Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Additional Mathematics (Formulas)
Uploaded by
Yousuf MemonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Additional Mathematics (Formulas)
Uploaded by
Yousuf MemonCopyright:
Available Formats
Additional Mathematics
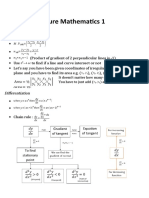
Formula that are within the syllabus and which need to be learnt.
The remainder theorem
Given the polynomial f(x), then remainder when f(x) is divided by (x – a) is f(a).
The factor theorem
If the remainder when f(x) is divided by (x – a) is 0, then (x – a) is a factor of f(x) and x = a is a root
of the equation f(x) = 0
Solution of quadratic equations
By formula and completing the square
For the quadratic equation ax 2 + bx + c = 0
−b ± b 2 − 4ac
x=
2a
Binomial expansion
Know how to derive terms in the expansions of (1 + x)n and (a + b)n where n is a positive integer.
n n!
The coefficients may be expressed in the form Cr = ÷ =
n
r r !(n − r )!
n n n
Be aware that Cr = ÷ = Cn − r =
n
÷
r n−r
Coordinate Geometry
Straight line
Know the forms of the straight line, including
y = mx + c
y − y1 = m( x − x1 )
y − y1 x − x1
=
y2 − y1 x2 − x1
Condition for parallel lines: m1 = m2
Condition for perpendicular lines: m1 × m2 = −1
( x1 − x2 ) + ( y1 − y2 )
2 2
Distance between two points ( x1 , y1 ), ( x2 , y2 ) =
x + x y + y2
Midpoint of two points ( x1 , y1 ), ( x2 , y2 ) = 1 2 , 1 ÷
2 2
The Circle
( x − a) + ( y − b ) = r 2 has centre (a, b) and radius r.
2 2
© MEI Additional Mathematics Formula sheet. Draft 1 Page 1
Trigonometry
In a right-angled triangle:
opposite adjacent opposite
sin θ = , cos θ = , tan θ =
hypotenuse hypotenuse adjacent
Identities:
sinθ
tanθ =
cosθ
sin θ + cos 2 θ = 1
2
Sin rule:
a b c
= =
SinA SinB SinC
Cos rule:
a 2 = b 2 + c 2 − 2bc cos A
b2 + c2 − a 2
cos A =
2bc
Calculus
dy
y = ax n ⇒ = nax n −1
dx
dy
Stationary points occur when =0
dx
b
Area under curve between x = a and x = b is ∫ y dx
a
Kinematics
Constant acceleration formulae
1
s = ut + at 2
2
s=
( u + v) t
2
v = u + at
v 2 = u 2 + 2as
© MEI Additional Mathematics Formula sheet. Draft 1 Page 2
You might also like
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Additional Mathematics: Formula That Are Within The Syllabus and Which Need To Be LearntDocument2 pagesAdditional Mathematics: Formula That Are Within The Syllabus and Which Need To Be LearntJames SimNo ratings yet
- FMSQ Revision NotesDocument5 pagesFMSQ Revision NotesJay AmbadkarNo ratings yet
- Edexcel - As Levels MathsDocument4 pagesEdexcel - As Levels MathsAhmad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Exs 6-1-60v1 SLHL Further DifferentiationDocument3 pagesExs 6-1-60v1 SLHL Further DifferentiationASYA HIZLINo ratings yet
- Act-Sat Formulas NotesDocument3 pagesAct-Sat Formulas Notesapi-372775136No ratings yet
- IGCSE Mathematics Formula SheetDocument7 pagesIGCSE Mathematics Formula Sheetburner bNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 1 - Mathematics For Physics PDFDocument50 pagesPhysics Chapter 1 - Mathematics For Physics PDFShweta JainNo ratings yet
- Add Math Formula SheetDocument3 pagesAdd Math Formula SheetjokuxkunNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE 2008 Paper 1 Solutions by FIITJEEDocument23 pagesIIT JEE 2008 Paper 1 Solutions by FIITJEEAbhinav100% (43)
- Add Maths Formulae List Form 4Document16 pagesAdd Maths Formulae List Form 4Hasbull97No ratings yet
- Calculus Test12 Sol 20191015Document7 pagesCalculus Test12 Sol 20191015Mạc Hải LongNo ratings yet
- FRM 2023Document4 pagesFRM 2023olemas1984No ratings yet
- Math Workshop by SlidesgoDocument35 pagesMath Workshop by SlidesgoAyesha Nayyer100% (1)
- Ib Math Applications and Interpretations Summer PacketDocument21 pagesIb Math Applications and Interpretations Summer Packetapi-327140356No ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry FormulasDocument11 pagesAnalytic Geometry FormulasZack D. SnutssNo ratings yet
- Formulae To KnowDocument4 pagesFormulae To KnowWINGWARSNo ratings yet
- Cal1 TD2 (2023 24)Document2 pagesCal1 TD2 (2023 24)Da VyNo ratings yet
- End of Stage 1/AS Mathematics:: Mathematics A (H230, H240) Paper 2: Pure Mathematics and MechanicsDocument21 pagesEnd of Stage 1/AS Mathematics:: Mathematics A (H230, H240) Paper 2: Pure Mathematics and MechanicsrebeccaNo ratings yet
