Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 - Introfuction To Nursing Informatics-1
Uploaded by
Karl LintanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 - Introfuction To Nursing Informatics-1
Uploaded by
Karl LintanCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Informatics - Lecture 03/12/23
INTRODUCTION TO NURSING
INFORMATICS Prelims
Prof. Jett Estioco Trans 1
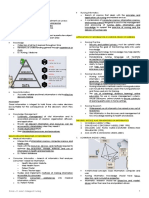
OUTLINE II. BUILDING BLOCKS OF NURSING INFORMATICS
I. Nursing Informatics II. Building Blocks of
Nursing Informatics Nursing Science Cognitive Science
Computer Science Information Science
I. NURSING INFORMATICS
• Introduction
→ Nurses are expected to provide safe, competent, and
compassionate care in an increasingly technical and
digital environment.
→ A major theme in this new healthcare environment is
the use of information systems and technologies to
improve the quality and safety of patient care.
→ Nurses are directly engaged with information systems
and technologies.
• Nursing Informatics
→ Supports the collection, storage, analysis, retrieval,
communication, and use of information to help nurses
to: A. NURSING SCIENCE
o Care for patients to the highest quality. • Nurses must possess the following skills:
o Share data, knowledge, and information.
→ Technical skills
o Compare theory and practice advance nursing
o To manage equipment and perform procedures.
knowledge and practice.
→ Interpersonal skills
• Importance of Nursing Informatics
o To interact appropriately with people.
→ Ensures that nursing practice is adequately
→ Cognitive skills
represented in HIT development, implementation,
o To observe, recognize, and collect data, analyze
training, and evaluation. It also ensures that HITs are
and interpret data and reach a reasonable
created to support the information needs of nurses to
conclusion that forms the basis of a decision.
provide enhanced patient care.
→ Information-sensitive skills
→ Foundation to all aspects of nursing practice. It is
o Nursing is an information-intensive profession.
important for nurses to obtain comprehensive nursing
• Nursing Science
informatics competencies to remain familiar in using
HITs and reap the benefits HITs provide for nursing → The ethical application of knowledge acquired through
practice and patient care. education research and practice to provide services
and interventions to patients in order to maintain,
→ Enhances clinical decision-making in all nursing roles.
enhance, or restore their health; to advocate for health
Constant access to patient data and information,
and to acquire, process, generate, and disseminate
provided by HITs, has supported nurses and other
nursing knowledge to advance the nursing profession.
health professionals in managing and improving the
health of patients. • Foundation of Knowledge Model
→ “Framework for examining the dynamic
Nursing Informatics Model interrelationships among data, information, and
knowledge used to meet the needs of healthcare
delivery systems, organizations, patients, and nurses.”
Nursing Informatics - Lecture Claudel, C. & Ramos, F. 1 of 3
• The Nature of Knowledge
→ Explicit knowledge B. INFORMATION SCIENCE
o Convey with letters, numbers, and words. • Information Science
o Can be shared in the form of data, manuals, → Primarily concerned with the input, processing, output,
product specifications, principles, and policy. and feedback of data and information through
o Example: Nursing model or Theory technology integration with a focus on comprehending
→ Tacit knowledge the perspective of the stakeholders involved and then
o Difficult to transmit, convey, or share with others. applying IT as needed.
o Consists of one’s insights, perceptions, intuitions, → It is systematically based and deals with the big
or gut feelings. picture, rather than the individual pieces of
o Example: one’s values or emotions technology.
• The Nurse as a Knowledge Worker • Information Processing
→ All nurses use data and information. → Information
→ This information is then converted to knowledge. o Data that are processed using knowledge.
→ The nurse then acts on this knowledge by initiating a → Processing
plan of care, updating an existing one, or maintaining o Retrieval, analysis or synthesis of data.
the status quo. o Alteration and transformation of data into useful
→ The term knowledge worker was first coined by Peter information and outputs.
