Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maternal Nursing Notes
Uploaded by
Monica Sabarre0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pagesOriginal Title
MATERNAL NURSING NOTES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pagesMaternal Nursing Notes
Uploaded by
Monica SabarreCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
MATERNAL NURSING NOTES
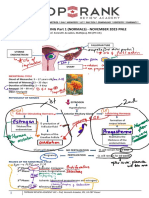
PREGNANCY FETAL DEVELOPMENT
–"gravida" Ovum – Zygote – Blastocyst – Embryo (5–
▪Primigravida – first pregnancy 8 weeks) – Fetus (from embryo to term).
▪Multigravida – pregnant for at least a 2nd ZYGOTE
time. –product of fertilization
▪Grand multigravida – pregnant five times BLASTOCYST
or more. ▪trophoblast – outer, later will form
PREGNANCY DURATION placenta
▪months – 9 months ▪embryoblast –inner, later will form
▪weeks – 40 weeks embryo/fetus.
▪days – 280 days EMBRYO –after implantation
▪trimesters – 3 trimesters
Lifespan of sperm
▪ans: 3 days —LABOR & DELIVERY—
Lifespan of egg (ovum) STAGES OF LABOR
▪ans: 1 day 1st: Dilation – longest stage
Age of viability — The earliest age at 2nd: Expulsion – expulsion of fetus
which fetuses survive if they are born. 3rd: Placental – expulsion of placenta
▪ans: 24 weeks (or 500–600 g in weight) 4th: Recovery – recovery stage
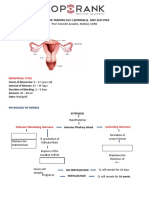
MENSTRUATION | Glands & Hormones 4 Ps OF LABOR
▪Hypothalamus – GnRH Power – uterine contraction
▪APG – FSH/LH Passenger – fetus
▪Ovaries – estrogen/progesterone Passageway – pelvis
Effects Psyche
▪FSH – follicle maturation Dystocia – difficulty in giving birth.
▪LH – follicle rupture (ovulation) Oxytocin – let-down reflex, uterine
▪Progesterone – increase contraction.
vascularity/blood flow in endometrium. PROlactin – PROmotes breastmilk
▪Estrogen – increase thickening/cell PROduction.
proliferation in endetrium. PERINEAL LACERATION
FOLLICLE ▪First degree: Vaginal mucous membrane
▪Graafian follicle – mature follicle (high in and skin of the perineum to the
estrogen) fourchette
▪Corpus luteum – ruptured follicle (high in ▪Second degree: Vagina, perineal skin,
progesterone) fascia, levator ani muscle, and perineal
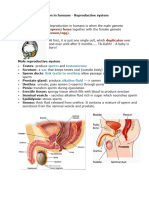
EJACULATION: average 2.5 ml of semen body
(containing 50–200 million sperm). ▪Third degree: Entire perineum, extending
OLIGOSPERMIA – Low sperm count to reach the external sphincter of the
ans: 15 million sperm. rectum
GENETIC DISORDER SCREENING & ▪Fourth degree Entire perineum, rectal
sphincter, and some of the mucous
DIAGNOSTIC TEST
membrane
▪Chorionic Villi Sampling – 10-12 weeks
of the rectum
▪Amniocentesis – 15-18 weeks
DISORDERS
Ectopic – extrauterine (sa labas ng uterus)
implantation.
▪Common organ affected in ectopic –
fallopian tube/tubal pregnancy.
▪Common site of ectopic – ampulla
Abruptio – early placental separation.
Previa – low placenta implantation.
Postpartum Hemorrhage
▪above 500 ml blood loss
▪leading cause of maternal mortality
PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
(PID)
–common caused by chlamydia &
gonorrhea
–can lead to ectopic pregnancy
–Contraception that can cause PID
▪ans: IUD
DRUGS/MEDS
Clomiphene (Clomid)
–can stimulate ovulation (fertility
problem)
Methotrexate
–can destroy the ectopic
Misprostol
–can use in labor induction
Corticosteroid
–for premature baby (to increase lung
surfactant) – prevent ARDS.
