Professional Documents
Culture Documents
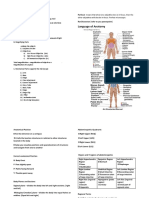
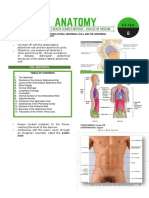
Abdomen
Uploaded by
Monica SabarreOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abdomen
Uploaded by
Monica SabarreCopyright:
Available Formats
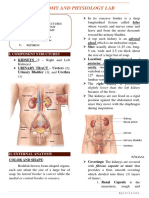
ABDOMEN 3.
Left ureter
4. Pancreas (body and tail)
▪ Bordered posteriorly by the costal
5. Spleen
margins, inferiorly by the symphysis pubis,
6. Splenic flexure of colon
and inguinal canals, and laterally by the
7. Stomach
flanks.
8. Transverse descending colon
▪ Anatomic Divisions:
Abdominal Quadrants LEFT LOWER QUADRANT (LLQ)
Abdominal Wall Muscles
1. Left kidney (lower pole)
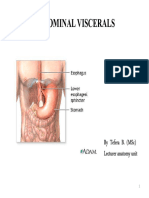
Internal anatomy of the abdominal
2. Left ovary and tube
cavity.
3. Left ureter
ABDOMINAL QUADRANTS 4. Left spermatic cord
5. Descending and sigmoid colon
▪ Abdomens have four quadrants:
• Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ) MIDLINE
• Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ)
1. Bladder
• Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ) 2. Uterus
• Left Lower Quadrant (LLQ) 3. Prostate gland
▪ Quadrants are determined by an
imaginary vertical line (midline) extending ABDOMINAL WALL MUSCLES
from the tip of the sternum (xiphoid) ▪ Outermost layer – external abdominal
through the umbilicus to the symphysis oblique
pubis. ▪ Middle layer – internal abdominal oblique
RIGHT UPPER QUADRANT (RUQ) ▪ Innermost layer – transverse abdominis
▪ Rectus abdominis – vertical muscle of the
1. Ascending and Transverse Colon anterior abdominal wall.
2. Duodenum ▪ Abdominal wall muscles protect the
3. Gallbladder internal organs and allow normal
4. Hepatic flexure of Colon compression during functional activities
5. Liver
6. Pancreas (Head) INTERNAL ANATOMY
7. Pylorus (small bowel or ileum – traverses ▪ Peritoneum lines – thin, shiny, serous
all quadrants) membrane; lines the abdominal cavity
8. Right Adrenal Gland ▪ Also provides a protective covering for
9. Right Kidney (Upper pole) most of the internal abdominal organs
10. Right Ureter (visceral peritoneum)
RIGHT LOWER QUADRANT (RLQ) ▪ Abdominal Viscera – gastrointestinal,
reproductive (female), lymphatic, and
1. Appendix urinary
2. Ascending colon ▪ Solid Viscera – organs that maintain their
3. Cecum shapes consistently: liver, pancreas,
4. Right kidney (lower pole) spleen, adrenal glands, kidneys, ovaries,
5. Right ovary and tube and uterus.
6. Right ureter ▪ Hollow Viscera – consists of structures
7. Right spermatic cord that change the shape depending on their
LEFT UPPER QUADRANT (LUQ) contents: stomach, gallbladder, small
intestine, colon, and bladder.
