0% found this document useful (0 votes)
239 views2 pagesStatics Problems for Engineering Students
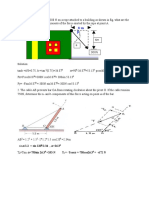
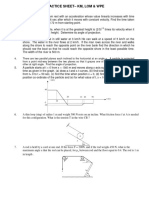
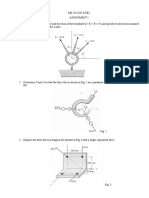
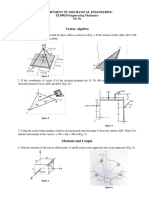
1. The document contains 7 situations involving forces and moments acting on various structures and objects. Forces include tension in cables, perpendicular forces on bars, and resultant forces.
2. Each situation contains multiple questions asking learners to calculate magnitudes of forces, directions of resultants, moments of forces about points, angles between forces, and distances related to the forces.
3. The questions and diagrams provide information needed to use principles of statics, such as resolving forces into components, taking moments, and determining resultants, to solve for unknown values requested in each question.
Uploaded by
JA MantalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
239 views2 pagesStatics Problems for Engineering Students
1. The document contains 7 situations involving forces and moments acting on various structures and objects. Forces include tension in cables, perpendicular forces on bars, and resultant forces.
2. Each situation contains multiple questions asking learners to calculate magnitudes of forces, directions of resultants, moments of forces about points, angles between forces, and distances related to the forces.
3. The questions and diagrams provide information needed to use principles of statics, such as resolving forces into components, taking moments, and determining resultants, to solve for unknown values requested in each question.
Uploaded by
JA MantalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd