Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit5
Uploaded by
Băng Di TrầnOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit5
Uploaded by
Băng Di TrầnCopyright:
Available Formats
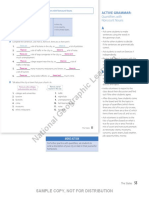
ACTIVE GRAMMAR Present Continuous: Who Questions
ACTIVE GRAMMAR:
Present Continuous:
When Who is the subject of a sentence, it is always singular.
Who is buying a computer? Laura is. Who Questions
Who is fixing the computer? Henry and Ivan are.
When Who is the object of a sentence, it can be singular or plural.
Who is Max calling? He is calling his sister.
A
Who are Ali and Kim talking to? They are talking to their friends. • Read the questions in the grammar
chart out loud.
• Ask students to make additional
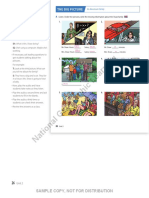
A Answer the questions. Use your imagination. Answers will vary.
examples of each type of who
1. Who is taking a photo? Mark is. question. Give prompts with different
2. Who is he taking a photo of? His daughter verbs. For example:
T: Who / Sarah / write to
S1: Who is Sarah writing to? (object)
T: Who / talking on the phone
S2: Who is talking on the phone?
ng
3. Who is writing an email? Jessica is.
4. Who is she writing to? Her professor (subject)
• Ask students to look at the photos
ni
in Exercise A and describe what is
ar
happening in each.
5. Who is driving? Paul is.
• Then, ask students to complete
Le
6. Who is taking a trip? Margo and Paul are.
the exercise. Check the answers as
a class.
c B
hi
B LET’S TALK. Two or three students will act out each Lynn Martha
• Point out the photo and ask students
situation for the class. Ask two Who questions about
ap
each situation. what is happening in the picture.
1. Student 1 is giving a book to Student 2. • Read the two speech bubbles aloud
gr
2. Student 1 is taking a photo of two students.
and explain that students need to
write two types of who questions
eo
3. Student 1 is helping Student 2 with homework.
about each situation—one using
4. Student 1 is inviting Student 2 to a party.
who as the subject, and one using
5. Student 1 is texting Student 2.
lG
who as the object.
6. Three students are talking to the teacher. Who is Lynn Who is giving a • Have students work in pairs to write
giving a book to? book to Martha?
the questions and then act out the
na
Technology 71 situations.
io
at
N
Technology 71
SAMPLE COPY, NOT FOR DISTRIBUTION
ACTIVE GRAMMAR Nonaction Verbs
ACTIVE GRAMMAR:
Nonaction Verbs agree hate love seem
Some verbs in English do
not usually take the present believe have need smell
A continuous. They are called belong hear own sound
• Explain that nonaction verbs nonaction verbs. These verbs
often refer to the senses, to cost know prefer taste
(intransitive verbs) describe feelings, feelings, or to beliefs, or they feel like remember think
senses, beliefs, and possession. (They show possession.
forget look see understand
do not usually describe actions.)
Write these four categories on the
board and ask students to identify Some verbs can show both action and nonaction.
the verbs in the box with each I have a computer. I’m having a good time.
category. (Feelings: feel, hate, like, She’s having a party.
love, prefer; Senses: forget, hear, know, I think he’s a good teacher. I’m thinking about my boyfriend.
look, need, remember, see, seem, smell, More information in Appendix A.
sound, taste, understand; Beliefs: agree,
ng
believe, think; Possession: belong, cost, A Complete the sentences. Use the present or the present continuous form of the verb
have, own) in parentheses.
ni
• Read the second grammar chart, do prefer
1. Which weather app (prefer) you ?
which contains exceptions to the
ar
2. I (remember / not) don’t remember my password for this site.
rule about not using nonaction
verbs in the present continuous. Give 3. I (try) am trying to find a good recipe for banana bread. This one
Le
additional examples as necessary. (sound) sounds good.
