Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Combatting Corrosion in Hydrocracker Units
Uploaded by
Jeffrey Ryan Lindmark0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesCombatting Corrosion in Hydrocracker Units
Uploaded by
Jeffrey Ryan LindmarkCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Network S
Home My Network Jobs Messaging Notifications Me For Business Try Premiu
Combatting Corrosion
in Hydrocracker Units:
An Overview of
Damage Mechanisms
and Metallurgy
Selection
Orion Swanson
Corrosion and Materials Discipline Engineer | 39 articles Follow
Individual Contributor | Oil & Gas | Chemica…
January 17, 2023
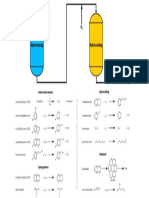
Corrosion is a major concern in hydrocracker units, as it can
lead to equipment failure and downtime. There are several
mechanisms of corrosion that can occur in these units,
including:
1. High Temperature Corrosion: Hydrocracker units
operate at high temperatures, which can cause
corrosion of the equipment. High temperature
corrosion can be caused by the presence of sulfur,
chlorine, and other impurities in the feedstock.
2. Hydrogen Attack: Hydrogen can react with the steel
equipment in the hydrocracker unit, causing hydrogen
embrittlement and cracking. This type of corrosion is
often caused by the presence of hydrogen sulfide
(H2S) and other sulfur compounds in the feedstock.
3. Stress Corrosion Cracking: This type of corrosion
occurs when the equipment is subject to both tensile
stress and a corrosive environment. It is often caused
by the presence of chloride ions in the feedstock.
To defend against these damage mechanisms, various
metallurgy selection options are available such as :
1. Stainless steels: Stainless steels are known for their
corrosion resistance and are often used in
hydrocracker units. Type 316L stainless steel is a
popular choice due to its resistance to high
temperature corrosion and hydrogen attack.
2. Nickel-based alloys: Nickel-based alloys such as
Inconel 625 and Incoloy 800 are also commonly used
in hydrocracker units due to their excellent resistance
to high temperature corrosion and hydrogen attack.
3. Duplex Stainless Steel: Duplex stainless steel, such as
2205 and 2507, provide a good combination of
corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. They
are often used in situations where chloride-induced
stress corrosion cracking is a concern.
4. Clad materials: Cladding is a method of providing
corrosion resistance to the surface of carbon steel. This
method allows for the use of a corrosion-resistant alloy
as a cladding on the surface of the carbon steel.
In conclusion, corrosion is a significant concern in
hydrocracker units, and various mechanisms of corrosion
can occur. To defend against these damage mechanisms,
various metallurgy selection options such as stainless steel,
nickel-based alloys, duplex stainless steel and clad materials
are available, each with its own set of advantages and
disadvantages. The selection of the appropriate metallurgy
will depend on the specific conditions and requirements of
the hydrocracker unit.
Report this
You might also like
- Chapter 5 - CORROSION AND NON-FERROUS METALDocument60 pagesChapter 5 - CORROSION AND NON-FERROUS METALتاج نيسها33% (3)
- Case Presentation On Management of Depressive Disorders-1Document40 pagesCase Presentation On Management of Depressive Disorders-1Fatima MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Presentation On CorrosionDocument7 pagesPresentation On CorrosionBemgbaNo ratings yet
- B737 AutothrottleDocument103 pagesB737 AutothrottleZaw100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Metallic Corrosion 0849382432Document750 pagesFundamentals of Metallic Corrosion 0849382432Carlos de la TorreNo ratings yet
- Saes TABLEDocument13 pagesSaes TABLERiyaz BasheerNo ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument64 pagesCorrosionOmar Ezzat100% (1)
