Professional Documents
Culture Documents
V0L2 PDF
Uploaded by
Johannie Nina ClaridadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
V0L2 PDF
Uploaded by
Johannie Nina ClaridadCopyright:
Available Formats
PRACTICE PROBLEMS
VOLUME 2
SOLVE THE FOLLOWING PROBLEMS AND WRITE YOUR SOLUTIONS BELOW EACH PROBLEM IN A LONG BOND PAPER.
1. A solid circular brass 25 mm in diameter is subjected to an axial tensile force SITUATION 4 (NOS. 13-15) -A 6-meter simply supported beam is loaded with
of 50 kN. Determine the decrease in the diameter of the bar due to this triangular loading varies 20 kN/m at the right support to 0 kN/m at the left
load. For brass, E = 90 GPa and poisson's ratio = 0.28 support.
A. 0.008 mm B. 0.005mm
C. 0.0125 mm D. 0.002 mm 13. Compute shear force in kiloNewtons at the midspan.
A. 2.60 B. 3.00
C. 5.00 D. 6.00
SITUATION 1 (NOS. 2-3) - A 500-mm-long, 16 mm-diameter rod made of a
homogeneous, isotropic material is observed o increase in length by 300 mm 14. Compute moment value in kiloNewton-meter at the midspan.
and to decrease in diameter by 2.4 mm when subjected to an axial 12- kN load. A. 27.00 B. 36.00
C. 45.00 D. 21.00
2. Compute the modulus of elasticity of the material in GPa.
A. 99.50 B. 120.00 15. Compute the location of the maximum moment from the right support.
C. 88.40 D. 72.50 A. 0.54 B. 2.54 m
C. 3.46 m D. 0.46 m
3. Compute the Poisson's ratio of the material.
A. 0.21 B. 0.28
C. 0.25 D. 0.32 16. A 15-meter-simple beam is loaded with two concentrated loads P1 and P2.
P1 is applied 5 m from left support and P2 is located 7 meter from P1. If
P1 = P2 = 120 kN. Compute the slope at the left support.
4. Two shafts A and B transmit the same power. The speed of shaft A is 300
rpm and that of shaft B is 200 rpm. Which of the following is true.
A. 2531/EI B. 3796/EI
A. shaft A has greater dia. B. both shafts have equal torque
C. 2995/EI D. 2180/EI
C. shaft B has greater dia. D. shafts have equal shearing stress
SITUATION 5 (NOS. 17-18) - A 15-meter-simple beam is loaded with clockwise
SITUATION 2 (NOS. 5-7) - The homogeneous 1200-N plate is suspended from moment M at one of the supports. If M = 60 kN-m
three cables as shown in MTE-STAT-001, 17. Which of the ff. most nearly gives the location of the maximum deflection
5. Compute the tension of cable at A in Newtons. of the beam from the point of application of M if EI is constant (in meters).
A. 119.60 B. 128.60 A. 7.46 B. 5.76
C. 50.40 D. 90.80 C. 6.34 D. 8.66
6. Compute the tension of cable at B in Newtons. 18. Compute the maximum deflection (in mm) of the beam if its flexural
A. 684 B. 846 rigidity is 49 840 kN-m^2.
C. 648 D. 486 A. 18.60 B. 15.70
C. 17.40 D. 21.10
7. If the tensile stress of a 5 mm diameter cable at C is limited to 50 MPa
compute the maximum weight (in Newtons) of the plate.
A. 1954 B. 2456
SITUATION 6 (NOS. 19-20) - A 25 m. long girder of the bridge is simply
C. 1476 D. 1658
supported at the right end and at 3 m. from the left end.
