Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pythagore
Pythagore
Uploaded by
ri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesPythagoras was an ancient Greek mathematician who founded the Pythagorean Brotherhood in Croton, Italy around 530 BC. He is most famous for discovering the Pythagorean Theorem, which states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. The theorem is a fundamental concept in geometry that has been proven in multiple ways and has applications in fields like engineering, trigonometry, and calculus. It remains an important mathematical relationship with a long history of influence on subjects from Euclid's geometry to modern interpretations involving complex numbers and non-Euclidean geometries.
Original Description:
Original Title
pythagore
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPythagoras was an ancient Greek mathematician who founded the Pythagorean Brotherhood in Croton, Italy around 530 BC. He is most famous for discovering the Pythagorean Theorem, which states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. The theorem is a fundamental concept in geometry that has been proven in multiple ways and has applications in fields like engineering, trigonometry, and calculus. It remains an important mathematical relationship with a long history of influence on subjects from Euclid's geometry to modern interpretations involving complex numbers and non-Euclidean geometries.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesPythagore
Pythagore
Uploaded by
riPythagoras was an ancient Greek mathematician who founded the Pythagorean Brotherhood in Croton, Italy around 530 BC. He is most famous for discovering the Pythagorean Theorem, which states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. The theorem is a fundamental concept in geometry that has been proven in multiple ways and has applications in fields like engineering, trigonometry, and calculus. It remains an important mathematical relationship with a long history of influence on subjects from Euclid's geometry to modern interpretations involving complex numbers and non-Euclidean geometries.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
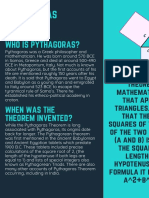
Title: Pythagoras and the Pythagorean Theorem
I. Introduction
A. Pythagoras of Samos
1. Ancient Greek mathematician and philosopher
2. Founded the Pythagorean School
B. Pythagorean Theorem
1. Fundamental concept in geometry
2. Relationship between the sides of a right triangle
II. Pythagoras' Life and Contributions
A. Early Life
1. Born around 570 BC in Samos, Greece
2. Traveled to Egypt and Babylon, learning mathematical and philosophical concepts
B. The Pythagorean Brotherhood
1. Founded a school in Croton, Italy, around 530 BC
2. Focused on mathematics, philosophy, and mysticism
C. Pythagorean Discoveries
1. Pythagorean Theorem
2. Mathematical principles such as ratios and proportionality
3. Music and the harmony of the spheres
D. Influence on Western Mathematics and Philosophy
1. Impact on Euclid's "Elements" and later mathematical developments
2. Connection between mathematics and philosophy
III. The Pythagorean Theorem
A. Statement of the Theorem
1. In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal
to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
2. Mathematically: a² + b² = c²
B. Proof of the Theorem
1. Geometric proof using squares and triangles
2. Algebraic proof using similar triangles
C. Applications of the Theorem
1. Distance calculations in 2D and 3D space
2. Construction and engineering
3. Trigonometry and navigation
IV. Examples and Practical Uses
A. Real-life Examples
1. Calculating distances on maps
2. Determining the length of a ladder needed to reach a certain height
B. Engineering and Architecture
1. Ensuring structural stability in buildings
2. Designing ramps and inclined planes
C. Mathematics and Geometry
1. Pythagorean triples (e.g., 3-4-5, 5-12-13)
2. Trigonometric applications
V. Modern Interpretations and Variations
A. Non-Euclidean Geometry
1. Pythagorean Theorem's validity in different geometries
B. Complex Numbers
1. Extension of the theorem to complex numbers
C. Pythagorean Theorem in Algebra
1. Algebraic proofs and applications
D. Pythagorean Theorem in Calculus
1. Integration and differentiation related to the theorem
VI. Conclusion
A. Pythagoras' legacy in mathematics and philosophy
B. The enduring importance of the Pythagorean Theorem
C. Its application in various fields and disciplines
D. A fundamental concept in geometry with a rich history and ongoing relevance.
You might also like
- Lesson Plan - Pythagorean TheoremDocument3 pagesLesson Plan - Pythagorean TheoremGim Sadol100% (4)
- Maths ProjectDocument25 pagesMaths ProjectArun Ahirwar68% (69)
- Architectural Standard - Paul Calter - Geometry in Art & ArchitectureDocument377 pagesArchitectural Standard - Paul Calter - Geometry in Art & ArchitectureÆon Teseract100% (2)
- First World WarDocument2 pagesFirst World WardefaultNo ratings yet
- The Origin of Angle-Geometry - Solomon GandzDocument31 pagesThe Origin of Angle-Geometry - Solomon GandzGènny GìnnyNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument6 pagesTrigonometryapi-251902500No ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theoram: Essays TopicsDocument3 pagesPythagorean Theoram: Essays TopicsSpirals AcademyNo ratings yet
- 02 GeometryDocument5 pages02 GeometryhongnhNo ratings yet
- Answer SPM Additional Mathematics Project Work 2 2011Document32 pagesAnswer SPM Additional Mathematics Project Work 2 2011Geinini NiniNo ratings yet
- With NameDocument65 pagesWith NameAbdul FattahNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bhs. Inggris Kelompok 5Document13 pagesMakalah Bhs. Inggris Kelompok 521 015 MD GD A Manu PratekaNo ratings yet