4. They (save) are saving money to buy a computer. Their children
• Have students complete Exercise A
need
c
individually. Then, have students (need) one for school.
is sitting looks
hi
exchange books to check each 5. Hannah (sit) at her computer. She (look)
other’s answers. confused. She (know / not) doesn’t know how to use this software.
ap
6. My sister (belong) belongs to her high school basketball team.
• Review the answers as a class. Write
any common errors on the board 7. We (think / not) don’t think that our car gets good gas
gr
(without calling out the students mileage. We (look / not) are not looking at SUVs or vans. We (think)
are thinking about buying a hybrid.
who made the errors) and review any
eo
pertinent parts of the grammar rules 8. Our neighbor (have) is having a party next week. (you / have)
as necessary. Do you have an invitation?
lG
9. I (listen / not) am not listening to music. I (listen) am listening
to a podcast.
10. That tablet (cost) costs too much!
na
72 Unit 5
io
at
MORE ACTION
N
Write a mix of correct and incorrect sentences
with nonaction verbs on the board and have
students decide if each sentence uses the
verb correctly. If a sentence is incorrect, have
students fix the sentence. For example:
I’m owning a car. (incorrect)
I own a car. (correct)
72 Unit 5
SAMPLE COPY, NOT FOR DISTRIBUTION
ACTIVE GRAMMAR Simple Present and Present Continuous
ACTIVE GRAMMAR:
Time Expressions with Time Expressions Adverbs of Frequency
Simple Present and
Present Continuous with Simple Present always Present Continuous
now once a day usually
today
at this moment
every day
every morning
sometimes
never A
at this time all the time
• Check that students understand the
meaning of the time expressions and
adverbs in the charts at the top of
A Circle the correct time expression. the page.
1. Linda is checking her email now / in the morning. • If necessary, explain the meaning
2. She receives about twenty emails right now / every day. of the time expressions by giving
3. Shanta is listening to a podcast now / every day. She listens to the podcast examples for each. For example:
now / every morning. Mario exercises once a day. He exercises
4. The students are putting their cellphones in their backpacks right now / all the time. at 10:00 a.m. each day.
ng
5. Sarah just finished her report for science. She is using spell check right now / in the • Ask students to complete Exercise A
evening. individually.
6. Stanley is taking a break at this moment / twice a day. He’s playing a card game.
ni
• Check the answers as a class.
7. My wi-fi isn't working very well every day / right now.
ar
B LET'S TALK. In a group, write three sentences about what you are doing in class now. Then, write B
Le
three sentences on a separate sheet of paper about what you do in class every day. • Give one example sentence for each
category. Then, set a time limit for
C Ask and answer the questions with a partner. students to write their sentences.
1. Do you have a computer?
c
6. Do you have a credit card? • Invite volunteers to write their
hi
2. Are you using a computer now? 7. Are you working with a partner?
sentences on the board.
ap
3. Do you have a phone with you? 8. Do you often work with a partner? • Ask the other students to correct the
4. Are you talking on your phone? 9. Are you writing now? sentences as necessary.
gr
5. Are you carrying a wallet? 10. Are you talking with the teacher?
C
eo
Yes, I am. Yes, I do. • Ask a volunteer to read the first
No, I’m not. No, I don’t. question aloud.
lG
• Answer using one of the four choices
in the boxes.
na
• Have students complete the exercise
Technology 73 with a partner. Explain that students
should answer using the phrases in
io
the boxes.
at
MORE ACTION
N
For homework, ask students to bring in a
photograph of a person from a magazine. Have
them write an imaginary description of what
this person does every day and what he / she is
doing right now (or at the moment the photo
was taken). Remind students to use the present
continuous. Then, have students share their
pictures and sentences with the class.