Given: Highway live load
W1 = 19.6 kN
8. The buckling load will be maximum for column, if...... W2 = 78.4 kN
A. both ends are hinged Distance on center of wheels = 4.3 m.
B. one end is free and the other end is hinged
C. both ends are clamp 19. Which of the ff. most nearly gives the maximum shear in kiloNewtons.
D. one end of the column is clamp and the other is free A. 101.50 B. 107.50
C. 103.50 D. 105.50
SITUATION 3 (NOS. 9 - 11) - The entrance of a warehouse has a roof that 20. Which of the ff. most nearly gives the maximum shear in kN-m
supports a roof load w = 20 kN/m as shown in MTE-SOM-001. The A. 478 B. 498
supports B and C are considered as simply supported. C. 488 D. 458
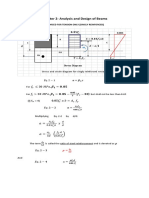
9. Compute the vertical reaction at C in kiloNewtons.
A. 54 B. 36 21. A tee section is made up of a 30 x 150 mm flange and a 20 mm x 200 mm
C. 45 D. 75 web. Which of the ff. most nearly gives the location of NA above the
lowest fiber of the section in mm.
10. Determine the maximum negative moment at BC in kiloNewton-meter. A. 140.82 B. 140.82
A. 36 B. 24 C. 69.12 D. 160.88
C. 21 D. 40
11. Which of the following gives the location of the maximum moment from 22. A rectangular cantilever beam 60 mm wide by 100 mm deep is 2 m long
point A. and with E = 200 GPa. A 40 kg mass falling thru a height of 200 mm strikes
A. 4.25 m B. 6.25 m and sticks at the free end of the beam. Calculate the maximum deflection
C. 4.75 m D. 5.25 m
caused by impact. Neglect the weight of the beam.
A. 15.60 mm B. 26.90 mm
C. 32.50 mm D. 21.50 mm
12. The 4- mm diameter cable is made of a steel with E = 200 GPa. Knowing
that the maximum stress in the cable must not exceed 190 MPa and that
the elongation is limited to 6 mm, compute the maximum safe value of P
in kiloNewtons. Length of the cable is 7.58 meters.
A. 1.30 B. 2.30
C. 2.99 D. 1.99
CECC 483 MIDTERM EXAM - 1ST SEMESTER 2 0 2 2 SET A
SET A
SITUATION 7 (NOS. 23-25) - Refer to the figure shown in MTE-SOM-002, the 37. A bar of cross-section 10 mm x 10 mm is subjected to an axial pull of 8000
hinged support at A is in double-shear connection while the support at B in N. The lateral dimension of the bar is found to be changed to 9.9985 mm x
single shear shear connection. Forces P is applied at C and F is an axial force 9.9985 mm. If the modulus of rigidity of the material is 800 000 N/mm².
produced from a member BD connected at B. Given data: x = 2 m, y = 3 m and Calculate the Poisson's ratio?
z = 4 m. Ø = 30 degrees A. 0.35 B. 0.43
C. 0.24 D. 0.67
23. Which of the following most nearly gives the diameter of pin at B in mm if
P = 50 kN and the shear capacity of the pin at B is 140 MPa.
A. 22 B. 25 SITUATION 10 (NOS. 38 -40) - Refer to a robot shown in MTE-STAT-002 if P =
C. 28 D. 32 200 N.
24. Which of the following most nearly gives the maximum value of P in 38. Which of the following most nearly gives the vertical component of the
kiloNewtons if the shearing stress of 16-mm-dia. pin at A is 120 MPa. The force P in Newtons.
horizontal distance between point A and B is 0.75x. A. 153.20 B. 160.70
A. 102.50 B. 86.20 C. 216.50 D. 191.50
C. 78.40 D. 90.30
39. Which of the following most nearly gives the moment at point O in
25. If the axial stress of BD is limited to 180 MPa, wherein BD is made of Newton-meter.
40-mm square tubing with thickness is one-tenth of its dimension, which A. 179.90 B. 151.70
of the ff. most nearly gives the shearing stress of the 16- mm dia. pin at A C. 168.30 D. 189.60
in MPa.
