Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CE Board Nov 2023 - Engineering Mechanics - Set 2
Uploaded by
Vincent VillalobosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CE Board Nov 2023 - Engineering Mechanics - Set 2
Uploaded by
Vincent VillalobosCopyright:
Available Formats
Review Innovations CE Review for November 2023 – Engineering Mechanics 2
EQUILIBRIUM OF FORCE SYSTEMS Methods in Truss Analysis:
Equilibrium is the term to designate the condition where the 1. Method of Joints
resultant force is zero. It can be characterized as, The equilibrium equations are applied to individual
joints (or pins) of the truss.
1. Static or at rest
2. ∑F = 0 2. Method of Sections
3. If dynamic, acceleration is zero. Analyzes the free-body diagram of a part of a truss that
contains two or more joints.
Different Support Reactions
PROBLEMS:
Situation 1: In the frame shown, members ACE and BCD are
connected by a pin at C and by the link DE. For the loading
shown, determine the
1. reaction at B
2. force in link DE
3. force exerted at C on member BCD
Situation 2: In the figure below, if P = 80 lb, determine the
following:
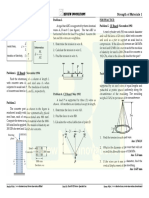
ANALYSIS OF CABLES
A. Cables under concentrated loads
B. Cables under distributed loads
1. Parabolic Cables
The loading is distributed uniformly along the
1. reaction at A
horizontal
2. reaction at B
2. Catenary Cables 3. tension in segment AC of the cable
The loading is distributed along the length of the 4. tension in segment CD of the cable
cable 5. tension in segment BD of the cable
6. the cable’s total length.
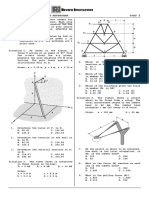
TRUSS ANALYSIS
Situation 3: As shown in the figure, cable ACB supports a
Truss is defined as a structure that is made of straight, load uniformly distributed along the horizontal. The lowest
slender bars that are joined together to form a pattern of point C is located 9 m to the right of point A. Determine the
triangles. Trusses are usually designed to transmit forces value of the following:
over relatively long spans such as roof and bridges.
1. the value of the vertical distance a
The analysis of trusses is based on the following three 2. the minimum tension, in N
assumptions: 3. the maximum tension, in N
1. The weights of the members are negligible. 4. tension at B, in N
2. All joints are pins. 5. slope at A, in degrees
3. The applied forces act at the joints. 6. slope at B, in degrees
Manila FB: @ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao FB: Review Innovations Davao Branch
( (02) 8735-9161 0919-227-9194 ( (082) 221-1121 0930-256-0998
Review Innovations CE Review for November 2023 – Engineering Mechanics 2
7. the total length of cable
1. Determine the tension in the cable.
2. Determine the reaction at the upper wheel.
Situation 4: Flexible cables CF and DE brace the truss at its
central panel. 3. Determine the reaction at the lower wheel.
Given: h = 4m Situation 3: Knowing that dc = 3 m, determine the following:
s = 3m
W = 30 kN
C D
A B
E F
s s s 1. reaction at A
2. reaction at E
W 3. maximum tension
1. Determine the force in member CD, in kN. 4. minimum tension
2. Determine which diagonal is acting and the force in it, in 5. total length of the cable
kN. 6. distance dB
3. Determine the resulting force in member BD, in kN 7. distance dD
PROBLEMS FOR PRACTICE: Situation 4: For the cable loaded as shown in the figure,
determine the following:
Situation 1: From the figure shown, two spheres having
equal weights of 360 N each is placed on top of the three
identical spheres. The radius of the upper two spheres is 0.80
m while that at the bottom is 1.0 m having equal weights of
420 N. Determine the:
1. angle β1
2. angle β2
3. tensile force in segment A-1 of the cable
1. reaction at A 4. tensile force in segment 1-2 of the cable
2. reaction at C 5. tensile force in segment 2-B of the cable
3. reaction at B 6. length of the cable
Situation 2: A loading car is at rest on a track forming an Situation 5: The cable shown supports a horizontal uniform
angle of 25° with the vertical. The gross weight of the car and load of 10 kN/m. Determine the:
its load is 5500 lb, and it is applied at G. The car is held by a
cable.
