Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ge103 Lesson 7 El Nino La Nina
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ge103 Lesson 7 El Nino La Nina
Copyright:
Available Formats
GE103 – LESSON 7 – EL NINO & LA NINA from the west and excessive rainfall often turn to
dangerous typhoons.
OUTLINE
Hangin Amihan (Northeast monsoon) - Towards
I. Introduction
Japan or South
II. Origin of El Nino and La Nina
III. Global Effect of El Nino and La Nina The winds need to rotate to scatter the heat
IV. The Effect of El Nino and La Nina in the in the planet and blow it into different
Philippines directions.
V. The Different regions affected by El Nino o The pressure of many areas will
and La Nina in the Philippines normalized
o Scatter the heat to make the
OUTCOMES
temperature normal
This chapter must be able to:
Normal
1. Describe the events experienced having El
Nino and La Nina phenomenon
2. Where do El Nino and La Nina occur?
3. What are the cause of an irregular global
climate
4. How do El Nino and La Nina affect global
climate
5. What are the Effects of El Nino and La Nina
in the Philippines
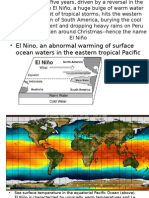
"El Nino" and "La Nina"
These are variations in The easterly winds pushes the warm water
tropical Pacific Ocean from the east of the Pacific Ocean to the west
and atmosphere of the Pacific Ocean or to Asia
conditions that have Heat is a factor of precipitation
global weather and Movement of cold water is Upwelling
climate impacts. They
Two types of water: Cold waters and Warm
are the most well-known
waters
of several cyclical and
Thermocline - a steep temperature gradient
non-cyclical patterns
in a body of water such as a lake, marked by
operating on time scales
a layer above and below which the water is
from years to decades
at different temperatures.
El Nino
Arrows tell us the direction of the wind and
the occurrences of El Nino and La Nina
Hangin Habagat (Southwest monsoon) – at the
Australian continent, and the low-pressure area is at Warm winds towards the West
North China, Mongolia, and Siberia. The gusty winds Intense heat at the Center
Warm waters, dry areas in the Philippines
More rains, wet, warm waters in America
La Nina
Wind moves westernly
El Nino
Gush of wind strongly pushing the warm
wind towards the West (Philippines)
Very wet and warm water in the Philippines
How to detect El Nino or La Nina?
Measure the temperature of Pacific ocean
most especially at the eastern part
Very warm in the Philippines, rainfall and
landslides
Opposite side – Cold waters, very cold temp
La Nina
History and Origin of El Nino
El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is an
atmosphere disturbance and recurrent
ocean warming. The warming cause massive
orange to red – intense heat warming kills many sea birds and fish by
Yellow - warm wind preventing nutrient rich cold water from rising
Black – landforms to the surface
No intense heat, hence NORMAL The cloud formation results in heavy rainfall,
floods, hurricanes, cyclones etc. In the
countries of South America.
This weakens the cloud oration in western
equatorial Pacific which reduces rainfall and
causes drought in west countries of the 5. Planting drought-resistant trees during
Pacific like Australia, Indonesia. Thailand. reforestations
Philippines 6. Conservation in the use of household water.
Occurrence of El Nino LA NINA PHENOMENON
Observed in 150 happens in the Pacific Translated as the
Weather pattern that has returned 28 times “little girl” or also known as "cold tongue"
worldwide for the past centuries Characterized by abnormally cold ocean and
Occurs every 5 to 8 years but it comes tropical cyclones in the eastern equatorial
earlier from 3 to 5 Years pacific
Prolonged heavy rains, climatic condition
Global Effect of El Nino
after El Nino
1. The effect on marine water, brackish, and Wetter than normal in Australia and
fish ponds have due to reduction of rainfall Indonesia
and increase in the salinity of tidal water. Rise in temperature in China, Peru,
2. Host of planetary climate changes altering Carribean Island and United States have
high level winds, and in, some cases, more hurricanes and tropical cyclones
typhoons and storms.