Magnesium Sulfate (MgSO4)
CNS depressant & muscle relaxant
–for preclampsia/eclampsia (CNS
depressant)
–for premature labor (muscle relaxant)
–risk for toxicity
Antidote for MgSO4 toxicity
▪ans: Calcium gluconate
You might also like
- ?maternal Nursing NotesDocument2 pages?maternal Nursing NotesHannah GarapanNo ratings yet
- Fertilization, Pregnancy and Lactation: Dedi ArdinataDocument26 pagesFertilization, Pregnancy and Lactation: Dedi ArdinataHalseyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Activities: A. Pre - ConsultationDocument13 pagesClinical Activities: A. Pre - ConsultationerykafadsNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionDocument22 pagesFemale Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionAecille VillarNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionDocument22 pagesFemale Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Review LecDocument5 pagesObstetric Review LecKevin PatrickNo ratings yet
- BNS Physiology of Mare PregnancyDocument21 pagesBNS Physiology of Mare Pregnancyvasant kalariyaNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health IDocument772 pagesMaternal and Child Health Ikarendelarosa06100% (6)
- Fertilization and Implantation Copy To StudentsDocument40 pagesFertilization and Implantation Copy To StudentsRiya SinghNo ratings yet
- Sexual Response Fertiliztion ImplantationembryoDocument38 pagesSexual Response Fertiliztion ImplantationembryoHana-Lou TaquiquiNo ratings yet
- (Zerrudo) OB Refresher NotesDocument13 pages(Zerrudo) OB Refresher NotesKatrina CaveNo ratings yet
- Perinatal PeriodDocument3 pagesPerinatal PeriodApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- The Nursing Role in Reproductive and Sexual HealthDocument34 pagesThe Nursing Role in Reproductive and Sexual Healthcoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Lec. 3Document112 pagesAntenatal Lec. 3Jesusa AbanesNo ratings yet
- Ob Refresher Part 1 Normals Nov 2023 Pnle For Davao BabiesDocument12 pagesOb Refresher Part 1 Normals Nov 2023 Pnle For Davao BabiesKristine QuindozaNo ratings yet
- Fertilization & ImplantationDocument18 pagesFertilization & ImplantationArunashree ajayNo ratings yet
- Lec1st DR - TalibDocument27 pagesLec1st DR - Talibvanobestoon223No ratings yet
- Ob 1Document28 pagesOb 1Hana Marie AlayonNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery HormonesDocument7 pagesLabor and Delivery HormonesMikaella CondeNo ratings yet
- Obstetric NursingDocument14 pagesObstetric NursingreooooNo ratings yet
- Process of ConceptionDocument42 pagesProcess of ConceptionimnasNo ratings yet
- Reproduction NotesDocument27 pagesReproduction NotesAyra AlbairaNo ratings yet
- MCHN 3RD LectDocument9 pagesMCHN 3RD LectZahNo ratings yet
- 4 ProcessDocument12 pages4 ProcessTel EscorialNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument22 pagesMaternal and Child Health NursingRam Van MunsterNo ratings yet
- SVF 12O Tut 1 (Reproduction)Document7 pagesSVF 12O Tut 1 (Reproduction)Roseanne MugariNo ratings yet
- MCN Lec Reviewer FinalsDocument7 pagesMCN Lec Reviewer Finalszyyw.abello.uiNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics Day 1Document26 pagesObstetrics Day 1maggan donnaNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument61 pagesHuman Reproductionmammuammu005No ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Tract NotesDocument57 pagesFemale Reproductive Tract NotesjayakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing: Pregnancy StagesDocument8 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing: Pregnancy StagesBing58No ratings yet
- MCN Nursing 1Document107 pagesMCN Nursing 1Fau Fau DheoboNo ratings yet
- The Growing Fetus For CPDocument19 pagesThe Growing Fetus For CPyzaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Sex and FertDocument17 pagesWeek 2 Sex and FertAbmil Ching TinggalongNo ratings yet