Manila FB: @ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao FB: Review Innovations Davao Branch
( (02) 8735-9161 0919-227-9194 ( (082) 221-1121 0930-256-0998
Review Innovations CE Review for November 2023 – Engineering Mechanics 2
1. tension at A
2. slope of the cable at A Situation 9: The tower shown is subjected to three forces as
3. tension at the lowest point C follows:
F1 = 4 kN
Situation 6: A uniform 80-m pipe that weighs 960 kN is F2 = 6 kN
supported entirely by a cable AB of negligible weight. F3 = 6 kN
Determine the
Given: a = 5.8 m
b = 3.2 m
c = 4.8 m
d = 2.0 m
d c
G H
F1
1. horizontal distance of the lowest point from point A b
2. length of the cable E F
F2
3. the minimum force in the cable K
4. the maximum force in the cable b
C D
F3
Situation 7: A cable AB shown supports a uniformly J
distributed load of 200 N/m. Determine the value of the b
following: A I B
1. the minimum tension
2. the maximum tension a a
3. tension at B
4. slope at A in degrees 1. Determine the resultant reaction at B, in kN.
5. slope at B in degrees 2. Determine the force in member AC, in kN.
6. the length of cable 3. Determine the force in member GE, in kN
Situation 10: Using the figure below,
Situation 8: The walkway ABC of the footbridge is stiffened
by adding the cable ADC and the short post of length L. If
the tension in the cable is not to exceed 2000 N, determine the
smallest value of L for which the 80-kg person can be
supported at B.
1. If P = 3,000 N and Q = 1,000 N, determine the force in
member CD.
2. If P = 3,000 N and Q = 1,000 N, determine the force in
member JK.
Manila FB: @ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao FB: Review Innovations Davao Branch
( (02) 8735-9161 0919-227-9194 ( (082) 221-1121 0930-256-0998
Review Innovations CE Review for November 2023 – Engineering Mechanics 2
3. If FCD = 6,000 N and FGD = 1,000 N (both under 5. Force in member FH
compression), determine the value of P. 6. Force in member GH
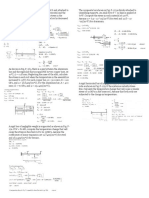
Situation 11: A couple acting on the winch at G slowly raises
the load W by means of a rope that runs around the pulleys
attached to the derrick at A and B. Assuming the diameters Situation 14: A transmission tower is subjected to the wind
of the pulleys and the winch are negligible. loads shown.
1. Determine the vertical reaction (kN) at support A.
1. Determine the force in member EF of the derrick. 2. Determine the axial force (kN) at member GK.
2. Determine the force in member KL of the derrick. 3. Determine the axial force (kN) at member EG.
Answer Key for Problems for Practice:
Situation 12: A plane truss is loaded as shown. Determine 1. RA = 216.48 N, RC = 780 N, RB = 120.27 N
the: 2. T = 4,984.69 lb, RU = 564.04 lb, RL = 1,760.36 lb
3. RA = 28.36 kN, RE = 21.48 kN, Tmax = 28.36 kN, Tmin = 21.48
kN, L = 11.25 m, dB = 1.73 m, dD = 4.20 m
4. β1 = 49.78°, β2 = 19.08°, TA-1 = 2,961 N, T1-2 = 2,023 N, T2-B
= 2,334 N, 29.48 m
5. TA = 217.75 kN, θA = 53.79º, TC = 128.63 kN
6. 50 m, 86 m, 750 kN, 960 kN
7. Tmin = 20.15 kN, Tmax = 25.13 kN, TB = 22.06 kN, θA =
36.70°, θB = 24.02°, L = 127.91 m
8. 0.80 m
9. RB = 18.014 kN, FAC = 9.253 kN (Tension), FGE = 2.752 kN
1. force in member BC (Tension)
2. force in member CE 10. FCD = 5,250 N (Compression), FJK = 2,250 N (Tension), P
3. force in member BF = 5,167.95 N
11. FEF = 1.828W (Tension), FKL =2.83W (Compression)
Situation 13: Given the truss below, determine the: 12. FBC = 16.67 kN (Compression), FCE = 0, FBF = 10.68 kN
(Tension)
13. FAC = 50 kN (Compression), FAD = 0, FDE = 40 kN
(Tension), FGI = 0, FFH = 30 kN (Compression), FGH = 0
14. AV = 9.176 kN, FGK = 2.11 kN (Compression), FEG = 5.35
kN (Compression)
1. Force in member AC
2. Force in member AD
3. Force in member DE
4. Force in member GI