Drucker in his 1959 book, Landmarks of Tomorrow. • Characteristics of the Integrity of Data
o Drucker described a knowledge worker as one → Whole
who has advanced formal education and is able to → Complete
apply theoretical and analytical knowledge. → Correct
o According to Ducker, the knowledge worker must → Consistent data
be a continuous learner and a specialist in a field. • Threats to Data Integrity
→ Knowledge Work → Human error
o Defined as nonrepetitive, nonroutine work that o Incorrect data entry
entails a significant amount of cognitive activity. o Spelling errors
→ Characteristics of Knowledge Worker → Malware
o Knowledge Consumers o Viruses
▪ Mainly users of knowledge who do not have o Worms
the expertise to provide the knowledge they o Spam
need for themselves. o Ransomware
▪ Novice nurses can be thought of as → Machine error
knowledge consumers who use the o Hardware failures
knowledge of experienced nurses or search o Software crashes
information systems for the knowledge
→ Transmission errors
necessary to apply to their practice.
o Connectivity issues
▪ As responsible knowledge consumers, they
o Data corruption
must also question and challenge what is
o Lost data
known to help them and learn and
understand. Their questioning and
C. COMPUTER SCIENCE
challenging facilitate critical thinking and the
development of new knowledge. • Computer Science
o Knowledge Brokers → A valuable tool, when used skillfully, which facilitates
▪ Know where to find information and the acquisition and manipulation of data and
knowledge. information by nurses who then can synthesize the
▪ They generate some knowledge but are data into evolving knowledge and wisdom.
mainly known for their ability to find what is • Components of Computer
needed. → Hardware
▪ More experienced nurses and nursing o Physical body of the computer.
students become knowledge brokers out of ▪ Central Processing Unit
necessity because they need to know (a) Acts as the brain of the computer.
something. (b) Executes and calculates the binary
o Knowledge Generators computer code.
▪ “Primary sources of new knowledge” ▪ Motherboard
▪ They include nursing researchers and (a) Central nervous system of the
nursing experts – the people who know. computer.
▪ They are able to answer questions, craft (b) Facilitates communication among all
theories, find solutions to nursing problems or computer components.
concerns, and innovate as part of their ▪ Power Supply
practice.
Nursing Informatics - Lecture Introduction to Nursing Informatics 2 of 3
(a) Gives the electrical energy supply for
the computer to operate.
▪ Random Access Memory (RAM)
(a) A temporary storage system that allows
the processor to access program code
and data while working on a task.
→ Software
o Comprises the application of programs
developed to facilitate various user functions.
▪ OS Software
(a) The most important software in any
computer.
D. COGNITIVE SCIENCE
• Cognitive Science
→ The interdisciplinary field of cognitive science that is
the mind, intelligence, and behavior from an
information processing perspective.
→ Connectionism
o A component of cognitive science that gives us
computer modeling through artificial neural
networks to explain human intellectual abilities.
o Explains how human intellectual abilities work.
→ Epistemology
o The study of the nature and origin of knowledge.
