Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Muscle Biochemistry
Muscle Biochemistry
Uploaded by
Santino Majok0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views19 pagesMuscle contracts by converting chemical energy from ATP into mechanical motion. The sarcomere is the basic unit of muscle contraction. It involves myosin binding to actin and using ATP to go through conformational changes that pull actin inward, shortening the muscle. Key players in this process are the myosin head hydrolyzing ATP, the formation of actin-myosin complexes, and the power stroke resulting from Pi release followed by ADP release as myosin changes shape.
Original Description:
Biochemistry of muscle
Original Title
Muscle_Biochemistry
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMuscle contracts by converting chemical energy from ATP into mechanical motion. The sarcomere is the basic unit of muscle contraction. It involves myosin binding to actin and using ATP to go through conformational changes that pull actin inward, shortening the muscle. Key players in this process are the myosin head hydrolyzing ATP, the formation of actin-myosin complexes, and the power stroke resulting from Pi release followed by ADP release as myosin changes shape.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views19 pagesMuscle Biochemistry
Muscle Biochemistry
Uploaded by
Santino MajokMuscle contracts by converting chemical energy from ATP into mechanical motion. The sarcomere is the basic unit of muscle contraction. It involves myosin binding to actin and using ATP to go through conformational changes that pull actin inward, shortening the muscle. Key players in this process are the myosin head hydrolyzing ATP, the formation of actin-myosin complexes, and the power stroke resulting from Pi release followed by ADP release as myosin changes shape.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
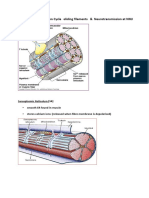
Muscle transduces chemical energy
into mechanical energy.
TheSarcomere is the functional unit
of muscle.
(1) In the relaxation phase of muscle
contraction;
the S-1 head of myosin hydrolyzes
ATP to ADP and Pi,
but these products remain bound. The
resultant ADP and Pi-
myosin complex has been energized
and is in a so called high-energy
conformation.
(2) When contraction of muscle is
stimulated via;
events involving Ca2+, troponin,
tropomyosin, and actin, which are
described below), actin becomes
accessible
and the S-1 head of myosin finds it,
binds it, and
forms the actin-myosin-ADP-Pi complex
indicated.
(3) Formation of this complex promotes the
release of Pi, which initiates the power
stroke. This is followed by release of ADP
and is accompanied by a large
conformational change in the head of
myosin in relation to its tail , pulling actin
about 10 nm toward the center of the
sarcomere.
This is the power stroke.
The myosin is now in a so-called low-energy
state, indicated as actin-myosin.
(4) Another molecule of ATP binds to
the S-1 head, forming an actin-
myosin-ATP complex.
(5) Myosin-ATP has a low affinity for
actin, and actin is thus released.
This last step is a key component of
relaxation and is dependent upon the
binding of ATP to the actin-myosin
complex.
Tropomyosin and the Troponin
Complex
Presentin Thin Filaments Perform
Key Functions in Striated Muscle.
You might also like
- CSCS Study GuideDocument50 pagesCSCS Study GuideMatt Siniscalchi100% (6)
- Biochem Report Muscle and CytoskeletonDocument87 pagesBiochem Report Muscle and CytoskeletonKate Lynne CamonayanNo ratings yet
- Molecular Motors: Ms. M. Banda (B.Pharm, MSC Biochem)Document25 pagesMolecular Motors: Ms. M. Banda (B.Pharm, MSC Biochem)David HamalalaNo ratings yet
- Energy For Muscle ContractionDocument32 pagesEnergy For Muscle ContractionAndy SkatePunkNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesAnaphy Muscular SystemYo1No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document25 pagesChapter 5أمال داودNo ratings yet
- MUSCLESDocument3 pagesMUSCLESalihusseinNo ratings yet
- 122 3 Long Exam: Muscles and Animal MovementDocument3 pages122 3 Long Exam: Muscles and Animal MovementPia BlancaflorNo ratings yet
- Myofilaments: A) Thick Filaments - The Thick Filament Is Composed of Myosin. TheDocument3 pagesMyofilaments: A) Thick Filaments - The Thick Filament Is Composed of Myosin. TheMichaelJackson Didnt TouchMeNo ratings yet
- Lifs 1902 Muscle Lecture #2 2021-1Document109 pagesLifs 1902 Muscle Lecture #2 2021-1KenjiNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology (Autosaved)Document16 pagesAnimal Physiology (Autosaved)Shalinie ChittarasuNo ratings yet
- Physio NoteDocument135 pagesPhysio NoteZiyad AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Muscle Contraction DMSDocument27 pagesMuscle Contraction DMSHany Theresya Vilienster100% (2)
- Miranti Dewi Pramaningtyas Departemen Fisiologi FK UIIDocument37 pagesMiranti Dewi Pramaningtyas Departemen Fisiologi FK UIIFathiZainurohmanNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Muscle Contraction 2010Document69 pagesKuliah Muscle Contraction 2010bagir_dm10No ratings yet
- Fisiologi MusculoskeletalDocument25 pagesFisiologi MusculoskeletalSuardimanAchoNo ratings yet
- Muscle Mechanics and Control: Adenosine TriphosphateDocument22 pagesMuscle Mechanics and Control: Adenosine TriphosphateSoji AdimulaNo ratings yet
- Muscle: Myofilaments: Actin & MyosinDocument23 pagesMuscle: Myofilaments: Actin & MyosinDarla FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Excitation Contraction CouplingDocument34 pagesExcitation Contraction CouplingRUdraNo ratings yet