- PythagoreanDocument2 pagesPythagoreanMark SmithNo ratings yet
- Story of Trigonometry: BY:-Name: Rakshit Gupta Class: - XTH - B ROLL NO.: - 13Document13 pagesStory of Trigonometry: BY:-Name: Rakshit Gupta Class: - XTH - B ROLL NO.: - 13Akshat JainNo ratings yet
- Persembahan Slaid Utk PameranDocument58 pagesPersembahan Slaid Utk PameranMista VinzNo ratings yet
- The Pythagorean Theorem Concept and ProofDocument1 pageThe Pythagorean Theorem Concept and ProofJejomar MotolNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem Is 250 Words.Document1 pagePythagorean Theorem Is 250 Words.GuNo ratings yet
- History and Nature of Mathematics - by - DR Marsigit MADocument24 pagesHistory and Nature of Mathematics - by - DR Marsigit MAAKANTO NANDINo ratings yet
- Essay AHistoryofMathematicsDocument14 pagesEssay AHistoryofMathematicsZeref V. DragNellNo ratings yet
- Add MathDocument11 pagesAdd MathIzzy WoozieNo ratings yet
- TRIGNOMETRYDocument11 pagesTRIGNOMETRYAditi KumariNo ratings yet
- The Metaphysics of The Pythagorean Theorem Thales Pythagoras Engineering Diagrams and The Construction of The Cosmos Out of Right TrianglesDocument301 pagesThe Metaphysics of The Pythagorean Theorem Thales Pythagoras Engineering Diagrams and The Construction of The Cosmos Out of Right Triangleskamal75% (4)
- Arturo Sangalli-Pythagoras' Revenge - A Mathematical Mystery-Princeton University Press (2009)Document301 pagesArturo Sangalli-Pythagoras' Revenge - A Mathematical Mystery-Princeton University Press (2009)Mónica MondragónNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry and Its Applications: U. DeepikaDocument22 pagesTrigonometry and Its Applications: U. Deepikaletter2lalNo ratings yet
- 3D Structure Analysis Architecture As AnDocument10 pages3D Structure Analysis Architecture As AnKiki WachukaNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem in BusinessDocument4 pagesPythagorean Theorem in BusinessDeelanshiNo ratings yet
- 105Document3 pages105isele1977No ratings yet
- History of TrigDocument19 pagesHistory of TrigacqacqNo ratings yet
- 0005 0008Document4 pages0005 0008AnkitNo ratings yet
- PYTHAGORAS THEOREM Project (Simple Holiday Package)Document8 pagesPYTHAGORAS THEOREM Project (Simple Holiday Package)helloandhaiNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean TheoremDocument1 pagePythagorean TheoremGuNo ratings yet
- Objective:: Study of Various Aspects of Pythagoras TheoremDocument8 pagesObjective:: Study of Various Aspects of Pythagoras TheoremPriyanka PilaniaNo ratings yet
- Geometry DefinitionDocument4 pagesGeometry Definitionapi-174638550No ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Trigonometry (From Greek Trigōnon, "Triangle" and Metron, "Measure"Document4 pagesTrigonometry: Trigonometry (From Greek Trigōnon, "Triangle" and Metron, "Measure"praveen_449No ratings yet
- The Pythagorean TheoremDocument3 pagesThe Pythagorean TheoremMark Cristian SaysonNo ratings yet
- Medical AssistanceDocument2 pagesMedical Assistance;-;No ratings yet
- History Course OverviewDocument12 pagesHistory Course OverviewBuen Caloy LlavoreNo ratings yet
- History of MathematicsDocument11 pagesHistory of MathematicsSsentongo NazilNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document10 pagesUnit 2agre226644No ratings yet
- Add Maths Project FolioDocument29 pagesAdd Maths Project FolioCorbyn BessonNo ratings yet
- MathDocument7 pagesMathalwynlaricaliNo ratings yet
- HBMT4103 710104026050 TrigonometryDocument5 pagesHBMT4103 710104026050 TrigonometryMu'azah Mohd GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics Project Work 3 2001Document40 pagesAdditional Mathematics Project Work 3 2001Mis Adilina100% (3)
- 1.1 Abstract: History of Mathematics GreekDocument15 pages1.1 Abstract: History of Mathematics GreekAnnisa FauziaNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematic Project Work 1/2012 SarawakDocument21 pagesAdditional Mathematic Project Work 1/2012 Sarawakchristie_balan100% (1)
- HBMT 4103Document68 pagesHBMT 4103Aimy RaisNo ratings yet
- The Area of The Square Built Upon The Hypotenuse of A Right Triangle Is Equal To The Sum of The Areas of The Squares Upon The Remaining Sides.Document3 pagesThe Area of The Square Built Upon The Hypotenuse of A Right Triangle Is Equal To The Sum of The Areas of The Squares Upon The Remaining Sides.Richel B. BalidoyNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras TheoremDocument8 pagesPythagoras TheoremhelloandhaiNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean TheoremDocument2 pagesPythagorean TheoremStephenNo ratings yet
- History of TrigonometryDocument3 pagesHistory of Trigonometrymidori_06No ratings yet
- Pythagoras TheoremDocument29 pagesPythagoras TheoremSahil JindalNo ratings yet
- Math 1330Document2 pagesMath 1330Siddharth VNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: "Trig" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument10 pagesTrigonometry: "Trig" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeAurelio BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Arts Design and ArchitectureDocument1 pageArts Design and ArchitectureLouela Jean EspirituNo ratings yet
- The Pythagorean TheoremDocument2 pagesThe Pythagorean Theoremjeehoonkim78No ratings yet
- Father of GeometryDocument11 pagesFather of GeometrymohammedismayilNo ratings yet
- Math ProjectDocument8 pagesMath ProjectknjhNo ratings yet
- Perfect Design: Using Mathematics and Geometry to Build Great Landscape Designs: How to Forever Think Differently about Visual DesignFrom EverandPerfect Design: Using Mathematics and Geometry to Build Great Landscape Designs: How to Forever Think Differently about Visual DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)