- Corrosion Assessment in Reinforced Concrete StructuresDocument32 pagesCorrosion Assessment in Reinforced Concrete Structuresdineshkumar rNo ratings yet
- Qatar OM PART C PDFDocument796 pagesQatar OM PART C PDFBobi Guau100% (3)
- Cathodic Protection: Industrial Solutions for Protecting Against CorrosionFrom EverandCathodic Protection: Industrial Solutions for Protecting Against CorrosionNo ratings yet
- SAP Group Reporting 1909Document28 pagesSAP Group Reporting 1909SUDIPTADATTARAY86% (7)
- Cathodic Corrosion Protection Systems: A Guide for Oil and Gas IndustriesFrom EverandCathodic Corrosion Protection Systems: A Guide for Oil and Gas IndustriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Unit 2 CorrosionDocument37 pagesUnit 2 CorrosionRohan PolNo ratings yet
- Kadry - EJSR2 Corrosion Analysis of Stainless SteelDocument10 pagesKadry - EJSR2 Corrosion Analysis of Stainless SteelPrateep UntimanonNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Testing of Welded Ss FabricationsDocument12 pagesHydrostatic Testing of Welded Ss FabricationsKarin Soldatelli Borsato100% (1)
- Oil and Gas Corrosion Prevention: From Surface Facilities to RefineriesFrom EverandOil and Gas Corrosion Prevention: From Surface Facilities to RefineriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Stress Corrosion Cracking PDFDocument48 pagesStress Corrosion Cracking PDFPako RosasNo ratings yet
- Language - Introduction To The Integrated Language Arts CompetenciesDocument7 pagesLanguage - Introduction To The Integrated Language Arts CompetenciesHari Ng Sablay100% (1)
- What Is CorrosionDocument4 pagesWhat Is CorrosionOsransyah Os100% (1)
- PCS#176, Low-Capital Crude Unit Revamp Increases Product YieldDocument4 pagesPCS#176, Low-Capital Crude Unit Revamp Increases Product YieldJeffrey Ryan LindmarkNo ratings yet
- Selection of MaterialDocument16 pagesSelection of MaterialRiyaNo ratings yet
- Smarter Materials Selection For Corrosion Control PDFDocument12 pagesSmarter Materials Selection For Corrosion Control PDFAsyraf Nordin100% (1)
- Cornelia - Mima Maxey (1933) PDFDocument97 pagesCornelia - Mima Maxey (1933) PDFrodrigo estrasulasNo ratings yet
- Corrosion, Prevention and ControlDocument60 pagesCorrosion, Prevention and ControlCherry Obias100% (1)
- Electrocorrosion and Protection of Metals: General Approach with Particular Consideration to Electrochemical PlantsFrom EverandElectrocorrosion and Protection of Metals: General Approach with Particular Consideration to Electrochemical PlantsNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Protection Underground PipelinesDocument34 pagesCorrosion Protection Underground PipelinesLuis Bohr Ruda Valencia100% (2)
- Corrosion Engineering and Cathodic Protection Handbook: With Extensive Question and Answer SectionFrom EverandCorrosion Engineering and Cathodic Protection Handbook: With Extensive Question and Answer SectionNo ratings yet
- Heat Radiation From FlaresDocument90 pagesHeat Radiation From FlaresAman Goel100% (3)
- Hakeem Babatunde PHD Research ProposalDocument7 pagesHakeem Babatunde PHD Research ProposalNwachukwu Obi100% (2)
- Corrosion and Degradation of MaterialsDocument22 pagesCorrosion and Degradation of MaterialsSiddharth Patel100% (1)
- Cooling Tower Efficiency Calculations PDFDocument4 pagesCooling Tower Efficiency Calculations PDFhbithoNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower Efficiency Calculations PDFDocument4 pagesCooling Tower Efficiency Calculations PDFhbithoNo ratings yet
- Keeping Down The Cost of Revamp InvestmentDocument6 pagesKeeping Down The Cost of Revamp InvestmentdanimmhNo ratings yet
- Engineering Corrosion OH-7: University of Hafr Al BatinDocument27 pagesEngineering Corrosion OH-7: University of Hafr Al BatinHussain Al-DawoodNo ratings yet
