Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio 统一小考-chapter 14
Uploaded by
22 Lee Xin Yong 李芯瑢0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views10 pagesOriginal Title
Bio 统一小考—chapter 14
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views10 pagesBio 统一小考-chapter 14
Uploaded by
22 Lee Xin Yong 李芯瑢Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Bio 统一小考—chapter 14
Support and locomotion in human and animals
Movement: same position
Locomotion: Different position
Types of skeleton
Endoskeleton 内骨骼
Exoskeleton外骨骼
made up of chitin 几丁质 or calcium
Ecdysis蜕皮
Ex: Lobster龙虾, Spider, Cicada 蝉
Hydrostatic skeleton
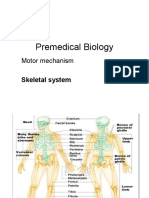
Musculoskeletal肌肉骨胳 system of human
Made up of 206 bones硬骨 and cartilage软骨
Function:
Enables movement
Provides shape and support for so body tissue
Protects internal organs
Produces blood cell
Stores certain minerals such as calcium and phosphate
Skeletal system
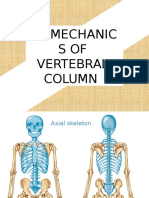
Axial skeleton 中轴骨
Skull 头骨
cranial bones颅骨 (x8)- protect the brain
facial bones面部骨骼(x14) - formed mouth and nose
Ribcage胸廓
Ribs肋骨
Costal cartilage肋软骨
Sternum胸骨
Vertebral column脊柱
made up of 33 small bones call vertebrae脊椎
extends from the base of the skull to the pelvic girdle骨盆带
Each vertebra is separated from each other by disc 阀瓣of cartilage called
intervertebral椎间 dics. The cartilage dics absorbs the impact of shock冲击
and serves as a flex point for bending.
Vertebral column is S-shaped and function:
support and balance the body
protect the spinal cord骨髓
support the skull
provide surfaces for the attachment of muscles
Cervical vertebrae 颈椎 (7)
Atlas vertebra (first cervical vertebra)
located in the neck
No centrum椎体
Has a large neural canal椎管
Has small transverse processes横突(長且尖細的橫突,為腰部原
來的肋骨退化而成)
Has a pair of transverse foramina颈椎横突孔(在颈椎椎体侧面,
由椎弓根,横突前、后根及肋横突板围成一个卵圆形孔), one
on each transverse process
Has a short spinous process棘突:脊椎骨上的一种突起,位于椎
体后方,起到支持和保护脊髓的作用
Joins with the base of cranium 头盖骨to support the head and to
enable nodding of the head
Axial vertebra (second cervical vertebra)
Has a projection from the centrum called odontoid process 齿状突
(使头左右旋转)to airticulate with the atlas
Has small transverse processes
Has a pair of transverse foramina
Has a large spinous process
Joins with the atlas vertebra to enable the head to move from le
to right
Third to seventh cervical vertebra
Has a pair of transverse foramina which contain artery, vein and
nerve to carry blood to and from the brain
Has a short spinous process
Has a flat centrum
Has small and broad 广泛transverse process
Thoracic vertebrae胸椎(12)
located at the thorax胸腔
Extra facets at the end of transverse processes and sides of centrum to
articulate with ribs肋骨
A long spinous process and tranverse process for the attachment of
back muscles
Has a thick and big centrum
Lumbar vertebrae腰椎(5)
Located at the waist腰
The biggest and strongest vertebra
Short spinous process
Thick and large centrum
Long transverse processes for muscle attachment
Sacrum骶骨(5)
located at the hip臀部
Sacral vertebrae fused to each other to form sacrum
Has four openings through which nerves leave the spinal cord
Triangle in shape
Neural canal gradually becomes narrower and finally disappear
Facet at the back of the first transverse processes on each side
articulates with the pelvic girdle
Coccyx尾骨(4)
4 vertebrae fused together to form coccyx(the tail)
Transverse process: provides a large surface area for attachment of
muscles and ligament
Articulating surface (facet): Provides surface which articulates with the
next vertebra
Spinous process: Provides a large surface area for attachment of muscles
and ligaments
Neural arch: Protects the spinal cord
Neural canal: Contains the spinal cord
Centrum: Provides support and absorbs shock.
