Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To The Human Body
Uploaded by
Anna Carmella PascualOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To The Human Body
Uploaded by
Anna Carmella PascualCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to the human • If you did something like
body exercise or running and
you’re not sick then your
• Importance, health BP goes high or low
awareness • Physical response to
Anatomy environmental change
• The study of the Hypothalamus- responsible for
structure of the body and our feelings
how the body parts are Structural and Functional
organized. Organization
• Where are your parts, how
do we distinguish body 6 levels from chemical to
parts, forms of the human organism
parts !. Chemical
• Structural details
• Smallest level
Physiology
• Chemical first because
• Body function/ body our body is made up of
process. chemicals
• What they do and how they 2. Cellular
do it.
• Cells: basic units of
Gross anatomy life
• Large or something we can • Compartments and
easily distinguish organelles
Regional 3. Tissue
• Certain areas of the body • Made up of a group of
cells with a similar
Systematic structure that performs a
similar function
• Best for relating
structure to function 4. Organs
Surface Anatomy • Similar tissues that
group together in
• Superficial different proportion
shapes/marking
5. Organ system
Heart rate response
• Group of organs
1. Pathologic response
contributing to some
• Didn’t do anything but function
the bp suddenly goes up
or low 6. Organism
• May health problems or
• All organ systems working
may sira sa hormones
together
2. Physiologic Response
Organ System and Major • Brings oxygen to the
Function blood and remove carbon
dioxide from the body.
Integumentary
Digestive system
• Skin, hair, nails, sweat
glands • Mouth, esophagus,
• Isolation of the body, stomach,small and large
protecting the body from intestine,rectum,, and
the sun/ environmental anus.
hazard • Grind or convert food
into a simpler substance
Skeletal system
• Eliminate indigestible
• Protects and support body waste
(soft and vital parts) • Large intestine absorb
• Joints for movements undigested food fluid and
• Bone marrow produce blood older cell.
cells Urinary system
Muscular
• 2 kidneys, 2 bladder and
• Construction of muscle urethra
for posture. • Formation and elimination
• Back muscle work to week of homeostasis
us upright or postured • Filter our excess fluid
from the bloodstream.
Nervous
Characteristic of life
• Control the
sensory/reflex Organization
• Brain,nerves,spinal cord, • Functional
motor structure interrelationship between
Endocrine parts (similarity)
• Glands; produce growth Metabolism
hormones that go to the • Sum of all chemical and
bone for growth. physical change
• Pancreas, ovary, testis sustaining an organism
Lymphatic system • Ability to acquire and
use energy in support of
• Immune system; defense these changes
mechanism
Facts
Respiratory system
Chocolate doesn’t make
• Lungs, nasal cavities, you/the child hyper, it
pharynx, trachea, won’t reach the brain.
bronchi.
Good hormone is responsible
for it; it is sweet.
Responsiveness EX. Body temp, blood glucose
level, heart and respiratory
• Ability to sense and rate, blood pressure, and
respond to blood cell count.
environmental changes
• Includes both internal Set point
and external
• Normal or average value
environment.
of a variable
Growth
Normal range
• Can increase in size
• The normal extent of
• Size of cells, group of increase or decrease
cells, extracellular around asset point
materials.
Negative feedback loop
Development
• Mechanism that maintains
• Changes in form and size homeostasis.
• Change in cell structure • If there’s a change in
and function from value or it exceeds the
generalized to normal range or
specialized. unbalanced, negative
Difference between growth feedback will balance it
and development
Components of negative
feedback
1. Receptor– detects change
in variable
2. Control center- receives
receptor’s signal.
(Sasabihin kay effector
Homeostasis kung ano gagawin)
3. Effector- the action;
• Balance point directly causes change in
• A state of balance variable. Is a muscle or
among all the body gland that secretes/
systems needed for the produce
body to survive and
function correctly Positive feedback loop
• Maintenance of • Makes it worst
constant internal • Kung tumaas, tataasan pa;
environment pag bumababa, babaan pa
Variables Ex. Lactating, contraction in
• Measure of body property giving birth
that may change in value
Terminology of body planes • Towards front
Anatomical position
• Person standing erect
with face and palm
forward
• It is called superior
Medial
• Towards the midline
Supine Lateral
• Person lying face up palm • Away from the midline
downward
medial
Prone
Axial Body
• Person lying face down
(naka dapa) • found around the vertical
axis of the body and
includes the skull,
vertebral column, sternum
Superior (cranial)(upper) (breastbone), and ribs.