Nursing Informatics - Lecture Introduction to Nursing Informatics 3 of 3
You might also like
- A simplified Nursing Informatics. A Modern Age Health Technology for Nurses and MidwivesFrom EverandA simplified Nursing Informatics. A Modern Age Health Technology for Nurses and MidwivesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics Unit 1 and 2 - 015803Document23 pagesNursing Informatics Unit 1 and 2 - 015803Lexyl CampoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics (CU 15)Document1 pageNursing Informatics (CU 15)Bianca BautistaNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument33 pagesPDF DocumentScarlet BalaoroNo ratings yet
- What Is Information TechnologyDocument3 pagesWhat Is Information TechnologySoriano RegeneNo ratings yet
- Nursing InformaticsDocument18 pagesNursing InformaticstabiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - The Practice Specialty of Nursing InformaticsDocument6 pagesChapter 15 - The Practice Specialty of Nursing InformaticsAllyssa Leila Estrebillo OrbeNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document3 pagesModule 1Forky DorkyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatic - Midterm - CompleteDocument5 pagesNursing Informatic - Midterm - CompleteMaria Emmaculada ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- NIDocument21 pagesNIAlyssa MasacayanNo ratings yet
- NCM110 NI LectureDocument10 pagesNCM110 NI LectureSherinne Jane CariazoNo ratings yet
- Nur 1211: Nursing InformaticsDocument29 pagesNur 1211: Nursing InformaticsAllyza EspirituNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 IntroDocument5 pagesTopic 1 Introsammydels98No ratings yet
- Nursing InformaticsDocument4 pagesNursing InformaticsRandy AminolaNo ratings yet
- 2practice Application2Document17 pages2practice Application2YongNo ratings yet
- Nursing InformaticsDocument16 pagesNursing InformaticsRosechelle Baggao Siupan-ElarcoNo ratings yet
- 1 Nursing Informatics: Remember!Document2 pages1 Nursing Informatics: Remember!LAXA FRANCINENo ratings yet
- I-PPT - I-Fundamentals-1-31-2020Document61 pagesI-PPT - I-Fundamentals-1-31-2020Kaye Cor0% (1)
- MT Nursing InformaticsDocument13 pagesMT Nursing InformaticspriyankaNo ratings yet
- NCM 110 Nursing Informatics TRANSESDocument6 pagesNCM 110 Nursing Informatics TRANSESJAMES ANDRE RENDONNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics Quizzes (Lab)Document58 pagesNursing Informatics Quizzes (Lab)Raquel Monsalve100% (1)
- St. Paul University Philippines St. Rita of Cascia 2023Document6 pagesSt. Paul University Philippines St. Rita of Cascia 2023Aaron ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Ethical AspectsDocument6 pagesTopic 3 Ethical Aspectssammydels98No ratings yet
- NCM 110 1-A LectureDocument22 pagesNCM 110 1-A Lecture1G - Kyle Kenjie DahiliNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Nursinng Plancare of Standard - EdelDocument43 pagesFoundation of Nursinng Plancare of Standard - EdelEdelrose LapitanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics in The Health Care Profession by Juvy CarameDocument23 pagesNursing Informatics in The Health Care Profession by Juvy CarameJUVY CARAMENo ratings yet
- Green Orange Blue Creative Healthcare Facility Presentation - 20240204 - 205128 - 0000Document38 pagesGreen Orange Blue Creative Healthcare Facility Presentation - 20240204 - 205128 - 0000AndrewNo ratings yet
- Informatics L1Document4 pagesInformatics L1RYZELLE SCHWEIN MIRANDANo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics TheoriesDocument11 pagesNursing Informatics TheoriesFilamae Jayahr Caday60% (5)
- Practice Application of Nursing InformaticsDocument3 pagesPractice Application of Nursing Informaticscayla mae carlos100% (3)