A. 175.40 B. 167.20 40. Which of the following most nearly gives the moment at point A in
C. 184.10 D. 156.70 Newton-meter.
A. 87.40 B. 102.40
C. 109.20 D. 96.80
26. Consider a thin-walled cylindrical pressure vessel with mean diameter 150
mm subject to a twisting moment of 1 kN-m together with an internal
pressure of 3 MPa. If the allowable working stress in tension is 150 MPa, 41. A 10-m long beam is simply supported at the left end and at 2 m from the
compute the wall thickness of the vessel in millimeters. right end. The beam will be analyzed for the maximum moment at the
A. 1.15 B. 2.25 midspan that can be induced by a moving load.
C. 2.95 D. 1.55 What is the ordinate of the influence diagram at the midspan?
A. 2 B. 1
C. 3 D. 4
27. The deflection due to couple M at the free end of a cantilever beam with
length L is.. 42. If a member, whose tensile strength is more than two times the shear
A. ML²/4EI B. ML²/EI strength, is subjected to an axial load up to failure, the failure of the
C. ML²/3EI D. ML²/2EI member will occur by....
A. maximum shear stress B. normal or shear stress
C. maximum normal stress D. minimum shear stress
28. The ratio of the maximum deflections of a beam simply supported at its
ends with an isolated central load and that of with a uniformly distributed
load over its entire length is...
A. 5/8 B. 3/2 43. A cantilever wood pole carries a force P = 300 N at its free end as well . The
C. 5/3 D. 8/5 length of the pole is 0.75 m and the allowable bending stress is 14 MPa.
The required diameter of the pole is nearest to...
A. 75 mm B. 55 mm
SITUATION 8 (NOS. 29-31) - A hollow steel bar (G = 80 GPa) is twisted by C. 35 mm D. 45 mm
torques T . The twisting of the bar produces a maximum shear strain of
640 x 10^-6 radians. The bar has outside and inside diameters of 150 mm
x 120 mm respectively. 44. Given the parallel forces shown in figure MTE-STAT-003:
P = 20 kN, Q = 30 kN, S = 25 kN, T = 50 kN, a = 3 m, b = 4 m, c = 5 m,
29. Determine the maximum tensile strain in the bar d = 2 m, e = 5 m, f = 3 m
A. 0.00032 B. 0.00128 Compute the z-coordinate of the resultant force.
C. 0.00064 D. 0.00016 A. 3.96 m B. 4.20 m
C. 4.84 m D. 4.32 m
30. Determine the maximum tensile stress (MPa) in the bar.
A. 51.20 B. 25.60
C. 12.80 D. 102.4
45. A 12-meter span non-symmetrical parabolic cable carries a uniform
31. What is the magnitude of the applied torques T in kiloNewton-meter? horizontal load of 40 kN/m. The left support is 6 m higher than the right
A. 5 B. 40 support and 9 m above the lowest sag. Determine the maximum tension
C. 10 D. 20 of the cable.
A. 128.69 kN B. 64.35 kN
C. 330.49 kN D. 165.24 kN
32. A shaft was initially subjected to bending moment and torsion. If the
magnitude of moment and torsion are equal, what is the ratio of max.
46. An 9-meter propped beam is loaded with 20 kN/m uniformly distributed
bending stress to shear stress?
load applied at the right two-thirds of the span and a concentrated load of
A. 2 B. 0.50
50 kN at the midspan. Determine the moment at the fixed support at the
C. 0.25 D. 1
left in kiloNewton-meter.
A. 124 B. 224
C. 142 D. 214
SITUATION 9 (NOS. 33 - 36) - A propped beam with span L carries a
concentrated moment M at the simple end.
47. A load of "x" lbs is hung from the middle of a rope which is stretched
33. What is the moment a the fixed support? between two rigid walls 20 ft apart. Due to the load, the rope sags 2 ft in
A. M/2 B. M the middle. If the tension of the rope is 100 lbs, compute the value of x.
C. 2M D. 3M/2 A. 22.39 B. 32.92
C. 39.22 D. 29.32
34. Compute the location of the maximum deflection from the free end.
A. 3L/4 B. 2L/3 48. Which of the following nearly gives the centroidal polar moment of inertia
C. L/4 D. L/3 (mm^4) of a steel T-section with 300 mm x 20 web and 200 mm x 20 mm
flange.