Manila FB: @ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao FB: Review Innovations Davao Branch
( (02) 8735-9161 0919-227-9194 ( (082) 221-1121 0930-256-0998
You might also like
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- CE Board Nov 2022 Engineering Mechanics Set 1Document3 pagesCE Board Nov 2022 Engineering Mechanics Set 1Meverlyn RoqueroNo ratings yet
- Sec - PS1Document2 pagesSec - PS1Monica Amor AbengozaNo ratings yet
- CE 010 Module 1.2-1.3Document29 pagesCE 010 Module 1.2-1.3NIÑO LEANDRO LEYESNo ratings yet
- Approximate Analysis of Statically Indeterminate StructuresDocument36 pagesApproximate Analysis of Statically Indeterminate StructuresRommel BaesaNo ratings yet
- MATH Final PreboardDocument8 pagesMATH Final PreboardKristelle V. TorrealbaNo ratings yet
- April 2024 - PSAD 2Document2 pagesApril 2024 - PSAD 2rando12345No ratings yet
- Level 4 Practice ModuleDocument8 pagesLevel 4 Practice ModuleJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 5 Reflection On Virtual Plant Visits - Concrete and Rebars Rehabilitations and Webinar - Tunneling (Tunnel Boring Machine) v.2Document1 pageAssignment No. 5 Reflection On Virtual Plant Visits - Concrete and Rebars Rehabilitations and Webinar - Tunneling (Tunnel Boring Machine) v.2John Rhey Almojallas BenedictoNo ratings yet
- REFRESHER COURSE MODULE ON STRUCTURAL ENGINEERINGDocument1 pageREFRESHER COURSE MODULE ON STRUCTURAL ENGINEERINGMohammad Hussein Masiu BacaramanNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 Strength of Materials Set 1Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2020 Strength of Materials Set 1Eugenio Genesis AbadNo ratings yet
- M-1ppt741 ShodanaDocument62 pagesM-1ppt741 ShodanaSupriya Xavier LopesNo ratings yet
- The Poisson DistributionDocument13 pagesThe Poisson DistributionShehzad khanNo ratings yet
- Ce0061 Professional Course 4 - (Specialized 2) Ste Track: Prestressed Concrete DesignDocument40 pagesCe0061 Professional Course 4 - (Specialized 2) Ste Track: Prestressed Concrete DesignjerichoNo ratings yet
- "Gtfiuctural Steel Dkign: Yletd Stress, Fy - Is That Unit Tensile Stress atDocument13 pages"Gtfiuctural Steel Dkign: Yletd Stress, Fy - Is That Unit Tensile Stress atMhiaBuenafeNo ratings yet
- Policarpio 4 - Refresher GEODocument2 pagesPolicarpio 4 - Refresher GEOJohn RoaNo ratings yet
- Nov 2021 CoachingDocument71 pagesNov 2021 CoachingKenny CaluzaNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering November 2020 Review Innovations Hydraulics ProblemsDocument1 pageCivil Engineering November 2020 Review Innovations Hydraulics ProblemsJustine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- BrasdaDocument3 pagesBrasdaJayson Brylle MojaresNo ratings yet
- Quiz No. 4Document1 pageQuiz No. 4Cristina SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Sas 1 - 7Document50 pagesSas 1 - 7jaira.masuangatNo ratings yet
- Permeability Test in The Field by Pumping From WellsDocument16 pagesPermeability Test in The Field by Pumping From WellsGed CudiamatNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems - Midterm ExamDocument5 pagesSample Problems - Midterm ExamWafa A. NasserNo ratings yet
- Strength 4 May 2021Document3 pagesStrength 4 May 2021Jon SnowNo ratings yet
- Solved A Permeable Soil Layer Is Underlain by An Impervious La...Document1 pageSolved A Permeable Soil Layer Is Underlain by An Impervious La...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Determinacy and IndeterminacyDocument12 pagesDeterminacy and IndeterminacyMode NaseerNo ratings yet
- TENSION MEMBERS STRENGTHDocument10 pagesTENSION MEMBERS STRENGTHRi MarkuNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete - Shear StrengthDocument7 pagesReinforced Concrete - Shear StrengthDenice CastroNo ratings yet
- SeatworkDocument7 pagesSeatworkRA KirongNo ratings yet
