23 pagesProject Filekajobin645No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument25 pagesElectromagnetic Inductionnivasan aNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 ElectromagnetismDocument29 pagesChapter 26 ElectromagnetismGiovanni SlackNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: A Project By: Faraz ThakurDocument16 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: A Project By: Faraz ThakurFaraz Thakur50% (2)
- Harshitha 12 SapDocument19 pagesHarshitha 12 SapKheerthna GNo ratings yet
- EMINewDocument10 pagesEMINewMohith DasNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines AssignmentDocument95 pagesElectrical Machines AssignmentNivedNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction ExplainedDocument49 pagesElectromagnetic Induction ExplainedthebestNo ratings yet
- Faraday's & Lenz LawDocument14 pagesFaraday's & Lenz LawPnDeNo ratings yet
- ECEG-3131 Introduction to Electrical MachinesDocument52 pagesECEG-3131 Introduction to Electrical Machinesollata kalanoNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument15 pagesPhysics ProjectDebkanti Gupta Bhaya0% (1)
- ElectromagnetDocument4 pagesElectromagnetftplevel1No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction LecturesDocument9 pagesElectromagnetic Induction LecturesDoyen DanielNo ratings yet
- Ch31&32 Electromagnetism SlidesDocument38 pagesCh31&32 Electromagnetism SlidesVent101No ratings yet
- Magnetic Field of a Current Carrying SolenoidDocument20 pagesMagnetic Field of a Current Carrying SolenoidMushtaq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Induction and Faraday's LawsDocument13 pagesMagnetic Induction and Faraday's LawsShara TayonaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project: Reliance Foundation School KoparkhairaneDocument18 pagesPhysics Project: Reliance Foundation School KoparkhairanePrerana PorechaNo ratings yet
- More Thoughts On The Uwe Jarck DeviceDocument5 pagesMore Thoughts On The Uwe Jarck DeviceMladen MuskinjaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 NotesDocument57 pagesModule 3 NotesMani RohithNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Abhishek Class Xii Electromagnetic PDFDocument19 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Abhishek Class Xii Electromagnetic PDFDevang HandaNo ratings yet
- q3 Sci10 Lesson1 Pic1Document47 pagesq3 Sci10 Lesson1 Pic1Tash Marcelo Olo-anNo ratings yet
- 3.1 - Analysing The Magnetic Effect of A Current-Carrying ConductorDocument28 pages3.1 - Analysing The Magnetic Effect of A Current-Carrying ConductorsfwongNo ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronic Laws & Circuits PDFDocument61 pagesElectrical & Electronic Laws & Circuits PDFclubtown paradiseNo ratings yet
- Magnetics Part 3Document5 pagesMagnetics Part 3AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Aakash Modules 01Document172 pagesAakash Modules 01Satish PatelNo ratings yet
- JEE Main all shift session 2 solvedDocument287 pagesJEE Main all shift session 2 solvedSatish PatelNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual Elementary Problems in Organic Chemistry For JEE by M.S. Chouhan (9th Edition)Document285 pagesSolution Manual Elementary Problems in Organic Chemistry For JEE by M.S. Chouhan (9th Edition)Satish Patel100% (18)
- Truvi PlusDocument27 pagesTruvi PlusSatish PatelNo ratings yet
- 1 GBNagaDocument842 pages1 GBNagaSatish PatelNo ratings yet
- 2020 11 09 - 08 39 07Document2 pages2020 11 09 - 08 39 07Satish PatelNo ratings yet
- ABPXX Alternator BrochureDocument22 pagesABPXX Alternator BrochureJonah RagleNo ratings yet
- Meti 31 Directional RelayDocument10 pagesMeti 31 Directional Relayjuanovaller0% (1)
- High Voltage Modular Training SetDocument16 pagesHigh Voltage Modular Training Settareen372aNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Boost-Type Grid-Connected InverterDocument9 pagesThree-Phase Boost-Type Grid-Connected Inverterareti gopiNo ratings yet
- Akpc551 080g0281 Quick EnglishDocument6 pagesAkpc551 080g0281 Quick EnglishtahlokoNo ratings yet
- Driver LCI 150W 500-850ma FlexC NF h28 EXC3 enDocument7 pagesDriver LCI 150W 500-850ma FlexC NF h28 EXC3 enMoustafa HelalyNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 3 Measurement of VoltageDocument10 pagesExperiment No. 3 Measurement of VoltageLynndon VillamorNo ratings yet
- Half and Full Wave RectifierDocument12 pagesHalf and Full Wave Rectifierlucy lucy50% (2)
- Exds EstroboDocument3 pagesExds EstroboKUNONo ratings yet
- ManualDocument8 pagesManualnassarkiNo ratings yet
- Finder Catalogo 95.15.2SMA - Relay Socket, Through Hole, Through Hole, 8 PinsDocument16 pagesFinder Catalogo 95.15.2SMA - Relay Socket, Through Hole, Through Hole, 8 PinsJMSNo ratings yet
- Control PanelDocument9 pagesControl PanelPEMELIHARAAN LISTRIKNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Sunny Central Inverters CP-SeriesDocument4 pagesData Sheet Sunny Central Inverters CP-SeriesErik Alecsandru BranNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument55 pagesNotesKhushi TiwariNo ratings yet
- S100 CatalogDocument52 pagesS100 CatalogMunk OzoraNo ratings yet
- Understanding Color Coding of Resistors and CapacitorsDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Color Coding of Resistors and CapacitorsChirag PatelNo ratings yet
- Safety Standards for PV SystemsDocument24 pagesSafety Standards for PV SystemsSabri BouloumaNo ratings yet
- SSV Cougar XTC Operatorsl Technical Training Syllabus PDFDocument7 pagesSSV Cougar XTC Operatorsl Technical Training Syllabus PDFlchurch13No ratings yet
- DC Motors ExplainedDocument31 pagesDC Motors ExplainedRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Kaise SK-20 22 30 ManualDocument6 pagesKaise SK-20 22 30 ManualAdriano Trigo Lopes50% (2)
- RCS-985T Instruction Manual Standard V1.02 (EN YJBH2003.0086.0003) PDFDocument258 pagesRCS-985T Instruction Manual Standard V1.02 (EN YJBH2003.0086.0003) PDFDipak Kumar PatelNo ratings yet
- NetSure 701 A61 Emerson Network PowerDocument2 pagesNetSure 701 A61 Emerson Network PowerDmitrij sovetowNo ratings yet
- Power System Control and Automation SyllabusDocument23 pagesPower System Control and Automation SyllabusSrikanth Mutyala100% (1)
- 5v Power SupplyDocument34 pages5v Power Supplyapi-311762270No ratings yet
- Sliding-Mode Control of a Charger/Discharger DC/DC ConverterDocument27 pagesSliding-Mode Control of a Charger/Discharger DC/DC ConvertergemejiaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Summer Model Answer PaperDocument17 pages2016 Summer Model Answer PaperAbhishek ChavanNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual: Am/Fm/Shortwave RadioDocument42 pagesOperation Manual: Am/Fm/Shortwave Radioegeotomasyon100% (1)
- Electrical Design Manual: Metropolitan Water District of Southern CaliforniaDocument210 pagesElectrical Design Manual: Metropolitan Water District of Southern CaliforniakakagoNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument108 pagesManualCamiloNogueraRiascosNo ratings yet
- Current Mirrors 20Document45 pagesCurrent Mirrors 20api-3750190No ratings yet