35. What is the maximum deflection of the beam if EI is constant? A. 107 000 000 B. 136 000 000
A. ML²/18EI B. ML²/21EI C. 120 000 000 D. 112 000 000
C. ML²/36EI D. ML²/27EI
36. Compute the slope at the midspan if EI is constant.
A. ML/4EI B. 3ML/8EI 49. If the area of cross-section of a wire is circular and if the radius of this wire
decreases to half of its original value due to stretch to the wire by a load,
C. 3ML/16EI D. 5ML/16EI
then modulus of elasticity of the wire will be...
A. doubled B. unaffected
C. halved D. one-fourth of its original value
CECC 483 MIDTERM EXAM - 1ST SEMESTER 2 0 2 2 SET A
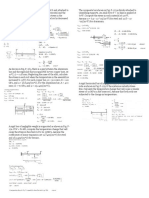
SITUATION 17 (NOS. 50-52) - Refer to the figure shown in MTE-STAT-004, if F 63. Determine the ratio of the shear modulus to the modulus of elasticity of a
= 855 kN, material whose Poisson's ratio is 0.25.
A. 0.40 B. 0.25
50. Which of the ff. most nearly gives the moment of the force about x-axis in C. 0.30 D. insufficient data
kN-m.
A. 122 B. 195
64. A steel tube with diameters d2 = 84 mm and d1 = 52 mm is twisted by
C. 169 D. 136
torques at the ends. The diameter of a solid steel shaft that resists the same
51. Which of the ff. most nearly gives the moment of the force about z-axis in torque at the same maximum shear stress is nearest to:
kN-m. A. 56 mm B. 82mm
A. 122 B. 195 C. 79 mm D. 75 mm
C. 169 D. 136
65. A steel pipe of length L = 4 ft , outside diameter D = 6 in. and inside
52. Which of the ff. most nearly gives the angle in degrees between the force diameter d = 4.5 in. is compressed by an axial force P = 140 kips. The
and the z-axis. material has modulus of elasticity E = 30,000 ksi and Poisson's ratio = 0.30.
A. 70.80 B. 109.40 Determine the increase in the wall thickness in inches.
B. 55.50 D. 124.50 A. 0.00033953 B. 0.00008488
C. 0.00113177 D. No increase
SITUATION 11 (NOS. 53-54)- A simply supported beam, 150 mm wide by 350
mm high and 8 m long is subjected to a concentrated load of 50 kN at a 66. A body is subjected to a tensile stress of 1200 MPa on one plane and
point 3 meters from one of the supports. another tensile stress of 600 MPa on a plane at right angles to the former. It
is also subjected to a shear stress of 400 MPa on the same planes. The
53. Determine the maximum fiber stress in megaPascals. maximum normal stress nearly equal to....
A. 26.34 B. 20.54 A. 1400 MPa B. 400 MPa
C. 16.74 D. 30.61 C. 900 MPa D. 500 MPa
54. Determine the stress in a fiber located 20 mm from the topmost fiber of SITUATION 15 (NOS. 67-69) - The length of a solid bar is 1.20 m and is twisted
the beam in megaPascals. torques, T acting at the ends. lt has a diameter of 30 mm and of a shear
A. 40.31 B. 32.89 modulus G = 28 GPa.
C. 46.54 D. 27.11
67. Determine the torsional stiffness of the bar.
A. 2075.0 N.m B. 2258.2 N.m
SITUATION 12 (NOS. 55-57) -A three-legged stool is subjected to the load "P" as C. 1552.4 N.m D. 1855.5 N.m
shown in MTE-STAT-005, P = 200 N.
68. Determine the maximum shear stress if the angle of twist of the bar is 1/90
55. Which of the following gives the nearest value of the vertical force reaction of the complete revolution in megaPascals.
under leg A. A. 30.78 B. 18.79
A. 113.3 N B. 126.70 N C. 24.43 D. 22.12
C. 93.30 N D. 106.70 N
69. Determine the maximum shear strain in radians.
56. Which of the following gives the nearest value of the vertical force reaction A. 0.000958 B. 0.000725
under leg B. C. 0.000873 D. Not found in the list
A. 53.30 N B. 43.30 N
C. 36.70 N D. 46.70 N
70. A simple beam with span L is applied with concentrated moment M at the
57.Which of the following gives the nearest value of the vertical force reaction midspan. Compute its maximum moment.
