Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kami Export - Appc - 1.1 - Packet
Uploaded by
eenamorataOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kami Export - Appc - 1.1 - Packet
Uploaded by
eenamorataCopyright:
Available Formats
AP Precalc 1.1 Change in Tandem 1.
1 Notes
Write your questions
and thoughts here!
Function
A function is a mathematical relation that maps a set of _____ values to a set of
______ values such that each input value is mapped to exactly ___ output value.
Input values = Domain = I ndependent variable (𝒙)
Output values = Range =D ependent variable (𝒚)
Often, it is useful to use other variables that help us recognize the
representation. For example, if we throw a football and measure the
height, we could use variables where 𝒉 is the height of the football
and 𝒕 is the number of seconds since the football was thrown.
Function notation helps us immediately identify which variables are the input and which are the output.
For the football example, we would use…
𝒉(𝒕)
1. 𝑤(𝑥) is a function where 𝑤 is the amount of water in a pool measured in gallons, and 𝑥 is the length
of the pool.
a. What does the independent variable represent? The length of the pool.
b. What does the dependent variable represent? The amount of water in the pool.
These two variables will vary in tandem according to the function rule that is established. That rule can
be expressed Verbally, Analytically, Numerically, or Graphically…VANG . Throughout this course,
you will use all four of these types of expressions to represent a function.
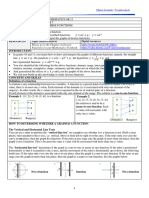
Increasing function if…
Verbally: …as the input values increase, the output values always increase.
Analytically: …for all 𝑎 and 𝑏 in the interval, if 𝒂 < 𝒃, then 𝒇(𝒂) < 𝒇(𝒃).
Graphically:
© The Algebros from FlippedMath.com
Write your questions
and thoughts here!
Decreasing function if…
Verbally: …as the input values increase, the output values always decrease.
Analytically: …for all 𝑎 and 𝑏 in the interval, if 𝒂 < 𝒃, then 𝒇(𝒂) > 𝒇(𝒃).
Graphically:
2. Example of numerically: Let the function 𝑓 be increasing or decreasing, but not both. State whether
the function is increasing or decreasing on the interval and justify.
𝑥 4 6 7 10 20
𝑓(𝑥) 1 1.01 1.04 1.06 1.29
Basic elements of a function’s graph 𝑓(𝑥)y
• Zero
The graph intersects the 𝑥-axis (independent) when the __________
value is zero. We call the INPUT values _____________________.
• 𝑦-intercept
The graph intersects the 𝑦-axis (dependent) when the ________ x
value is zero. We call the output value the _______________.
• Concavity.
Concave UP
Concave DOWN
Straight lines don’t have concavity.
Point of inflection (point where the concavity changes)
Use the graph of 𝑓 below to answer the following questions. 𝑓(𝑥)y
a. When is the graph concave up?
b. When is the graph concave down? 𝑔 ℎ 𝑖 𝑗 𝑘 𝑙 𝑚
x
c. Find the zero(s) of the function.
d. Find the 𝑦-intercept(s) of the function.
𝑓 (0) = 𝑎
e. When is the graph increasing?
f. When is the graph decreasing?
© The Algebros from FlippedMath.com
1.1 Change in Tandem
AP Precalculus
1.1 Practice
For each function, identify what the dependent and independent variables represent.
1. 𝑏(𝑠) is a function where 𝑏 is the 2. 𝑝(𝑡) is a function where 𝑡 is the 3. 𝑐(𝑡) is a function where 𝑐 is the
number of books in the library number of years since number of cups of coffee
and 𝑠 is the number of students in kindergarten and 𝑝 is the number consumed and 𝑡 is the number of
the school. of Pokemon cards. teachers at the school.
Dep: Dep: Dep:
Indep: Indep: Indep:
4. area of a circle 5.
volume of a box
radius of a circle
side length of a box
Dep: Dep:
Indep: Indep:
Let the function 𝒇 be increasing or decreasing, but not both. State whether the function is increasing or
decreasing on the given interval and justify your answer.
