Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Type of Cells
Uploaded by
Jean pierre rivasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Type of Cells
Uploaded by
Jean pierre rivasCopyright:
Available Formats
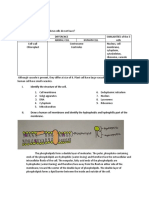
The Cell
The basic membrane-bound unit that contains the
fundamental molecules of life and of which all
living things are composed. A single cell is often a
complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium
or yeast. Other cells acquire specialized functions
as they mature.
Types of
Organelles: (eukaryotic) cell
Organelles:
1. Plasma membrane
2. Nucleus 1. Cell wall
3. Nucleolus 2. Plasma membrane
4. Ribosomes 3. Nucleus
5. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) 4. Nucleolus
6. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SRE) 5. Ribosomes
7. Golgi apparatus 6. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
8. Mitochondria 7. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
9. Lysosomes Animal Cell Plant Cell 8. Golgi apparatus
10. Centrosome and centrioles 9. Mitochondria
11. Cytoskeleton 10. Plastids (chloroplasts, leukoplasts, chromoplasts,
chromoplasts)
11. Central vacuole
12. Cytoskeleton
13. Centrosome and centrioles
An animal cell is a type of eukaryotic A plant cell is the type of eukaryotic cell
cell that lacks a cell wall and has a true, of which many plant tissues are
Funtion (5 organelles) membrane-bound nucleus along with composed. Often, it is described with
other cellular organelles. the features of a parenchyma cell of a Funtion (5 organelles)
vascular plant.
Golgi apparatus:
Modifies, sorts, packages, and transports proteins and lipids produced in the cell.
Materials enter the Golgi from the endoplasmic reticulum and undergo various Funtion: Main Characteristics: Vacuole:
chemical modifications before being directed to their final destination, either inside Main Characteristics: Function: Stores water, nutrients, wastes and various substances, helping
or outside the cell. to maintain cell turgor and regulating the concentration of solutes
in the cell.
Ribosomes:
They are responsible for protein synthesis from the genetic information contained in Chloroplasts:
messenger RNA (mRNA). They can be found free in the cytoplasm or attached to Contain pigments such as chlorophyll and perform
the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). photosynthesis, converting solar energy into chemical energy
(glucose) and releasing oxygen.
Centrioles:
They are involved in the formation and organization of microtubules during cell Leukoplasts:
division. They help form the mitotic spindle, which is essential for chromosome Function: store nutrients such as starch, oils and proteins.
separation during mitosis and meiosis.
Chromoplasts:
Lysosomes: Plant cells have a cell wall as well as a Function: contain pigments that provide color to flowers and
They are eukaryotic cells, their genetic cell membrane. In plants, the cell wall fruits.
Contain digestive enzymes that break down worn-out cellular materials, defective Some important functions of an animal Photosynthesis is the major function
content is enclosed in a membranous surrounds the cell membrane. This
organelles and particles captured from the environment. They are responsible for cell include giving the animal's body its performed by plant cells.
structure called the nucleus. gives the plant cell its typical Cell wall:
cellular digestion and recycling of components. structure, absorbing nutrients to Photosynthesis occurs in the
rectangular shape. Animal cells have chloroplasts of the plant cell. It is the Provides structural support and protection to the plant cell. It is
convert to energy, and helping animals They have variable shapes and sizes. only a cell membrane, and lack a cell composed mainly of cellulose, which gives it rigidity.
Mitochondria: move. They also contain all the process of preparing food by the
They are known as the "powerhouses" of the cell. They perform cellular respiration, wall.
hereditary material of an organism and They do not have a cell wall, unlike plants, by utilising sunlight, carbon
a process in which they convert nutrients (such as glucose) and oxygen into usable plant cells. dioxide and water. Energy is produced
can make copies of themselves. Only plant cells have chloroplasts.
energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), along with the release of carbon in the form of ATP in the process.
Plants do not get their sugars from
dioxide and water. They have organelles, which are eating food, so they have to make
membrane-bound compartments within sugars from sunlight. This process
the cell, with specific functions. (photosynthesis) happens in the
chloroplast.
