Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BEEE Unit 4.3
Uploaded by
NivashCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BEEE Unit 4.3
Uploaded by
NivashCopyright:
Available Formats
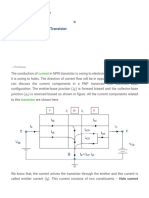
Unipolar Junction Transistor
n-p-n Transistor INTRODUCTION
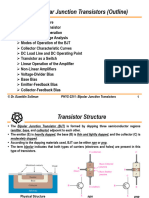
Bipolar Junction Transistor
p-n-p Transistor
Working of a n-p-n transistor
Energy Bands in Solids
Working of a p-n-p transistor
TRANSISTOR OPERATION INTRODUCTION Semiconductors
Current components in a transistor
Current Amplification Factor (α ) Symbol of Diode
Common – Base (CB) configurations:
Total Collector Current Working Principle of Diode
DIODE
Current Amplification Factor (β) Types of Diode
COMMON-EMITTER (CE) CONFIGURATION TRANSISTOR CIRCUIT CONFIGURATIONS
Total Collector Current
Current Amplification Factor(γ) COMMON – COLLE CTOR (CC) CONFIGURATION Forward Biasing Characteristic of Diode
Reverse Biasing Characteristic of Diode
E arly effect (or) Base – Width modulation DIODE CHARACTERISTICS Avalanche Breakdown
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
SEMICONDUCTOR DIODE AND BIPOLAR Zener Effect
Output Characteristics
JUNCTION TRANSISTOR AND
Punch Through (or) Reach Through APPLICATIONS P-N JUNCTION DIODE AND CHARACTERISTICS OF P-
N JUNCTION
Input Impedance (hib)
Output Admittance (hob) P-N Junction Diode Equation
Forward Current Gain (hfb) Transistor Parameters P-N Junction Band Diagram APPLICATIONS OF DIODES
Reverse Voltage Gain (hrb)
Circuit Diagram of Half Wave Rectifier
HALF WAVE DIODE RECTIFIER
Input Characteristics
Input voltage and Output Voltage Waveforms
Output Characteristics
FULL WAVE DIODE RECTIFIER Circuit Diagram of Full Wave Diode Rectifier
Active Region
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMMON-EMITTER CIRCUIT RECTIFIERS HALF WAVE RECTIFIERS
Saturation Region
FULL WAVE RECTIFIERS
Cut-Off Region
BRIDGE RECTIFIERS
Input Characteristics
Output Characteristics Characteristics of common collector circuit
You might also like
- 1 Electronic SymbolsDocument33 pages1 Electronic SymbolsOnil Alex VeranoNo ratings yet
- Computed Radiographic Testing (CRT) Qualification Report: Rev. ADocument12 pagesComputed Radiographic Testing (CRT) Qualification Report: Rev. ATrung Tinh HoNo ratings yet
- IET Poster SymbolsDocument1 pageIET Poster SymbolsTony De GennaroNo ratings yet
- LV Relay SettingDocument12 pagesLV Relay SettingRatheesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 18CS44 MES Module3Document184 pages18CS44 MES Module3Madhu CkNo ratings yet
- Newnes Electronics Engineers Pocket BookFrom EverandNewnes Electronics Engineers Pocket BookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- GRS 77/GMU 44: Installation ManualDocument65 pagesGRS 77/GMU 44: Installation Manualtunahan karacaNo ratings yet
- VD Calculation & Cable Schedule for 35 MLD STP at Zoo IndoreDocument4 pagesVD Calculation & Cable Schedule for 35 MLD STP at Zoo IndoreElectrical RadicalNo ratings yet
- High Definition Induction Log (HDIL)Document10 pagesHigh Definition Induction Log (HDIL)Djibril Idé AlphaNo ratings yet
- Databook Zener Diodes (SMD) PDFDocument369 pagesDatabook Zener Diodes (SMD) PDFgondoNo ratings yet
- Relay Symbols and Fuction NumDocument14 pagesRelay Symbols and Fuction NumPrasanna DharmapriyaNo ratings yet
- MA5600T&MA5603T&MA5608T Hardware Description 23Document973 pagesMA5600T&MA5603T&MA5608T Hardware Description 23ibitisamNo ratings yet
- AP Chem Lab Report - Galvanic CellDocument8 pagesAP Chem Lab Report - Galvanic CellGokce GozekNo ratings yet
- Reference Power Systems Protection Handbook PDFDocument196 pagesReference Power Systems Protection Handbook PDFJavier Condori Quilla100% (1)
- Basic Electronics by Bakshi PDFDocument226 pagesBasic Electronics by Bakshi PDFnijuNo ratings yet
- 1 - Schematic DiagramsDocument32 pages1 - Schematic DiagramsAgustina Gutierrez PariNo ratings yet
- ECE502 - BJT and FET Transistor FundamentalsDocument5 pagesECE502 - BJT and FET Transistor FundamentalsMurad89No ratings yet