1. Left adrenal gland
2. Left kidney (upper pole) Liver is the largest solid organ in the body.
You might also like
- Sample Questions: 1 Midterm PracticeDocument6 pagesSample Questions: 1 Midterm PracticeValdimiro BelezaNo ratings yet
- Physiol and OP Abdominal Region 2022Document44 pagesPhysiol and OP Abdominal Region 2022Zuko JamangileNo ratings yet
- Transes - AbdomenDocument8 pagesTranses - AbdomencamatoviancaNo ratings yet
- HA Notes Whole Term 2Document21 pagesHA Notes Whole Term 2kpv454yk7mNo ratings yet
- GH 2023 - Modul 1 Anatomi GEH 1 (Anatomi Permukaan, Cavum Abdomen, Peritoneum, Mulut Dan Oesophagus)Document58 pagesGH 2023 - Modul 1 Anatomi GEH 1 (Anatomi Permukaan, Cavum Abdomen, Peritoneum, Mulut Dan Oesophagus)Farhanah FathiyahNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY - Body SystemsDocument13 pagesANAPHY - Body SystemsPearl FllominNo ratings yet
- Development of The Alimentary System - IDocument27 pagesDevelopment of The Alimentary System - Iمعاذ القحطانيNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 OutlineDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 OutlineCJ DaodaoenNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Esophagus and Stomach-1Document34 pagesHistology of The Esophagus and Stomach-1kuchipuchi12No ratings yet
- 1 - Anatomical LanguageDocument21 pages1 - Anatomical Languageshahd elmaghraby (user206)No ratings yet
- Kidney and Ureter For Paramedical StudentsDocument53 pagesKidney and Ureter For Paramedical Studentslakshmiraman1770No ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document4 pagesLecture 12A-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- 1 - Anatomical Language and Orientational TermsDocument18 pages1 - Anatomical Language and Orientational Termszena khaledNo ratings yet
- DR Mohit Goel JR 11-05-2012Document51 pagesDR Mohit Goel JR 11-05-2012nailul rosyidaNo ratings yet
- GRP 3 - Human Anatomy With Physiology and Pathophysiology Lab - Review of The BasicsDocument27 pagesGRP 3 - Human Anatomy With Physiology and Pathophysiology Lab - Review of The BasicsJamil Leander BorjaNo ratings yet
- Introduction Abdomen DR 130818235819 Phpapp02Document11 pagesIntroduction Abdomen DR 130818235819 Phpapp02Namrata GabaNo ratings yet
- Acd 13 PDFDocument62 pagesAcd 13 PDFIgor AnsoffNo ratings yet
- Surface TopographyDocument8 pagesSurface Topographyferdinand padillaNo ratings yet
- Pa of Abdomen PrintDocument14 pagesPa of Abdomen PrintAnj LTNo ratings yet
- CH 21 Abdomen JARVISDocument34 pagesCH 21 Abdomen JARVISAndy NguyenNo ratings yet
- The Abdomen: Parts of Abdominal WallDocument20 pagesThe Abdomen: Parts of Abdominal Wallhibonuura798No ratings yet
- Module 14 AbdomenDocument22 pagesModule 14 Abdomenjohn maikeilNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Gi - Dr. AhmadDocument77 pagesAnatomi Gi - Dr. AhmadBarfat AkbarNo ratings yet
- Intro To Abdominal Cavity (Merrick)Document35 pagesIntro To Abdominal Cavity (Merrick)Sidiq AboobakerNo ratings yet
- Language of AnatomyDocument5 pagesLanguage of AnatomyMaria Brooklyn Pacheco100% (2)
- Anatomyofabdominalorgans 140520021826 Phpapp01Document65 pagesAnatomyofabdominalorgans 140520021826 Phpapp01Axmed Abdi HasenNo ratings yet
- Seminar Cs 15 NovDocument24 pagesSeminar Cs 15 Novzeenatn1995No ratings yet
- AbdomenDocument142 pagesAbdomenleul TizazuNo ratings yet
- Lab Prelims ReviewerDocument6 pagesLab Prelims ReviewerememememeNo ratings yet
- Thursday, April 09, 2009 4:45 PMDocument266 pagesThursday, April 09, 2009 4:45 PMkcs2012No ratings yet
- Yyyyycrash Course Anatomy - AbdomenDocument31 pagesYyyyycrash Course Anatomy - Abdomen黃芳昌No ratings yet