Technology 73
SAMPLE COPY, NOT FOR DISTRIBUTION
You might also like
- SM2ed Teacher's Resources Worksheet D L2 U3Document5 pagesSM2ed Teacher's Resources Worksheet D L2 U3Mayra MartinezNo ratings yet
- ELEPHANTDocument10 pagesELEPHANTmjoy ManzanasNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Unit 1 Super Minds 5 2nd EditionDocument5 pagesWorksheet Unit 1 Super Minds 5 2nd EditionDagmar Yunuel RiveraNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit1Document3 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit1Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science IV: I. ObjectivesDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in Science IV: I. ObjectivesSeven Seven100% (1)
- ODI AmE TE6 Review12Document2 pagesODI AmE TE6 Review12Alma Morales CamposNo ratings yet
- SM2ed Teacher's Resources Worksheet C L4 U2Document5 pagesSM2ed Teacher's Resources Worksheet C L4 U2Dagmar Yunuel RiveraNo ratings yet
- CD-ROM Course Resource NotesDocument10 pagesCD-ROM Course Resource NotestrivanthNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit5Document3 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit5Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- SM2ed Teacher's Resources Worksheet F L4 U5Document5 pagesSM2ed Teacher's Resources Worksheet F L4 U5Fernanda SerralNo ratings yet
- Intermediate - TBDocument204 pagesIntermediate - TBBalázs László100% (10)
- New Hot Spot 1 Teachers NoteDocument153 pagesNew Hot Spot 1 Teachers NoteMichiyoNo ratings yet
- Day 5 7Document7 pagesDay 5 7Jirah Joy MontejoNo ratings yet
- Units: Carlos 18-JulDocument2 pagesUnits: Carlos 18-JulCarlos AguirreNo ratings yet
- Let's Begin 2 Workbook KeyDocument7 pagesLet's Begin 2 Workbook KeyJian TanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Math 4 Q3Document9 pagesLesson Plan in Math 4 Q3Gracelyn PatacNo ratings yet
- English Chest 1 Teachers Guide Lesson PlanDocument59 pagesEnglish Chest 1 Teachers Guide Lesson PlanParamitha Anggraini100% (1)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 3 Q3Document5 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 3 Q3Lordiel Miasco94% (18)
- Lesson 3 Reading 1, 2 and 3 Lesson 4 Speaking 1 and 2: Unit 3 Unit 3Document4 pagesLesson 3 Reading 1, 2 and 3 Lesson 4 Speaking 1 and 2: Unit 3 Unit 3najak1234No ratings yet
- Multimodal Texts DLPDocument30 pagesMultimodal Texts DLPveronica dumanopNo ratings yet
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN IN ENGLISH 3 LoidaDocument7 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN IN ENGLISH 3 LoidaVergiel Abellano100% (6)
- Market Leader 3rd Edition - PreIntermediate - Teachers Book - CuttedDocument2 pagesMarket Leader 3rd Edition - PreIntermediate - Teachers Book - CuttedEra B. LargisNo ratings yet
- SM2ed Teacher's Resources Worksheet B L4 U1Document5 pagesSM2ed Teacher's Resources Worksheet B L4 U1Dagmar Yunuel RiveraNo ratings yet
- Cot Math 4-2ND QuarterDocument5 pagesCot Math 4-2ND QuarterEvelyn100% (5)
- Gateway A2 Student's Book Pask Full Answers PDFDocument186 pagesGateway A2 Student's Book Pask Full Answers PDFТеодор Желев80% (10)
- ExcerptDocument7 pagesExcerptHanan badranNo ratings yet
- Session 5 Sequence of Activities What If?: Name/type of Activity Aims Procedures Materials TimeDocument2 pagesSession 5 Sequence of Activities What If?: Name/type of Activity Aims Procedures Materials TimeMihaNo ratings yet
- I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesI. ObjectivesNoralinda M. RascalNo ratings yet
- CuttingEdge Elementary Student PDFDocument30 pagesCuttingEdge Elementary Student PDFRoberto RuízNo ratings yet
- Cutting Edge - Elementary - Student's BookDocument30 pagesCutting Edge - Elementary - Student's BookRoberto RuízNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Creative Writing 11Document6 pagesLesson Plan in Creative Writing 11Jinken Shane SalvatierraNo ratings yet
- Teachers NotesDocument66 pagesTeachers Notescooleugene64No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3 3 Ready Steady Go GE2Document2 pagesLesson Plan 3 3 Ready Steady Go GE2Loan NgôNo ratings yet
- Class 1Document86 pagesClass 1Saurabh RajNo ratings yet
- Cambridge English Empower Empower A2 Reading Plus Teacher U03 WorksheetDocument2 pagesCambridge English Empower Empower A2 Reading Plus Teacher U03 WorksheetВенцислав БорисовNo ratings yet
- DLP Parallelogram Demo 1Document5 pagesDLP Parallelogram Demo 1Vincent A LazaroNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ArtsDocument10 pagesLesson Plan in ArtsChenie Mae B. PerezNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 4 q3 w2Document5 pagesDLL Mathematics 4 q3 w2Jessamyn Flor RosarioNo ratings yet
