Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Physics 2
Uploaded by
John Ahron BalinoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
General Physics 2
Uploaded by
John Ahron BalinoCopyright:
Available Formats
General Physics 2
Electric Fields
● The fundamental entity in electrostatics is electric
charge.
● Charge cannot be created or destroyed. It can
only be transferred from one body to another by
friction or rubbing.
● There are two ways of charging an object. It can
be through direct contact, which is called
conduction. Another way of charging does not
need direct contact and we call it charging by
means of induction.
● There are two kinds of charges – positive and
Electric Field
negative. Like charges repel while unlike charges • Michael Faraday - “Every charged object
attract. generates an electric field that permeates space
● Materials that permit electric charge to move and exerts a force on all charged particles it
within them are called conductors while those encounters.”
that do not are called insulators. Most metals are • Each particle has a charge that may be either
good conductors while most nonmetals are good positive or negative, and we used Coulomb's
insulators. Law to determine how much force is created
● Coulomb’s law governs the interaction of charges. when two charged particles come into
The electrostatic force between charges q1 and contact with each other.
q2 is directly proportional to the magnitude of the • Now when we discuss two charges, what
product of the charges and inversely proportional happens if we're dealing with charged
to the square of the separation distance between objects of varying forms and sizes?
them. The direction of the force is always along • In physics, we deal with a wide variety of
the line connecting the charges. If the charges are forms and sizes and we use Coulomb's Law
both positive or both negative the force is
to determine the force between two tiny
repulsive; if the charges have opposite signs, the
things, such particles.
force is attractive. The force of interaction obeys
Newton’s third law of motion. • In order to power your house, your
computer, and the screen on which you’re
● The strength of the field at a particular point is
attending the class, electric forces are used.
directly proportional to the magnitude of the
Each pixel on this screen contains millions of
charge producing the field and inversely
proportional to square of the distance between electrons that are excited by your computer.
the field point and the location of the charge. The • Charged particles must be manipulated in
closer is the field point from the source charge, order for these ordinary electrical
the stronger is the field strength. occurrences to take place.
● As we learn more about electricity, we have to • However, how can we construct a device
talk about fields. Electric fields may seem that transmits precisely the proper quantity
complicated, but they're really fascinating and a of electric power?
crucial part of physics. Inquire about the concept • A few additional equations and notions will
of a field. (What is a field? e.g. What is meant by a help us comprehend how charged particles
gravitational field? How do we know that a can be controlled and how electricity can be
gravitational field exists in the room where we are expanded.
in?) A gravitational field is a kind of force. Is
• The total strength of an electric field may be
detected when masses are attracted to each
shown in a pictorial form. The electric field
other.
lines are a visual depiction of this
● Gravity is a force of attraction that exists between phenomenon. Lines of electric field have a
any two masses, any two bodies, any two definite set of characteristics, laws, and uses.
particles. Gravity is not just the attraction
By drawing a tangent across the center of an
between objects and the Earth. It is an attraction
electric field line, we can simply characterize
that exists between all objects, everywhere in
the universe. it as a curve indicating the direction of the
electric field.
• Michael Faraday was the first to suggest the Electric Fields is a VECTOR
idea of an electric field in the 19th century. • Positive charge going to form a force that
In Faraday's mind, electric field lines are a accelerated in the same direction as the
means of describing and interpreting the electric field.
unseen electric field. The electric field that • Negative charge going to form a force that
surrounds a system of charges may be more accelerated in the opposite direction as the
simply described using electric field lines electric field.
rather to the more sophisticated vector
diagrams that are often used.
E = F/q
● These vectors are called electric field lines and
their purpose is to show the magnitude and
direction of the force exerted on any nearby
positive test charge.
● Say we have one positively charged particle and
one negatively charged particle that are some
distance apart with an equal and opposite
magnitude of charge.
● This pair of particle is known as an electric
dipole.