• Toward the head end of Appendicular Body
the of the body
• consists of the upper and
Inferior (caudal)(lower) lower limbs and the
girdles that attach the
• Away from the head;
limbs to the axial
skeleton.
AX Body AP Body
Posterior (dorsal)
• Towards back
Anterior (ventral) Proximal (proximity)
• closer to the axial body; • divide body into superior
towards the trunk and inferior
Distal (distant)
• away from the axial body:
further from the trunk
4 abdominal quadrants
Superficial (surface) Left and right lower quadrant,
left and right upper quadrant
• If we move closer to the
surface of the body
• closer to the surface of
the body
Deep
away from the surface
9 abdominal regions
Right and left hypochondriac,
Epigastric, Right and left
lumbar, Umbilical, Right and
left iliac, Hypogastric region
4 major types of body plane
S- SAGITTAL (VERTICAL)
• divides body from left
and right from top to
bottom
Body Cavities
O- OBLIQUE
• stars from top; ventral
• odd angles and dorsal
F- FRONTAL/ coronal (VERTICAL) • separate; spaces
• divides the body into Mediastinum
anterior and posterior
• space between lungs
T-TRANSVERSE (HORIZONTAL)
Thoracic cavity:
• Space w/in chest wall and
diaphragm contains heart
and lungs
Abdominal Cavity
• Spaces between diaphragm
and pelvis
Pelvic Cavity
• space within the pelvis
FACTS
w/out cavities organs or heart
and thorax will make friction
that will damage them
heart and thorax have diff
cavities
every time heart contract,
blood vessels get cracks and
tissue repairs it.
You might also like
- Outline of Anatomy and Physiology (Prelim-Midterm)Document11 pagesOutline of Anatomy and Physiology (Prelim-Midterm)Jhason John J. Cabigon100% (3)
- Principles and Practice of Stress Management, Fourth Edition (Paul M. Lehrer, Robert L. Woolfolk)Document691 pagesPrinciples and Practice of Stress Management, Fourth Edition (Paul M. Lehrer, Robert L. Woolfolk)priyadarshini100% (3)
- An Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology MidwiferyDocument108 pagesAn Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology MidwiferyGayuh Kartika100% (3)
- Carotenoids in Nature - Biosynthesis, Regulation and FunctionDocument454 pagesCarotenoids in Nature - Biosynthesis, Regulation and FunctionyaswanthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Human Body Anatomy: Cute Si SachikoDocument236 pagesChapter 1: The Human Body Anatomy: Cute Si SachikoKristil Chavez100% (1)
- Anaphy (Lec & Lab)Document16 pagesAnaphy (Lec & Lab)lavetorianicholeNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Reviewer MidtermDocument23 pagesANAPHY Reviewer MidtermCherubin DacumaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Human Body Anatomy: Cute Si SachikoDocument100 pagesChapter 1: The Human Body Anatomy: Cute Si SachikoRAFAEL PINEDANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Noteserika sabelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologylectureDocument46 pagesAnatomy and Physiologylecturequehaizelmaepau31No ratings yet
- The Human Body An OrientationDocument6 pagesThe Human Body An OrientationPrecious CortadoNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument106 pagesAnaphyKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Human Body ReviewerDocument20 pagesHuman Body ReviewerVictoria Ellex TiomicoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2022 1Document78 pagesAnatomy 2022 1kel GetanehNo ratings yet
- Happ Chapter 1Document9 pagesHapp Chapter 1Raniel SilimNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Human Organism SCDocument110 pagesWeek 1 - Human Organism SCJackieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document22 pagesChapter 3ulynieveraNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Modules 1 7 ReviewerDocument24 pagesAnaphy Modules 1 7 ReviewerJAYMAYMA ELGARIONo ratings yet
- HR Quiz 2 ReviewerDocument2 pagesHR Quiz 2 ReviewerNathaniel LinaoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument21 pagesAnaphy ReviewerBianca Paulyn CastilloNo ratings yet