- Abdominal Wall Edited WordDocument13 pagesAbdominal Wall Edited WordKennie RamirezNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Organs Essay SolutionDocument77 pagesAbdominal Organs Essay SolutionEmmanuel IshiomaNo ratings yet
- Organization and General Plan of The BodyDocument4 pagesOrganization and General Plan of The BodyJeanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Liver and Pancreas by Kazim AliDocument32 pagesAnatomy of Liver and Pancreas by Kazim AliAhmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Gross - 1S01 - Intro To AnatomyDocument3 pagesGross - 1S01 - Intro To AnatomyjandaniellerasNo ratings yet
- Abdominal ReviewerDocument4 pagesAbdominal ReviewerJoshua Diaz FloroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Abdomen FinalDocument31 pagesAnatomy Abdomen FinalShakthivel ManiNo ratings yet
- Abdomen Engl PDFDocument51 pagesAbdomen Engl PDFShuler0071No ratings yet
- The Concise Medical Encyclopedia - AnnDocument520 pagesThe Concise Medical Encyclopedia - AnnANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- NCM 101 Health Assessment AbdomenDocument30 pagesNCM 101 Health Assessment AbdomenSherinne Jane CariazoNo ratings yet
- DSystemDocument17 pagesDSystemJelly beansNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Plain Film Radiography For Emergency Cases: Preceptor: Dr. NOVITA Sp. RadDocument50 pagesAbdominal Plain Film Radiography For Emergency Cases: Preceptor: Dr. NOVITA Sp. RadViviAnisaPutriNo ratings yet
- 15b - Digestive System Anatomy and Physiology SeriesDocument100 pages15b - Digestive System Anatomy and Physiology SeriesNickson OnchokaNo ratings yet
- Transes - Assessing AbdomenDocument3 pagesTranses - Assessing AbdomencamatoviancaNo ratings yet
- Zool Post Lab Act 11 12Document3 pagesZool Post Lab Act 11 12Raiden EiNo ratings yet
- DIgestive System EmbDocument85 pagesDIgestive System EmbDanish GujjarNo ratings yet
- Git 2014Document41 pagesGit 2014Axmed Abdi HasenNo ratings yet
- AP2 Lab11 Anatomy of Digestion SP21Document16 pagesAP2 Lab11 Anatomy of Digestion SP21chasek76icloud.comNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesUrinary SystemCUESCANO, CRISTEL G. BSMT 2-ANo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Basic LecturesDocument64 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Basic LecturesRamil Ephrem L. SanchezNo ratings yet
- 9region 170425213100Document12 pages9region 170425213100Ashraf SidrahNo ratings yet
- STOMACH (1 Lect)Document23 pagesSTOMACH (1 Lect)hharshhhtyagiNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Walls - HB 2Document92 pagesAbdominal Walls - HB 2akosuaaniiwaa09No ratings yet
- Abdomen II: Handout VersionDocument68 pagesAbdomen II: Handout VersionTdoc TonyNo ratings yet
- Lect 4 Urinary SystemDocument42 pagesLect 4 Urinary Systemnightter4No ratings yet
- Health Assessment Exam 4 Study GuideDocument31 pagesHealth Assessment Exam 4 Study GuideCeciliaNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Abdominal Wall f2f-s1b2Document43 pages6.1 Abdominal Wall f2f-s1b2shlokNo ratings yet
- UGS - MaleDocument44 pagesUGS - MaleSʌɩĸʌt PʌʋɭNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Abdominal VisceralsDocument189 pagesAnatomy of Abdominal VisceralsademabdellaaleNo ratings yet
- Nervous Part 4Document8 pagesNervous Part 4Monica SabarreNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument10 pagesCardioMonica SabarreNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disease (NCD) : o CORONARY HEART DISEASE (Ischemic Heart Disease)Document4 pagesCardiovascular Disease (NCD) : o CORONARY HEART DISEASE (Ischemic Heart Disease)Monica SabarreNo ratings yet
- BREASTFEEDINGDocument2 pagesBREASTFEEDINGMonica SabarreNo ratings yet
