Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Groups Chart
Uploaded by
Anthony GergesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Groups Chart
Uploaded by
Anthony GergesCopyright:
Available Formats
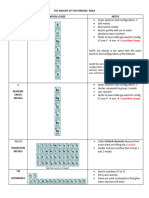
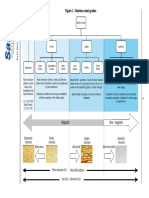
Groups (aka Families) of the Periodic Table
Metals/ # of Valence Physical Properties Chemical Properties Element Uses in Life
Non Metals/ Electrons in its Examples
Metalloids outer shell
Alkali Metals 1 valence electron Lustre, high thermal Alkali metals are highly Lithium, Sodium is used to
(Group 1)
and electrical reactive, because they sodium, add taste to food
Metals conductivity, readily lose their only potassium, etc.
ductility, and outermost electron to rubidium,
malleability. form cations with charge cesium, and
+1. (Most reactive group francium
on this chart)
Alkaline Earth Metals 2 valence electrons Lustre, high Alkaline earth metals are Magnesium, Laptops, car seats,
(Group 2)
electrical highly reactive, because strontium, luggages,
Metals conductivity, they give up there two calcium, cameras, and even
valence electrons, to barium, power tools are
achieve a full outer beryllium, and made out of
energy level.(Second radium magnesium etc.
most reactive group on
this chart)
Halogens 7 valence electrons Low melting point, Halogens have high Iodine, Chlorine is used to
(Group 7b)
low boiling point reactivity, because of high bromine, treat swimming
Non-metal electronegativity, and high fluorine, pools, and to make
effective nuclear charge. chlorine, drinking water safe
(second least reactive astatine, etc.
group on this chart) tennessine
Nobel Gasses 8 valence electrons Colorless, They have very low Argon, neon, Helium is used for
(Group 8b)
odourless, reactivity, because they helium, medicine, scientific
Non metal tasteless, and have the full 8 valence xenon, research,
nonflammable electron shell. They are krypton, refrigeration, gas
stable, and it’s very radon, for aircraft, and arc
unlikely for them to bond. oganesson welding etc.
(the least reactive group
on this chart)
You might also like
- 4500-CO Carbon Dioxide : 4-28 Inorganic Nonmetals (4000)Document7 pages4500-CO Carbon Dioxide : 4-28 Inorganic Nonmetals (4000)Ronald Figo Torres EcheNo ratings yet
- S BlockDocument20 pagesS BlockMeenakshi SuhagNo ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Study Materials English MediumDocument13 pages11th Chemistry Study Materials English Mediumprathiksha6660No ratings yet
- A. Lavoisier: History of Periodic TableDocument10 pagesA. Lavoisier: History of Periodic TableHaziraAzlyNo ratings yet
- S Block ElementsDocument16 pagesS Block Elementsyashvir.lko4963No ratings yet
- NCERT Book Class 11 Chemistry Chemistry II Chapter 10 The S Block Elements PDFDocument16 pagesNCERT Book Class 11 Chemistry Chemistry II Chapter 10 The S Block Elements PDFSubham RajputNo ratings yet
- Group II Elements - NCUKDocument8 pagesGroup II Elements - NCUKphonepyaehtut2006No ratings yet
- The Atoms Family Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesThe Atoms Family Cheat Sheet: by VianyellutlaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic S BlockDocument16 pagesInorganic S Blockakash yadavNo ratings yet
- MCAT Chem Periodic Table QuizletDocument2 pagesMCAT Chem Periodic Table QuizletAnjali PradhanNo ratings yet
- CM116 M2 ReviewerDocument19 pagesCM116 M2 ReviewerVeraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project (Purnendu)Document3 pagesChemistry Project (Purnendu)Purnendu JhaNo ratings yet
- The Groups of The Periodic TableDocument4 pagesThe Groups of The Periodic TableHannahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chp4Document3 pagesChemistry Chp4serene xuanNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of ElementsDocument5 pagesThe Periodic Table of ElementsSalvador DominiqueNo ratings yet
- Tarnish and Corrosion 2021Document6 pagesTarnish and Corrosion 2021eslamezzat21061990No ratings yet
- MIDTERMS - InOrgLec - Lesson 1Document4 pagesMIDTERMS - InOrgLec - Lesson 1Ayee Allyra Mocaram EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 4: Metals: by Team Meow Meow (Halimeow and 3 Headed Creature)Document3 pagesChemistry Chapter 4: Metals: by Team Meow Meow (Halimeow and 3 Headed Creature)Bren Jousef BayhonNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure and PeriodicityDocument68 pagesElectronic Structure and PeriodicityRANETHUBNo ratings yet