● Objects with greater charge create stronger
● The total strength of an electric field may be electric fields. By surrounding a highly charged
shown in a pictorial form. The electric field lines object with more lines, one can communicate
are a visual depiction of this phenomenon. Lines the strength of an electric field in the space
of electric field have a definite set of surrounding a charged object by the line
characteristics, laws, and uses. By drawing a density. This convention is depicted in the
tangent across the center of an electric field diagram below.
line, we can simply characterize it as a curve
indicating the direction of the electric field. ● Not only does the density of lines surrounding
any given object reveal information about the
● Now, when we express it as an equation, the quantity of charge on the source charge, the
electric field created by a charged object is the density of lines at a specific location in space
electric force between the objects and the test reveals information about the strength of the
charge divided by the magnitude of that test field at that location.
charge.
● Since we have two particles that each generate
their own electric field, we can add the fields
together to create a total electric field.
● This is the principle known as superposition.
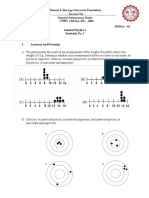
1. Check your understanding. Counter Clockwise
0, 90, 180, 270 degrees
270 degree
● Point A North (opposite) south
1. Sample Problem 2
A positive charge of +50𝜇𝐶 is placed in on electric field
of 50, 000 N/C directed upward. What mass should the
charge have to remain suspended in the air?
𝜮𝑭𝒚 = 𝑭𝑬 − 𝑾 = 𝟎
2. Check your understanding.
𝑭𝒚 = 𝑾
𝑬𝒒
𝑴=
𝒈
𝑁
50,000 𝐶 (50 × 10−6 𝐶)
𝑀=
9.8 𝑚
𝑠2
𝑀 = 0.26 𝑁 ∙ 𝑚/𝑠 2 or kg
1. Sample Problem 3
An electron is released from rest in a uniform electric
field and accelerates to the east of a rate of 4.0 ×
3. Example 1 106 𝑚/𝑠 2 . What is the magnitude.
• Point A North 𝒎𝒂
+ 𝑬=
• Point B West 𝒒
• Point C Southeast
106 𝑚
• Point D North East (9.11 × 10−31 𝑘𝑔)(4 × )
𝐸= 𝑠2
4. Example 2 1.6 × 10−19 𝐶
• Point A East (opposite) West 𝐸 = 2.27 × 10−5 𝑁/𝐶
• Point B North (opposite) South PROBLEMS
• Point C South East (opposite) North West
• Point D West (opposite) East 1. A small charge (q = 6 × 10−3C) is found in a uniform
Electric field (E = 2.9 N/C). Determine the force on the
charge.
F = qE
- 2. Find the electric field acting on a 2.0 C charge if an
electrostatic force of 10,500 N acts on the particle.
3. A force of 70 N is directed South on −5 × 10−6 C
point charge. What is the magnitude and direction of
the electric field at this point?
Sample Problem 1
4. A proton is released from rest in a uniform electric
A force of 100 N is directed north on -20𝜇C point field and accelerates to the north of a rate of 2.5 ×
charge. What is the magnitude and direction of the 103 𝑚/𝑠 2 . What is the manitude?
electric field at this point?