You might also like
- Cell anatomy and divisionDocument4 pagesCell anatomy and divisionMarielle SaymanNo ratings yet
- Living Parts: Plant Parts Ofa CellDocument11 pagesLiving Parts: Plant Parts Ofa CellGarvNo ratings yet
- Jayden Smith - Handout - Cell Organelle Review WorksheetDocument2 pagesJayden Smith - Handout - Cell Organelle Review WorksheetJayden SmithNo ratings yet
- History of Cells in 40 CharactersDocument9 pagesHistory of Cells in 40 CharacterslutfiNo ratings yet
- Pidlaoan Coleen - Cell-Organelles WorksheetDocument3 pagesPidlaoan Coleen - Cell-Organelles WorksheetColeenNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Session 6 Lesson PreviewDocument2 pagesLaboratory: Session 6 Lesson PreviewzimoneNo ratings yet
- Human Bio Basic NotesDocument5 pagesHuman Bio Basic Notessrmnt.egNo ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument4 pagesExerciseFrancine RoxasNo ratings yet
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 - Cell Structure And-FunctionsDocument23 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 - Cell Structure And-FunctionsEmer Perez50% (2)
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 Cell Structure and Functions 1Document17 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 Cell Structure and Functions 1Dette Dominic Ballano67% (3)
- Unique Structure Organelles: Bacteria Cell 3 Common Things FlagellaDocument1 pageUnique Structure Organelles: Bacteria Cell 3 Common Things FlagellaBiNo ratings yet
- Terms of Use: Graphics Used in This PackDocument15 pagesTerms of Use: Graphics Used in This PackclauspNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Review Worksheet 14-15Document2 pagesCell Organelle Review Worksheet 14-15Kirsten Troupe100% (1)
- Cells: Prepared By: Keith R. Mausisa, PTRP, PTDocument54 pagesCells: Prepared By: Keith R. Mausisa, PTRP, PTCharm AngelesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (CELLS)Document52 pagesChapter 2 (CELLS)hilmanNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Bio400Document11 pages3.1 Bio400Aayan HaydarNo ratings yet
- Color The Animal CellDocument6 pagesColor The Animal Cellyuefen tohNo ratings yet
- Learning about Cell TypesDocument3 pagesLearning about Cell TypesSean LestherNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles 943Document1 pageCell Organelles 943Tony Puac-LopezNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts2Document2 pagesCell Parts2api-257166615No ratings yet
- Bio Ms Sally Part 1Document2 pagesBio Ms Sally Part 1romaehab201912No ratings yet
- Nashra U. Sindatoc Concept Map of Cells 20212244873: Cell TypesDocument1 pageNashra U. Sindatoc Concept Map of Cells 20212244873: Cell TypesiamNashix22No ratings yet
- Cells WorksheetDocument2 pagesCells WorksheetJake FacciobeneNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesCell Organelle Review WorksheetMae SilogNo ratings yet
- Cell The Unit of Life - Old NmodDocument37 pagesCell The Unit of Life - Old NmodShreyaa SiddarthNo ratings yet
- The Cell: The Cytoplasm and Nucleus: Cytoplasmic Organelles MitochondriaDocument5 pagesThe Cell: The Cytoplasm and Nucleus: Cytoplasmic Organelles Mitochondriavinnie0905No ratings yet
- Unit 4 PDFDocument45 pagesUnit 4 PDFSUSHANT SenNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity #1 The Cell (1) (1) 2Document3 pagesLaboratory Activity #1 The Cell (1) (1) 2Kim VenturaNo ratings yet
- The Cell ActivitiesDocument3 pagesThe Cell Activitiestiareximena0308No ratings yet
- Chapter 3.1 CELLDocument28 pagesChapter 3.1 CELLShiela Marie BanggotNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lab Dent 1Document6 pagesGenetics Lab Dent 1FRANCHEZKA ANGELICA TANIEGRANo ratings yet