- Gateway Plus 1 TRF Unit 3 Teacher's NotesDocument1 pageGateway Plus 1 TRF Unit 3 Teacher's NotesAgnieszka WNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 EnglishDocument8 pagesGrade 3 EnglishNissi LumantasNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit3Document3 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit3Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan May-June 2023Document14 pagesLesson Plan May-June 2023Hasmen AndalNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English 9Document4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in English 9marinel de claroNo ratings yet
- NHS 3 Książka NauczycielaDocument115 pagesNHS 3 Książka NauczycielaMonika aqwerNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Let's Go, Unit 1, at School, Page 6 1. 2-3 Minutes: Warm Up (What Should I Do?)Document1 pageVocabulary Let's Go, Unit 1, at School, Page 6 1. 2-3 Minutes: Warm Up (What Should I Do?)CliffordBosaingNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit3Document3 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit3Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English 9docxDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in English 9docxMary Lyn ObejasNo ratings yet
- Grammar Extra: Elementary Unit 1Document2 pagesGrammar Extra: Elementary Unit 1Daniela Reyes100% (1)
- Math9 DLL Q3 1Document5 pagesMath9 DLL Q3 1Danielle DuplonNo ratings yet
- Speakout Grammar Extra Elementary Unit 1Document2 pagesSpeakout Grammar Extra Elementary Unit 1Frank Dotcom100% (1)
- DLL - Mathematics 4 - Q3 - W2Document4 pagesDLL - Mathematics 4 - Q3 - W2Ana May DeLa PeñaNo ratings yet
- 08 - Units 11-12 & Revision 6Document13 pages08 - Units 11-12 & Revision 6giula777No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English 2Document5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in English 2John Paul SanchezNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 DLL MATH 4 Q3 Week 3Document2 pagesGrade 4 DLL MATH 4 Q3 Week 3Reina Jaerhel JabonallaNo ratings yet
- LP Alphabet of Lines Ideas Here!Document7 pagesLP Alphabet of Lines Ideas Here!Grace Villanueva Palit100% (1)
- Teacher's NotesDocument53 pagesTeacher's NotesE Story EnglishNo ratings yet
- MultigradeDocument8 pagesMultigradeJena Eroles100% (1)
- DLP Conditions Parallelogram NataldarleneDocument12 pagesDLP Conditions Parallelogram Nataldarleneakosidar2000No ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 AudioScripts 1Document2 pagesEnglishInAction3 AudioScripts 1Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit7Document2 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit7Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 AudioScripts 2Document2 pagesEnglishInAction3 AudioScripts 2Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit7Document2 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit7Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit7Document2 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit7Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit6Document2 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit6Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit7Document2 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit7Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit6Document2 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit6Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit6Document2 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit6Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit7Document2 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit7Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit7Document2 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit7Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit6Document2 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit6Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit3Document3 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit3Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit4Document3 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit4Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit6Document2 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit6Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit6Document2 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit6Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit4Document4 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit4Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit3Document4 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit3Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit4Document3 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit4Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit3Document3 