𝑭
E=𝒒
𝟏𝟎𝟎 𝑵
𝑬 = 𝟐𝟎×𝟏𝟎−𝟔𝑪
E = 𝟓 × 𝟏𝟎𝟔 N/C
You might also like
- Generalphysics2 230414042355 d328d383Document55 pagesGeneralphysics2 230414042355 d328d383Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- OCR A Physics A Level: Topic 6.2: Electric FieldsDocument8 pagesOCR A Physics A Level: Topic 6.2: Electric FieldsjmsonlNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument18 pagesElectricitySam LoveNo ratings yet
- GeneralPhysics2 Week 1Document9 pagesGeneralPhysics2 Week 1Altea EvaNo ratings yet
- AP10006 Physics II: ElectricityDocument38 pagesAP10006 Physics II: Electricity白卡持有人No ratings yet
- Electric Field and The Movement of ChargeDocument118 pagesElectric Field and The Movement of ChargeChan Tse WeiNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - ElectrostaticsDocument73 pagesModule 4 - ElectrostaticsIntilegienceNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 Chapter 1 Electric Forces and FieldsDocument4 pagesPhysics 1 Chapter 1 Electric Forces and FieldsNico San AgustinNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 PDFDocument23 pagesPhysics 2 PDFFranchezca ChavezNo ratings yet
- Physics Electrostatics Lecture SlideDocument67 pagesPhysics Electrostatics Lecture SlideJeffrey ChanNo ratings yet
- 1 ElectricityDocument30 pages1 ElectricitySajid AmanullahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document88 pagesLecture 1rafiqshariatpur1200No ratings yet
- Electic Charge, Electric Fields & ElectrostaticsDocument55 pagesElectic Charge, Electric Fields & Electrostaticscrizel in nameNo ratings yet
- Lesson#1 - Electric ChargesDocument14 pagesLesson#1 - Electric Chargesjerikbenito46No ratings yet
- +2 Physics Full Material E.MDocument90 pages+2 Physics Full Material E.MBalajiNo ratings yet
- Physics - Electric Field - Electrostatic ForceDocument3 pagesPhysics - Electric Field - Electrostatic ForceRichelleNo ratings yet
- Coulombs Law, Gauss Law, Electric PotentialDocument50 pagesCoulombs Law, Gauss Law, Electric Potentialbryan valle100% (1)
- Q3PT Genphy2 Rev PDFDocument17 pagesQ3PT Genphy2 Rev PDFCharlie jamesNo ratings yet
- Physics 1510Document41 pagesPhysics 1510Pramod RajanNo ratings yet
- Copy of 2 GEN.PHY 2 12-Q3-SLM-2-ELECTRIC FORCES AND FIELDS students copyDocument10 pagesCopy of 2 GEN.PHY 2 12-Q3-SLM-2-ELECTRIC FORCES AND FIELDS students copyjoshandersonbutoy08No ratings yet
- Electricity I 1Document9 pagesElectricity I 1Charles Daniel Torre MalolesNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Complete NotesDocument35 pagesElectrostatics Complete NotescßNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics PDFDocument51 pagesElectrostatics PDFDanish JunejaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term - General Physics 2Document8 pages2nd Term - General Physics 2Jerica NapayNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS PresentationDocument22 pagesPHYSICS PresentationlynkimjoanNo ratings yet
- Electric charges and fields explainedDocument55 pagesElectric charges and fields explainedHitesh Bhatia100% (2)
- CoulombsDocument47 pagesCoulombsTrishia LimpinNo ratings yet
- F2 MAR 01 Electric ChargeDocument25 pagesF2 MAR 01 Electric ChargeJack OlanternNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Stem ADocument29 pagesLesson 1 Stem AWen SeulNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument12 pagesScience ReviewerLance Christian PascuaNo ratings yet
- NEO JEE 11 P1 PHY H Electric Charges and Fields 09 211Document95 pagesNEO JEE 11 P1 PHY H Electric Charges and Fields 09 211annNo ratings yet
- How electric forces enable chemical reactions in our bodiesDocument1 pageHow electric forces enable chemical reactions in our bodiesMamamoisda BatungbakalNo ratings yet
- ENGT 103 Principlesof Electricalengineering (Autosaved)Document100 pagesENGT 103 Principlesof Electricalengineering (Autosaved)dockanye3No ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument18 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsYashwanthNo ratings yet