6. 7. 𝑓(𝑥)y
𝑥 1 2 3 4 5
𝑓(𝑥) 95 90 75 50 10
2
9 x
© The Algebros from FlippedMath.com
8. 9. 𝑓(𝑥)y
𝑥 12 16 18 25 31
𝑓(𝑥) 8 7.99 7.8 7.75 7.7
6
x
1
10. 11. 𝑓(𝑥)y
𝑥 101 201 301 401 501
𝑓(𝑥) 10 11 12 13 14
x
5 12
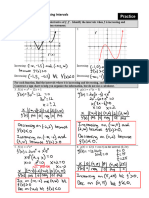
Use the graph of 𝒇 to answer the question below.
12. 𝑓(𝑥)y 13. 𝑓(𝑥)y
𝑓 (0) = 𝑒 𝑓 (0) = 𝑑
𝑎 𝑏 𝑐
x
x
𝑎 𝑏 𝑐 𝑑
a. On what interval(s) is the graph concave up?
a. On what interval(s) is the graph concave up?
b. On what interval(s) is the graph concave down?
b. On what interval(s) is the graph concave down?
c. On what interval(s) is the graph increasing?
c. On what interval(s) is the graph increasing?
d. On what interval(s) is the graph decreasing?
d. On what interval(s) is the graph decreasing?
e. Find the zeros of the function.
e. Find the zeros of the function.
f. Find the 𝑦-intercept of the function.
f. Find the 𝑦-intercept of the function.
© The Algebros from FlippedMath.com
14. 𝑓(𝑥)y 15. 𝑓(𝑥)y
𝑎 𝑏 𝑐 𝑔 ℎ 𝑖 𝑗 𝑚 𝑛𝑜
x
0 𝑑 𝑒 𝑘 𝑙
x
𝑓 (0) = 𝑝
a. On what interval(s) is the graph concave up?
a. On what interval(s) is the graph concave up?
b. On what interval(s) is the graph concave down?
b. On what interval(s) is the graph concave down?
c. On what interval(s) is the graph increasing?
c. On what interval(s) is the graph increasing?
d. On what interval(s) is the graph decreasing?
d. On what interval(s) is the graph decreasing?
e. Find the zeros of the function.
e. Find the zeros of the function.
f. Find the 𝑦-intercept of the function.
f. Find the 𝑦-intercept of the function.
1.1 Change in Tandem 1.1 Test Prep
Multiple Choice
16. Let the function 𝑓 be defined as a function that is always decreasing. The table shows values for the function 𝑓 at
selected values of 𝑥. Which of the following represents all possible values for 𝑎 ?
(A) −5 < 𝑎 < 7 𝒙 𝒇(𝒙)
(B) −2 < 𝑎 < 0 −5 12
(C) 0 < 𝑎 < 3 −2 4
(D) −2 < 𝑎 < 4 0 𝑎
3 −2
(E) −15 < 𝑎 < 12
7 −15
© The Algebros from FlippedMath.com
For questions 17-18 use the graph of 𝒇.
graph of 𝒇
17. The figure shows the graph of a function 𝑓 . Let a, b, c, d, and e represent the x-coordinates at those points. Of the
following, which is a point of inflection?
(A) point a
(B) point b
(C) point c
(D) point d
(E) point e
18. The figure shows the graph of a function 𝑓 . Let a, b, c, d, and e represent the x-coordinates at those points. Of the
following, on which interval is 𝑓 decreasing and the graph of 𝑓 concave down?
(A) The interval from a to b.
(B) The interval from b to c.
(C) The interval from c to d.
(D) The interval from d to e.
(E) None of the above.