- Gen Bio I - ReviewerDocument6 pagesGen Bio I - ReviewerJen Laurine CosicolNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell FeaturesDocument26 pagesEukaryotic Cell FeaturesHridyanshu Singh RoyNo ratings yet
- Bio IpassDocument15 pagesBio IpassmonreNo ratings yet
- Term 1 - Grade 8 Science CH 7 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument3 pagesTerm 1 - Grade 8 Science CH 7 Cell Structure and Functionprakashjoshi23aprilNo ratings yet
- Cell Part 2Document8 pagesCell Part 2Harshit Mishra 09 2865No ratings yet
- The Cell: Anatomy and FunctionsDocument5 pagesThe Cell: Anatomy and FunctionsJapet Floyd AlipioNo ratings yet
- Cell Anatomy OrganellesDocument7 pagesCell Anatomy OrganellesGoogle BackupNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells AnswersDocument3 pagesProkaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Answersboney67% (3)
- 4 Structures and OrganellesDocument5 pages4 Structures and Organellessalmasadiq2008No ratings yet
- Ej Eldeson DeatrasDocument3 pagesEj Eldeson DeatrasedeatrasNo ratings yet
- Building Blocks of Life - Cell and TissuesDocument2 pagesBuilding Blocks of Life - Cell and TissuesAlbus SeverusNo ratings yet
- Biotech CellsDocument1 pageBiotech CellsChynna Elohnna CarreonNo ratings yet
- The Musculoskeletal System: ObjectivesDocument22 pagesThe Musculoskeletal System: ObjectivesMay Myat MonNo ratings yet
- BIOL 213 UNIT 2 (CHAPTER 5) (14) SLIDES (Compatibility Mode)Document85 pagesBIOL 213 UNIT 2 (CHAPTER 5) (14) SLIDES (Compatibility Mode)KimNo ratings yet
- Cells Review Ws AnswersDocument4 pagesCells Review Ws AnswersTongtun TuntunNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy-lab ACTSDocument5 pagesAnaPhy-lab ACTSCEEJNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: Anatomy and FunctionsDocument6 pagesCells and Tissues: Anatomy and FunctionsAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cells 2023 (1) - TaggedDocument37 pagesEukaryotic Cells 2023 (1) - Taggedvalkrye.100servesNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Review WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Organelles Review WorksheetRajeem Outlaw WrightNo ratings yet
- Deloviar Cell Organelle Review Worksheet 1Document4 pagesDeloviar Cell Organelle Review Worksheet 1daRain100% (1)
- REV Micro HSB RemedsDocument16 pagesREV Micro HSB RemedsPatricia HariramaniNo ratings yet
- PRELIMS BIOLOGY - Yrielleeeee: Biology - Organelles - Cell OrganelleDocument8 pagesPRELIMS BIOLOGY - Yrielleeeee: Biology - Organelles - Cell OrganelleYhazmin Iris IlustrisimoNo ratings yet
- Cells & Organelles CompleteDocument33 pagesCells & Organelles CompleteShiffa SaheedNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec (Chapter 3)Document6 pagesAnaphy Lec (Chapter 3)Aya MojicaNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellAlexa MacailoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Week 2Document6 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Week 2Florene Bhon GumapacNo ratings yet
- Notes - For - Cell (BOOK)Document10 pagesNotes - For - Cell (BOOK)Macchi MagsNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY REVIEWE-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesBIOLOGY REVIEWE-WPS OfficeLeanna DaneNo ratings yet
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesFrom EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNo ratings yet
- Art PDFDocument10 pagesArt PDFbobNo ratings yet
- A Review of High School Economics Textbooks: February 2003Document27 pagesA Review of High School Economics Textbooks: February 2003Adam NowickiNo ratings yet
- SAP HCM - Default Wage Types - Info Type 0008Document6 pagesSAP HCM - Default Wage Types - Info Type 0008cjherrera2No ratings yet