- NCM 110 (Prelims) - Lesson 1Document3 pagesNCM 110 (Prelims) - Lesson 1nianNo ratings yet
- INFOLECDocument4 pagesINFOLECRomm JacobNo ratings yet
- Nursing InformaticesDocument18 pagesNursing InformaticesSakthi DeviNo ratings yet
- Nursing InformaticsDocument102 pagesNursing InformaticsYumeko JabamiNo ratings yet
- First Lecture - Nursing InfoDocument3 pagesFirst Lecture - Nursing InfoAndrea Marie SevillaNo ratings yet
- Dental Informatics IntroductionDocument4 pagesDental Informatics IntroductionDANA ISABELLE PILAPILNo ratings yet
- NCM210 PrelimDocument10 pagesNCM210 PrelimJasmine Angeli ObilloNo ratings yet
- Nursing InformaticsDocument27 pagesNursing InformaticsSarte Rachelle AnneNo ratings yet
- NI - Handout No.2Document44 pagesNI - Handout No.2Yuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- History, Definition and Evolution of Nursing InformaticsDocument3 pagesHistory, Definition and Evolution of Nursing InformaticsFebelyn PollentesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics Task 1Document1 pageNursing Informatics Task 1Concepcion NazaredoNo ratings yet
- Ni MidterDocument5 pagesNi MidterKristine KrisNo ratings yet
- PrelimReviewer NCM110LectDocument18 pagesPrelimReviewer NCM110LectJustine Simeon lagunzadNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics: P.Vijayalakshmi Clinical InstructorDocument46 pagesNursing Informatics: P.Vijayalakshmi Clinical InstructorGracy CasañaNo ratings yet
- Historical Perspective 2022Document24 pagesHistorical Perspective 2022Nikky SilvestreNo ratings yet
- NCM110 NI CompiledNotesDocument6 pagesNCM110 NI CompiledNotesSherinne Jane CariazoNo ratings yet
- NI 1 WordDocument5 pagesNI 1 WordLeigh Angelika Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document37 pagesWeek 3Rasmina Jhoy Roque Quintana33% (3)
- Use of NIS in Acute Care Settings - NI in Discharge PlanningDocument5 pagesUse of NIS in Acute Care Settings - NI in Discharge PlanningRomhea MatmyrNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document10 pagesLesson 3KANT JAMES D. MAHANNo ratings yet
- Data, InformationDocument2 pagesData, InformationAnna FrankNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics: Unit 1 Introduction To Informatics: The American Nurses Association (ANA)Document3 pagesNursing Informatics: Unit 1 Introduction To Informatics: The American Nurses Association (ANA)Gabbi Kim100% (1)
- Nursing InformaticsDocument24 pagesNursing InformaticsOsama ramadanNo ratings yet
- Informatics Topic No.1Document3 pagesInformatics Topic No.1Hecia Gaga-aNo ratings yet
- NSG InfoDocument6 pagesNSG InfoGummy BearsNo ratings yet
- What Is InformaticsDocument38 pagesWhat Is Informaticsapi-239123914No ratings yet
- Graves and Corocorans ModelDocument8 pagesGraves and Corocorans ModelMikaela FuentesNo ratings yet
- Turley ModelDocument12 pagesTurley ModelJustine Joy Solano50% (2)
- EXTRA!!! The Evolution of Nursing InformaticsDocument15 pagesEXTRA!!! The Evolution of Nursing InformaticsMhay Villamor RNNo ratings yet
- What Is InformaticsDocument17 pagesWhat Is InformaticsMaria Erica Jan MirandaNo ratings yet
- Care of Mother and Adolescent Well Client RLE Skills Lab ReviewerGonzalesDocument22 pagesCare of Mother and Adolescent Well Client RLE Skills Lab ReviewerGonzalesKarl LintanNo ratings yet
- C GELIT02 PrelimsDocument9 pagesC GELIT02 PrelimsKarl LintanNo ratings yet
- STS ExamDocument11 pagesSTS ExamKarl LintanNo ratings yet
- C GELIT02 PrelimsDocument9 pagesC GELIT02 PrelimsKarl LintanNo ratings yet
- 1 Week 1 World LiteratureDocument3 pages1 Week 1 World LiteratureKarl LintanNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introfuction To Nursing Informatics-1Document3 pages1 - Introfuction To Nursing Informatics-1Karl LintanNo ratings yet