Compare and contrast the types of vertebrae
Appendicular skeleton附肢骨
Forelimb前肢
Humerus肱骨
Radius桡骨
Ulna尺骨
Carpals腕骨
Metacarpals掌骨
Phalanges指骨
Hindlimb后肢
Femur 股骨
Tibia胫骨
Fibula腓骨
Tarsals跗骨
Metatarsals跖骨
Pectoral girdle 肩带
Scapula
Clavicle
Pelvic girdle骨盆
Ilium髂骨
Ischium坐骨
Pubis耻骨
Compare and contrast the types of vertebrae
Similarities
All vertebrae have spinous and transverse processes, centrum (except the atlas
vertebra) and neural canal,
The neural canal of all the vertebrae contains the spinal cord脊髓.
Differences
Spinous cord
Cervical vertebrae : Short
Thoracic vertebrae : Long
Lumbar vertebrae :Short
Sacral vertebrae : None
Caudal vertebrae : None
Transverse process
Cervical vertebrae : Wide and short
Thoracic vertebrae : Long
Lumbar vertebrae :Long
Sacral vertebrae : Becomes shorter gradually
Caudal vertebrae : None
Centrum
Cervical vertebrae : Small
Thoracic vertebrae : Big
Lumbar vertebrae :Large
Sacral vertebrae :Centrum of sacral vertebrae fused to form the sacrum
Caudal vertebrae :Centrum of caudal vertebrae fused to form the coccyx
Transverse foramina
Cervical vertebrae : One transverse foramen at each transverse procss
Thoracic vertebrae :None
Lumbar vertebrae :None
Sacral vertebrae :None
Caudal vertebrae :None
Extra facets
Cervical vertebrae : None
Thoracic vertebrae :Facets at the end of transverse processes and sides of
centrum for articulation with the ribs
Lumbar vertebrae :None
Sacral vertebrae :Facets at transverse processes of first sacral vertebrae to
join with the pelvic girdle
Caudal vertebrae : None
Joint
Immovable joint 不动连结
Gliding joint 微动连结
the joint between vertebrae (by cartilage disc) at the vertebral column allow the
vertebral column to bend slightly forward, backward and to the sides
the joint between the ribs and the sternum胸骨 (by cartilage) that allow the ribs
to move slightly during the breathing process
Movable joint 活动关节
also known as synovial joint
made up of cartilage, synovial membrane, synovial fluid, capsule and ligament
Ligament
joins bone to bone and holds the bones in position
Elastic and can be stretched to allow movement at the joint
Holds the bone together at the joint
Prevents dislocation of bones and gives support and strength to the
joint.
Synovial fluid - fills the cavity between the bones, acts as a lubricant to
reduce friction between the bones at the joint
Cartilage - at the surface of bones that meet and absorb shocks and
reduces frictions between bones
Capsule-the fibrous connective tissue that encloses and protects the joint
Synovial membrane
located at the joint cavity
secretes synovial fluid into synovial cavity
The synovial fluid acts as a lubricant to reduce friction between the
bones at the joint
Ex:
Hinge joint
allows movement in one place
found at the elbow, knee and phalanges趾骨
Ball and socket joint
allows movement in all planes - allow rotational movement in all
directions
Found at the shoulder joint and hip joint.
Mechanism in Human Forearm
Bending of the arm
Biceps contracts while triceps relaxes.