- Corrosion and Its Types: Engineering Material AssignmentDocument6 pagesCorrosion and Its Types: Engineering Material AssignmentHasieb Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Failure of Stainless Steel Tubes in Transit Storage at Power PlantsDocument6 pagesCase Study of Failure of Stainless Steel Tubes in Transit Storage at Power PlantsNaima SadiqNo ratings yet
- Chloride Induced Stress Corrosion Cracking (CISCC) in PipelinesDocument6 pagesChloride Induced Stress Corrosion Cracking (CISCC) in PipelinesMohamed AtefNo ratings yet
- Material of ConstructionDocument43 pagesMaterial of ConstructionMohammed.abudi1996No ratings yet
- Material of ConstructionDocument43 pagesMaterial of ConstructionMohammed.abudi1996No ratings yet
- Final Presentation - Corrected (1) .PPTX RaviDocument15 pagesFinal Presentation - Corrected (1) .PPTX RavisudamNo ratings yet
- HeliCoil Technical Information Corrosion Screw ThreadsDocument6 pagesHeliCoil Technical Information Corrosion Screw ThreadsAce Industrial SuppliesNo ratings yet
- Stanley Engineering TB68-1 Corrosion MethodsDocument8 pagesStanley Engineering TB68-1 Corrosion MethodskpNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Analysis of Stainless Steel: Seifedine KadryDocument9 pagesCorrosion Analysis of Stainless Steel: Seifedine KadryMarcos GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Metal Corrosion and Its Prevention: Material ScienceDocument49 pagesMetal Corrosion and Its Prevention: Material Sciencedr nfNo ratings yet
- 9 - Introduction To Corrosion-1Document43 pages9 - Introduction To Corrosion-1Ridzaldi AldiNo ratings yet
- Materials Selection For Corrosive EnvironmentDocument8 pagesMaterials Selection For Corrosive EnvironmentShakeela AhmadNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemical Engineering: Prepared byDocument9 pagesDepartment of Chemical Engineering: Prepared byحسين ميثم سعيد مهديNo ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument33 pagesCorrosionSherina Mae GonzalesNo ratings yet
- "Why Are My Stainless Steel Filters Getting Pin-Hole Leaks?Document2 pages"Why Are My Stainless Steel Filters Getting Pin-Hole Leaks?Tahseen ShNo ratings yet
- Corrosion PresentationDocument51 pagesCorrosion PresentationJawad AslamNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Hydrogen Embrittlement of High Strength Alloy Steel Using Surface Coating TechniquesDocument14 pagesPrevention of Hydrogen Embrittlement of High Strength Alloy Steel Using Surface Coating TechniquesTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Hydrogen Embrittlement of High Strength Alloy Steel Using Surface Coating TechniquesDocument14 pagesPrevention of Hydrogen Embrittlement of High Strength Alloy Steel Using Surface Coating TechniquesTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Basic'sDocument58 pagesCorrosion Basic'sMayang Centya FebriaryNo ratings yet
- Corrosion and Its Prevention in Petroleum IndustriesDocument32 pagesCorrosion and Its Prevention in Petroleum Industriesz_sheerazNo ratings yet
- Stress-Corrosion Cracking (SCC) : TheoryDocument4 pagesStress-Corrosion Cracking (SCC) : Theorykitt poungNo ratings yet
- Materials Today: ProceedingsDocument6 pagesMaterials Today: ProceedingsSREEJITH S NAIRNo ratings yet
- 1.economics of Corrosion.Document36 pages1.economics of Corrosion.Takudzwa MbengoNo ratings yet
- Equinox International LTD - Stainless Steel - ST ST Corrosion Resistance - 106 PDFDocument2 pagesEquinox International LTD - Stainless Steel - ST ST Corrosion Resistance - 106 PDFeugenio.gutenbertNo ratings yet
- CORROSIONDocument19 pagesCORROSIONTH Rongon100% (1)
- Unit 2 Corrosion - 2019Document31 pagesUnit 2 Corrosion - 2019Abhay hNo ratings yet
- تقرير تأكل (Anodic Protection)Document10 pagesتقرير تأكل (Anodic Protection)ياسر نوفل ورد100% (1)
