Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Recombinant DNA Technology
Recombinant DNA Technology
Uploaded by
Lora BellOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Recombinant DNA Technology
Recombinant DNA Technology
Uploaded by
Lora BellCopyright:
Available Formats
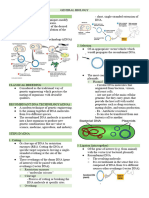
Recombinant DNA Technology Recombinant DNA
Cloning – purify and propagate a piece of DNA 1. Cut the DNA (cut both plasmid and the
source of DNA
Application: if you want to study the gene use the
gene elsewhere *enzymes that could cut the DNA (DNAes)
*DNAes
-exonuclease – way of correcting the
reference by changing
-endonuclease
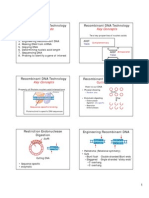
*Restriction endonuclease/ restriction
enzymes
*plasmids (extra chromosomal) *Palindromes (enzyme restriction)
-replicates independently 2. Mix plasmids & DNA and ligates
-some harbor genes that confer antibiotic
resistance
DNA Ligate
3. Transformation – culture cell
*you are trying to get the recombinant DNA
*can be done through heat shock
4. Screening
*put in a petri dish
RESULT:
*in the petri dish, choose which has
recombinant DNA
*SCREENING TECHNIQUES
a) Antibiotic Screening
b) Functional Compensation
• Auxotrophs – mutant (i.e
Arg auxotrophs – does not
produce Arginine)
(organisms fail to produce
essential nutrients)
• Prototrophs – able to
produce an essential
nutrients
c) Functional Complementation]
*control gene expression (turning
on/off gene)
*When do you want to turn on lac Z?
When lactose is present.
↓ 𝑔𝑙𝑢 ↑ 𝑙𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑠𝑒 – could remove
repressor by adding inducer
(allolactose)
→
𝑙𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑠𝑒 𝛽 − 𝑔𝑎𝑙𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑎𝑠𝑒 𝑔𝑙𝑢 + 𝑔𝑎𝑙
Blue-white screening
E-coli M15 string – has division in 11-41
(has la forming omega peptide)
Lac Z’ – plasmid lac Z’ codes α-peptide only
You might also like
- Learning Packet in Level 2 RLE - RED: College of Nursing School Year 2020-2021Document28 pagesLearning Packet in Level 2 RLE - RED: College of Nursing School Year 2020-2021Nur SetsuNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 RDT 1.02.2023 PDocument20 pagesLecture2 RDT 1.02.2023 Palka mehraNo ratings yet
- 11 Biotechnology-Principles N Processes - FOCUS AREA 2021Document3 pages11 Biotechnology-Principles N Processes - FOCUS AREA 2021Ujval j nairNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principle and Processes-NotesDocument4 pagesBiotechnology Principle and Processes-NotesRohan MohantyNo ratings yet
- DNA Technology/ Genetic EngineeringDocument15 pagesDNA Technology/ Genetic Engineeringapi-19783425No ratings yet
- 11 Biotechnology-Principles N Processes-Notes - ToDocument4 pages11 Biotechnology-Principles N Processes-Notes - ToArjun GowdaNo ratings yet
- 4 R DNADocument22 pages4 R DNArustyryan77No ratings yet
- 4 R DNADocument22 pages4 R DNASandesh PoudelNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Technology Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument18 pagesRecombinant DNA Technology Recombinant DNA Technologysupraja nandhuNo ratings yet
- 9 DNA-Technology PDFDocument18 pages9 DNA-Technology PDFNikki YadavNo ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument13 pagesBiotechnologyranvir madaviNo ratings yet
- BIOTECHNOLOGYDocument9 pagesBIOTECHNOLOGYtamalbio7No ratings yet
- Hsslive XII Botany CH 11 Minhad NewDocument4 pagesHsslive XII Botany CH 11 Minhad NewAKUULLLNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Notes-1Document6 pagesBiotechnology Notes-1Exporting WarriorNo ratings yet
- DNA Recombinant Bio Score-1Document17 pagesDNA Recombinant Bio Score-1jiunpyeducationNo ratings yet
- Bio2 Reviewer HuhuDocument15 pagesBio2 Reviewer HuhuPeachy JaemNo ratings yet
- Describe The Natural Function of Restriction Enzymes (RE)Document9 pagesDescribe The Natural Function of Restriction Enzymes (RE)Liling CassiopeiaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetic TechniquesDocument44 pagesMolecular Genetic TechniquesTaran LuthraNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology - Principles and ProcessesDocument4 pagesBiotechnology - Principles and ProcessesMohit Devraj ParasharNo ratings yet