© The Algebros from FlippedMath.com
You might also like
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- PC CH5 2inverse Invest Part 2 2020Document4 pagesPC CH5 2inverse Invest Part 2 2020T. B.No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Exponential FunctionsDocument29 pagesLesson 4 - Exponential FunctionsFregie LerionNo ratings yet
- Inverse Test ReviewDocument2 pagesInverse Test ReviewLandrie PolkNo ratings yet
- Appc Unit 1a ReviewDocument5 pagesAppc Unit 1a ReviewhdhdhebeNo ratings yet
- General MathematicsDocument6 pagesGeneral MathematicsFelipe AlfonsóNo ratings yet
- QA Basic Calculus Quarter 3 Week 6 FinalDocument7 pagesQA Basic Calculus Quarter 3 Week 6 Finalelyzaventura8No ratings yet
- Reciprocal Functions: Lesson 6Document4 pagesReciprocal Functions: Lesson 6luluhbelle cruzNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Polynomial CurvesDocument6 pagesModule 6 - Polynomial CurvesJohn Michael CubarNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 10: Intercepts, Zeroes and Asymptotes of Rational FunctionsDocument15 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 10: Intercepts, Zeroes and Asymptotes of Rational FunctionsAshley Kait Marcelo100% (1)
- Continuous CalculusDocument22 pagesContinuous Calculusmn Kim100% (1)
- Inverse FunctionsDocument6 pagesInverse FunctionsNareema HendricksNo ratings yet
- MAT Lecture2Document47 pagesMAT Lecture2Deniz Egemen YılmazNo ratings yet
- Fundamental differentiation formulasDocument5 pagesFundamental differentiation formulasPrincess Shyne PeñaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 ContinuityDocument8 pagesChapter 7 ContinuitySong KimNo ratings yet
- DERIVATIVEDocument8 pagesDERIVATIVENoel S. De Juan Jr.No ratings yet
- Calc 5.3 SolutionsDocument3 pagesCalc 5.3 Solutionsphiphers1No ratings yet
- PAK 6A - Exponential and Logarithm Graphs1Document19 pagesPAK 6A - Exponential and Logarithm Graphs1Mahek MotlaniNo ratings yet
- Cal 11 Q3 0402 Final PDFDocument20 pagesCal 11 Q3 0402 Final PDFKat DumpNo ratings yet
- LAB#2 Implementation of Constants, Variables and ExpressionsDocument6 pagesLAB#2 Implementation of Constants, Variables and ExpressionskhawarNo ratings yet
- Inverse FunctionsDocument11 pagesInverse Functionsdanaismaill42No ratings yet
- General Mathematics 11 Notes 1ST SemDocument25 pagesGeneral Mathematics 11 Notes 1ST SemPhilippine Expeditionary Force to RonogradNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Differential CalculusDocument26 pagesIntroduction to Differential CalculusKimberly DNo ratings yet
- Lecture#3Document3 pagesLecture#3Qaisar ShahNo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument24 pagesCalculusLorraine SabbaghNo ratings yet
- Cal 11 Q3 0403 Final PDFDocument25 pagesCal 11 Q3 0403 Final PDFKat DumpNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 Week 4 Module 11Document12 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 Week 4 Module 11MaeNo ratings yet
- Gen. Math Chapter 1 4 OtherDocument2 pagesGen. Math Chapter 1 4 OtherMary Beth Ed MartelNo ratings yet
- 11 Analysis & Approaches SL Unit 6 - Applications of Differentiation 6.1 Increasing & Decreasing Functions (Ch. 5.4a)Document16 pages11 Analysis & Approaches SL Unit 6 - Applications of Differentiation 6.1 Increasing & Decreasing Functions (Ch. 5.4a)Ryan KantonoNo ratings yet
- Diff. Calc. Module 1 Functions - Limits.ContinuityDocument17 pagesDiff. Calc. Module 1 Functions - Limits.ContinuityWild RiftNo ratings yet
- Module BasicCal Quarter 3 Week 3Document24 pagesModule BasicCal Quarter 3 Week 3ezrajoice17No ratings yet
- WEEK 8.3 Intercepts, Zeroes, and Asymptotes of Logarithmic FunctionsDocument11 pagesWEEK 8.3 Intercepts, Zeroes, and Asymptotes of Logarithmic FunctionsOreo ProductionsNo ratings yet
- Lec1 2 3math PDocument31 pagesLec1 2 3math Pyalaaeldin622No ratings yet