- EDC PreparationDocument2 pagesEDC PreparationUppalaguptam Hari Satya PriyaNo ratings yet
- Modulation Formats Using Direct DetectionDocument63 pagesModulation Formats Using Direct DetectionErasmo VizzaccaroNo ratings yet
- Current Components in A Transistor - Electrical4uDocument8 pagesCurrent Components in A Transistor - Electrical4umanoj reddyNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument17 pagesElectronicsxkryxxzNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Test Results For DBDocument6 pagesSchedule of Test Results For DBAtish KissoonNo ratings yet
- BJT CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesBJT CharacteristicsTadapaneni SnehithaNo ratings yet
- TL071ckt PDFDocument1 pageTL071ckt PDFAhmad FauziNo ratings yet
- Schematic (Each Amplifier) : SLOS080J September 1978 Revised March 2005Document1 pageSchematic (Each Amplifier) : SLOS080J September 1978 Revised March 2005killerjackassNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Thyristor PDFDocument6 pagesCharacteristics of Thyristor PDFAkcfaNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Lecture NotesDocument39 pagesChapter4 Lecture Notesfarahk77737No ratings yet
- Load PullDocument2 pagesLoad PullNabil DakhliNo ratings yet
- 28 Semiconductors Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument7 pages28 Semiconductors Formula Sheets QuizrrDhairya SharmaNo ratings yet
- units-and-symbolsDocument8 pagesunits-and-symbolsstellariumNo ratings yet
- Active Components Part 1Document3 pagesActive Components Part 1Dhiraj PatilNo ratings yet
- Strong Fet Irfb7430Pbf: V 40V R Typ. 1.0M Max. 1.3M I 409A I 195ADocument10 pagesStrong Fet Irfb7430Pbf: V 40V R Typ. 1.0M Max. 1.3M I 409A I 195AdixonNo ratings yet
- Beee 4Document42 pagesBeee 4SARTHAK SHROFF (RA2111030010023)No ratings yet
- Reconfigurable AntennaDocument29 pagesReconfigurable AntennaBalaraviteja KunaniNo ratings yet
- Module-5 SemiconductorsDocument9 pagesModule-5 SemiconductorsKedar PunaginNo ratings yet
- Study of BJT: Presented by Dr. Anita K.Patil (PHD Electronics) Professor & Head E&TcDocument43 pagesStudy of BJT: Presented by Dr. Anita K.Patil (PHD Electronics) Professor & Head E&TcTushar ParmarNo ratings yet
- ACION 1042 1G Datasheet RevO 20190612 Du ThauDocument8 pagesACION 1042 1G Datasheet RevO 20190612 Du ThauHoa TongNo ratings yet
- 2sc6011 Ds enDocument7 pages2sc6011 Ds enCah YonoNo ratings yet
- 28 Semiconductors Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument5 pages28 Semiconductors Formula Sheets QuizrrMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)Document23 pagesLesson 7 Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)Chacko MathewNo ratings yet
- 28 Semiconductors Formula Sheets Getmarks AppDocument7 pages28 Semiconductors Formula Sheets Getmarks Appf20230796No ratings yet
- RINA LV Relay Settings-11062021Document4 pagesRINA LV Relay Settings-11062021rahul patraNo ratings yet
- BXE(UNIT-2)(PPT) (1)Document220 pagesBXE(UNIT-2)(PPT) (1)Atharv DanaveNo ratings yet
- 5.2. HVDCDocument40 pages5.2. HVDCDavid GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices and ApplicationsDocument89 pagesSemiconductor Devices and ApplicationsMahendra DixitNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Transistors Opamp: December 17, 2021 1Document73 pagesUnit 2 Transistors Opamp: December 17, 2021 1Abhishek SataleNo ratings yet
- Irl40b215 N Mos 40V 140aDocument10 pagesIrl40b215 N Mos 40V 140arem remNo ratings yet
- 01-1 Intro To Radio Systems 2010-05-31-R10ADocument25 pages01-1 Intro To Radio Systems 2010-05-31-R10AMehza SayedNo ratings yet
- DRA OverviewDocument6 pagesDRA OverviewQuan nguyen hongNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument2 pagesDatasheetRobertoNo ratings yet
- SentinelDocument4 pagesSentinelBunea PetricaNo ratings yet