- .Pre-Calculus 8416 02Document8 pages.Pre-Calculus 8416 02Yaman TahirNo ratings yet
- AMA1110 Tutorial - 2sDocument3 pagesAMA1110 Tutorial - 2sBrian LiNo ratings yet
- N Naf Yad: PrepaDocument7 pagesN Naf Yad: Prepanasru hajiNo ratings yet
- Formula BookDocument16 pagesFormula BookaNo ratings yet
- Middle School Mathematics: 1 Introduction of This ClassDocument9 pagesMiddle School Mathematics: 1 Introduction of This Class01. ZUENo ratings yet
- Math Tutorial SheetDocument3 pagesMath Tutorial SheetKondwani BandaNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics 1: It Doesn't Matter How Many Coordinates Are Given You Have To Just Add and Then Same ProcessDocument12 pagesPure Mathematics 1: It Doesn't Matter How Many Coordinates Are Given You Have To Just Add and Then Same ProcessAttique Rehman100% (1)
- Quadratic Functions in the Real WorldDocument6 pagesQuadratic Functions in the Real WorldCameron TomNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision in P1, P2, P3Document26 pagesQuick Revision in P1, P2, P3surendrakumar.adhikari2023No ratings yet
- Memory Aid 2Document2 pagesMemory Aid 2julsaujaNo ratings yet
- N Naf Yad: 1. Ratory SchoolDocument7 pagesN Naf Yad: 1. Ratory SchoolNasruNo ratings yet
- Integration of Rational FractionsDocument7 pagesIntegration of Rational FractionsCyrah maeNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Tutorial 2 (Week 3) : Lecturers: Daniel Daners and James ParkinsonDocument9 pagesSolutions To Tutorial 2 (Week 3) : Lecturers: Daniel Daners and James ParkinsonTOM DAVISNo ratings yet
- (M) Tangent & NormalDocument40 pages(M) Tangent & NormalSocial Credits Positive Million AspirantNo ratings yet
- Análise Matemática II Exame ResoluçãoDocument6 pagesAnálise Matemática II Exame ResoluçãoJorge Dinis ManhepeNo ratings yet
- Artar AC EY: N 2n 2n+1 N N 1Document2 pagesArtar AC EY: N 2n 2n+1 N N 1TrungNguyễnChíNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A Level Maths Formula SheetDocument3 pagesEdexcel A Level Maths Formula SheetSanveer GroverNo ratings yet
- D 5 Mathi Inf 2309 1h eDocument13 pagesD 5 Mathi Inf 2309 1h emavelNo ratings yet
- Maths Exam Solution for Finance and EconomicsDocument11 pagesMaths Exam Solution for Finance and EconomicsjeanboncruNo ratings yet
- 2223 Fall MATH1012 Mid-Term Test SolutionsDocument3 pages2223 Fall MATH1012 Mid-Term Test Solutions策略王1No ratings yet
- Laplace EquationDocument3 pagesLaplace Equationapi-3839714No ratings yet
- Model Exam 2022 N.SDocument10 pagesModel Exam 2022 N.STesfamichael FufaNo ratings yet
- 3 MathematicsDocument12 pages3 MathematicsHugoSalidoNo ratings yet
- Fourier SeriesDocument12 pagesFourier SeriesChrysanthos KoutsoyiannisNo ratings yet
- Main 2021 SoltnDocument4 pagesMain 2021 SoltnEVIN S MANOJNo ratings yet
- 7B Areas Under Curves PDFDocument35 pages7B Areas Under Curves PDFvikranth chittimallaNo ratings yet
- 5 Separation of VariablesDocument10 pages5 Separation of VariablesFrancis Marc AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 2 - Differential Equations 2020Document41 pagesLecture Notes 2 - Differential Equations 2020Alucard FighterNo ratings yet
- Finding Tangents and Normals at Points on CurvesDocument8 pagesFinding Tangents and Normals at Points on CurvesHin Wa LeungNo ratings yet
- LIST OF FORMULAEDocument4 pagesLIST OF FORMULAEMohamed TahmeedNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivative in Mathematics (JEE-AdvancedDocument58 pagesApplication of Derivative in Mathematics (JEE-Advancedparita adhiaNo ratings yet
- Graphing Rational FunctionsDocument7 pagesGraphing Rational FunctionsKANG ZHEN YU, IAN (TJC)No ratings yet
- Solving ODEs and finding Fourier series for spring-mass systemsDocument8 pagesSolving ODEs and finding Fourier series for spring-mass systemsNALUGOODHA MUSANo ratings yet
- Equations of Order One: Differential Equations Module 2ADocument5 pagesEquations of Order One: Differential Equations Module 2AJuvilee RicoNo ratings yet
- Lec 8Document3 pagesLec 8Gourab HazraNo ratings yet
- Cartesian CoordinatesDocument3 pagesCartesian CoordinatesmahitumikoiNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee 2005 Maths Sol Screening)Document5 pagesIit Jee 2005 Maths Sol Screening)premsempireNo ratings yet
- PrelimExam SolutionDocument3 pagesPrelimExam SolutionNeil MonteroNo ratings yet
