Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3RD GRADING - Physics
Uploaded by
LJ Princess Mary MontenegroOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3RD GRADING - Physics
Uploaded by
LJ Princess Mary MontenegroCopyright:
Available Formats
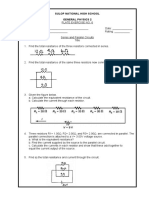
3RD GRADING- PHYSICS
Potential difference- the work done to move positive
CHARGED+ NOT CHARGED= ATTRACT test charge from one location to another.
CHARGED+ CHARGED= REPEL
Charges: Neutral- has equal amount of protons and Capacitor- a device used to store electric charge and
electrons. electrical energy.
Positive- more protons -total charge stored is zero
Negative- more electrons -stores charges
Charging by conduction- transfer of electron by direct It consists of two conducting objects (usually plates or
contact. sheets) separated by some distance.
Charging by induction- electrons can react to the electric
field of a charged object without touching the object Simple capacitor- consists of two parallel metal plates
itself. separated by a small distance.
Only negative charge can move. If the battery voltage is increased, the number of
charges stored in the plates also increase.
Electric charge- the amount of charge that is on or
carried by a particle determines how the particle reacts Law of Conservation of Energy- energy cannot be
to electric fields. created or destroyed but may only change form.
Static electricity- an electrical charge caused by an Conductors- materials that allow the easy flow of
imbalance of electrons on the surface of material. electrons.
Insulators- material that do not allow the easy flow of
Electrostatics- the study of electric charges, forces, and electrons.
fields.
Current- rate of flow of charge
Coulomb’s law- two charged objects attract each other
with a force that is proportional to the charge on the Circuit- complete path for the electrons to follow as they
objects and inversely proportional to the square of the flow, if the path is not complete, there can be no flow
distance. between points.
Short circuit- a circuit which contains little or no
Electric field- a region around a charged particle or resistance.
object within a force would be exerted on other charge
particles or objects. The faster the movement of electron, the higher the
current.
The strength of electric field is operationally defined as
the ratio of the electric force. Large current= many charges flowing
Small current= few charges flowing
Electric flux- the amount of electric field penetrating a
surface area. The flow of electrons is slowed down by any number of
-this is the total number of electric field lines passing a factors:
given area. 1.Materials- what the electrons are moving through.
2.Temperature- how warm or cold the materials are.
Surface area=total area 3.Length- how far the electrons need to move.
4.Cross-section- how wide the area is the electrons are
trying to move.
Gauss’s law- the total electric flux through any closed
surface is proportional to the total (net) electric charge Electromotive force (EMF)- source of the electric current
inside the surface. in every circuit.
-a charge pump
Ex. Batteries and generators
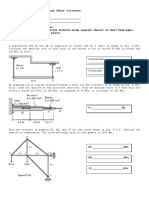
3 types of electric circuits:
1. Series circuits- there is a single conducting path
without junctions for electricity to flow.
2. Parallel circuits- where components are connected
across common points and provides separate
conducting paths for electricity to flow.
3. Complex circuits- with other segments being in series
and other segments being in parallel to take advantage
of the benefits of both.
Resistor- device that offers resistance to flow of charge.