A pulling force is produced by the contraction of the biceps
This force is transmitted through the tendon to the radius
The radius is pulled upwards and cause the arm to bend at the elbow
The forearm moves upwards
Straightening of the arm
Triceps contracts while biceps relaxes
A pulling force is produced by the contraction of the triceps
This force is transmitted through tendon to the ulna
The ulna is pulled downwards and causes the arm to straighten at the elbow joint
The forearm moves downwards
Mechanism in Human Leg
Leg movement is produced by the action of the antagonistic muscle in the leg:
The biceps femoris as the flexor muscle
The quadriceps femoris as the extensor muscle
These muscles in the leg act to
bend the leg at the knee and to raise up the femur for the leg to move forward
lower the femur and straighten the leg at the knee
过程
脚尖碰地
The right calf muscle contracts to straighten the leg at the ankle
The heel of the foot is raised from the ground
脚抬起
The flexor muscle of the thigh called biceps femoris contracts while the extensor
muscle called quadriceps femoris relaxes to bend the leg at the knee
The foot is raised up and the body thrusts forward
脚往前走
The quadriceps femoris contracts while the biceps femoris relaxes to straighten
the leg
The tibialis at the shank contracts to lower the heel of the foot onto the ground.
Mechanism of Locomotion in Earthworm
wall of earthworm is made up of a pair of antagonistic muscles
Circular muscles - surround the body of earthworm
Longitudinal muscles - extend from one end of body to the other
The circular muscles contract , Longitudinal muscles relax and the body become thin
and long
The circular muscles relax, longitudinal muscles contract and the body become thin and
short
The peristaltic wave along the body of the earthworm enables the earthworm to move
forward
Mechanism of locomotion of fish
has an endoskeleton for the attachment of muscles
muscles in fish are in the form of segmental blocks calles myotomes on both sides of the
flexible backbone
fish move forward due to the contraction and relaxation of myotomes on either side of
the body
Myotomes act antagonistically
when myotomes on the right contract , myotomes on the l relax
the body bends to the right
the alternate contractions of right and le myotomes cause the body and the tail to
sweep from side to side
this produces a forward thrust that propels the fish forward in a straight path
the lateral thrusts produced in opposite directions cancel off each other
fish has fins to balance the body in the water and to control the direction of
movement
Mechanism of locomotion of grasshopper
The antagonistic flexor and extensor muscles are attached to the inner surface of the
exoskeleton
The flexor muscle bends a joint while the extensor straightens it
The hind legs of a greasshopper are long and muscular especially adapted for jumping
First , the hind legs are folded in the shape of Z due to the contraction of the flexor
muscles. The hind legs are fully flexed and prepared for jump
Then, the extensor muscle contracts while the flexor muscle realxes. The hind legs
are extended and straightened
A force is produced downwards and backwards. This causes an upward and forward
force which propels the grasshopper to jump into the air.
Mechanism of locomotion of bird
Flight in bird is due to the action of the large and strong breast muscles
Pectoralis major - lower part of the humerus
Pectoralis minor - upper part of the humerus
Muscle act antagonistically enables the wings to flap downwards or upwards during
flight
flapping of the wings is due to the antagonistic action of the breast muscles
Downstroke of wings
When the pectoralis major on both wings contrascts, pectoralis relaxes
Wings are pulled dowmwards and backwards
Air resistance produces an upthrust on the wings
The upthrust is transmitted from the wings to the coracoid to li up the whole
body upwards and onwards
Upstroke of wings
The pectoralis minor on both wings contracts, the pectoralis major relaxes.
Wings are pulled up.
Air resistance is low
The wings return to the starting position.
Health Issues Related to the Human Musculoskeletal System
Osteoporosis
bone disorder due to the thinning of bone mass or low bone mass
有这种病的人:light , so and porous bones
导致bones become brittle and fragile.
通常发生在年老的妇女身上
the rate of calcium loss is higher compared to the rate of calcium absorption.
This results in a loss of bone mass.
In women who reach menopause, the oestrogen level is low. Oestrogen is
required to help the body to absorb calcium and reduce calcium loss from the
bone. Hence, a low level of oestrogen can reduce bone mass due to the loss of
calcium from the bones.