- Shalini Menon - EXERCISE PHYSIOLOGYDocument23 pagesShalini Menon - EXERCISE PHYSIOLOGYriturajrastogibpt22-26No ratings yet
- Individual Tissue ConspeqtiDocument16 pagesIndividual Tissue ConspeqtianaNo ratings yet
- Physiological Change During ExerciseDocument3 pagesPhysiological Change During ExerciseClairyssa Myn D CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Muscle Contraction: Section G1 - Group 5Document31 pagesMuscle Contraction: Section G1 - Group 5anon_622497859No ratings yet
- Motor ProteinsDocument9 pagesMotor Proteinsazazel666No ratings yet
- Muscle ContractionDocument15 pagesMuscle ContractionAdam PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Nerve Muscle Physiology 4Document19 pagesNerve Muscle Physiology 4priyanshuraj717No ratings yet
- MusclesDocument29 pagesMusclesMaaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle ContractionDocument5 pagesSliding Filament Theory of Muscle ContractionRica NorcioNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 3. Physiology of Muscles: 1. Functional Anatomy of Skeletal MuscleDocument11 pagesLECTURE 3. Physiology of Muscles: 1. Functional Anatomy of Skeletal MuscleVivek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Biology - Topic 7Document15 pagesUnit 5 Biology - Topic 7ladzville1014860100% (1)
- DR - Nuraiza Meutia, M.Biomed: Dept - Fisiologi FK USU Prof. Yasmeiny YazirDocument49 pagesDR - Nuraiza Meutia, M.Biomed: Dept - Fisiologi FK USU Prof. Yasmeiny YazirXeniel AlastairNo ratings yet
- 9# Fisiologi OtotDocument25 pages9# Fisiologi OtotfaizalalkharismaNo ratings yet
- Week 8 Anph111 MidtermDocument17 pagesWeek 8 Anph111 MidtermCASTRO, ANDREI KARL Z.No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Muscle PhysiologyDocument21 pagesChapter 12 - Muscle PhysiologyAlec McIntoshNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15. Biochemistry of Muscle, Connective and Nervous Tissues, Markers of Damage, PathologyDocument46 pagesLecture 15. Biochemistry of Muscle, Connective and Nervous Tissues, Markers of Damage, PathologyВіталій Михайлович НечипорукNo ratings yet
- Sliding Filament Model of ContractionDocument3 pagesSliding Filament Model of ContractionRATU ZULFI AMALIAHNo ratings yet
- L3. Muscle Contraction Cycle - Sliding Filaments & Neurotransmission at NMJDocument9 pagesL3. Muscle Contraction Cycle - Sliding Filaments & Neurotransmission at NMJYolande ClothierNo ratings yet
- 225 AssignmentDocument7 pages225 AssignmentsadiqNo ratings yet
- Control of Skeletal Muscle ContractionsDocument3 pagesControl of Skeletal Muscle ContractionsTofik MohammedNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Muscle ContractionDocument3 pagesPhysiology of Muscle ContractionAJ AbraganNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument9 pagesThe Muscular SystemKathleenJoyGalAlmasinNo ratings yet
- Muscle Physiology and NeurophysiologyDocument68 pagesMuscle Physiology and NeurophysiologyAlan MagpantayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Structure and FunctionDocument15 pagesChapter 1 - Structure and Functiontjewert23No ratings yet
- Myosin, Actin & Contraction NotesDocument4 pagesMyosin, Actin & Contraction NotesGhazali BalochNo ratings yet
- 16 Skeletal Muscle 3 - Electrical Phenomena in Contracting Skeletal Muscle PDFDocument1 page16 Skeletal Muscle 3 - Electrical Phenomena in Contracting Skeletal Muscle PDFVikiNo ratings yet
- FILE - 20220120 - 124136 - Cơ TimDocument3 pagesFILE - 20220120 - 124136 - Cơ TimĐào Ngô AnhNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Otot Dan TulangDocument26 pagesMetabolisme Otot Dan TulangKhalida Nacharyta FailasufiNo ratings yet
- 7 Actin Bascis Regulation and MuscleDocument25 pages7 Actin Bascis Regulation and Musclezj5bnxbymzNo ratings yet
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument25 pagesMuscle PhysiologyhazelelNo ratings yet
- Rigor MortisDocument2 pagesRigor Mortisapi-238242929No ratings yet
- L 9 MyosinDocument22 pagesL 9 Myosindiksha singhNo ratings yet
- Muscle Contraction & Purkinje FibresDocument4 pagesMuscle Contraction & Purkinje FibresWilson NgNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision Notes: Topic 7 Run For Your Life: Slow Twitch MusclesDocument18 pagesBiology Revision Notes: Topic 7 Run For Your Life: Slow Twitch MusclesDontNo ratings yet
- (Review) Winter Term Test Review AnswersDocument5 pages(Review) Winter Term Test Review AnswersJamie SamuelNo ratings yet
- Muscle System 2019Document32 pagesMuscle System 2019ZNA EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- Muscle Physiology NotesDocument20 pagesMuscle Physiology NotesPisiform90100% (1)
- Connective Tissue:myofibril and Muscle ContractionDocument17 pagesConnective Tissue:myofibril and Muscle ContractionJayeeta BhadraNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsFrom EverandThe Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Metabolism1Document61 pagesCarbohydrates Metabolism1Santino MajokNo ratings yet
- TCA Cycle, ETC, and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument56 pagesTCA Cycle, ETC, and Oxidative PhosphorylationSantino MajokNo ratings yet
- TCA CycleDocument35 pagesTCA CycleSantino MajokNo ratings yet
- Lipid TransportDocument31 pagesLipid TransportSantino MajokNo ratings yet
- Human Genetics VariationDocument48 pagesHuman Genetics VariationSantino MajokNo ratings yet
- 1.acids PH and BuffersDocument25 pages1.acids PH and BuffersSantino MajokNo ratings yet