- KP201-CC - CV Mode Charger Design Spreadsheet 24V 1.5aDocument8 pagesKP201-CC - CV Mode Charger Design Spreadsheet 24V 1.5aVishal dtuNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Phase Controlled ConvertersDocument102 pagesUnit Ii Phase Controlled ConverterscoolrajeeeNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Basic Circuit Theory: Graphics Used With Permission From AspencoreDocument47 pagesIntroduction and Basic Circuit Theory: Graphics Used With Permission From AspencoreManigandanNo ratings yet
- Transistor DesignDocument51 pagesTransistor DesignJohn GentileNo ratings yet
- SCNAKODA-1Document5 pagesSCNAKODA-1ChanakyaNo ratings yet
- 2SB892/2SD1207: Large-Current Switching ApplicationsDocument4 pages2SB892/2SD1207: Large-Current Switching ApplicationsIrwantoirwanNo ratings yet
- Rotary Encoders Tech en 180917 WDocument6 pagesRotary Encoders Tech en 180917 Wphth411No ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument63 pagesTransistorsSoumitra MahatoNo ratings yet
- Non-Contact Shaft-to-Shaft Rotary Torque Sensor With EncoderDocument3 pagesNon-Contact Shaft-to-Shaft Rotary Torque Sensor With EncoderMichaelNo ratings yet
- PSM Series: Feed-Through Insertion LossDocument3 pagesPSM Series: Feed-Through Insertion Lossisma807No ratings yet
- Fuzzy Logic Microcontroller Implementation FOR Motor Speed ControlDocument6 pagesFuzzy Logic Microcontroller Implementation FOR Motor Speed ControlMorel SangangNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Tensite Batteries AGM 12 300Document3 pagesDatasheet Tensite Batteries AGM 12 300Juan F. MarínNo ratings yet
- EK-RA6M4 Example Project BundleDocument6 pagesEK-RA6M4 Example Project Bundlemar_barudjNo ratings yet
- Multiturn Solid Shaft Encoder: 1 M4 Depth 6 MMDocument2 pagesMultiturn Solid Shaft Encoder: 1 M4 Depth 6 MMSoha EzzaldenNo ratings yet
- SF15-SFX25 DS en PDFDocument2 pagesSF15-SFX25 DS en PDFpradityo jwuNo ratings yet
- Chinese PL 2023Document50 pagesChinese PL 2023mohamadNo ratings yet
- EX NO 3 Temperature MonitoingDocument3 pagesEX NO 3 Temperature MonitoingP.Rajeswari PSG-PTCNo ratings yet
- Pe - Chapter 4Document40 pagesPe - Chapter 4Lê ĐạtNo ratings yet
- HVDC Asemavastuuhenkilon Katselmus FennoSkanDocument24 pagesHVDC Asemavastuuhenkilon Katselmus FennoSkanLauri LahtinenNo ratings yet
- AC Combiner Box Specification 400vac)Document7 pagesAC Combiner Box Specification 400vac)emilNo ratings yet
- Hall Sensor KSY 13: Data Sheet 1 1999-04-01Document4 pagesHall Sensor KSY 13: Data Sheet 1 1999-04-01Wilker Iuri SouzaNo ratings yet
- Entrelec 05Document56 pagesEntrelec 05baurzhan.kunkuzhayevNo ratings yet
- Product SpecificationDocument58 pagesProduct Specification123No ratings yet
- Tdq-172718De-65Fv02: Xxpol 1710 2690Mhz×2 65° 18dbi 0° 10° Manual or by Optional Rcu (Remote Control Unit) AntennaDocument1 pageTdq-172718De-65Fv02: Xxpol 1710 2690Mhz×2 65° 18dbi 0° 10° Manual or by Optional Rcu (Remote Control Unit) Antennakamel7777100% (1)
- Fyreye Mkii Addressable Detector Bases: (Mkii-Cb, Mkii-Cb/D, Mkii-Ib, Mkii-Iso, Mkii-Cbi & Mkii-Cb/Dap)Document2 pagesFyreye Mkii Addressable Detector Bases: (Mkii-Cb, Mkii-Cb/D, Mkii-Ib, Mkii-Iso, Mkii-Cbi & Mkii-Cb/Dap)motaNo ratings yet
- x86 StderrDocument3 pagesx86 Stderromreth nhemchanNo ratings yet
- RTD Temperature Sensor Experiment GuideDocument4 pagesRTD Temperature Sensor Experiment GuideHem DaveNo ratings yet
- Ziv M0rtvp1812iv04Document378 pagesZiv M0rtvp1812iv04Muhammad YusriNo ratings yet
- A Project Reports On SMOKE DETECTORDocument27 pagesA Project Reports On SMOKE DETECTORd3rfrefrfNo ratings yet
- Fire Alarm Siren BaseDocument5 pagesFire Alarm Siren BaseLado RostiashviliNo ratings yet
- PW460 Universal Test System SpecificationsDocument1 pagePW460 Universal Test System SpecificationsAdrian PramantaNo ratings yet
- AIR-Intelligence Manual - 33-308100-003 - ASD-640Document84 pagesAIR-Intelligence Manual - 33-308100-003 - ASD-640Andrew PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Application Note: KVP Measurements On Ge Amx-4Document15 pagesApplication Note: KVP Measurements On Ge Amx-4Bashir MtwaklNo ratings yet