LA NINA PHENOMENON in the Philippines
The Effects of El Nino in the Philippines
1. Heavy rains and floods
1. Decrease in agricultural products 2. Central Luzon suffered flashfloods and rise
2. Affected largest production of fishmeal of water
3. Affect water sources, hydropower 3. Agricultural land went underwater and many
generators, health and sanitation and crops were destroyed
socioeconomic conditions 4. Food supply and production suffered due to
4. Long famine and extreme heat continuous flooding of the rice fields
5. Extreme conditions in the weather 5. Tremendous weather disturbance
6. Damage infrastructures, farms, markets,
Worst scenarios: roads, and irrigation channels
1. Change in the surface temperature 7. Landslides, huge losses of livestock and
2. Lack of water supply fishponds
3. Arid lands Department of Agriculture stated that provinces
4. Dry irrigation of the country are vulnerable
5. Poor harvest
6. Poor fish catch Rice producing:
7. Bad effect on animals and plants in the
Southern Tagalog, Central Luzon, LeYte and
environment
the Caraga in Mindanao
8. forest fires
9. damaging natural parks and reserves River basins:
Some Measures of the Government: Agusan
1. There should be massive dissemination of Bicol
information about the phenomenon Cagayan
2. Construction of Small Farm Reservoir (SFR) Cotabato
which can hold the rainfall through the earth llog.Hilatagan
embarkment Pampanga River
3. Introducing mulching, covering the ground
Watesheds:
with straw or leaves around the plants to
reduce the water loss Albay
4. Planting drought-tolerant plant varieties Agusan del Norte
Benguet
Bukidnon
Cagayan
Camarines
Sur
Davao
Ifugao
Isabela
North Cotabato
South Cotabato
Maguindanao
You might also like
- Calculate Lightning Protection For BuildingDocument4 pagesCalculate Lightning Protection For BuildingKamran Afzal100% (2)
- What are El Nino and La Nina? The climate phenomena explainedDocument3 pagesWhat are El Nino and La Nina? The climate phenomena explainedDhanya CharithaNo ratings yet
- El Nino and La Nina PPTDocument35 pagesEl Nino and La Nina PPTBon PatiñoNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - Q3 - Module 5 - Climatic Phenomena Occurring On A Global LevelDocument25 pagesScience 9 - Q3 - Module 5 - Climatic Phenomena Occurring On A Global LevelMelanie Trinidad100% (1)
- 3rd Quarter - Week 6Document74 pages3rd Quarter - Week 6angelie.cardanoNo ratings yet
- El Niño and La Niña EventsDocument7 pagesEl Niño and La Niña Eventslallu24No ratings yet
- El Nino and La Nina PPTDocument16 pagesEl Nino and La Nina PPTMeanNo ratings yet
- Parameters of Site SelectionDocument80 pagesParameters of Site SelectionVienci Haya AlbaNo ratings yet
- El Niño and La Niña: How These Climate Phenomena Affect Global ConditionsDocument53 pagesEl Niño and La Niña: How These Climate Phenomena Affect Global ConditionsCalvin Paulo MondejarNo ratings yet
- El Nino & La Nina EssayDocument4 pagesEl Nino & La Nina EssayAaron Dela Cruz100% (1)
- El Nino and La Nina Upsc Notes 27Document5 pagesEl Nino and La Nina Upsc Notes 27Mohd AshrafNo ratings yet
- El Niño and La Niña (ESS Assignment)Document21 pagesEl Niño and La Niña (ESS Assignment)akshat5552No ratings yet
- El Nino and La NinaDocument6 pagesEl Nino and La NinaEdit O Pics StatusNo ratings yet
- El Nino La Nina weather patterns explainedDocument6 pagesEl Nino La Nina weather patterns explainedalaxyadNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Fundamentals Fundamentals of Crop Science of Crop Science of Crop ScienceDocument24 pagesFundamentals Fundamentals Fundamentals of Crop Science of Crop Science of Crop ScienceAlthea DoradoNo ratings yet
- El Nino-La NinaDocument63 pagesEl Nino-La NinaHimangshu BoraNo ratings yet
- The El Niño Southern Oscillation - El Niño and La NiñaDocument14 pagesThe El Niño Southern Oscillation - El Niño and La NiñaSean PhilippeNo ratings yet
- Effects of El Nino and La Nina on Weather and ClimateDocument41 pagesEffects of El Nino and La Nina on Weather and ClimateK Sai maheswariNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument2 pagesGreenhouse EffectGiejill SomontanNo ratings yet
- El Niño-La Niña: The Southern OscillationDocument2 pagesEl Niño-La Niña: The Southern OscillationAMAARREENo ratings yet
