Professional Documents
Culture Documents
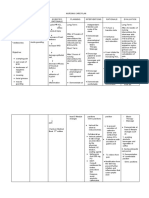
Respiratory Drugs
Respiratory Drugs
Uploaded by
kylaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Respiratory Drugs
Respiratory Drugs
Uploaded by
kylaCopyright:
Available Formats
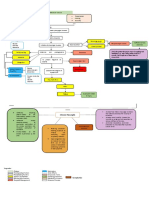
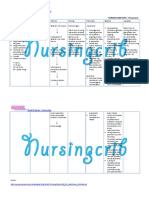
MOA: aid in the expectoration of
excessive mucus in respiratory tract, by
breaking down and thinning out
secretions
loosening and thinning of respiratory
tract secretions Therapeutic effects
Productive cough
Common colds
Bronchitis
laryngitis
Indications
Expectorants
pharyngitis
pertussis MOA: compete to block histamine to
prevent histamine which include
influenza vasodilation, ^secretions, ^ capillary
permeability and edema
measles
relax smooth muscle in bronchial tree
Known drug allergy Contraindication
reduce secretions (salivary, lacrimal,
bronchial, gastric) exerts a drying (
nausea anticholinergic) effect
Therapeutic Effects
vomiting Adverse Effects reduces dilation and permeability of
blood vessels, capillaries
gastric irritation
reduces itching, edema
MOA: Suppress cough reflex through Allergic reactions
direct action on cough center in CNS (
medulla)
Nasal allergies
Suppresses cough
Nausea and vomiting
analgesia
Therapeutic Effect Anaphylaxis
Indications
^ viscosity of secretion
Seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis (
dry effect on mucosa of respi tract hay fever)
Decreases runny nose
Motion sickness
Known hypersensitivity or allergy to Antihistamines
codeine or morphine
Parkinson’s disease symptoms
In respiratory depression, increased
Sleep disorders
intracranial pressure, seizure disorders, Opioids
or severe respiratory disorders.
known drug allergy
Known opioid dependency, and
contraindicated with alcohol use not recommended (as only treatment)
Contraindication for acute asthma attack, open angle
glaucoma, heart disease, kidney disease,
Pts with CNS depression, hypercapnia, hypertension, bronchial asthma, chronic
impaired kidney function, liver disease, Contraindicated obstructive lung disease, peptic ulcer
BPH, Addison’s disease, COPD disease, benign prostatic hypertrophy, or
during pregnancy
Interacts with other opioids, general
anesthetics, tranquilizers, sedatives, use with caution for children, lactating
hypnotics, tricyclic antidepressants, mothers, people with kidney and liver
alcohol, and other CNS depressants disease
Antitussives
cause sedation, nausea, vomiting, light- Drowsiness - mild to deep sleep, sedation
headedness, constipation Adverse effects more pronounced with traditional
antihistamines
Non opioids usually in combination with
other products: Dextromethorphan Dysrhythmias, hypotension,
hydrobromide and diphenhydramine palpitations, syncope, muscular
weakness, paradoxical excitement,
Therapeutic effects: same as opioid restlessness, nervousness, seizures
Adverse Effects
Dextromethorphan Drug allergy, Anticholinergic effects: dry mouth, nose,
hyperthyroidism, advanced heart and throat, urinary retention, , constipation,
vessel disease, hypertension, glaucoma, vision changes
and MAOI use in last 14 days Non-Opioid
Diphenhydramine: hypersensitivity, use nausea, vomiting, hepatitis
with caution in nursing mothers,
neonates, and patients with lower
respiratory tract infections vertigo, tinnitus, headaches
Dextromethorphan - Dizziness,
drowsiness, nausea
Diphenhydramine - sedation, dry mouth,
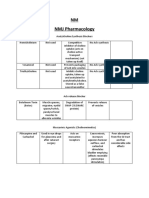
anticholinergic effects MOA: relax bronchial smooth muscle
Contraindication and Adverse Effects that are constricted as a result of a
Respiratory disease process. (causes dilation of the
bronchi and bronchioles)
Able to shrink engorged nasal mucous
membranes and relieve nasal stuffiness.
Drugs MOA: activation of 2 receptors relaxes
smooth muscles of the airway, dilates
bronchi, reduces airway constriction
Adrenergics constrict small arterioles
that supply the structures of the upper
Prevention/relief of acute attacks of
respiratory tract, primarily the blood
bronchospasm salbutamol is ‘a reliever’
vessels surrounding the nasal sinuses.