You might also like
- Electric Charge-It Determines The: Gen. Physics 2 Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesElectric Charge-It Determines The: Gen. Physics 2 Lecture NotesDaryllNo ratings yet
- Emags and Circ1Document14 pagesEmags and Circ1Compl3x CSGONo ratings yet
- Physics STM 004 ReviewerDocument3 pagesPhysics STM 004 ReviewerDrake AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Physics Section D-Electricity and MagnetismDocument10 pagesPhysics Section D-Electricity and MagnetismNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Content Basic Terminology Subject Physics Class XII Date 27/03/2020 Subject Teacher Satish PatidarDocument3 pagesContent Basic Terminology Subject Physics Class XII Date 27/03/2020 Subject Teacher Satish PatidarConcepts Classes IndoreNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM LessonDocument8 pagesELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM LessonBernard PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms in Electrostatics and Electricity and MagnetismDocument4 pagesDefinition of Terms in Electrostatics and Electricity and MagnetismCaca HutajuluNo ratings yet
- (Charging by Contact) :: Rubbing of Two Materials Does Not Create AnDocument7 pages(Charging by Contact) :: Rubbing of Two Materials Does Not Create AnErika Jayne TipaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: Coulomb's LawDocument16 pagesElectrostatics: Coulomb's LawTafazzul HazqueelNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electricity: Circuits 1 Fall 2005 Harding University Jonathan WhiteDocument23 pagesFundamentals of Electricity: Circuits 1 Fall 2005 Harding University Jonathan Whitegobra senNo ratings yet
- Technological I-Wps OfficeDocument38 pagesTechnological I-Wps OfficePhilip MiguelNo ratings yet
- Physics 1.8Document14 pagesPhysics 1.8Priya MalpaniNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2Document2 pagesGeneral Physics 2Ryan GañaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electricity: Physics Dr. AlexanderDocument39 pagesFundamentals of Electricity: Physics Dr. AlexanderPatrickNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledJoyce LonzagaNo ratings yet
- P6 NotesDocument5 pagesP6 NotesWaynie SusonNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Notes For Iit Jee 33 PDFDocument19 pagesElectrostatics Notes For Iit Jee 33 PDFDipayan DasNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Notes For Iit Jee 33 PDF PDFDocument19 pagesElectrostatics Notes For Iit Jee 33 PDF PDFAryanNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument18 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsYashwanthNo ratings yet
- RT4 - Reviewer For Comprehensive Exam 1Document11 pagesRT4 - Reviewer For Comprehensive Exam 1Aj PlacidoNo ratings yet
- Coulombs Law, Gauss Law, Electric PotentialDocument50 pagesCoulombs Law, Gauss Law, Electric Potentialbryan valle100% (1)
- Physics 2 ReviewerDocument2 pagesPhysics 2 ReviewerChickenOn TheRoofNo ratings yet
- Kahatdugan NG PhysicsDocument9 pagesKahatdugan NG PhysicsGeminiNo ratings yet
- Gen Phy 2 Week 1Document6 pagesGen Phy 2 Week 1GeminiNo ratings yet
- The Fallacy of Conductors (Eric P. Dollard)Document1 pageThe Fallacy of Conductors (Eric P. Dollard)~ScaLaR~No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 10 ElectricityDocument12 pagesLesson Plan 10 Electricityjatinder kaur100% (7)
- PhysicsDocument2 pagesPhysicsAlyssa BihagNo ratings yet
- Circuits ReviewerDocument5 pagesCircuits ReviewerMatthew JordanNo ratings yet
- Electricity I 1Document9 pagesElectricity I 1Charles Daniel Torre MalolesNo ratings yet
- Generalphysics2 230414042355 d328d383Document55 pagesGeneralphysics2 230414042355 d328d383Idris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Electric Circuits - Vocabulary WordsDocument4 pagesElectricity and Electric Circuits - Vocabulary WordsalmolauraaNo ratings yet