Causes
Insufficient intake of calcium and phosphorus
Insufficient intake of vitamin D which helps in the absorption of calcium
Lack of exercise
Symptoms
Fractures of the vertebrae, wrist or hips, loss of height and stooped posture
Prevention
Diet rich in calcium, phosphorus and vitamin D
Regular exercise
Osteomalacia
due to the so ening of bones in adults
caused by a severe vitamin D deficiency during the bone maturing process in
children and young adults
these so ened bones can lead to bowed legs and fracture
Causes
Lack of calcium and phosphorus to build strong bones
Lack of vitamin D to help in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus
Symptoms
Dull, aching pain in the lower back, pelvis, hips, legs and ribs
Decreased muscle tone and leg weakness cause difficulty in walking
Treatment
Sufficient intake of vitamin D and calcium to strengthen the bones
Rickets
so ening and weakening of bones in children
due to the lack of vitamin D and calcium which is needed to build strong bones
The bones especially in the legs are bowed because they are weak and cannot
support the body
Cause
Lack of vitamin D due to lack of exposure to sunlight or a diet deficient in
vitamin D
Lack of calcium during formation of bones in children
Can be due to genetic factors in some cases
Symptoms
Pain at the affected bones causes difficulty in walking in children
Thickening of the ankles, wrists and knees, bowed legs, so skull bones
Stunted growth due to poor growth and development of the skeleton
Bones can becomes weaker and prone to fractures in severe cases
Treatment
Intake of food rich in calcium and vitamin D
Take vitamin D supplement
以上内容整理于 幕布文档
You might also like
- Anatomy of SpineDocument77 pagesAnatomy of SpineJoy SahaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 - MSKDocument3 pagesChapter 24 - MSKannoja selvaNo ratings yet
- Bones & Joints of the Spine ExplainedDocument83 pagesBones & Joints of the Spine ExplainedJoy SahaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in SportDocument64 pagesUnit 1 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in Sportdomhughes1093No ratings yet
- Skeleton & LocomotionDocument10 pagesSkeleton & Locomotionali mtNo ratings yet
- A Basic UnderstandingDocument6 pagesA Basic Understandingjessica160793No ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 Chapter 2:locomotion and Support: To: Mrs AnnamalDocument25 pagesBiology Form 5 Chapter 2:locomotion and Support: To: Mrs AnnamalAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- The Ligamentum Flavum:: Present Throughout Vertebral ColumnDocument9 pagesThe Ligamentum Flavum:: Present Throughout Vertebral ColumnUmar JawadNo ratings yet
- Verterbral Column Assingment Takunda MakondoDocument58 pagesVerterbral Column Assingment Takunda MakondomakondotakundaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyGretchen BadayosNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesThe Skeletal SystemP17212215123 SELVIANo ratings yet
- Veterinary OsteologyDocument279 pagesVeterinary OsteologyTatenda Mageja100% (2)
- Hyoid BoneDocument14 pagesHyoid BoneAl-Shuaib Astami SonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The SpineDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The SpineKinahZildredBibitNo ratings yet
- The Back 2023Document29 pagesThe Back 2023AniesNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Overview of The SystemDocument56 pagesANAPHY Overview of The SystemLalajimNo ratings yet
- BONEDocument27 pagesBONEVIJAYA KUMAR YNo ratings yet
- Axial SkeletonDocument65 pagesAxial Skeletonfatimamuzammil406No ratings yet
- Laboratory 3 SkeletalDocument9 pagesLaboratory 3 SkeletalKyla InoferioNo ratings yet
- Vertebra: StructureDocument9 pagesVertebra: StructureayudhyaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument32 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemArmine Angela SolimanNo ratings yet
- Konsep Dasar MuskuloskeletalDocument42 pagesKonsep Dasar Muskuloskeletalkhayree100% (2)