- Brigada Narrative Report 2021Document2 pagesBrigada Narrative Report 2021KIARA CAMILLE RIBANONo ratings yet
- NUR4108 Policy Brief Guideline/Rubric: Course Objectives, Program Outcomes, and AACN EssentialsDocument3 pagesNUR4108 Policy Brief Guideline/Rubric: Course Objectives, Program Outcomes, and AACN EssentialsDanson Githinji ENo ratings yet
- Practise Test 909Document4 pagesPractise Test 909BruhNo ratings yet
- L.P. of Transcultural NursingDocument14 pagesL.P. of Transcultural Nursingvikas takNo ratings yet
- Garces PsychDocument2 pagesGarces PsychSherlyn Miranda GarcesNo ratings yet
- Queenie Amigale K To 12 Nail Care Learning ModuleDocument126 pagesQueenie Amigale K To 12 Nail Care Learning Modulemagtakaanamarie100% (2)
- FLT Module2 Lesson 2 EngageDocument17 pagesFLT Module2 Lesson 2 EngageKim So-HyunNo ratings yet
- Salbutamol PDFDocument3 pagesSalbutamol PDFRahmadona NandaNo ratings yet
- Proproff MCQ LMNDocument3 pagesProproff MCQ LMNGulfam ZamiNo ratings yet
- PST Inspection Report MS Leisure Company IncDocument6 pagesPST Inspection Report MS Leisure Company IncChris Gothner100% (1)
- Reviewer in PhCh2Document9 pagesReviewer in PhCh2prinz1mendezNo ratings yet
- Study Stack - OBGYN SHelf SR Table ReviewDocument7 pagesStudy Stack - OBGYN SHelf SR Table Reviewece142No ratings yet
- List of Youngest Birth M..Document12 pagesList of Youngest Birth M..Daniela BatrinuNo ratings yet
- 525ds ConcentratorDocument44 pages525ds Concentratorjohn clevelandNo ratings yet
- Css Week 5 Day 2 FinalcoDocument5 pagesCss Week 5 Day 2 FinalcoMGracey BayNo ratings yet
- 2019-20-ELE-Field Technician Air Conditioning-Q3102-L4-Class-11-12Document34 pages2019-20-ELE-Field Technician Air Conditioning-Q3102-L4-Class-11-12Parag ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Retention NCP GARCIA J.Document2 pagesUrinary Retention NCP GARCIA J.Jimlord GarciaNo ratings yet
- Sampling Theory and Generalizability in Nursing ResearchDocument4 pagesSampling Theory and Generalizability in Nursing ResearchANDREWNo ratings yet
- EncephaloceleDocument15 pagesEncephalocelePerpolNo ratings yet
- Moral StandardsDocument3 pagesMoral StandardsKyla Angela Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- Public Health ConceptsDocument9 pagesPublic Health ConceptsSucheta MitraNo ratings yet
- Specific Groups EssayDocument1 pageSpecific Groups Essaysunilvajshi2873No ratings yet
- Nafasi Za Kazi UdomDocument25 pagesNafasi Za Kazi UdomSwalau OmaryNo ratings yet
- Psychological TestingDocument149 pagesPsychological Testingxiejie22590No ratings yet
- Meta 2Document14 pagesMeta 2S2-IKM ULMNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics in ObsDocument5 pagesThesis Topics in Obslorifloresalbuquerque100% (2)
- Vesalio Initiates Clinical Study Evaluating Innovative Thrombectomy Technique For Patients With STEMIDocument3 pagesVesalio Initiates Clinical Study Evaluating Innovative Thrombectomy Technique For Patients With STEMIPR.comNo ratings yet
- 2015 ESC Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Management of Pericardial Diseases European Heart Journal Oxford AcademicDocument1 page2015 ESC Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Management of Pericardial Diseases European Heart Journal Oxford AcademicM Yusuf Arief AkbarNo ratings yet
- 13 Reasons Why Character DiagnosisDocument9 pages13 Reasons Why Character DiagnosisVutagwa JaysonNo ratings yet
- Your Clinic Name Here: Feline Acute Pain Scale Canine Acute Pain ScaleDocument1 pageYour Clinic Name Here: Feline Acute Pain Scale Canine Acute Pain ScalevetthamilNo ratings yet