- Corrosion and Its Prevention CHANGDDocument24 pagesCorrosion and Its Prevention CHANGDRahul YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Materials and Fabrication SelectionDocument11 pagesChapter Five Materials and Fabrication SelectionKom MieNo ratings yet
- ENG6Document3 pagesENG6Jayri FelNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - 2Document8 pagesUnit 3 - 2Pratik KikaniNo ratings yet
- 53 - CSE - VAIBHAV RAKESH SINGHcorrosion ChemistryDocument16 pages53 - CSE - VAIBHAV RAKESH SINGHcorrosion Chemistry53 CS&E Vaibhav Rakesh SinghNo ratings yet
- A Seminar On Cathodic Protection TechniquesDocument9 pagesA Seminar On Cathodic Protection TechniquesDevashish JoshiNo ratings yet
- What Is Stainless SteelDocument3 pagesWhat Is Stainless SteelmadzieuuuuNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Embrittlement: Causes, Effects & Prevention: Sidheshwar Kumar 107MM024Document24 pagesHydrogen Embrittlement: Causes, Effects & Prevention: Sidheshwar Kumar 107MM024Jogi Oscar SinagaNo ratings yet
- Using Hydrogen in Fuel To Eliminate CO2 Emissions in Fired HeatersDocument5 pagesUsing Hydrogen in Fuel To Eliminate CO2 Emissions in Fired HeatersJeffrey Ryan LindmarkNo ratings yet
- Train To City Level 4: With Walking TimesDocument1 pageTrain To City Level 4: With Walking TimesJeffrey Ryan LindmarkNo ratings yet
- Hetero-Atom Removal HydrocrackingDocument1 pageHetero-Atom Removal HydrocrackingJeffrey Ryan LindmarkNo ratings yet
- Alternative Refrigerants Manny A PresentationDocument29 pagesAlternative Refrigerants Manny A PresentationEmmanuel Zr Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Inspection and Test Plan (ITP) For Spherical Storage Tanks: Dehloran Olefin PlantDocument9 pagesInspection and Test Plan (ITP) For Spherical Storage Tanks: Dehloran Olefin PlantbahmanNo ratings yet
- ESET TechnologyDocument21 pagesESET TechnologyValentin SalcianuNo ratings yet
- Henry's Bench: Keyes Ky-040 Arduino Rotary Encoder User ManualDocument4 pagesHenry's Bench: Keyes Ky-040 Arduino Rotary Encoder User ManualIsrael ZavalaNo ratings yet
- Prakhar Gupta Epics and Empires-Game of Thrones Make Up EssayDocument5 pagesPrakhar Gupta Epics and Empires-Game of Thrones Make Up EssayGat DanNo ratings yet
- Chords, Arcs, and Central and Inscribed AngleDocument14 pagesChords, Arcs, and Central and Inscribed AngleAlice KrodeNo ratings yet
- 2006 317Document13 pages2006 317LonginoNo ratings yet
- Water Cement RatioDocument5 pagesWater Cement RatioCastro FarfansNo ratings yet
- DSP UPG CU EngDocument1 pageDSP UPG CU EngArtur KwiatkowskiNo ratings yet
- Portal 2 PresDocument15 pagesPortal 2 Presapi-666608332No ratings yet
- Juan LunaDocument2 pagesJuan LunaClint Dave OacanNo ratings yet
- Output D4Document34 pagesOutput D4Angel MingaNo ratings yet
- Review Problems Chapter 6Document8 pagesReview Problems Chapter 6Yue FeiNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme According To AIDocument2 pagesMarking Scheme According To AIAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Physics 715 HW 1Document13 pagesPhysics 715 HW 1Antonildo PereiraNo ratings yet
- How To Draw The Platform Business Model Map-David RogersDocument5 pagesHow To Draw The Platform Business Model Map-David RogersworkneshNo ratings yet
- ADCD LowDocument8 pagesADCD LowrahulmultivisionNo ratings yet
- Dassault Systems Academic CalenderDocument5 pagesDassault Systems Academic CalenderSarath KumarNo ratings yet
- Teacher Thought For InterviewDocument37 pagesTeacher Thought For InterviewMahaprasad JenaNo ratings yet
- IIRDocument2 pagesIIRJagan FaithNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Dm3220-Servicemanual PDFDocument62 pagesDokumen - Tips Dm3220-Servicemanual PDFwalidsayed1No ratings yet
- Affidavit of Insurance ClaimsDocument2 pagesAffidavit of Insurance Claimsشزغتحزع ىطشفم لشجخبهNo ratings yet
- Sociology Internal AssessmentDocument21 pagesSociology Internal AssessmentjavoughnNo ratings yet