- Dhev Emt 1Document12 pagesDhev Emt 1CharavanaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocument7 pages3rd Quarter ReviewerJohn Dareen CabelloNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Electric FieldDocument15 pagesCh1 Electric FieldAkash tech. videoNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Notes For Iit Jee 33 PDF PDFDocument19 pagesElectrostatics Notes For Iit Jee 33 PDF PDFAryanNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Notes For Iit Jee 33 PDFDocument19 pagesElectrostatics Notes For Iit Jee 33 PDFDipayan DasNo ratings yet
- _Plus Two Physics Full Chapters-Seema TrDocument219 pages_Plus Two Physics Full Chapters-Seema Tranjimarv43No ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields ExplainedDocument6 pagesElectric Charges and Fields ExplainedNiranjan RajaNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields ExplainedDocument35 pagesElectric Charges, Forces, and Fields ExplainedKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Quantization of ChargeDocument28 pagesQuantization of ChargeKim Ashley Padernal MandronNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Electric FieldsDocument57 pages5.1 Electric FieldsSho baconNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3: Physics Reviewer G12Document8 pagesQuarter 3: Physics Reviewer G12AzefNo ratings yet
- Electrical Quantities ExplainedDocument16 pagesElectrical Quantities ExplainedHong ZiunNo ratings yet
- Aanhin Ko Ang Mahal Na Araw Kung Mahal Kita Araw ArawDocument7 pagesAanhin Ko Ang Mahal Na Araw Kung Mahal Kita Araw ArawJuan Carlos Viaje PimentelNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge and Electric FieldDocument76 pagesElectric Charge and Electric FieldGladys Lambayong100% (1)
- 5.1 Electric FieldsDocument42 pages5.1 Electric FieldsJiwoo SeoNo ratings yet
- leph101.pdf-WT_SummariesDocument6 pagesleph101.pdf-WT_SummariesArnnav MarwahNo ratings yet
- Electric FieldDocument12 pagesElectric FieldNilesh ku. BeheraNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument22 pagesElectricity and Magnetismkhrisannmiller12No ratings yet
- Electric Flux and Field RelationshipDocument3 pagesElectric Flux and Field RelationshipMarc Lawrence Tiglao INo ratings yet
- SEE 230 - Lecture 05Document43 pagesSEE 230 - Lecture 05Tran Thanh NamNo ratings yet
- 2.-GEN.PHY-2-12-Q3-SLM2-Electric-Forces-and-Electric-Field-LinesDocument31 pages2.-GEN.PHY-2-12-Q3-SLM2-Electric-Forces-and-Electric-Field-Linesjuleanorpilla513No ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Lecture noteADSADQWEDocument24 pagesExperiment 3 Lecture noteADSADQWEemreNo ratings yet
- Electric Field p1Document24 pagesElectric Field p1Sumaya Akter Ruhi 2022610642No ratings yet
- PHYSICS REVIEWER 3rd GradingDocument81 pagesPHYSICS REVIEWER 3rd GradingBeefWith PorkNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Physics Unit 1 Study Material TMDocument14 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Physics Unit 1 Study Material TMAakaash C.K.No ratings yet
- Seatwork 2Document2 pagesSeatwork 2John Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- Benchyell Final NaDocument3 pagesBenchyell Final NaJohn Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1Document3 pagesGeneral Physics 1John Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document1 pageActivity 2John Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- A - Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageA - Untitled DocumentJohn Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- PR 1Document72 pagesPR 1redgeNo ratings yet
- Seatwork 2Document2 pagesSeatwork 2John Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- III Worksheet 01 BalinoDocument3 pagesIII Worksheet 01 BalinoJohn Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- III Worksheet 01 BalinoDocument3 pagesIII Worksheet 01 BalinoJohn Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Philosophy of the Human PersonDocument2 pagesIntroduction to Philosophy of the Human PersonJohn Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- MOD 1 HOPE 3 1st QDocument11 pagesMOD 1 HOPE 3 1st QJohn Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- MOD 1 HOPE 3 1st QDocument8 pagesMOD 1 HOPE 3 1st QJohn Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- Homeroom Orientation Stem12a5Document51 pagesHomeroom Orientation Stem12a5John Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- Aut. Letter - Maternity FilingDocument1 pageAut. Letter - Maternity FilingJohn Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocument13 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society and PoliticsJohn Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document2 pagesTask 1John Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- Research Agenda Planning: Crafting a Clear FocusDocument34 pagesResearch Agenda Planning: Crafting a Clear FocusJohn Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 20140621 - 2 Physics - Konvertiert - SGDocument150 pagesModule 2 20140621 - 2 Physics - Konvertiert - SGAnandaMandalNo ratings yet