Short-acting ß-agonist (SABA) inhalers for acute asthma, pulmonary diseases
Also called sympathomimetics. Dry MOA
secretions
Hypotension and shock
Steroids cause inflammatory response to
be turned off or rendered unresponsive. Indications Short term treatment of hyperkalemia (
They target inflammatory response to stimulates potassium to shift from blood
organisms and allergens. vessels into cells)
Both relieve excessive nasal secretions Can cause uterine relaxation
and inflamed and swollen nasal mucosa
Respiratory controllers
Nasal secretions in swollen mucous
membranes are able to drain Therapeutic Effect
prevention of bronchospasm caused by
asthma or chronic obstructive lung
reduced inflammatory symptoms and Indication disease
improved air exchange
Known allergy to -Agonist
colds, chronic rhinitis, sinusitis, and hay
fever or allergies. To reduce swelling of
nasal passages and facilitate Uncontrolled cardiac dysrhythmias
visualization of pharyngeal membranes Contraindication
before surgery or diagnostic procedures Indications
Nasal Decongestants->
Intranasal Anticholinergic, High risk of stroke due to
vasoconstrictive action
Drug allergy Intranasal Corticosteroids
mixed ⍺ and agonists- Insomnia,
Acute angle glaucoma, uncontrolled anorexia, restlessness, hyperglycemia,
cardiovascular disease, hypertension, vascular headache, tremor, cardiac
diabetes, hyperthyroidism, prostatitis, stimulation
not recommended in conditions where
Contraindiations
patients cannot close their eyes, such as Long-Acting Beta2 Adrenergic
a stroke, with a history of stroke or TIA, Nonselective -Agonists (ß1 and ß2)-
Bronchodilators LABA
cerebral arteriosclerosis, long standing anginal pain, tremor palpitations,
Bronchodilators
asthma, or diabetes. tachycardia, vascular headache
depress body’s immune response 2-Agonists (SABA, LABA) hypertension
Adverse Effect or hypotension, vascular headaches,
tremor
systemic sympathomimetic drugs and
monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
to cause hypertension. Interact with If larger doses of salbutamol used too
methyldopa, urinary acidifiers, frequently, loses its 2-specific actions,
alkalinizers. Interactions stimulating 1 receptors causing nausea,
increased anxiety, palpitations, tremors,
and increased heart rate
nervousness, insomnia, palpitations,
and tremors
Diminished bronchodilation when
nonselective ß-blockers are used with
hypertension and palpitations, the ß-agonist bronchodilators
Adverse Effects
headache, dizziness
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors
mucosal irritation, dryness, epistaxis
Interaction Sympathomimetics
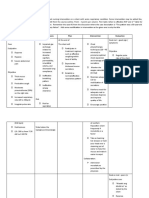
MOA: Stabilize membranes of
leukocytes (white blood cells) that Monitor patients with diabetes; an
release harmful inflammatory increase in blood glucose levels can
bronchoconstricting substances occur.
inflammation MOA: Anticholinergics bind to the
acetylcholine (Ach) receptors,
Therapeutic effects
preventing ACh from binding to receptor
enhance activity of B-agonist sites
Indications: as primary treatment of Therapeutic effects: prevention of
bronchospastic disorders to control the bronchoconstriction Indirectly causes
inflammatory responses believed to dilation of bronchial airways, decreases
cause these disorders; DO NOT relieve Corticosteroids - secretions
symptoms of acute asthmatic attacks Glucocorticoids
Indications: prevention of
Drug allergy or hypersensitivity to bronchospasm associated with COPD,
glucocorticoids not for management of acute symptoms
Anticholinergic Bronchodilators
Patients whose sputum tests are positive
Contraindication
for Candida organisms Contraindication: Allergy (to atropine):
Caution with acute angle glaucoma or
BPH
Patients with systemic fungal infection
Dry mouth, throat, nasal congestion
Pharyngeal irritation Subtopic 2
Heart palpitations
Coughing
Adverse Effects
Gastrointestinal irritation
Dry mouth Adverse Effects
Urinary retention
Oral fungal infections
Increased intraocular pressure
More likely to occur with systemic (
versus inhaled) corticosteroids.