- Functions and InversesDocument32 pagesFunctions and InversesWooNo ratings yet
- SLG 7.1.1 Functions That Have Inverses 1Document8 pagesSLG 7.1.1 Functions That Have Inverses 1Faye AbianNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Functions, Limits & Continuity, DerivativesDocument14 pagesModule 1 - Functions, Limits & Continuity, DerivativesSteve RogersNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 Week 4 Module 11Document12 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 Week 4 Module 11CristinaO'Shopping Reyes DG80% (5)
- Chapter 2 NotesDocument22 pagesChapter 2 Notesrachel4uclaNo ratings yet
- Calc 2.1 Ca1Document1 pageCalc 2.1 Ca1Nino TedoradzeNo ratings yet
- Notes 2.1 Day 3 Graphs of Functions and Their DerivativesDocument2 pagesNotes 2.1 Day 3 Graphs of Functions and Their DerivativesAlexandra BragaNo ratings yet
- Summary (Preliminaries)Document16 pagesSummary (Preliminaries)Beyzanur BektaşNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Week 6Document55 pagesGen Math Week 6Kevin De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Ariysha SHAHEEN - Inverse FunctionsDocument8 pagesAriysha SHAHEEN - Inverse FunctionsAriysha SHAHEENNo ratings yet
- 1 A 2 AfcDocument8 pages1 A 2 AfcYazan ZamelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - The DerivativeDocument8 pagesChapter 3 - The DerivativeERJEAN SILVERIONo ratings yet
- Module Six Lesson Four Notes Guided NotesDocument31 pagesModule Six Lesson Four Notes Guided NotesJazmyn DavisNo ratings yet
- Inverse, Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDocument8 pagesInverse, Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsRobert John Basia BernalNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Sulaimani Polytechnic University/ Technical College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument28 pagesChapter One: Sulaimani Polytechnic University/ Technical College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DepartmentAll TutorialNo ratings yet
- Backward Forward PropogationDocument19 pagesBackward Forward PropogationConrad WaluddeNo ratings yet
- BC q4wk1 2dlp Done Qa RodelDocument16 pagesBC q4wk1 2dlp Done Qa RodelMaynard CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NotesDocument17 pagesChapter 2 Notessesirekha@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- 2-2 NotesDocument3 pages2-2 Notesapi-375455087No ratings yet
- EXPONENTIAL FunctionsDocument2 pagesEXPONENTIAL FunctionsbenedictaguinaldeNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus Ab Review BookletDocument15 pagesAP Calculus Ab Review BookletTristan BeliganNo ratings yet
- math project activities 1Document6 pagesmath project activities 1api-696786602No ratings yet
- Business Maths-Differential CalculusDocument18 pagesBusiness Maths-Differential Calculusपशुपति नाथNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Four Ways To Represent A Function EMDocument28 pages1.1 Four Ways To Represent A Function EMNomhleNo ratings yet
- 16351509-024 - Presentation - MATH-101 - Sec B - Spring 2021Document11 pages16351509-024 - Presentation - MATH-101 - Sec B - Spring 2021Ch M Sami JuttNo ratings yet
- DETERMINING INVERSE FUNCTIONSDocument47 pagesDETERMINING INVERSE FUNCTIONSNorman JadumasNo ratings yet
- Even Odd FunctionsDocument5 pagesEven Odd FunctionsTamar Y.No ratings yet
- Unit: FORCES Law of Universal Gravitation: Variables WorkDocument4 pagesUnit: FORCES Law of Universal Gravitation: Variables WorkeenamorataNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument16 pagesMagnetismeenamorataNo ratings yet
- 18 The Gas LawsDocument34 pages18 The Gas LawseenamorataNo ratings yet
- 18 Electrical QuantitiesDocument35 pages18 Electrical QuantitieseenamorataNo ratings yet
- 19 Expansion SLGDocument1 page19 Expansion SLGeenamorataNo ratings yet
- 17 MoleculesDocument16 pages17 MoleculeseenamorataNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument63 pagesForceseenamorataNo ratings yet