- UEP Organization ChartDocument1 pageUEP Organization ChartChan OrsolinoNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument11 pagesStatics of Rigid Bodiesdonald escalanteNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Progression (A.P.) Infinite Geometric Progression (I.G.P.)Document2 pagesArithmetic Progression (A.P.) Infinite Geometric Progression (I.G.P.)Denver John ColoradoNo ratings yet
- Solve For X If 8Document3 pagesSolve For X If 8Gellie BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Head Losses LectureDocument1 pageHead Losses Lecturebang sieNo ratings yet
- CE Reference: Working Stress Analysis For Concrete BeamsDocument5 pagesCE Reference: Working Stress Analysis For Concrete BeamsYamil Camilo Bastidas ArciniegasNo ratings yet
- FA NO. 7 (Problem Set)Document2 pagesFA NO. 7 (Problem Set)Peter Adrian Ngo100% (1)
- Midterm 20210405 SolutionDocument12 pagesMidterm 20210405 SolutionSelf SevNo ratings yet
- Pre-Stressed Elective EngineeringDocument7 pagesPre-Stressed Elective EngineeringJonas FernandezNo ratings yet
- 2022 Nov Algebra 4Document2 pages2022 Nov Algebra 4Meverlyn RoqueroNo ratings yet
- Refresher (Probability Discussion)Document33 pagesRefresher (Probability Discussion)sadonNo ratings yet
- Review Module 45-RCD 5 - Part 1 & 2Document2 pagesReview Module 45-RCD 5 - Part 1 & 2Arlyn ConsumeNo ratings yet
- 3331 ST7008 Prestressed Concrete QBDocument11 pages3331 ST7008 Prestressed Concrete QBsundar100% (1)
- Quiz No 1Document2 pagesQuiz No 1Tris ZackNo ratings yet
- CE EVALUATION EXAM No. 7 - Soil Testing, Foundations, Retaining Wall (Answer Key)Document6 pagesCE EVALUATION EXAM No. 7 - Soil Testing, Foundations, Retaining Wall (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Ce 343L - Fluid Mechanics - 1 ExamDocument2 pagesCe 343L - Fluid Mechanics - 1 ExamMichelle Daarol100% (1)
- Prismoidal Formula 2Document11 pagesPrismoidal Formula 2anggaxkusumaNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Problems and SolutionsDocument18 pagesSoil Mechanics Problems and SolutionsBemzar SamsonNo ratings yet
- Subject 1 Algebra Trigonometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Analytic Geometry Probability PhysicsDocument49 pagesSubject 1 Algebra Trigonometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Analytic Geometry Probability PhysicsDani LubosNo ratings yet
- Calculus Problem SetDocument1 pageCalculus Problem SetJoyce DueroNo ratings yet
- V0L2 PDFDocument4 pagesV0L2 PDFJohannie Nina ClaridadNo ratings yet
- Design and Const2Document101 pagesDesign and Const2Sigue Ramel HinayasNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Beam Design ProblemsDocument8 pagesReinforced Concrete Beam Design ProblemsNajib A. CasanNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics SolutonsDocument20 pagesSoil Mechanics SolutonsRoberto CarlosNo ratings yet
- Falcon RCD ColumnsDocument4 pagesFalcon RCD ColumnsJerome Adduru100% (1)
- Chapter 3b - Analysis of Tension MembersDocument56 pagesChapter 3b - Analysis of Tension MembersRami DemachkiNo ratings yet
- Gis Located Above B)Document10 pagesGis Located Above B)Apple AterradoNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies Tutorial QuestionsDocument2 pagesEquilibrium of Rigid Bodies Tutorial QuestionsZulfadzli RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Cable: Fundamental Characteristic of Cable & ArchDocument15 pagesCable: Fundamental Characteristic of Cable & ArchSiddharth Singh JeenaNo ratings yet
- Strength 3 May 2021Document4 pagesStrength 3 May 2021Jon SnowNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document6 pagesTutorial 2A SкNo ratings yet
- 2010 Christian Religious Education Past Paper - 1Document1 page2010 Christian Religious Education Past Paper - 1lixus mwangiNo ratings yet