- Biology Score: Chapter 8: Recombinant Dna TechnologyDocument13 pagesBiology Score: Chapter 8: Recombinant Dna TechnologyabbyNo ratings yet
- Recombinant Gene TechDocument7 pagesRecombinant Gene TechHannah LeianNo ratings yet
- Principles of BiotechnologyDocument4 pagesPrinciples of BiotechnologyGauri PalikondawarNo ratings yet
- MIC 210 Basic Molecular Biology: Dna CloningDocument46 pagesMIC 210 Basic Molecular Biology: Dna CloningDrAhmedSalimNo ratings yet
- Recombinant Dna TechniquesDocument15 pagesRecombinant Dna TechniquesFock StudentNo ratings yet
- 8 Compressed Notes Recombinant Technology SdsDocument7 pages8 Compressed Notes Recombinant Technology SdsSYAZWAN BIN MUSTAFA MoeNo ratings yet
- Aula BMol 2Document35 pagesAula BMol 2Diogo MadalenoNo ratings yet
- Restriction Enzyme DigestionDocument3 pagesRestriction Enzyme DigestionMahathir Mohmed100% (1)
- Gene Tech Essay PDFDocument4 pagesGene Tech Essay PDFdev_nakomNo ratings yet
- Techniques in Nucleic Acid AnalysisDocument15 pagesTechniques in Nucleic Acid AnalysisgaleNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 (Prelims)Document21 pagesGen Bio 2 (Prelims)mornin mizzyNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument54 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular BiologyQuintero MerylNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument18 pagesGeneral Biologybiancaeunicebarbaral8No ratings yet
- Contents:: Project Report 1. Introduction To Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument15 pagesContents:: Project Report 1. Introduction To Recombinant DNA TechnologyShivraj GundayyaNo ratings yet
- GENETICDocument15 pagesGENETICLyna VillasNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio-Q1Document5 pagesGen Bio-Q1hilaryblancelinsanganNo ratings yet
- Molecular Cloning: Dr. Robin Herlands Genetics, Biology 300, Nevada State CollegeDocument56 pagesMolecular Cloning: Dr. Robin Herlands Genetics, Biology 300, Nevada State CollegeSamir PatelNo ratings yet
- CHEM 291 - Lecture No. 43-45Document45 pagesCHEM 291 - Lecture No. 43-45faiyaznoorshaelNo ratings yet
- Recombinant Dna Technology & It's ApplicationDocument20 pagesRecombinant Dna Technology & It's Applicationiamcold866No ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering and Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument38 pagesGenetic Engineering and Recombinant DNA Technologyseada JemalNo ratings yet
- BME 203 - Lecture No. 18-19Document45 pagesBME 203 - Lecture No. 18-19SagorNo ratings yet
- Recombinant Dna Tech SaswatDocument8 pagesRecombinant Dna Tech SaswatSaswat Anurag RoutNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Steps: Dna ReplicationDocument2 pagesPreliminary Steps: Dna Replicationbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Manipul. of Gene Expression in ProkaryotesDocument34 pagesManipul. of Gene Expression in ProkaryotesLeviathan ValleyNo ratings yet
- Mollecular and Cellular Biology: Lecture - 2Document31 pagesMollecular and Cellular Biology: Lecture - 2sk3 khanNo ratings yet
- CAPE 1 Biology - Genetic EngineeringDocument80 pagesCAPE 1 Biology - Genetic EngineeringTamicka BonnickNo ratings yet
- 618 Restriction Enzymes and VectorsDocument25 pages618 Restriction Enzymes and Vectorsakshif KhanNo ratings yet
- Biology Module 1Document4 pagesBiology Module 1Danielle Raven GarciaNo ratings yet
- Biotech 9 Part 2Document3 pagesBiotech 9 Part 2semalmarezNo ratings yet
- 8.0 RECOMBINANT DNA JJDocument23 pages8.0 RECOMBINANT DNA JJROS EZRA HANNY A/P ROSLI MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document62 pagesChapter 5mlNo ratings yet
- Recombinant Dna TechnologyDocument4 pagesRecombinant Dna TechnologyrengachenNo ratings yet
- Inheritance and Regulation ReviewerDocument7 pagesInheritance and Regulation ReviewerAngelo LopezNo ratings yet
- Tools of Recombinant Dna TechnologyDocument3 pagesTools of Recombinant Dna Technologyamora eliNo ratings yet
- Engenharia GenéticaDocument34 pagesEngenharia GenéticaPatricia LopesNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Technology - OurvleDocument30 pagesRecombinant DNA Technology - Ourvledpkf6dj725No ratings yet