- Anaphy TransesDocument3 pagesAnaphy TransesJoyce ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- Importance of Anatomy & Physiology: (Nur 1101) Chapter 01: The Human OrganismDocument5 pagesImportance of Anatomy & Physiology: (Nur 1101) Chapter 01: The Human OrganismRycel ChloeNo ratings yet
- 01 A - Human AnatomyDocument23 pages01 A - Human Anatomymat rodNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyTreshia SusonNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Human Body: - AnatomyDocument28 pagesAn Introduction To The Human Body: - AnatomyZakiyahulfahdwNo ratings yet
- 06 Inquirybio ch06Document42 pages06 Inquirybio ch06HabzboiiNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Human Body: - AnatomyDocument28 pagesAn Introduction To The Human Body: - AnatomydishkuNo ratings yet
- The Human Body SystemsDocument41 pagesThe Human Body SystemsAnthony FajardoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy TransDocument5 pagesAnaphy TransMARYA AJI ADANNo ratings yet
- Human OrganismDocument117 pagesHuman OrganismLYRA GUEVARRANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document40 pagesChapter 1John Lloyd EspirituNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 - Introduction To Human Physiology and Cell Physiology PowerpointDocument43 pagesWEEK 1 - Introduction To Human Physiology and Cell Physiology PowerpointJulia MundoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chap1 TransesDocument4 pagesAnaphy Chap1 TransesSophia Margarette CawalingNo ratings yet
- A. Module 1.1 (The Human Body)Document39 pagesA. Module 1.1 (The Human Body)Violet andfriendsNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument49 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyAnthonio Muenho100% (1)
- Chapter 1 PPT CRLDocument40 pagesChapter 1 PPT CRLRozel EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- 1 HomeostasisDocument19 pages1 HomeostasisRulani PrinceNo ratings yet
- Unit 1B - Characteristics of LifeDocument16 pagesUnit 1B - Characteristics of LifeRodge AniceteNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Prelim ReviewerDocument12 pagesAnaphy Prelim ReviewerJamaica TuellaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument141 pagesAnaphy ReviewerStar ChainzNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis and Cell StructureDocument10 pagesHomeostasis and Cell Structuredenniesjrelefante101622No ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument15 pagesAnaphy ReviewerAltheya MagbooNo ratings yet
- The Human Body: An Orientation: Slides 1.1 - 1.8Document39 pagesThe Human Body: An Orientation: Slides 1.1 - 1.8PiereNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument15 pagesAnaphyjeraldine gumpalNo ratings yet
- Beef Module 2Document28 pagesBeef Module 2Allena VillarinNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Homeostasis 2023Document46 pagesWeek 1 Homeostasis 2023Hashley CastellyNo ratings yet
- CH 01 Lecture OverviewDocument6 pagesCH 01 Lecture OverviewAccey RamirezNo ratings yet
- Ana Lect & Lab ReviewerDocument11 pagesAna Lect & Lab ReviewerLora Mae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Intro To PhysiologyDocument29 pagesLecture 1 - Intro To PhysiologyYu muhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document15 pagesChapter 2ulynieveraNo ratings yet
- Medterm NotesDocument23 pagesMedterm NotesRaniel SilimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 LectureDocument13 pagesChapter 1 Lecturestepps09No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument68 pagesHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyAbby Umali-Hernandez100% (3)
- Organization of The Human BodyDocument20 pagesOrganization of The Human Bodycristina caratihanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy LectureDocument20 pagesAnatomy Lectureshiba ngujo100% (1)
- Chapter 17 Biology 2nd Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT by FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Document36 pagesChapter 17 Biology 2nd Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT by FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Suffa Academy100% (3)