under leg C. A. ML/4 B. M/2
A. 53.30 N B. 43.30 N C. M D. M/4
C. 36.70 N D. 46.70 N
SITUATION 16 (NOS. 71 - 73) - A 4-meter cantilever beam supports a uniform
load of 25 kN/m throughout its length. The beam deflects 20 mm at the
SITUATION 13 (NOS. 58-59)- A 4-meter wide flange is simply supported at each free end. Flexural rigidity is equal to 50 000 kN-m².
ends and supports the concentrated load at the midspan W and a total
uniformly distributed load (loaded throughout the span) of 2W. 71. What force at the free end is required to eliminate the deflection at
Properties of section: that end in kiloNewtons?
bf = 200 mm d = 220 mm tf = tw = 20 mm A. 46.88 B. 37.50
C. 42.75 D. 51.25
58. Which of the following most nearly gives the value of W that will not
exceed the flexural stress of 10 MPa. 72. What force at the midspan is required to reduce the deflection at
A. 6.54 KN B. 2.73 KN the free end by 16 mm in kiloNewtons?
C. 4.09 KN D. 6.14 kN A. 60 B. 30.00
C. 40 D. 37.50
59. Which of the following most nearly gives the value of W that will not
exceed the shearing stress of 1.4 MPa. 73. What force at the free end is required to reduce the deflection at that end
A. 1.16 KN B. 1.75 KN to 8 mm in kiloNewtons?
C. 3.49 KN D. 2.15 kN A. 22.25 B.18.75
C. 31.225 D.28.125
SITUATION 14 (NOS. 60-62) -Beam ABC is on fixed supports at A and C. Its on 74. A triangular section has base of 150 mm and depth of 300 mm. What is its
roller support at B. The beam carries a uniformly distributed load W, moment of inertia about its base in mm^4?
throughout the 2 spans(L1 and L2). If W = 36 kN/m, L1 = L2 = 8 meters. A. 150 x 10^6 B. 337.5 x 10^6
C. 450 x 10^6 D. 112.5 x 10^6
60. What is the degree of indeterminacy of the beam ABC?
A. 5th degree B. 3rd degree
C. 4th degree D. 2nd degree
75. The slope at the free end of a cantilever beam of length L =1 meter is 1°. If
61. Due to W, the resulting reaction at B = 288 kN, what is the maximum shear the cantilever beam carries a uniformly distributed load over the whole
at span AB? length, then the deflection at the free end is approximately equal to..
A. 120 kN B. 132 kN A. 2.67 cm B. 1.31 cm
C. 144 kN D. 156 kN C. 1 cm D. 3.93 cm
62. Find the maximum positive moment (kN-m) if the roller support is removed
at the support B.
A. 182 B. 768
C. 288 D. 384
CECC 483 MIDTERM EXAM - 1ST SEMESTER 2 0 2 2 SET A
1.50 m 5m 1.50 m
w
A C
2m 2m
2m B 8m
B C
6m
1.50 m
2.50 m
MTE-SOM-001
A
MTE-STAT-001 20°
400 mm
C
P
A
C
P
B 60°
500 mm
300 mm
y
O
B D
F
MTE-STAT-002
y
z
A
S Q
f a
O
x b
T
MTE-SOM-002 P
z x
e c
y
d MTE-STAT-003
300 mm
P
200 mm 100 75 75
350 mm
F 325
B
200 mm
120° 120°
z x
400 mm 250 mm
A 120°
MTE-STAT-004
C
MTE-STAT-005
CECC 483 MIDTERM EXAM - 1ST SEMESTER 2 0 2 2 ILLUSTRATIVE DRAWINGS
You might also like
- House Plan PDFDocument10 pagesHouse Plan PDFLois Vincent94% (17)
- ABSTRACT Estimate of A Residential HOUSE BuildingDocument7 pagesABSTRACT Estimate of A Residential HOUSE BuildingMidhun Jyothis83% (12)
- Design and analysis of laterally supported steel beamsDocument9 pagesDesign and analysis of laterally supported steel beamsCristan RetuermaNo ratings yet
- Flexural Analysis of BeamsDocument50 pagesFlexural Analysis of BeamsIsmail FarajpourNo ratings yet
- Q3Document4 pagesQ3Ritsu Tainaka0% (1)
- CE19A Transportation Engineering Trip AnalysisDocument3 pagesCE19A Transportation Engineering Trip AnalysisFuaad Abdirizak ElmiNo ratings yet
- AISC - Engineering FAQsDocument3 pagesAISC - Engineering FAQsAshish SadaNo ratings yet