- Test1 FR KEYDocument11 pagesTest1 FR KEYUnitedSlayerNo ratings yet
- Grammar PracticeDocument20 pagesGrammar PracticeYousuf MemonNo ratings yet
- Election As KhalifaDocument5 pagesElection As KhalifaYousuf MemonNo ratings yet
- Vector Worksheet 1Document6 pagesVector Worksheet 1Yousuf MemonNo ratings yet
- Paper 6 NotesDocument28 pagesPaper 6 NotesDewan Anisha IslamNo ratings yet
- 3fourwaystolinksentences 201224 151311Document6 pages3fourwaystolinksentences 201224 151311Yousuf MemonNo ratings yet
- Monster Visual Discrimination CardsDocument9 pagesMonster Visual Discrimination CardsLanaNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide To E-Commerce TechnologyDocument420 pagesComplete Guide To E-Commerce Technologypilatus100% (4)
- British Isles Composition GuideDocument4 pagesBritish Isles Composition GuidesonmatanalizNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Lily ExamDocument3 pagesGrade 8 Lily ExamApril DingalNo ratings yet
- 20ME901 Automobile Engineering Unit 3Document74 pages20ME901 Automobile Engineering Unit 36044 sriramNo ratings yet
- Biamp Vocia Catalog Apr2020Document24 pagesBiamp Vocia Catalog Apr2020Mahavir Shantilal DhokaNo ratings yet
- PropensityModels PDFDocument4 pagesPropensityModels PDFSarbarup BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Steel Structures: Updates of Eurocode 8Document107 pagesSeismic Design of Steel Structures: Updates of Eurocode 8antonio111aNo ratings yet
- Pure and Applied Analysis Problems Solved Step-by-StepDocument8 pagesPure and Applied Analysis Problems Solved Step-by-Stepalpha2122No ratings yet
- CHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF WATER SAMPLEDocument5 pagesCHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF WATER SAMPLEAiron Fuentes EresNo ratings yet
- More Than Moore: by M. Mitchell WaldropDocument4 pagesMore Than Moore: by M. Mitchell WaldropJuanjo ThepresisNo ratings yet
- Barcelona Smart City TourDocument44 pagesBarcelona Smart City TourPepe JeansNo ratings yet
- Pebc CompilationDocument14 pagesPebc CompilationAarti AroraNo ratings yet
- Basic LCI To High LCIDocument3 pagesBasic LCI To High LCIIonut VladNo ratings yet
- Internal Resistance and Matching in Voltage SourceDocument8 pagesInternal Resistance and Matching in Voltage SourceAsif Rasheed Rajput100% (1)
- S06 - 1 THC560 DD311Document128 pagesS06 - 1 THC560 DD311Canchari Pariona Jhon AngelNo ratings yet
- Environmental Threats Differentiated Reading Comprehension Ver 1Document20 pagesEnvironmental Threats Differentiated Reading Comprehension Ver 1Camila DiasNo ratings yet
- Integrating Therapeutic Play Into Nursing and Allied Health PracticeDocument214 pagesIntegrating Therapeutic Play Into Nursing and Allied Health PracticeIbrahim SabraNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security 2017Document8 pagesCyber Security 2017Anonymous i1ClcyNo ratings yet
- MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDSDocument39 pagesMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDSAbdul Musavir100% (1)
- 3 - Content - Introduction To Java, JVM, JDK PDFDocument8 pages3 - Content - Introduction To Java, JVM, JDK PDFAnonymous zdY202lgZYNo ratings yet
- TNTCL Cost Data 2021 22Document95 pagesTNTCL Cost Data 2021 22Akd DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Marulaberry Kicad EbookDocument23 pagesMarulaberry Kicad EbookPhan HaNo ratings yet
- True False Survey FinalDocument2 pagesTrue False Survey Finalwayan_agustianaNo ratings yet
- $R6RN116Document20 pages$R6RN116chinmay gulhaneNo ratings yet
- Service Parts List: 54-26-0005 2551-20 M12™ FUEL™ SURGE™ 1/4" Hex Hydraulic Driver K42ADocument2 pagesService Parts List: 54-26-0005 2551-20 M12™ FUEL™ SURGE™ 1/4" Hex Hydraulic Driver K42AAmjad AlQasrawi100% (1)
- Organizational Behaviour Group Assignment-2Document4 pagesOrganizational Behaviour Group Assignment-2Prateek KurupNo ratings yet
- GRP Product CatalogueDocument57 pagesGRP Product CatalogueMulyana alcNo ratings yet
- Sia Mock+Test 1 Csat Updated CompressedDocument216 pagesSia Mock+Test 1 Csat Updated Compressedpooja bhatiNo ratings yet
- LNG Vaporizers Using Various Refrigerants As Intermediate FluidDocument15 pagesLNG Vaporizers Using Various Refrigerants As Intermediate FluidFrandhoni UtomoNo ratings yet