Headache, coughing, anxiety
May increase serum glucose levels,
possibly requiring adjustments in
dosages of antidiabetic drugs
May raise the blood levels of the
immunosuppressants cyclosporine and
Interactions
tacrolimus; itraconazole may reduce
clearance of the steroids
phenytoin, phenobarbital, and rifampin
Greater risk of hypokalemia with
concurrent diuretic use (e.g.,
furosemide, hydrochlorothiazide)
You might also like
- Brenau Urinary Patterns HESI Case StudyDocument3 pagesBrenau Urinary Patterns HESI Case StudyAna Bienne100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceMary Joyce Limoico100% (1)
- Recurrent Pregnancy Loss - Causes, Controversies, and Treatment, 2nd Edition PDFDocument444 pagesRecurrent Pregnancy Loss - Causes, Controversies, and Treatment, 2nd Edition PDFAhmed Abou SeifNo ratings yet
- Alf (Drug Study)Document6 pagesAlf (Drug Study)timmisarmientoNo ratings yet
- N AcetylcysteineDocument1 pageN AcetylcysteineHanna Se67% (3)
- Villareal - NCMA216 Drug StudyDocument10 pagesVillareal - NCMA216 Drug StudyRozen VillarealNo ratings yet
- Patient Care 1 Drugs ChartDocument13 pagesPatient Care 1 Drugs ChartKaitlyn CabreraNo ratings yet
- Chronic PharyngitisDocument1 pageChronic PharyngitisHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- CHECK-IN ACTIVITY Module 5.2Document4 pagesCHECK-IN ACTIVITY Module 5.2Thea MarieNo ratings yet
- Chronic PharyngitisDocument1 pageChronic PharyngitisHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument2 pagesConcept MapAnnie TicualaNo ratings yet
- Roel JohnDocument2 pagesRoel JohnRoel John Atamosa CasilacNo ratings yet
- A56665 PDFDocument1 pageA56665 PDFradha krishNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudyBadgal BazingaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyizzittyNo ratings yet
- PHINMA University of Pangasinan College of Health Sciences Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesPHINMA University of Pangasinan College of Health Sciences Nursing Care PlanJoeriel MontemayorNo ratings yet
- PHINMA University of Pangasinan College of Health Sciences Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesPHINMA University of Pangasinan College of Health Sciences Nursing Care PlanJoeriel MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: (NoDocument19 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: (NoKen BaxNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKristine Faith GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyGel Marie LobatonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SainzDocument3 pagesDrug Study SainzGEN COLLANTESNo ratings yet
- Acetylcysteine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAcetylcysteine Drug StudyJulienFrayNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: Mycobacterium BacilliDocument1 pageTuberculosis: Mycobacterium BacilliDeni Marie GomonidNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyatchiekNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaJojo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Pharma Reviewer (Midterm)Document7 pagesPharma Reviewer (Midterm)SaidinaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ni Pani 1Document3 pagesDrug Study Ni Pani 1Hennerose Delyne RogandoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Obstructed AirwayDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Obstructed AirwayNicolne LorraineNo ratings yet
- Gr.4 NCP Health AssessmentDocument3 pagesGr.4 NCP Health AssessmentAlessandro MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationMica OmotsosircNo ratings yet
- Tetanus NCPDocument3 pagesTetanus NCPMarc Jayson TobiasNo ratings yet
- Summary of Pharmacology1 by 3alam El Teb DR - MahmoudDocument41 pagesSummary of Pharmacology1 by 3alam El Teb DR - MahmoudaamirNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument2 pagesCEFUROXIMEJemuel Irasmus Mari RosalesNo ratings yet
- NCP FOR INEFFECTIVE AIRWAY CLEARANCEDocument2 pagesNCP FOR INEFFECTIVE AIRWAY CLEARANCELawrence AzicateNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCP PDFDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCP PDFFARAH MAE MEDINA100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPFARAH MAE MEDINANo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyManuel PascualNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyLizli LoredoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RleDocument3 pagesDrug Study RleJuzteen TandangNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Week 9 Charlene Fidellaga BSN Y2-11Document8 pagesDRUG STUDY Week 9 Charlene Fidellaga BSN Y2-11Charlene FidellagaNo ratings yet
- NCPPDocument11 pagesNCPPAngelo Miguel MuñozNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System DrugsDocument4 pagesRespiratory System DrugsArienne Janine MalabananNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FluimucilDocument2 pagesDrug Study FluimucilJemina Rafanan Racadio0% (1)
- Drug Study CetirizineDocument1 pageDrug Study CetirizineBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Copaxone - Ms Drug StudyDocument1 pageCopaxone - Ms Drug StudygraceNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired GasDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired GasRea LynNo ratings yet
- Icu DrugstudyDocument3 pagesIcu DrugstudyMary Grace AgataNo ratings yet