- Structural Engineering & ConstructionDocument13 pagesStructural Engineering & ConstructionREX AMPONGANNo ratings yet
- Gis Located Above B)Document10 pagesGis Located Above B)Apple AterradoNo ratings yet
- FoundationDocument43 pagesFoundationNel PaganaNo ratings yet
- Ce0061 Professional Course 4 - (Specialized 2) Ste Track: Prestressed Concrete DesignDocument40 pagesCe0061 Professional Course 4 - (Specialized 2) Ste Track: Prestressed Concrete DesignjerichoNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Exam - Mste (Solve Again)Document3 pagesComprehensive Exam - Mste (Solve Again)Ag OribianaNo ratings yet
- CE Practice ProblemsDocument5 pagesCE Practice ProblemsLyra GurimbaoNo ratings yet
- 112Document10 pages112Memo LyNo ratings yet
- 2-CE 305 MOD 2 Singly RCFDocument10 pages2-CE 305 MOD 2 Singly RCFLester Khiets RoaNo ratings yet
- FA NO. 7 (Problem Set)Document2 pagesFA NO. 7 (Problem Set)Peter Adrian Ngo100% (1)
- RCD AssignmentDocument3 pagesRCD AssignmentArj AsisNo ratings yet
- Falcon RCD ColumnsDocument4 pagesFalcon RCD ColumnsJerome Adduru100% (1)
- Philgeps 2022Document3 pagesPhilgeps 2022Edwin BuitaNo ratings yet
- Prismoidal Formula 2Document11 pagesPrismoidal Formula 2anggaxkusumaNo ratings yet
- Sas 1 - 7Document50 pagesSas 1 - 7jaira.masuangatNo ratings yet
- Pi Diagnostic Test 094Document13 pagesPi Diagnostic Test 094Marc Louiese Lagatao100% (1)
- CIVIL ENGINEERING BOARD EXAMDocument7 pagesCIVIL ENGINEERING BOARD EXAMConan EdogawaNo ratings yet
- F.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review Center: 2 Floor, Cartimar Building, C.M. Recto Avenue, Quiapo, ManilaDocument2 pagesF.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review Center: 2 Floor, Cartimar Building, C.M. Recto Avenue, Quiapo, ManilaBluezed14No ratings yet
- CE Reference: Working Stress Analysis For Concrete BeamsDocument5 pagesCE Reference: Working Stress Analysis For Concrete BeamsYamil Camilo Bastidas ArciniegasNo ratings yet
- Module 2 TranspoDocument95 pagesModule 2 TranspomarcusluismacusiNo ratings yet
- Mste 1Document4 pagesMste 1Mingjaw MingmingNo ratings yet
- Item 1018Document5 pagesItem 1018Ester MarianNo ratings yet
- Nov 2021 CoachingDocument71 pagesNov 2021 CoachingKenny CaluzaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Concrete With Coconut Husk and Dried Banana Leaffibers As Aggregate ReplacementintroductionrationaleDocument3 pagesProperties of Concrete With Coconut Husk and Dried Banana Leaffibers As Aggregate Replacementintroductionrationalejohn philip s garciaNo ratings yet
- Soil Lec SoilCompositionDocument4 pagesSoil Lec SoilCompositionMikaela LorescaNo ratings yet
- Plate No.6 - Autor, Joy LauriaDocument12 pagesPlate No.6 - Autor, Joy LauriaJoy lauriaNo ratings yet
- Prc-I Lec 7 - 18th March 014 - Flexural Analysis of BeamsDocument51 pagesPrc-I Lec 7 - 18th March 014 - Flexural Analysis of BeamsDavidm AndosNo ratings yet
- Trip Generation Section 8.4Document1 pageTrip Generation Section 8.4Eng-Mohammed TwiqatNo ratings yet
- PERMEABILITYDocument26 pagesPERMEABILITYChristian Felix MapilesNo ratings yet
- Solved A Permeable Soil Layer Is Underlain by An Impervious La...Document1 pageSolved A Permeable Soil Layer Is Underlain by An Impervious La...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Gillmore Needle ApparatusDocument14 pagesGillmore Needle ApparatusDRAWINGNo ratings yet
- Bridge 3Document7 pagesBridge 3binanceNo ratings yet
- Item 803Document8 pagesItem 803Ester MarianNo ratings yet