- El Nino La NinaDocument2 pagesEl Nino La Ninamariieya03No ratings yet
- El Nino La NinaDocument1 pageEl Nino La NinaJENNo ratings yet
- Understanding Earth's Climate Through ENSO as an Integrating ConceptDocument24 pagesUnderstanding Earth's Climate Through ENSO as an Integrating ConceptSUSHOVAN GHOSH100% (1)
- What Happens When El Niño Is Not Present?Document2 pagesWhat Happens When El Niño Is Not Present?Ivan RazoNo ratings yet
- El Niño and La Niña: Understanding the Climate CycleDocument17 pagesEl Niño and La Niña: Understanding the Climate CycleAndreaGabrielleNo ratings yet
- El Nino La Nina and Climate Change ModuleDocument3 pagesEl Nino La Nina and Climate Change ModuleGennelle GabrielNo ratings yet
- El Niño and La Niña: The Currents That Make Our WeatherDocument6 pagesEl Niño and La Niña: The Currents That Make Our WeatherMichael OuztsNo ratings yet
- El Nino and La Nina - 20240305 - 075027 - 0000Document33 pagesEl Nino and La Nina - 20240305 - 075027 - 0000Liejohn BaldadoNo ratings yet
- La Niña: By: Beverly PacerDocument26 pagesLa Niña: By: Beverly PacerBeverly PacerNo ratings yet
- Tropical Storms: Safety Measures Before, During, and After A TyphoonDocument24 pagesTropical Storms: Safety Measures Before, During, and After A TyphoonRyou KinoshitaNo ratings yet
- El Nino PhenomenonDocument2 pagesEl Nino Phenomenonk.agnes12No ratings yet
- Explain El Nino and The La Nina Weather PhenomenonDocument4 pagesExplain El Nino and The La Nina Weather Phenomenonjosephine_lim93No ratings yet
- Weather Phenomenon La NiñaDocument13 pagesWeather Phenomenon La Niñagiovannie alvarezNo ratings yet
- Effects of La Niña: Presented By: Group 5, 11-St. Isidore of SevilleDocument4 pagesEffects of La Niña: Presented By: Group 5, 11-St. Isidore of SevilleyurboivenNo ratings yet
- ENSO ImpactDocument4 pagesENSO ImpactangelNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q3 Week 7Document10 pagesScience 9 Q3 Week 7Mervin LudiaNo ratings yet
- La Niña: By: Marycon GandaDocument15 pagesLa Niña: By: Marycon GandaAriane CloresNo ratings yet
- El Nino Is A Weather Phenomenon Caused When Warm Water From The Western Pacific Ocean Flows EastwardDocument2 pagesEl Nino Is A Weather Phenomenon Caused When Warm Water From The Western Pacific Ocean Flows Eastwardabirami sNo ratings yet
- 6 7 9 Final EBE S9 Q3 Week 6 7Document4 pages6 7 9 Final EBE S9 Q3 Week 6 7Leah CasanoNo ratings yet
- Pacific Region EL NINO Fact Sheet ASamoa 2015 FINAL v2Document2 pagesPacific Region EL NINO Fact Sheet ASamoa 2015 FINAL v2Sr. RZNo ratings yet
- El Niño and La Niña climate patterns explainedDocument3 pagesEl Niño and La Niña climate patterns explainedRahul DekaNo ratings yet
- 2010-2011 La Nina GeofileDocument4 pages2010-2011 La Nina Geofileteacher.brandon.stewartNo ratings yet
- Activity Week 2 March 23 Grade 9Document3 pagesActivity Week 2 March 23 Grade 9LowelaNo ratings yet
- 2023 Geofile ENSODocument7 pages2023 Geofile ENSOteacher.brandon.stewartNo ratings yet
- How El Niño and La Niña affect global weather and climateDocument25 pagesHow El Niño and La Niña affect global weather and climatehimaniNo ratings yet
- EportfolioDocument9 pagesEportfolioapi-313993715No ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument29 pagesEnvironmental ScienceReizel GaasNo ratings yet
- El Nino: By: John Vincent M. RosalesDocument8 pagesEl Nino: By: John Vincent M. RosalesJohn Mark Manalo RosalesNo ratings yet
- What is El Niño? Causes and Effects of this Climate PatternDocument13 pagesWhat is El Niño? Causes and Effects of this Climate PatternFernan Lee R. ManingoNo ratings yet
- El Niño and La Niña climate patterns explainedDocument5 pagesEl Niño and La Niña climate patterns explainedMarlop CasicasNo ratings yet
- El Niño/ Southern Oscillation: WMO-No. 1145Document12 pagesEl Niño/ Southern Oscillation: WMO-No. 1145Ivonne MedinaNo ratings yet
- How Does El Nino Affects The EnvironmentDocument4 pagesHow Does El Nino Affects The Environment방탄소년단parkchimchimwaifuNo ratings yet
- Fgfa - El Nino and La NinaDocument3 pagesFgfa - El Nino and La NinaRahul DekaNo ratings yet