- Decongestant Mucolytic and Expectorant Nasal Corticosteroids Antihistamines Leukotriene Inhibitors MOADocument4 pagesDecongestant Mucolytic and Expectorant Nasal Corticosteroids Antihistamines Leukotriene Inhibitors MOAimperiouxxNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPRoger Jr PumarenNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaJhasmine MocnanganNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyMaribel Mallorca BellaNo ratings yet
- NMJ PharmacologyDocument3 pagesNMJ PharmacologyRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Explanation of The Problem Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Sto: StoDocument5 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Explanation of The Problem Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Sto: StoMaria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument13 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKen BaxNo ratings yet
- CALMA, Mary Ann C. BSN - Iv-Leininger Skill: Breathe Comfortably Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesCALMA, Mary Ann C. BSN - Iv-Leininger Skill: Breathe Comfortably Nursing Care PlanMaryann CalmaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short-Term: Independent: A) Elevated Head of A) To TakeDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short-Term: Independent: A) Elevated Head of A) To TakeANGEL AKIRA TORRESNo ratings yet
- Asessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Long Term: Independent: Long TermDocument3 pagesAsessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Long Term: Independent: Long TermSenyorita KHayeNo ratings yet
- Fluticasone Drug StudyDocument3 pagesFluticasone Drug StudyArabelle GONo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Plan of Care/Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvlatuationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Plan of Care/Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvlatuationgoyaNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction: Borborygmi Bacterial ActivityDocument1 pageIntestinal Obstruction: Borborygmi Bacterial ActivityShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument14 pages1 PBlauraNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Treatment: General Principles and ApproachDocument24 pagesTuberculosis Treatment: General Principles and ApproachRahul PatilNo ratings yet
- TracheostomyDocument6 pagesTracheostomynamithaNo ratings yet
- A STUDY ON WAITING TIME IN VARIOUS HOSPITAL DEPARTMENTS AND RECOMMENDATIONS TO DECREASE THE WAITING TIME Ijariie6859Document14 pagesA STUDY ON WAITING TIME IN VARIOUS HOSPITAL DEPARTMENTS AND RECOMMENDATIONS TO DECREASE THE WAITING TIME Ijariie6859Vikram AripakaNo ratings yet
- Peritoneal DialysisDocument31 pagesPeritoneal Dialysisapi-372245489% (9)
- Negations in Mullukurumba and Kattunaikka Tribes in NilgirisDocument5 pagesNegations in Mullukurumba and Kattunaikka Tribes in NilgirisEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Elimination Round 1Document38 pagesElimination Round 1Diksha chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Warm, Sweet, PinkDocument8 pagesWarm, Sweet, Pinkindirinoor5No ratings yet
- Upper Limb Stretching Terhadap Skala Dispnea Pada Pasien PPOKDocument7 pagesUpper Limb Stretching Terhadap Skala Dispnea Pada Pasien PPOKrifka riskaNo ratings yet
- The Language of Medicine 11Th Edition Davi Ellen Chabner Ebook Full ChapterDocument51 pagesThe Language of Medicine 11Th Edition Davi Ellen Chabner Ebook Full Chapterricky.ridenour341100% (16)
- Dade Actin FSL Activated PTT Reagent - Rev 10 DXDCM 09017fe9804eb3b9-1605649828217Document7 pagesDade Actin FSL Activated PTT Reagent - Rev 10 DXDCM 09017fe9804eb3b9-1605649828217Dany BatistaNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI)Document102 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI)Jasmin Jacob100% (2)
- 0849320518Document332 pages0849320518Hajilulung100% (1)
- ThesisDocument30 pagesThesissuhani singhNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Pilates Exercises in Patients With Knee OsteoarthritisDocument159 pagesThe Effectiveness of Pilates Exercises in Patients With Knee OsteoarthritisAyesha ShahNo ratings yet
- Vaccines 08 00321Document17 pagesVaccines 08 00321Kshitiz Raj ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Lipedema An Overview of Its Clinical ManifestationsDocument10 pagesLipedema An Overview of Its Clinical ManifestationsCarla a s MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Sun Dares An 2017Document8 pagesSun Dares An 2017Arya NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Peme Form B - Rev 20201020Document5 pagesPeme Form B - Rev 20201020Click TechnologyNo ratings yet
- IM361B-PathPhysio Orals 2020Document95 pagesIM361B-PathPhysio Orals 2020Mi PatelNo ratings yet
- Surgrescurric 1Document33 pagesSurgrescurric 1Sadashivayya SoppimathNo ratings yet
- 29primary AngleClosure GlauDocument9 pages29primary AngleClosure GlauShari' Si WahyuNo ratings yet
- A Profile of The Philippine Pharmaceutical SectorDocument73 pagesA Profile of The Philippine Pharmaceutical SectorGigi PaguiaNo ratings yet
- LTM KomkesDocument3 pagesLTM KomkesArdelia RaissaNo ratings yet
- RDB College of Nursing and Paramedical Science: DR M A Dawoodbatcha PH DDocument2 pagesRDB College of Nursing and Paramedical Science: DR M A Dawoodbatcha PH DYAMINIPRIYANNo ratings yet
- Uniform ESRD Transient Hemodialysis FormDocument3 pagesUniform ESRD Transient Hemodialysis FormacqueNo ratings yet
- Thiazide and Thiazide-Like DiureticsDocument3 pagesThiazide and Thiazide-Like DiureticsYohanes SutrisnoNo ratings yet
- Ministry of Defence KDF Recruitment Advertisement 2019 1Document6 pagesMinistry of Defence KDF Recruitment Advertisement 2019 1MasterNo ratings yet