- S-BlockDocument25 pagesS-BlockLakshya JainNo ratings yet
- 908 - CH 11 Alkali MetalsDocument42 pages908 - CH 11 Alkali MetalsPutri FatimahNo ratings yet
- 11 TH P Block MGKDocument14 pages11 TH P Block MGKChandrapal RathoreNo ratings yet
- Las 1-10 (Che 029)Document6 pagesLas 1-10 (Che 029)Lyna FloridaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Chart - METALSDocument1 pageComparative Chart - METALSlynnNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Solids SummaryDocument2 pagesBonding in Solids SummaryarachnidkatNo ratings yet
- Aadhithyaa Practice Periodic Table TestDocument2 pagesAadhithyaa Practice Periodic Table TestVikramaadhithyaa JagannathanNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 FrontDocument1 pageChem 1 Frontvighneshdp174No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chemical BondingDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Chemical BondingQutub KhanNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table ReportDocument7 pagesPeriodic Table Reportangelo pascuaNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document2 pagesModule 3Hazel MuñozNo ratings yet
- 10 S Block Formula Sheets Getmarks AppDocument13 pages10 S Block Formula Sheets Getmarks Appsamsung.galaxy.tab.345cNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Topic: S-Block Elements: Prepared By: Ahtasham Arshad Class: Bszoo Roll No: 010Document23 pagesInorganic Chemistry Topic: S-Block Elements: Prepared By: Ahtasham Arshad Class: Bszoo Roll No: 010Ahtasham ArshadNo ratings yet
- The Group 1 Elements: The Alkali Metals: "Read in The Name Your God Who Created " Chemistry of ElementsDocument44 pagesThe Group 1 Elements: The Alkali Metals: "Read in The Name Your God Who Created " Chemistry of ElementsFajar Sa'bandiNo ratings yet
- Gamma Ray LogDocument13 pagesGamma Ray LogMehsen OsamaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.3Document1 pageTopic 1.3duneraoreedNo ratings yet
- Watermark Chemistry Igcse Notes 2 PDFDocument15 pagesWatermark Chemistry Igcse Notes 2 PDFMeerab ShahNo ratings yet
- S Block ElementsDocument59 pagesS Block Elementsanikesh JainNo ratings yet
- Basic Properties: 1.alkali MetalsDocument5 pagesBasic Properties: 1.alkali MetalsGanesh sargarNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 IB Bridging Course Chemistry: Flow of This SectionDocument14 pagesGrade 10 IB Bridging Course Chemistry: Flow of This SectionMarc LoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - Part II - F-BlockDocument23 pagesCHAPTER 6 - Part II - F-BlockAdam BlerNo ratings yet
- Group A Elements CatalogDocument10 pagesGroup A Elements CatalogTony Customer RepNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document3 pagesChapter 5s1062579No ratings yet
- c3 Structure and BondingDocument2 pagesc3 Structure and BondingNavdha SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Uranium ProfileDocument23 pagesUranium ProfileAlejandra VeraNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 2023Document16 pagesElectrochemistry 2023Arush GautamNo ratings yet
- Atomic Radius: S-Block Elements The Elements Variation in Physical PropertiesDocument8 pagesAtomic Radius: S-Block Elements The Elements Variation in Physical PropertiesH.r. IndiketiyaNo ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument22 pagesRadioactivitymerezemenike272No ratings yet
- Compilation of DUDE and Name Reactions 2Document24 pagesCompilation of DUDE and Name Reactions 2Pratham SinghNo ratings yet
- The D and F Block ElementsDocument27 pagesThe D and F Block ElementsPiyush GautamNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity: by T.H. MusondelaDocument11 pagesRadioactivity: by T.H. MusondelaGrace jereNo ratings yet
- Chemistry F4 Topic 4 - 5Document16 pagesChemistry F4 Topic 4 - 5Sarah WongNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document44 pagesModule 1AnarchyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 9th CH 8Document16 pagesChemistry 9th CH 8Ahmad mehmoodNo ratings yet
- Group 8A ElementsDocument27 pagesGroup 8A ElementsNesa Salsabila BahriNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 4Document6 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 4Suriati Bt A Rashid100% (1)