- Impacts of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation Climate PatternDocument10 pagesImpacts of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation Climate PatternAbegail Pineda-MercadoNo ratings yet
- Currents, Upwelling & El NinoDocument12 pagesCurrents, Upwelling & El Ninoapi-26334461No ratings yet
- 9 HR0J 35 EnsoDocument9 pages9 HR0J 35 EnsoSanika SaniNo ratings yet
- La Niña: Noemie Rodriguez and Rica Mae B. PareñoDocument29 pagesLa Niña: Noemie Rodriguez and Rica Mae B. PareñoPatrick VerroyaNo ratings yet
- REVIEW EXAM FOR DRRM: KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTSDocument14 pagesREVIEW EXAM FOR DRRM: KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTSRyou KinoshitaNo ratings yet
- Climate Change - El Niño La NiñaDocument11 pagesClimate Change - El Niño La Niñarjkhu4500No ratings yet
- El NenoDocument1 pageEl Nenomuhammad imtinanNo ratings yet
- El Niño: Normal ConditionsDocument3 pagesEl Niño: Normal ConditionsMaria AbregoNo ratings yet
- El Niño-Southern Oscillation - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument17 pagesEl Niño-Southern Oscillation - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaakurilNo ratings yet
- HathigaonDocument3 pagesHathigaonShivani IyengarNo ratings yet
- Clozes 2021Document11 pagesClozes 2021María De Los Ángeles Guillén VivancosNo ratings yet
- Ninth Ward Study GuideDocument21 pagesNinth Ward Study GuidedaliaNo ratings yet
- Disaster NursingDocument5 pagesDisaster NursingJenny Juniora AjocNo ratings yet
- ARC 322 Term Project Part1Document2 pagesARC 322 Term Project Part1Yifan ShenNo ratings yet
- Toefl Itp - 2002 - 08Document44 pagesToefl Itp - 2002 - 08marchelita.daffiani.kaligisNo ratings yet
- Starkville Dispatch Eedition 9-13-18Document12 pagesStarkville Dispatch Eedition 9-13-18The DispatchNo ratings yet
- Presentation 6Document41 pagesPresentation 6Raizen AdlawanNo ratings yet
- Perfect Tenses-Present Perfect Vs Past SimpleDocument2 pagesPerfect Tenses-Present Perfect Vs Past SimpleNelson David Botero BaenaNo ratings yet
- Honey Tester Detector FT-FM2Document5 pagesHoney Tester Detector FT-FM2Satria WirangNo ratings yet
- Weather and Climate B2-C1Document7 pagesWeather and Climate B2-C1Alina YefimenkoNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Gases and Climate Change NotesDocument7 pagesGreenhouse Gases and Climate Change Notesshelter musasaNo ratings yet
- 150 HomophonesDocument34 pages150 HomophonesShahzad AliNo ratings yet
- MalagaDocument9 pagesMalagamitricdanilo1No ratings yet
- Ethiopai's Vision For A Climate Resilient Green EconomyDocument36 pagesEthiopai's Vision For A Climate Resilient Green EconomyyaredNo ratings yet
- Navigate Vessel Safetly at The Chittagong Port Bangladesh AnchorageDocument5 pagesNavigate Vessel Safetly at The Chittagong Port Bangladesh AnchorageEmir EnginNo ratings yet
- Basics of Irrigation SchedulingDocument4 pagesBasics of Irrigation SchedulingChala ChimdessaNo ratings yet
- Oscar Wilde's The Star-ChildDocument10 pagesOscar Wilde's The Star-ChildTahira NzimandeNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade Jumbled Words 1Document2 pages5th Grade Jumbled Words 1jairosafrika274No ratings yet
- S9 Q3 Hybrid Module 4 Week 6 and 7 Climatic Phenomena FinalDocument20 pagesS9 Q3 Hybrid Module 4 Week 6 and 7 Climatic Phenomena FinalSally CustodioNo ratings yet
- Aef2 File 2 WordlistDocument4 pagesAef2 File 2 WordlistJEAN-PIERRE RICHARDNo ratings yet
- 2021 Ef 001995Document17 pages2021 Ef 001995Jinxin ZhuNo ratings yet
- Phytogrographical Regions of IndiaDocument16 pagesPhytogrographical Regions of IndiaSukriti GopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Final Technical Report on ethnobotanical resources and livelihoodsDocument65 pagesFinal Technical Report on ethnobotanical resources and livelihoodsAnjuNo ratings yet
- Time Series Forecasting Methods for BusinessesDocument5 pagesTime Series Forecasting Methods for BusinessesDaphane Kate AureadaNo ratings yet
- Commercial Dispatch Eedition 3-31-19Document24 pagesCommercial Dispatch Eedition 3-31-19The DispatchNo ratings yet
- Worksheets: New Delhi - Mumbai - Chennai - Kolkata - Bengaluru - Hyderabad - Kochi - GuwahatiDocument46 pagesWorksheets: New Delhi - Mumbai - Chennai - Kolkata - Bengaluru - Hyderabad - Kochi - Guwahatishreyas100% (2)