- 3.part I-Foundations of Ed (III)Document25 pages3.part I-Foundations of Ed (III)Perry Arcilla SerapioNo ratings yet
- Parking Garage Design GuidelinesDocument17 pagesParking Garage Design GuidelinesCarlos Benjamin BCNo ratings yet
- BATCH Bat Matrix OriginalDocument5 pagesBATCH Bat Matrix OriginalBarangay NandacanNo ratings yet
- MgstreamDocument2 pagesMgstreamSaiful ManalaoNo ratings yet
- The Power of Prayer English PDFDocument312 pagesThe Power of Prayer English PDFHilario Nobre100% (1)
- Protective & Marine Coatings: Hi-Solids Alkyd Metal PrimerDocument4 pagesProtective & Marine Coatings: Hi-Solids Alkyd Metal PrimerAna CabreraNo ratings yet
- Bradley Et Al. 1999. Goal-Setting in Clinical MedicineDocument12 pagesBradley Et Al. 1999. Goal-Setting in Clinical MedicineFelipe Sebastián Ramírez JaraNo ratings yet
- Form of SpesDocument2 pagesForm of SpesMark Dave SambranoNo ratings yet
- You Write, It Types!: Quick Start GuideDocument21 pagesYou Write, It Types!: Quick Start Guidejean michelNo ratings yet
- Moldavian DressDocument16 pagesMoldavian DressAnastasia GavrilitaNo ratings yet
- DepEd Memorandum on SHS Curriculum MappingDocument8 pagesDepEd Memorandum on SHS Curriculum MappingMichevelli RiveraNo ratings yet
- 2013 SmartBUS Home Automation Product Catalogue English v.1.0Document108 pages2013 SmartBUS Home Automation Product Catalogue English v.1.0Smart-G4100% (3)
- VALUE BASED QUESTIONS FROM MATHEMATICS GRADE 10Document6 pagesVALUE BASED QUESTIONS FROM MATHEMATICS GRADE 10allyvluvyNo ratings yet
- Masai School Code of Conduct - Prefinal 11.10.2019Document3 pagesMasai School Code of Conduct - Prefinal 11.10.2019xavigatorNo ratings yet
- Calculating Calories for Weight Training SuccessDocument12 pagesCalculating Calories for Weight Training SuccessFadil Arif MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Organization Structure in SAP Plant Maintenance: CommentsDocument3 pagesOrganization Structure in SAP Plant Maintenance: CommentsMarco Antônio Claret TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Surrealismo TriplevDocument13 pagesSurrealismo TriplevVictor LunaNo ratings yet
- Mora Solvendi (Delay of The Debtor)Document11 pagesMora Solvendi (Delay of The Debtor)John Paul100% (1)
- IN SUNNY SPAIN, 1882-85: "My Country, My Love, My People, I Leave You Now, You Disappear, I Lose Sight of You"Document4 pagesIN SUNNY SPAIN, 1882-85: "My Country, My Love, My People, I Leave You Now, You Disappear, I Lose Sight of You"Mary Claire ComalaNo ratings yet
- Development Plan-Part IV, 2022-2023Document3 pagesDevelopment Plan-Part IV, 2022-2023Divina bentayao100% (5)
- Lab Manual 06 CSE 314 Sequence and Communication DiagramDocument6 pagesLab Manual 06 CSE 314 Sequence and Communication DiagramMufizul islam NirobNo ratings yet
- Obessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)Document10 pagesObessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)marketingmoneyindiaNo ratings yet
- Our Lady of Consolation Orchestra InstrumentsDocument2 pagesOur Lady of Consolation Orchestra InstrumentsCelestian Valensario PaderangaNo ratings yet
- Performance Theory For Hot Air Balloons: The Balloon Works, Inc., Statesville, N.CDocument4 pagesPerformance Theory For Hot Air Balloons: The Balloon Works, Inc., Statesville, N.CEbubekir ErkanNo ratings yet
- HamletDocument37 pagesHamlethyan teodoroNo ratings yet
- Row and Cluster Housing Building Codes and Bye LawsDocument1 pageRow and Cluster Housing Building Codes and Bye Lawssadhana illaNo ratings yet
- Merger Case AnalysisDocument71 pagesMerger Case Analysissrizvi2000No ratings yet
- Harsheen Kaur BhasinDocument20 pagesHarsheen Kaur Bhasincalvin kleinNo ratings yet
- Ky203817 PSRPT 2022-05-17 14.39.33Document8 pagesKy203817 PSRPT 2022-05-17 14.39.33Thuy AnhNo ratings yet