- Chapter 10 S Block Elements NCERT Class 11 SolutionsDocument20 pagesChapter 10 S Block Elements NCERT Class 11 SolutionsZagreus OfficialNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Metals: CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesAlkaline Metals: CharacteristicsMuhammad Ashraf Hafis Bin KamarudinNo ratings yet
- Stem 11 - General ChemistryDocument6 pagesStem 11 - General ChemistryLance CastroNo ratings yet
- BOF OperationDocument24 pagesBOF OperationMhd. Didi Endah PranataNo ratings yet
- Language of ChemistryDocument10 pagesLanguage of ChemistryMystic378 Tech GamerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19-Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsDocument22 pagesChapter 19-Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsNada MeselhyNo ratings yet
- Wades Rules 2Document5 pagesWades Rules 2api-350069945No ratings yet
- MSDS+Constellium+Aluminium+Alloys+EN+ 20160610-v2Document6 pagesMSDS+Constellium+Aluminium+Alloys+EN+ 20160610-v2HafidhSetiaNo ratings yet
- Perth Mining Geology Conference 2019 Special Report: A Selection of Resource and Exploration Analytical DataDocument20 pagesPerth Mining Geology Conference 2019 Special Report: A Selection of Resource and Exploration Analytical DatageyunboNo ratings yet
- Elements Compounds and Mixtures WorksheetDocument2 pagesElements Compounds and Mixtures WorksheetLiam PriceNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Osmeña BLVD., Cebu City Philippines 6000 College of Teacher Education Graduate SchoolDocument1 pageRepublic of The Philippines Osmeña BLVD., Cebu City Philippines 6000 College of Teacher Education Graduate SchoolCarzi CaneteNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Worksheet: The Number of Protons in The Nucleus of An AtomDocument2 pagesAtomic Structure Worksheet: The Number of Protons in The Nucleus of An AtomJosephine TabajondaNo ratings yet
- Specification Hydrate FinalDocument6 pagesSpecification Hydrate FinalSanjayNo ratings yet
- Metallic Materials Cross Reference ListDocument2 pagesMetallic Materials Cross Reference ListPlant Head PrasadNo ratings yet
- Cx5 14 Single Use Film Validation Guide REFER For ABOUT FILMDocument15 pagesCx5 14 Single Use Film Validation Guide REFER For ABOUT FILMCampaign MediaNo ratings yet
- Aluminia Hydrate Technical SpecificationDocument1 pageAluminia Hydrate Technical SpecificationAffy SydNo ratings yet
- Index: Brammer Standard Geological Materials Catalog - Under ConstructionDocument93 pagesIndex: Brammer Standard Geological Materials Catalog - Under ConstructionrizaedlysamNo ratings yet
- SCH 2100 Atomic StructureDocument3 pagesSCH 2100 Atomic StructureAllan MnangatNo ratings yet
- Valve Material EquivalentsDocument3 pagesValve Material EquivalentstungxuanbrNo ratings yet
- 316 Tech DataDocument1 page316 Tech Datatris khanNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xii-Chemistry-Qb-Anil-8. D and F Block ElementsDocument3 pagesHsslive-Xii-Chemistry-Qb-Anil-8. D and F Block ElementsererrerNo ratings yet
- Alloy Casting Institute - Big Chemical EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesAlloy Casting Institute - Big Chemical EncyclopediaJohn BoranNo ratings yet
- Oxidation of Alkenes With Potassium Manganate - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument5 pagesOxidation of Alkenes With Potassium Manganate - Chemistry LibreTextsDannyelle BaileyNo ratings yet
- Biofertilizer and BiopesticidesDocument24 pagesBiofertilizer and BiopesticidesMohit PassiNo ratings yet
- Metallurgical Engineering Department - HandbookDocument133 pagesMetallurgical Engineering Department - HandbookChandra Mouli BangaloreNo ratings yet
- Amines - JEE Main 2023 AprilDocument15 pagesAmines - JEE Main 2023 AprilSajjan BalasubramanyanNo ratings yet
- North Vista 2015 Prelim Paper 1Document20 pagesNorth Vista 2015 Prelim Paper 1GM MonsterEtaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Solubility - ExerciseDocument8 pagesEquilibrium of Solubility - ExerciseMeli SNo ratings yet
- KimDocument104 pagesKimBayby SiZzle'zNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel GradesDocument1 pageStainless Steel GradesRm1262No ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project On Consistuents of AlloysDocument11 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project On Consistuents of AlloysKrishna Singh Panwar XI BNo ratings yet
- D1072 (Total Sulfur in Fuel Gases by Combustion and Barium)Document6 pagesD1072 (Total Sulfur in Fuel Gases by Combustion and Barium)Ale Hurtado MartinezNo ratings yet