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit3Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit3Document3 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit3Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit2Document4 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit2Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit2Document3 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit2Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit1Document4 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit1Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit2Document3 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit2Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit2Document3 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit2Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit2Document3 pagesEnglishInAction3 Keyword Unit2Băng Di TrầnNo ratings yet
- Pre Joining Guidelines For InfosysDocument21 pagesPre Joining Guidelines For InfosysGokul0% (2)
- Case 3 GROUP-6Document3 pagesCase 3 GROUP-6Inieco RacheleNo ratings yet
- Divorced Women RightsDocument41 pagesDivorced Women RightsAnindita HajraNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science - 2Document5 pagesGrade 10 Science - 2Nenia Claire Mondarte CruzNo ratings yet
- Soal Pas Myob Kelas Xii GanjilDocument4 pagesSoal Pas Myob Kelas Xii GanjilLank BpNo ratings yet
- How To Use The ActionDocument3 pagesHow To Use The Actioncizgiaz cizgiNo ratings yet
- Bus Organization of 8085 MicroprocessorDocument6 pagesBus Organization of 8085 MicroprocessorsrikrishnathotaNo ratings yet
- Jesus Hold My Hand EbDocument2 pagesJesus Hold My Hand EbGregg100% (3)
- Visual Acuity: Opthalmology CEX StepsDocument5 pagesVisual Acuity: Opthalmology CEX StepsVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- Baybay - Quiz 1 Code of EthicsDocument2 pagesBaybay - Quiz 1 Code of EthicsBAYBAY, Avin Dave D.No ratings yet
- SOLO FrameworkDocument12 pagesSOLO FrameworkMaureen Leafeiiel Salahid100% (2)
- College PrepDocument2 pagesCollege Prepapi-322377992No ratings yet
- Industrial Cpmplus Enterprise Connectivity Collaborative Production ManagementDocument8 pagesIndustrial Cpmplus Enterprise Connectivity Collaborative Production ManagementEng Ahmad Bk AlbakheetNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Exam All Source g12Document314 pages2nd Quarter Exam All Source g12Bobo Ka100% (1)
- HSE Induction Training 1687407986Document59 pagesHSE Induction Training 1687407986vishnuvarthanNo ratings yet
- The Trial of Jesus ChristDocument10 pagesThe Trial of Jesus ChristTomaso Vialardi di Sandigliano100% (2)
- Solved SSC CHSL 4 March 2018 Evening Shift Paper With Solutions PDFDocument40 pagesSolved SSC CHSL 4 March 2018 Evening Shift Paper With Solutions PDFSumit VermaNo ratings yet
- Green IguanaDocument31 pagesGreen IguanaM 'Athieq Al-GhiffariNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Practitioner and Student WritingDocument28 pagesA Comparison of Practitioner and Student WritingMichael Sniper WuNo ratings yet
- EMP Step 2 6 Week CalendarDocument3 pagesEMP Step 2 6 Week CalendarN VNo ratings yet
- BUS 301 - Hospitality Industry Vietnam - Nguyễn Thị Thanh Thuý - 1632300205Document55 pagesBUS 301 - Hospitality Industry Vietnam - Nguyễn Thị Thanh Thuý - 1632300205Nguyễn Thị Thanh ThúyNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Designed Industrial Symbiosis Networks in The Ulsan Eco-Industrial Park - Research and Development Into Business ADocument10 pagesEvolution of Designed Industrial Symbiosis Networks in The Ulsan Eco-Industrial Park - Research and Development Into Business Asanyukta sinhaNo ratings yet
- HUAWEI P8 Lite - Software Upgrade GuidelineDocument8 pagesHUAWEI P8 Lite - Software Upgrade GuidelineSedin HasanbasicNo ratings yet
- Solution Document For Link LoadBalancerDocument10 pagesSolution Document For Link LoadBalanceraralNo ratings yet
- Tateni Home Care ServicesDocument2 pagesTateni Home Care ServicesAlejandro CardonaNo ratings yet
- Answer The Statements Below by Boxing The Past Perfect TenseDocument1 pageAnswer The Statements Below by Boxing The Past Perfect TenseMa. Myla PoliquitNo ratings yet
- Honey ProcessingDocument5 pagesHoney Processingvenkatrao_gvNo ratings yet
- Dry Wall, Ceiling, and Painting WorksDocument29 pagesDry Wall, Ceiling, and Painting WorksFrance Ivan Ais100% (1)
- Electric Trains and Japanese Technology: Breakthrough in Japanese Railways 4Document9 pagesElectric Trains and Japanese Technology: Breakthrough in Japanese Railways 4Aee TrDNo ratings yet
- Not Just Another Winter Festival: Rabbi Reuven BrandDocument4 pagesNot Just Another Winter Festival: Rabbi Reuven Brandoutdash2No ratings yet