- Biology Notes CHPTR 14Document7 pagesBiology Notes CHPTR 14Wan HasliraNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System Powerpoint 1227697713114530 8Document44 pagesThe Muscular System Powerpoint 1227697713114530 8ninya puella100% (1)
- Muscular SystemDocument33 pagesMuscular SystemChin Chin0% (1)
- Bones of The KneeDocument5 pagesBones of The KneeJessica AdhykaNo ratings yet
- Ball-and-socket hip joint anatomyDocument6 pagesBall-and-socket hip joint anatomyIshimaru ThorNo ratings yet
- Document 5Document22 pagesDocument 5dawidkubiak222No ratings yet
- Reviewer Skeletal To EndoDocument46 pagesReviewer Skeletal To EndoSophia CaisipNo ratings yet
- Skeletalsystem MRDDocument35 pagesSkeletalsystem MRDArnold Ashish GomesNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: IB Sport, Exercise and Health ScienceDocument33 pagesSkeletal System: IB Sport, Exercise and Health ScienceMaggie-Louise BellamyNo ratings yet
- Movement System: By: Fadhilah HarmenDocument30 pagesMovement System: By: Fadhilah HarmenFadhilah HarmenNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of The Vertebral ColumnDocument44 pagesBiomechanics of The Vertebral ColumnVijay PradeepNo ratings yet
- Skripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogDocument15 pagesSkripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogElizabetaNo ratings yet
- The Functions of The Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesThe Functions of The Muscular SystemJOSHUA ABELLANOSANo ratings yet
- Sport Presentation: by Scott CadmoreDocument55 pagesSport Presentation: by Scott CadmorescadmoreNo ratings yet
- Muscles of the Head and NeckDocument21 pagesMuscles of the Head and Neckdan_dezideriuNo ratings yet
- Premedical Biology: Motor MechanismDocument44 pagesPremedical Biology: Motor MechanismsheenaNo ratings yet
- PE-1-MIDTERM-EXAM-REVIEWER-2023-2024 (2) - CopyDocument2 pagesPE-1-MIDTERM-EXAM-REVIEWER-2023-2024 (2) - Copyxbautista124No ratings yet
- The Human SkeletonDocument10 pagesThe Human Skeletonanwar safwanNo ratings yet
- C11Document175 pagesC11azfdin100% (1)
- Musculoskeletal Assessment GuideDocument24 pagesMusculoskeletal Assessment GuideBSN 1-10 Dela Cruz Patrick RenNo ratings yet
- The Thorax: Axial & Appendicular Skeleton Mammary Glands Surface AnatomyDocument28 pagesThe Thorax: Axial & Appendicular Skeleton Mammary Glands Surface AnatomyDr-Arsalan ZahidNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesSkeletal SystemJovi Floresca AberinNo ratings yet
- Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Anatomy: DR .S.NizamudeenDocument57 pagesThoracic and Lumbar Spine Anatomy: DR .S.NizamudeenPogo LocoNo ratings yet
- Athletic HipDocument8 pagesAthletic HipjafrinkNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Hip JointDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Hip JointSundaraBharathiNo ratings yet
- Anatomi - Olah Raga 1st MeetingDocument79 pagesAnatomi - Olah Raga 1st MeetingR DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System UpdatedDocument55 pagesSkeletal System UpdatedAlthea OcaslaNo ratings yet
- Core 2 ADocument16 pagesCore 2 AJasmiine AlzateeNo ratings yet
- Back Pain PDFDocument40 pagesBack Pain PDFsana shiekhNo ratings yet
- 21 - MSK8 Carpal TunnelDocument51 pages21 - MSK8 Carpal TunnelNTRisforthinkersNo ratings yet
- The Musculoskeletal System Is Made Up of The Body's Bones (The Skeleton), MusclesDocument17 pagesThe Musculoskeletal System Is Made Up of The Body's Bones (The Skeleton), MusclesrajNo ratings yet
- StructureDocument7 pagesStructureNeirfla WassabiNo ratings yet
- IX. Anatomy and Physiology Functions of The Muscular System: Cilia Flagellum AmoeboidDocument4 pagesIX. Anatomy and Physiology Functions of The Muscular System: Cilia Flagellum AmoeboidJonathan DimaculanganNo ratings yet