- Ncma 217 MidtermsDocument15 pagesNcma 217 MidtermsCharmaine BautistaNo ratings yet
- PregnancyDocument51 pagesPregnancyKhlouda HamadaNo ratings yet
- Sex Hormones: Female Reproduction Male ReproductionDocument113 pagesSex Hormones: Female Reproduction Male ReproductionM HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- Fetal Development: Ms - Virgina Varghese and DR - SoniyaDocument37 pagesFetal Development: Ms - Virgina Varghese and DR - Soniyaalmayasa2002No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction PortfolioDocument19 pagesHuman Reproduction PortfolioIgnacio FelicityNo ratings yet
- Care For Childbearing & Its Family BC To Have Healthy Adults, MustDocument9 pagesCare For Childbearing & Its Family BC To Have Healthy Adults, MustShyenNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Physiology of Small Ruminants: Small Ruminant Conference July 31, 2015Document40 pagesReproductive Physiology of Small Ruminants: Small Ruminant Conference July 31, 2015hassanNo ratings yet
- 5.menstrual CycleDocument62 pages5.menstrual CycleQaiser InayatNo ratings yet
- The Human Reproductive SystemDocument53 pagesThe Human Reproductive Systemapi-406307933No ratings yet
- MCHNDocument6 pagesMCHNJohn KenNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Kehamilan Dan Maternal-Fetal Exchange: Acholder SiraitDocument61 pagesFisiologi Kehamilan Dan Maternal-Fetal Exchange: Acholder SiraitBunga sujatnikaNo ratings yet
- Embryology Lecture Note 2Document19 pagesEmbryology Lecture Note 2jestreametefiaNo ratings yet
- Tutor Inggris Blok5Document16 pagesTutor Inggris Blok5Rara Puspita BamesNo ratings yet
- CARE OF MOTHER AND CHILD: MENSTRUAL CYCLE, HORMONES, AND REPRODUCTIVE PROCESSDocument2 pagesCARE OF MOTHER AND CHILD: MENSTRUAL CYCLE, HORMONES, AND REPRODUCTIVE PROCESSEsarpy (Nana)No ratings yet
- Proses Persalinan Dan Konsep DasarDocument31 pagesProses Persalinan Dan Konsep DasarShella Ramashanti100% (1)
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing: Menstruation, Fertilization, and ImplantationDocument45 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing: Menstruation, Fertilization, and ImplantationKaye OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics and Genital DiseasesDocument21 pagesObstetrics and Genital DiseasesSajjad LaghariNo ratings yet
- The Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Ovarian TumorDocument25 pagesThe Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Ovarian TumorShanon LimNo ratings yet
- Revised OB Handout Part 1 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherDocument15 pagesRevised OB Handout Part 1 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherMatelyn OargaNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Review Pregnancy Fetal Development and Labor and DeliveryDocument84 pagesDay 2 Review Pregnancy Fetal Development and Labor and DeliveryInah SaritaNo ratings yet
- PregnancyDocument34 pagesPregnancyNamrata patelNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive System: Mr. LaingDocument66 pagesThe Reproductive System: Mr. LaingTyese DasilvaNo ratings yet
- LaborDocument25 pagesLaborSameera DahamNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction NotesDocument35 pagesSexual Reproduction NotesZelNo ratings yet
- How To Have an Easy and Safe Pregnancy and Bring Forth a Healthy Baby: A Pregnancy Book for First Time Moms for a Successful and Healthy Journey through Pregnancy, Childbirth and NewbornFrom EverandHow To Have an Easy and Safe Pregnancy and Bring Forth a Healthy Baby: A Pregnancy Book for First Time Moms for a Successful and Healthy Journey through Pregnancy, Childbirth and NewbornNo ratings yet