- Marine Ecotourism BenefitsDocument10 pagesMarine Ecotourism Benefitsimanuel wabangNo ratings yet
- Year 5 Reasoning Test Set 3 Paper A: Q Marks Answer Notes 1a 1b 7 6 4Document2 pagesYear 5 Reasoning Test Set 3 Paper A: Q Marks Answer Notes 1a 1b 7 6 4Amina Zeghar BNo ratings yet
- (Leon 2021) Pengaruh Financial Distress, Laverage Terhadap Konservatisme Akuntansi Pada Perusahaan Manfaktur Sektor Konsumsi 2016-2019Document24 pages(Leon 2021) Pengaruh Financial Distress, Laverage Terhadap Konservatisme Akuntansi Pada Perusahaan Manfaktur Sektor Konsumsi 2016-2019PUTRI AYU HASTUTINo ratings yet
- Internship Report On Incepta PharmaceutiDocument31 pagesInternship Report On Incepta PharmaceutihhaiderNo ratings yet
- H2 Physic 2010 A Level SolutionsDocument32 pagesH2 Physic 2010 A Level Solutionsonnoez50% (4)
- NIJ Sawmark Analysis Manual for Criminal MutilationDocument49 pagesNIJ Sawmark Analysis Manual for Criminal MutilationAntonio jose Garrido carvajalinoNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Internship ReportDocument69 pagesBajaj Internship ReportCoordinator ABS100% (2)
- (Nano and Energy) Gavin Buxton - Alternative Energy Technologies - An Introduction With Computer Simulations-CRC Press (2014) PDFDocument302 pages(Nano and Energy) Gavin Buxton - Alternative Energy Technologies - An Introduction With Computer Simulations-CRC Press (2014) PDFmarcosNo ratings yet
- Viennot - 1979 - Spontaneous Reasoning in Elementary DynamicsDocument18 pagesViennot - 1979 - Spontaneous Reasoning in Elementary Dynamicsjumonteiro2000No ratings yet
- Confidentiality Agreement With Undertaking and WaiverDocument1 pageConfidentiality Agreement With Undertaking and WaiverreddNo ratings yet
- Training Report PRASADDocument32 pagesTraining Report PRASADshekharazad_suman85% (13)
- Key Differences Between Natural Sciences and Social SciencesDocument6 pagesKey Differences Between Natural Sciences and Social SciencesAshenPerera60% (5)
- Business English 2, (ML, PI, U6, C3)Document2 pagesBusiness English 2, (ML, PI, U6, C3)Ben RhysNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Planter WaterproofingDocument8 pagesMethod Statement For Planter WaterproofingMonali Varpe0% (1)
- MS Excel Word Powerpoint MCQsDocument64 pagesMS Excel Word Powerpoint MCQsNASAR IQBALNo ratings yet
- CS Sample Paper 1Document10 pagesCS Sample Paper 1SpreadSheetsNo ratings yet
- Fraud Ebook Latest - Databricks PDFDocument14 pagesFraud Ebook Latest - Databricks PDFmohitbguptaNo ratings yet
- NWQSR - BodyDocument56 pagesNWQSR - BodyRonnie EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Examen TSMDocument4 pagesExamen TSMKaryna VeraNo ratings yet
- LEEA-030.2c2 Certificate of Thorough Examination (Multiple Items) (Overseas) (Dev)Document1 pageLEEA-030.2c2 Certificate of Thorough Examination (Multiple Items) (Overseas) (Dev)GaniyuNo ratings yet
- Letter of Invitation ESVC 3000 2024 1Document2 pagesLetter of Invitation ESVC 3000 2024 1pradeep kumarNo ratings yet
- Tem 2final PDFDocument9 pagesTem 2final PDFSkuukzky baeNo ratings yet
- Kaseya Performance and Best Practices Guide: Authors: Jacques Eagle Date: Thursday, April 29, 2010Document34 pagesKaseya Performance and Best Practices Guide: Authors: Jacques Eagle Date: Thursday, April 29, 2010markdavidboydNo ratings yet
- Fit Friend Business Game StrategiesDocument7 pagesFit Friend Business Game StrategiesSanchit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Marvin Elevate-Catalog Feb 2023 19981914Document27 pagesMarvin Elevate-Catalog Feb 2023 19981914DiegoNo ratings yet
- Parleremo Pzfra1Document218 pagesParleremo Pzfra1Lucia FerentNo ratings yet
- Sci10-Q4-M2_104804Document15 pagesSci10-Q4-M2_104804alindongaprilmaeNo ratings yet