- Organization and General Plan of The BodyDocument4 pagesOrganization and General Plan of The BodyJeanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without NotesDocument48 pagesLecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without NotesLuna EclipseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Atlas ADocument78 pagesChapter 1 Atlas Agabbs_123No ratings yet
- Study This To Ace The Pre-Quarterly Test in Biology!Document70 pagesStudy This To Ace The Pre-Quarterly Test in Biology!Rose MendizabalNo ratings yet
- 2 - HomeostasisDocument12 pages2 - HomeostasisJustin FungNo ratings yet
- Octopuses: Quick GuideDocument2 pagesOctopuses: Quick GuideHarshitaNo ratings yet
- Bpud, PathoDocument2 pagesBpud, PathoSheng GosepNo ratings yet
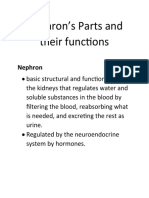
- Nephron WTFDocument9 pagesNephron WTFCatherine AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease: Neuroimaging Clinics of North America December 2005Document28 pagesPathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease: Neuroimaging Clinics of North America December 2005AnisNo ratings yet
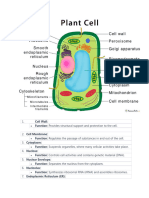
- CellsDocument4 pagesCellscalustre2016No ratings yet
- Acute InflammationDocument22 pagesAcute InflammationNicole Mae DavidNo ratings yet
- Case Study Bronchial Asthma - GROUP 2Document59 pagesCase Study Bronchial Asthma - GROUP 2Jimlord GarciaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Long-Term Aerobic Exercise Training On Signaling Molecules in VEGF Protein Expression in Human Skeletal MuscleDocument18 pagesEffect of Long-Term Aerobic Exercise Training On Signaling Molecules in VEGF Protein Expression in Human Skeletal Muscle전유나No ratings yet
- 1896 Kneipp The Kneipp CureDocument497 pages1896 Kneipp The Kneipp Curevaluecare1542No ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument23 pagesAnatomyMiracle For NursesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SpeechDocument22 pagesIntroduction To SpeechJoe AjibadeNo ratings yet
- Session No 1.1. A Tour of The CellDocument40 pagesSession No 1.1. A Tour of The CellShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Biology Group 2 NotesDocument116 pagesBiology Group 2 NotesAllacheruvu Venkata sai kumarNo ratings yet
- Unscramble Titles + Clozed Test - Có Đáp ÁnDocument11 pagesUnscramble Titles + Clozed Test - Có Đáp ÁnLê Hồng HuânNo ratings yet
- RPT SC Form 3 HSBM2021Document24 pagesRPT SC Form 3 HSBM2021Richard WongNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals in Nursing ExamDocument16 pagesFundamentals in Nursing ExamHazel Ann Gonzales100% (2)
- Fcps Guideline Vol.1: Perfect Time For PreparationDocument6 pagesFcps Guideline Vol.1: Perfect Time For PreparationFatima SagguNo ratings yet
- M 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument39 pagesM 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsamarendrar87No ratings yet
- Plant Growth and DevelopmentDocument13 pagesPlant Growth and DevelopmentthushyanthNo ratings yet
- FirstDocument16 pagesFirstangelNo ratings yet
- Theories of Aging 2022Document12 pagesTheories of Aging 2022Lara Victoria DuenasNo ratings yet
- TH THDocument12 pagesTH THchn pastranaNo ratings yet
- NEB Biology Syllabus XI & XIIDocument26 pagesNEB Biology Syllabus XI & XIIBhanu AryalNo ratings yet
- Basicos VenenosDocument28 pagesBasicos VenenosJavier MartinezNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of Articular CartilageDocument33 pagesBiomechanics of Articular CartilageLibbyNo ratings yet
- Epidermal Growth FactorDocument11 pagesEpidermal Growth FactorDanièle FeudjioNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses: Elaine N. MariebDocument75 pagesThe Lymphatic System and Body Defenses: Elaine N. MariebReysa ManulatNo ratings yet
- Autoverification Improved Process Efficiency, Reduced Staff Workload, and Enhanced Staff Satisfaction Using A Critical Path For Result ValidationDocument11 pagesAutoverification Improved Process Efficiency, Reduced Staff Workload, and Enhanced Staff Satisfaction Using A Critical Path For Result ValidationAli DokumaciogluNo ratings yet