- Spherical Trigonometry Activity ProblemsDocument1 pageSpherical Trigonometry Activity ProblemsEurydiceNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Singly Reinforced Rectangular Beam DesignDocument12 pagesAnalysis of Singly Reinforced Rectangular Beam DesignhasanainNo ratings yet
- Plate 1Document2 pagesPlate 1Dawnald Fortin PepitoNo ratings yet
- Short Bond Paper Landscape: Score Statics-Rb RubricDocument6 pagesShort Bond Paper Landscape: Score Statics-Rb RubricxVlad LedesmaNo ratings yet
- HAU Structural Loads LessonDocument14 pagesHAU Structural Loads Lessoncutie4everrNo ratings yet
- Commercial Building Doors and Windows FloorplanDocument1 pageCommercial Building Doors and Windows FloorplanAilanKhenDasallaNo ratings yet
- Eccentric Welded ConnectionsDocument35 pagesEccentric Welded ConnectionsDavid ReyesNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument12 pagesHydraulicsMugiwara Sparrow0% (1)
- T Beams 1Document27 pagesT Beams 1Jonniel De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Short Column ProblemsDocument2 pagesShort Column ProblemsJenny TubaranNo ratings yet
- 3331 ST7008 Prestressed Concrete QBDocument11 pages3331 ST7008 Prestressed Concrete QBsundar100% (1)
- Chapter 3b - Analysis of Tension MembersDocument56 pagesChapter 3b - Analysis of Tension MembersRami DemachkiNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Engineering QuizDocument29 pagesEarthquake Engineering Quizshivanandarcot0% (1)
- A. Read The Following Book Chapters and Other Readings For ReferenceDocument4 pagesA. Read The Following Book Chapters and Other Readings For ReferenceJomar LampitokNo ratings yet
- BrasdaDocument3 pagesBrasdaJayson Brylle MojaresNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete - Shear StrengthDocument7 pagesReinforced Concrete - Shear StrengthDenice CastroNo ratings yet
- Subject 1 Algebra Trigonometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Analytic Geometry Probability PhysicsDocument49 pagesSubject 1 Algebra Trigonometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Analytic Geometry Probability PhysicsDani LubosNo ratings yet
- Module 3 and 5 PDFDocument55 pagesModule 3 and 5 PDFSaptadip SahaNo ratings yet
- Wala LangDocument3 pagesWala LangEthyl Jean Monday GallarteNo ratings yet
- Irregular Section of Beams Reinforced For TensionDocument26 pagesIrregular Section of Beams Reinforced For TensionMadelyn Escaner MorilloNo ratings yet
- Vertical Stresses in Soil Mass - Part 1Document14 pagesVertical Stresses in Soil Mass - Part 1AbbyNo ratings yet
- Refresher (Surveying and Transportation Engineering)Document5 pagesRefresher (Surveying and Transportation Engineering)Ejay EmpleoNo ratings yet
- VOL1Document3 pagesVOL1Ho BiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Achievement Exam ReviewDocument12 pagesEngineering Achievement Exam ReviewJade Paul D. BesanaNo ratings yet
- ACI 341-C Retrofit Presentation - Part 1Document65 pagesACI 341-C Retrofit Presentation - Part 1raffikbashaNo ratings yet
- EFFICIENT BASEMENT EXCAVATIONDocument27 pagesEFFICIENT BASEMENT EXCAVATION04BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- Highway Bridge StructuresDocument52 pagesHighway Bridge StructuresJaireNo ratings yet
- How Much Cement, Sand and Water Is Required For 12mm Thick Plastering - HapphoDocument7 pagesHow Much Cement, Sand and Water Is Required For 12mm Thick Plastering - HapphoJatinder BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Concrete Pouring During The RainDocument3 pagesConcrete Pouring During The RainEvello MercanoNo ratings yet