- CoulombsDocument47 pagesCoulombsTrishia LimpinNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument7 pagesDefinitionsAnoushka PradhanNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Strengthin An Uniform Electric FieldDocument12 pagesElectric Field Strengthin An Uniform Electric Fieldadhitya2535No ratings yet
- Bu 2 ReviewerDocument13 pagesBu 2 Reviewercristian borjeNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Is The Study of Stationary Electric Charges and All The Effects They ProduceDocument53 pagesElectrostatics Is The Study of Stationary Electric Charges and All The Effects They ProduceNo PainNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldDocument42 pagesElectric Charges and FieldKunal ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Science Probe 9 Cheat Sheet Ch9-11Document2 pagesScience Probe 9 Cheat Sheet Ch9-11derpNo ratings yet
- Class 12 PhysicsDocument1 pageClass 12 PhysicsIshraq KhanNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument22 pagesElectricity and Magnetismkhrisannmiller12No ratings yet
- Electricity Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument64 pagesElectricity Magnetism and ElectromagnetismFe DNo ratings yet
- Physics Topic 5 Study GuideDocument8 pagesPhysics Topic 5 Study GuideSai 0235No ratings yet
- Electrical Terms (Incomplete)Document1 pageElectrical Terms (Incomplete)Liezel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Hoy Bakla Anong Cnasabe Mo Tungkol Sakin Ha Bakla Ayosin Mo LNG p666 1Document4 pagesHoy Bakla Anong Cnasabe Mo Tungkol Sakin Ha Bakla Ayosin Mo LNG p666 1ixiNo ratings yet
- Electric Current PresentationDocument10 pagesElectric Current PresentationMalik AyazNo ratings yet
- EEE6012 Lecture2Document48 pagesEEE6012 Lecture2hiransfNo ratings yet
- ELL 103 fUNDAMENTALS OF eLECTRICITYDocument4 pagesELL 103 fUNDAMENTALS OF eLECTRICITYHannah Cesaree Mae TadeoNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument39 pagesNotesprabh14jot123No ratings yet
- HandoutsDocument2 pagesHandoutsShiella BaculpoNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge: Topic 1Document36 pagesElectric Charge: Topic 1Muhammad Shaqeem RosdiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1A IntroductionDocument65 pagesChapter 1A IntroductionSiti HajarNo ratings yet
- Basic Principle of ElectricityDocument5 pagesBasic Principle of ElectricityFavour OgbonnaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Electricity Magnetism AnswersDocument3 pagesStudy Guide Electricity Magnetism Answersapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Main Topic Ce0053Document49 pagesMain Topic Ce0053JOSHUA MEYER ANGELESNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 Static ElectricityDocument32 pagesChap 2 Static ElectricityMuhammad MustaqeemNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 (3 Quarter) : Prepared by Engr. Jackielou D. Decena, Ms EceDocument55 pagesGeneral Physics 2 (3 Quarter) : Prepared by Engr. Jackielou D. Decena, Ms EceSpace Monkey100% (1)
- Tema 2 FizikaDocument6 pagesTema 2 Fizika4p4xvyqtfqNo ratings yet
- Electric ChargeDocument17 pagesElectric Chargeashraf khanNo ratings yet
- General Physics - Module 1 - Lesson 1-2Document25 pagesGeneral Physics - Module 1 - Lesson 1-2Desiree Joy Munda AbenionNo ratings yet
- UTS MaterialDocument12 pagesUTS MaterialLJ Princess Mary MontenegroNo ratings yet
- General Physics 4TH GradingDocument2 pagesGeneral Physics 4TH GradingLJ Princess Mary MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Gas Exchange BioDocument29 pagesGroup 4 Gas Exchange BioLJ Princess Mary MontenegroNo ratings yet
- PLATE EXERCISES No. 6Document2 pagesPLATE EXERCISES No. 6LJ Princess Mary MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Hope 4 ReviewerDocument4 pagesHope 4 ReviewerLJ Princess Mary MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Bonding TheoryDocument49 pagesAtomic Structure and Bonding TheoryLJ Princess Mary MontenegroNo ratings yet