- Nervous Part 4Document8 pagesNervous Part 4Monica SabarreNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument10 pagesCardioMonica SabarreNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disease (NCD) : o CORONARY HEART DISEASE (Ischemic Heart Disease)Document4 pagesCardiovascular Disease (NCD) : o CORONARY HEART DISEASE (Ischemic Heart Disease)Monica SabarreNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic and Modified DietsDocument2 pagesTherapeutic and Modified DietsMonica SabarreNo ratings yet
- Mental HealthDocument1 pageMental HealthMonica SabarreNo ratings yet
- BREASTFEEDINGDocument2 pagesBREASTFEEDINGMonica SabarreNo ratings yet
- AneurysmDocument22 pagesAneurysmRaymond SorianoNo ratings yet
- PI - PIL VaxigripTetra NH 2022 2023Document3 pagesPI - PIL VaxigripTetra NH 2022 2023Nadym DimitrijNo ratings yet
- Icds N AayDocument8 pagesIcds N AayMeghan PaulNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics 8 1202Document5 pagesPediatrics 8 1202ahmed yahyaNo ratings yet
- Nurses Knowledge and Performance On Colostomy CareDocument16 pagesNurses Knowledge and Performance On Colostomy CareGeeta ThakurNo ratings yet
- VISN16 Market RecommendationDocument58 pagesVISN16 Market RecommendationKALB DIGITALNo ratings yet
- Optima Health 2023 2024 Cova - Benefits Brochure FinalDocument8 pagesOptima Health 2023 2024 Cova - Benefits Brochure FinalKobusNo ratings yet
- Usher Syndrome Awareness DayDocument10 pagesUsher Syndrome Awareness DayakankshaNo ratings yet
- My S.M.A.R.T. Goal: Marina Di Pede NSGD 2016-Clinical Practicum Bonnie Masson November 7, 2022Document15 pagesMy S.M.A.R.T. Goal: Marina Di Pede NSGD 2016-Clinical Practicum Bonnie Masson November 7, 2022api-631170779No ratings yet
- Public Health MODULE 7 - Pharmacists, Vaccines, and Public HealthDocument13 pagesPublic Health MODULE 7 - Pharmacists, Vaccines, and Public HealthEmerson John TallodNo ratings yet
- 0814 Model Answer Paper Winter 2017Document28 pages0814 Model Answer Paper Winter 2017Akshay ShindeNo ratings yet
- Mosquito AuthorityDocument3 pagesMosquito AuthorityWACHNo ratings yet
- Presentasi DKT - Aditya - Kontrasepsi Di Masa Pandemi PDFDocument24 pagesPresentasi DKT - Aditya - Kontrasepsi Di Masa Pandemi PDFAnna Ukhti ILaNo ratings yet
- ASTHMADocument16 pagesASTHMAAyesigwa Gerald96100% (1)
- Sorbion SachetsDocument3 pagesSorbion SachetsReil_InsulaNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis Atoe and MoreDocument31 pagesViral Hepatitis Atoe and MoreAnkita SamantaNo ratings yet
- Wound Management With Excessive DrainageDocument6 pagesWound Management With Excessive DrainageMatthew RyanNo ratings yet
- WOCNews 10 Vol3Document23 pagesWOCNews 10 Vol3Agung GinanjarNo ratings yet
- C PRESNTATIONS21 UpdatedDocument4 pagesC PRESNTATIONS21 UpdatedFauzi SebunyaNo ratings yet
- How to Prepare for the FCPS Part 1 Exam in ENTDocument4 pagesHow to Prepare for the FCPS Part 1 Exam in ENTDoodNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Maternal - Fetal Attachment Education On Maternal MenDocument7 pagesThe Effect of Maternal - Fetal Attachment Education On Maternal MenNadia RifeldaNo ratings yet
- Dog Bite Facts: 4.5 Million Occur Yearly in USDocument5 pagesDog Bite Facts: 4.5 Million Occur Yearly in USDesta KirosNo ratings yet
- DISEASE Vs ILLNESS Vs SICKNESSDocument2 pagesDISEASE Vs ILLNESS Vs SICKNESSS. M. Nawroj ArefinNo ratings yet
- Who Pen 2020Document85 pagesWho Pen 2020Faye PalmaresNo ratings yet
- Ssi (Surgical Site Infection)Document31 pagesSsi (Surgical Site Infection)tugam umarNo ratings yet
- Legislator Email on Safe Patient HandlingDocument5 pagesLegislator Email on Safe Patient HandlingAnonymous dcpGmD60% (5)
- Lymphedema BrochureDocument8 pagesLymphedema BrochureJose MiaNo ratings yet
- Uputstvo Za OsiguranikaDocument1 pageUputstvo Za OsiguranikaSavkicZoranNo ratings yet
- Resbakuna - Comirnaty PoU Deck For Site Training and Education-FINAL-013122Document53 pagesResbakuna - Comirnaty PoU Deck For Site Training and Education-FINAL-013122toledanagerald516No ratings yet
- MastitisDocument2 pagesMastitisJuviely PremacioNo ratings yet