- 376 - Paragraph Completion Advanced Level Test Quiz Online Exercise With Answers 4Document8 pages376 - Paragraph Completion Advanced Level Test Quiz Online Exercise With Answers 42eemmee eeccoolleeNo ratings yet
- Is Space Created? Reflections On Akara's Philosophy and Philosophy of PhysicsDocument18 pagesIs Space Created? Reflections On Akara's Philosophy and Philosophy of PhysicsKaalaiyanNo ratings yet
- Free Fall Free Fall: When An Object Falls Under The Influence of Gravity Alone, It Is in A State of Free FallDocument10 pagesFree Fall Free Fall: When An Object Falls Under The Influence of Gravity Alone, It Is in A State of Free FallSynne Mae BorneaNo ratings yet
- Einsteins Unified Field Theory & Biefeld-Brown EffectDocument4 pagesEinsteins Unified Field Theory & Biefeld-Brown EffectzorrinNo ratings yet
- 100 Years of Math Milestones 9781470436520 PDFDocument597 pages100 Years of Math Milestones 9781470436520 PDFtito100% (2)
- Ebook College Physics Strategic Approach 2Nd Edition Knight Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument56 pagesEbook College Physics Strategic Approach 2Nd Edition Knight Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFStevenMillersqpe100% (9)
- Gravitational Problems WorksheetDocument2 pagesGravitational Problems WorksheetSachin SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Hinton - A New Era of ThoughtDocument276 pagesHinton - A New Era of ThoughtCelephaïs Press / Unspeakable Press (Leng)100% (16)
- Difference Between Theory and LawDocument17 pagesDifference Between Theory and Lawmira01No ratings yet
- Teaching Date & TimeDocument4 pagesTeaching Date & TimeNenia Claire Mondarte CruzNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion - FinalDocument33 pagesForce and Motion - FinalMarites FernandezNo ratings yet
- Relativity An Introduction To Special and General RelativityDocument418 pagesRelativity An Introduction To Special and General RelativitySoham Pal100% (18)
- Books by Taylor and FrancisDocument37 pagesBooks by Taylor and FrancisanilgouriNo ratings yet
- LoadDocument38 pagesLoadTrisit Tan100% (2)
- Mathematical Geography by Willis E JohnsonDocument344 pagesMathematical Geography by Willis E JohnsonvalmarnNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 ST Sem Study AnsDocument14 pagesPhysics 1 ST Sem Study AnsJoyce ChoiNo ratings yet
- Inference To The Best ExplanationDocument11 pagesInference To The Best ExplanationJona ThanNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument49 pagesPPTyunimulia100% (1)
- Week 2 - Day 4 I. Objectives: V Xkmhs4Qlj - S Tsyo4Z0EDocument8 pagesWeek 2 - Day 4 I. Objectives: V Xkmhs4Qlj - S Tsyo4Z0EBRIGIDA V.ADOPTANTENo ratings yet
- Year 10 FORCES - PPTDocument15 pagesYear 10 FORCES - PPTsharon_t_kempNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectsDocument14 pagesPhysics Projectsrairaicute67% (3)
- Coulombs Law 5Document7 pagesCoulombs Law 5Christopher VũNo ratings yet
- The Einstein Hoax (1997) ReticDocument110 pagesThe Einstein Hoax (1997) ReticEugene MalloveNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0098300402000742 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0098300402000742 MainTiagoNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Physics TermsDocument33 pagesGlossary of Physics TermsDjoanna Joy Carandang100% (1)
- Speed of Light - WikipediaDocument25 pagesSpeed of Light - WikipediamexcesNo ratings yet
- CH 1 HW SolutionsDocument26 pagesCH 1 HW Solutionsmoo86% (7)
- Vehicle: Kevin Kha Dennis PapeshDocument33 pagesVehicle: Kevin Kha Dennis PapeshJason ChenNo ratings yet
- Wipro Selection ProcedureDocument77 pagesWipro Selection ProcedureVasudhendra BadamiNo ratings yet