- Maternal Nursing NotesDocument2 pagesMaternal Nursing NotesMonica SabarreNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Energy Efficiency ComplianceDocument16 pagesA Guide To Energy Efficiency ComplianceOARIASCONo ratings yet
- Research InstrumentsDocument28 pagesResearch InstrumentsAnjeneatte Amarille AlforqueNo ratings yet
- Sri Anjaneya Cotton Mills LimitedDocument63 pagesSri Anjaneya Cotton Mills LimitedPrashanth PB50% (2)
- Eimco Elecon Initiating Coverage 04072016Document19 pagesEimco Elecon Initiating Coverage 04072016greyistariNo ratings yet
- Lattner HRT Power Plus Operations ManualDocument42 pagesLattner HRT Power Plus Operations Manualsabir_munnaNo ratings yet
- Product Management Software Director in Austin TX Resume Chad ThreetDocument2 pagesProduct Management Software Director in Austin TX Resume Chad ThreetChad ThreetNo ratings yet
- Freedom SW 2000 Owners Guide (975-0528!01!01 - Rev-D)Document48 pagesFreedom SW 2000 Owners Guide (975-0528!01!01 - Rev-D)MatthewNo ratings yet
- Netflix Annual Report 2010Document76 pagesNetflix Annual Report 2010Arman AliNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and Replication: Chapter Nine Khalid HussainDocument49 pagesDNA Structure and Replication: Chapter Nine Khalid HussainKhalid HussainNo ratings yet
- Microsoft 365 LicensingDocument18 pagesMicrosoft 365 Licensingwendy yohanesNo ratings yet
- Anilkumar Surendran 3-AdDocument4 pagesAnilkumar Surendran 3-AdAnil AmbalapuzhaNo ratings yet
- Beg 2018 XXDocument42 pagesBeg 2018 XXFranz Gustavo Vargas MamaniNo ratings yet
- Congenital Abnormalities of The Female Reproductive TractDocument14 pagesCongenital Abnormalities of The Female Reproductive TractMary SheshiraNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing The Selection Of: MaterialsDocument22 pagesFactors Influencing The Selection Of: MaterialsMaulik KotadiyaNo ratings yet
- DLL English 7-10, Week 1 Q1Document8 pagesDLL English 7-10, Week 1 Q1Nemfa TumacderNo ratings yet
- Effect of Water On Quality and Preservation of FoodDocument10 pagesEffect of Water On Quality and Preservation of FoodrupinisinnanNo ratings yet
- LAB - Testing Acids & BasesDocument3 pagesLAB - Testing Acids & BasesRita AnyanwuNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck Seminal Papers From Tata HospitalDocument29 pagesHead and Neck Seminal Papers From Tata HospitalSudhir NairNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry DPP-1Document2 pagesElectrochemistry DPP-1tarunNo ratings yet
- Appendix h6 Diffuser Design InvestigationDocument51 pagesAppendix h6 Diffuser Design InvestigationVeena NageshNo ratings yet
- COLUMNA A. Erosion B. Ecosystem C. Conservation D - .DDocument1 pageCOLUMNA A. Erosion B. Ecosystem C. Conservation D - .DkerinsaNo ratings yet
- ADM-FR-003 Student Directory FormDocument2 pagesADM-FR-003 Student Directory FormRahayuNo ratings yet
- Waste SM4500-NH3Document10 pagesWaste SM4500-NH3Sara ÖZGENNo ratings yet
- Barista TestDocument7 pagesBarista Testwinnie chanNo ratings yet
- Request Please Only Students Who Are Willing To Join in Haryana in Any District Are Requested To Apply For JobDocument2 pagesRequest Please Only Students Who Are Willing To Join in Haryana in Any District Are Requested To Apply For JobUdayan KarnatakNo ratings yet
- PRIMARY Vs Secondary Vs TertiaryDocument1 pagePRIMARY Vs Secondary Vs TertiaryIshi Pearl Tupaz100% (1)
- Harmonica IntroDocument5 pagesHarmonica Introapi-26593142100% (1)
- Welcome Speech For Seminar in College 2Document4 pagesWelcome Speech For Seminar in College 2Niño Jay C. GastonesNo ratings yet
- Assembling Your Antenna SystemDocument27 pagesAssembling Your Antenna SystemKam MusNo ratings yet