- Myology: Zhenmei Zhao, MD, Professor Department of Anatomy Taishan Medical UniversityDocument123 pagesMyology: Zhenmei Zhao, MD, Professor Department of Anatomy Taishan Medical UniversityAkshit SetiaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HipDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HipJayson OlileNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesSkeletal SystemMaureen Tianson DomingoNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument183 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemDanielShenfield100% (1)
- 18-Minute HIIT Miracle Workout Gets You Fitter FasterDocument10 pages18-Minute HIIT Miracle Workout Gets You Fitter Fastereloymg26gmailcomNo ratings yet
- Coping Skills: Emily Barth, LMFTDocument14 pagesCoping Skills: Emily Barth, LMFTSue CornwallNo ratings yet
- Offseason Basketball Workout TrackerDocument3 pagesOffseason Basketball Workout TrackerJc GoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Mascular Conditioning PrescriptionDocument2 pagesCardiovascular and Mascular Conditioning PrescriptionSheena AmitNo ratings yet
- Ido Portal Movement X NYC Notes 1Document11 pagesIdo Portal Movement X NYC Notes 1roninNo ratings yet
- Hope 3 Reviewer 1ST QuarterDocument3 pagesHope 3 Reviewer 1ST QuarterWarren PagsuyuinNo ratings yet
- 4 - The Resistance CurveDocument26 pages4 - The Resistance Curvebreinfout fotosNo ratings yet
- Master Soal PTS 1 2023Document5 pagesMaster Soal PTS 1 2023Kank AgoesNo ratings yet
- Complete Vocal Fitness PreviewDocument6 pagesComplete Vocal Fitness Previewvikas kunduNo ratings yet
- Differences in Muscle Shoulder External Rotation in Open Kinetic Chain and Closed Kinetic Chain Exercises PDFDocument3 pagesDifferences in Muscle Shoulder External Rotation in Open Kinetic Chain and Closed Kinetic Chain Exercises PDFLeonardiniNo ratings yet
- Sports Medicine Guide to Injuries and RehabilitationDocument20 pagesSports Medicine Guide to Injuries and RehabilitationSreenath SukumaranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document37 pagesChapter 21Ivan Olo SarumpaetNo ratings yet
- HOPE 2A MODULE 2 Safety and Health Benefits With Copyright Disclaimer PDFDocument10 pagesHOPE 2A MODULE 2 Safety and Health Benefits With Copyright Disclaimer PDFLeo PatrickNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Unit 1 Clubs and HobbiesDocument10 pagesModule 1 Unit 1 Clubs and HobbiesfabianNo ratings yet
- LONG Q GRADE 10Document10 pagesLONG Q GRADE 10Mark Johnson Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- OBJECTIVESDocument25 pagesOBJECTIVESPrinces Jane BaquiranNo ratings yet
- Causes of Knee TightnessDocument4 pagesCauses of Knee TightnessRatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- Upper middle income entrepreneur prioritizes health after heart strokeDocument1 pageUpper middle income entrepreneur prioritizes health after heart strokeAshish JainNo ratings yet
- PE and Health Fitness Tests and ConceptsDocument3 pagesPE and Health Fitness Tests and ConceptsCJ Bantang Yap87% (31)
- Enter your maxes and volume calculationsDocument20 pagesEnter your maxes and volume calculationsRaffoNo ratings yet
- The Quick, Safe and Low-Impact Way To FitnessDocument34 pagesThe Quick, Safe and Low-Impact Way To FitnessSimão Pedro Martins67% (3)
- Combined Approach To The SIJDocument61 pagesCombined Approach To The SIJSara Yasmin TalibNo ratings yet
- Basic Fundamentals of Wushu - 20230915 - 000726 - 0000Document13 pagesBasic Fundamentals of Wushu - 20230915 - 000726 - 0000DARSHAN UNo ratings yet
- HIIT Exercises ListDocument8 pagesHIIT Exercises ListJeanNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3: Engaging in Moderate To Vigorous Physical ActivityDocument12 pagesMODULE 3: Engaging in Moderate To Vigorous Physical ActivityJohn Erniest Tabungar Austria100% (3)
- Weight Training SyllabusDocument3 pagesWeight Training Syllabusapi-233936772No ratings yet
- Performance Task in P.E. ArtsDocument3 pagesPerformance Task in P.E. ArtsAisaNo ratings yet
- 12 Week ShredDocument13 pages12 Week ShredNorberto Mendoza GonzalezNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL EDUCATION lORIMARDocument7 pagesPHYSICAL EDUCATION lORIMARKazzanah PianaNo ratings yet
- Fitness Program DesignDocument6 pagesFitness Program Designmar poNo ratings yet