- High range water reducer for mass concreteDocument2 pagesHigh range water reducer for mass concreteAnonymous AO4q022cUxNo ratings yet
- Duo PDFDocument72 pagesDuo PDFAnubhav MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Materials Schedule for 1x3 Classroom Block ConstructionDocument5 pagesMaterials Schedule for 1x3 Classroom Block ConstructionEng Hinji Rudge100% (4)
- STRUCTURES INFLUENCE LINESDocument5 pagesSTRUCTURES INFLUENCE LINESChristian Paul RamosNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Interlocking Brick Structure Technical RequirementsDocument17 pagesReinforced Interlocking Brick Structure Technical RequirementserjuniorsanjipNo ratings yet
- 2.2. What Are The Types of Excavation Needed For This Foundation? Construction? Describe The Associated Temporary Works For The Construction of FoundationDocument14 pages2.2. What Are The Types of Excavation Needed For This Foundation? Construction? Describe The Associated Temporary Works For The Construction of FoundationMohamed ShibleyNo ratings yet
- ECS448 - Topic 5 (Deformation - Virtual Work For Frame & Truss)Document33 pagesECS448 - Topic 5 (Deformation - Virtual Work For Frame & Truss)darwishshahrir__No ratings yet
- Essentials of Eurocode 3 PDFDocument61 pagesEssentials of Eurocode 3 PDFSRARNo ratings yet
- Item No. Description Unit Derived/ Output (Unit/Mandays) (Unit/Hours) I. EarthworksDocument9 pagesItem No. Description Unit Derived/ Output (Unit/Mandays) (Unit/Hours) I. EarthworksBethune Mari Vino-MendozaNo ratings yet
- What Is Monolithic Concrete Construction - Is It Durable Like RCC - QuoraDocument1 pageWhat Is Monolithic Concrete Construction - Is It Durable Like RCC - QuoraATSEDENo ratings yet
- Tower Crane FDN On Permanent Raft Check For StabilityDocument5 pagesTower Crane FDN On Permanent Raft Check For Stabilityvenkatram PadalaNo ratings yet
- About Wind Load Calculation (As Per BNBC 2006) : Gable Frame InstructionDocument2 pagesAbout Wind Load Calculation (As Per BNBC 2006) : Gable Frame InstructionAdam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- ACI Concrete Design Mix ProcedureDocument4 pagesACI Concrete Design Mix ProcedureLan CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Check Existing Pump Skid Foundation Concrete SkidDocument4 pagesCheck Existing Pump Skid Foundation Concrete SkidJohn BuntalesNo ratings yet
- Buildind Model Estimate With All Data Excel With All Links SSR2017-18 (MPP Building)Document16 pagesBuildind Model Estimate With All Data Excel With All Links SSR2017-18 (MPP Building)Srinivas PNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Laterally Loaded Piles Using Finite ElementDocument14 pagesAnalysis of Laterally Loaded Piles Using Finite ElementravirainbowNo ratings yet
- Raigad DSR 1415Document256 pagesRaigad DSR 1415viralisursNo ratings yet
- First Class Brick Properties & Manufacturing ProcessDocument10 pagesFirst Class Brick Properties & Manufacturing ProcessSAURABH KUMAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Structure Supported On Elastic FoundationDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Structure Supported On Elastic Foundationtaosye100% (1)
- TSS 24.07.2018-9 PDFDocument1 pageTSS 24.07.2018-9 PDFAnubhav Hem Kumar JainNo ratings yet
- RetainingWall SBC 150Document35 pagesRetainingWall SBC 150Elvis GrayNo ratings yet
- Estimates Table ConstructionDocument3 pagesEstimates Table ConstructionReneNo ratings yet