- Biotechnology - Principles and Processes - Notes - June 2023Document15 pagesBiotechnology - Principles and Processes - Notes - June 2023Tahsinul islamNo ratings yet
- II ME NRP B SS 27. Biotechnology-Principles and Processes, Biotechnology - ApplicationsDocument8 pagesII ME NRP B SS 27. Biotechnology-Principles and Processes, Biotechnology - ApplicationsAmit RavindhraNo ratings yet
- Unit 9Document12 pagesUnit 9Rohan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Dr. V. P. Wankhade: Vidyabharti College of Pharmacy, AmravatiDocument31 pagesDr. V. P. Wankhade: Vidyabharti College of Pharmacy, AmravatiNikita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Microbial Genetics-ModifiedfinalDocument18 pagesChapter 4 - Microbial Genetics-ModifiedfinalZiad BinFarsNo ratings yet
- Britanny Venus First Mass at Limasawa by Botong FranciscoDocument2 pagesBritanny Venus First Mass at Limasawa by Botong FranciscoNisa MierNo ratings yet
- PapermineDocument6 pagesPaperminerikitasingh2706No ratings yet
- 71 Bed Bug Information HLDocument1 page71 Bed Bug Information HLMatthew SelfNo ratings yet
- Geometry Section 1 1Document9 pagesGeometry Section 1 1api-262621710No ratings yet
- Transport in Plants WsDocument4 pagesTransport in Plants Wsfirstclass67% (3)
- Bomb Calorimeter ReportDocument18 pagesBomb Calorimeter ReportRami Chaoul0% (1)
- TEMS Investigation 12.0 Getting Started Manual PDFDocument85 pagesTEMS Investigation 12.0 Getting Started Manual PDFyilkorkNo ratings yet
- The Life Cycle of GalaxiesDocument10 pagesThe Life Cycle of GalaxiesJessica RodriguesNo ratings yet
- How To Save Power by Induction MotorDocument3 pagesHow To Save Power by Induction Motorshamim islamNo ratings yet
- Niagara - Wiring Non Optoisolated DevicesDocument1 pageNiagara - Wiring Non Optoisolated DevicesHugo Alberto Hernández ClementeNo ratings yet
- WeltyDocument24 pagesWeltyFelipeNo ratings yet
- Durabuilt Vs NLRCDocument1 pageDurabuilt Vs NLRChello_hoarder100% (1)
- Earth Atmosphere Model - Metric UnitsDocument2 pagesEarth Atmosphere Model - Metric UnitschrtromNo ratings yet
- SHOT Peening EquipmentsDocument9 pagesSHOT Peening EquipmentssomujazNo ratings yet
- Farm Structures in Tropicalo ClimatesDocument421 pagesFarm Structures in Tropicalo Climatesed327100% (2)
- National Wildlife Day by SlidesgoDocument48 pagesNational Wildlife Day by SlidesgoCAMILLA MAJOLENo ratings yet
- ĐỀ MINH HỌA SỐ 40Document12 pagesĐỀ MINH HỌA SỐ 40Châu NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Converting Powerpoint Presentations To Video With Camtasia StudioDocument11 pagesConverting Powerpoint Presentations To Video With Camtasia StudioMarvin RetutalNo ratings yet
- Final Paper For PublicationDocument14 pagesFinal Paper For PublicationAyush Dutt TripathiNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Visualizing Substrata Data With CIVIL 3DDocument21 pagesModeling and Visualizing Substrata Data With CIVIL 3Dg5680No ratings yet
- Desiccated Coconut Group 2Document7 pagesDesiccated Coconut Group 2Anne Dominique QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Nemo Arms 2019 Winter CatalogDocument36 pagesNemo Arms 2019 Winter CatalogJan MoszczukNo ratings yet
- PWD JE SyllabusDocument4 pagesPWD JE Syllabus323 Aditya DhepeNo ratings yet
- GUIDE BOOK ON EVERYTHING ABOUT PLANTAR FASCIITIS Get To Understand How Your Plantar Fasciitis Function and Prevent Unwanted... (CLETA ARUN M.D)Document46 pagesGUIDE BOOK ON EVERYTHING ABOUT PLANTAR FASCIITIS Get To Understand How Your Plantar Fasciitis Function and Prevent Unwanted... (CLETA ARUN M.D)joseNo ratings yet
- Tecnical Reference WECC Dynamic Composite LoadDocument12 pagesTecnical Reference WECC Dynamic Composite LoadAriel Quispe RojasNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Rephrasing 2012 Doc 20216Document23 pagesEjercicios Rephrasing 2012 Doc 20216valeriaflaviaNo ratings yet
- 9th English - Annual Exam 2020 - Model Question Paper - English Medium PDF DownloadDocument5 pages9th English - Annual Exam 2020 - Model Question Paper - English Medium PDF Downloadselavakumar selvaNo ratings yet
- Zeljana Unit 1 Exercises (B2+)Document12 pagesZeljana Unit 1 Exercises (B2+)Andrijana GjorgjevskaNo ratings yet
- Butterfly ValveDocument4 pagesButterfly ValveFlowBiz Exports Pvt. Ltd.No ratings yet