- RC Phase Shift Oscillator Using Transistor (BJT) - Circuit & Working - Circuits GalleryDocument3 pagesRC Phase Shift Oscillator Using Transistor (BJT) - Circuit & Working - Circuits GalleryMarkNo ratings yet
- Administration Manual For Urbackup Server 2.4.X: Martin Raiber November 12, 2019Document36 pagesAdministration Manual For Urbackup Server 2.4.X: Martin Raiber November 12, 2019alyson.balbinoNo ratings yet
- 03 CTAL TM Sample ISTQB Questions - v2.04Document35 pages03 CTAL TM Sample ISTQB Questions - v2.04CorniciucOanaNo ratings yet
- Scoping and Testing: Professor Jennifer Rexford COS 217Document34 pagesScoping and Testing: Professor Jennifer Rexford COS 217DaWheng VargasNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Business AnalyticsDocument6 pagesAssignment On Business AnalyticsPreet BhatiaNo ratings yet
- LTO Student Permit Fees P..Document3 pagesLTO Student Permit Fees P..allovidNo ratings yet
- FM 124-Paper ModellDocument8 pagesFM 124-Paper ModellManjula Gayan JayawardenaNo ratings yet
- Edimax Ew 7206apg Wireless Access PointDocument12 pagesEdimax Ew 7206apg Wireless Access PointLasith HashanthaNo ratings yet
- Curriculume Vitae - DinalDocument1 pageCurriculume Vitae - DinaldainelNo ratings yet
- Real-Time Kinematic and Differential GPS: PrintDocument13 pagesReal-Time Kinematic and Differential GPS: PrintBijay Krishna Das100% (1)
- 6 Must-Have Features For An Insurance Customer Self-Service PortalDocument8 pages6 Must-Have Features For An Insurance Customer Self-Service PortalJuan perezNo ratings yet
- Michael B. White - Mastering C - (C Sharp Programming) - A Step by Step Guide For The Beginner, Intermediate and Advanced User, Including Projects and Exercises (2019) - Libgen - LiDocument522 pagesMichael B. White - Mastering C - (C Sharp Programming) - A Step by Step Guide For The Beginner, Intermediate and Advanced User, Including Projects and Exercises (2019) - Libgen - LiMartha Mattena100% (1)
- Selenium WebDriver NotesDocument12 pagesSelenium WebDriver Notesvvenkat123No ratings yet
- Fuzzy Project FinalDocument32 pagesFuzzy Project FinalAhmed RazaNo ratings yet
- E Studio Datasheet - 2040c 2540c 3040c 3540c 4540c Series PDFDocument2 pagesE Studio Datasheet - 2040c 2540c 3040c 3540c 4540c Series PDFAyman HammodehNo ratings yet
- EDI IDoc Failures Causes and ResolutionsDocument37 pagesEDI IDoc Failures Causes and Resolutionsmarisha100% (1)
- LCM and HCFDocument25 pagesLCM and HCFManoj Swags7No ratings yet
- MyVF Invoice 04 June 2023Document4 pagesMyVF Invoice 04 June 2023Karl Kenneth FloresNo ratings yet
- Organization of The IBM Personal Computer: Chapter-3Document41 pagesOrganization of The IBM Personal Computer: Chapter-3plabon kumar sahaNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Bundala, N.HDocument58 pagesPrepared by Bundala, N.HKanika RelanNo ratings yet
- ATM ProjectDocument36 pagesATM Projectv68whrmhwbNo ratings yet
- M25P80Document53 pagesM25P80api-3736976No ratings yet
- Yaskawa Yrc 1000 - Instruction ManualDocument580 pagesYaskawa Yrc 1000 - Instruction Manualkumar ujjwalNo ratings yet
- Nikon NR-5500 Auto-Refractometer Repair Parts ListDocument47 pagesNikon NR-5500 Auto-Refractometer Repair Parts ListARIF NAQSHBANDINo ratings yet
- Bar Chart & Kurva-SDocument25 pagesBar Chart & Kurva-SAnisah PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Hspice Sa PDFDocument1,156 pagesHspice Sa PDFnsrkntNo ratings yet
- ACDC and audio files metadataDocument531 pagesACDC and audio files metadataMarckie Roldan TajoNo ratings yet
- IJCRT22A6562Document8 pagesIJCRT22A6562sruthisrivenkateswaran SIESGSTNo ratings yet
- Oracle Apps Technical Materialdoc PDF FreeDocument336 pagesOracle Apps Technical Materialdoc PDF Freeherculean2010No ratings yet
- Shakespeare LanguageDocument15 pagesShakespeare LanguageMátyás HollóNo ratings yet