- 8rxCAT-en Catalog PDFDocument388 pages8rxCAT-en Catalog PDFanne smithNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 - Normal and Shear Stresses Name: - SectionDocument2 pagesProblem Set 1 - Normal and Shear Stresses Name: - SectionLorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Solutions Chapter 10Document7 pagesSolutions Chapter 10Nama SahajaNo ratings yet
- WMA12 01 Que 20220119Document36 pagesWMA12 01 Que 20220119Mysterio OfficiallyNo ratings yet
- Bose Einstein Condensation ThesisDocument5 pagesBose Einstein Condensation Thesisjessicadeakinannarbor100% (1)
- Lesson 2 Generalized Power FormulasDocument6 pagesLesson 2 Generalized Power Formulasomay12No ratings yet
- The Sokal Hoax Fifteen Years LaterDocument28 pagesThe Sokal Hoax Fifteen Years LaterblandblinnNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics: IntroductionDocument6 pagesSoil Mechanics: IntroductionKhan AdilNo ratings yet
- E705 User ManualDocument26 pagesE705 User ManualBibit GoelNo ratings yet
- Thermal Stress RumusDocument16 pagesThermal Stress RumusVakin Agung PermanaNo ratings yet
- Crossflow Turbine - A DIY Design ManualDocument6 pagesCrossflow Turbine - A DIY Design ManualAbhiroop89% (9)
- CubicandquarticequationsDocument6 pagesCubicandquarticequationssyed junaid ur rehmanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics WorksheetDocument5 pagesThermodynamics WorksheetMalcolmJustMalcolmNo ratings yet
- 4-Thick Cylinders-TutDocument2 pages4-Thick Cylinders-TutMohdYasirNo ratings yet
- Marks 10% of Total Marks For BMCG 2713 (LO2, PO2) Criteria For Assessment Maximum MarksDocument1 pageMarks 10% of Total Marks For BMCG 2713 (LO2, PO2) Criteria For Assessment Maximum MarksSyakir ImanNo ratings yet
- Haul Truck Tire Dynamics Due To Tire Condition PDFDocument12 pagesHaul Truck Tire Dynamics Due To Tire Condition PDFJo2020MeNo ratings yet
- Bright Project Defense 2Document25 pagesBright Project Defense 2bismarkob47No ratings yet
- Irregular Footing Soil PressureDocument1 pageIrregular Footing Soil Pressurejorge01No ratings yet
- Texts in Applied Mathematics: SpringerDocument349 pagesTexts in Applied Mathematics: Springersotorex7777No ratings yet
- Final Exam - Ing Iii 2020B - Campos Martel Lorgio SegundoDocument3 pagesFinal Exam - Ing Iii 2020B - Campos Martel Lorgio SegundoLORGIO SEGUNDO CAMPOS MARTELNo ratings yet
- Why We Study Engineering MathematicsDocument8 pagesWhy We Study Engineering MathematicsDanielNo ratings yet
- Course Structure: B.SC (MSCS)Document3 pagesCourse Structure: B.SC (MSCS)ariNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 3 Dosimetric Quantities and Biological EffectsDocument33 pagesLecture - 3 Dosimetric Quantities and Biological Effectsmz2v8rs7srNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Materials That Absorb WaterDocument28 pagesLesson 1 Materials That Absorb Waterjulie ann macapinigNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal and Random Vibration Testing PrimerDocument6 pagesSinusoidal and Random Vibration Testing PrimerMohamad AsrulNo ratings yet
- (Studies in Advanced Mathematics) Clark Robinson - Dynamical Systems - Stability, Symbolic Dynamics, and Chaos-CRC Press (1994) PDFDocument478 pages(Studies in Advanced Mathematics) Clark Robinson - Dynamical Systems - Stability, Symbolic Dynamics, and Chaos-CRC Press (1994) PDFCarlos GabrielNo ratings yet
- BBT 101Document27 pagesBBT 101Pathya SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Sheiling House School, Kanpur: Video / Audio / Online Sessions Class-XI DDocument1 pageSheiling House School, Kanpur: Video / Audio / Online Sessions Class-XI DShivaNo ratings yet
- 04 TimberDocument30 pages04 TimberolgaNo ratings yet
- Strength Efficiency of Commonly Used Block Work MasonryDocument13 pagesStrength Efficiency of Commonly Used Block Work Masonrymanish_shashikantNo ratings yet