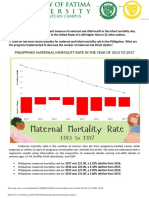
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Etic111 Prelim
Uploaded by
eli pascualOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Etic111 Prelim
Uploaded by
eli pascualCopyright:
Available Formats
PHED (Prelims)
PHED 213 5. Arm: Raise both arms overhead in a grace full
WEEKS 1-5: LESSONS curve.
BASIC FUNDAMENTAL STEPS Feet: Bring the heel of one foot to touch the toe of
the other.
FOLK DANCE
CARIÑOSA
- Many people enjoy learning basic steps in folk dance in
order to participate in either a social or religious tradition, or Cariñosa is a Spanish word meaning “loving” or “affectionate
sometimes just to get some exercise. Whatever your reason one”.
for learning, folk dancing is a fun form of movement that A Philippine Folk Dance of Hispanic Origin in the
involves dancers from all ages and backgrounds. Maria Clara suite.
- Folk dancing is a broad term used to describe a wide array This is a courtship dance that portrays acts of
of dances. Every culture around the world has its own folk flirtation between a man and a woman.
dances, and there are usually specific ones for big This is closely related in the Panay Islands of the
celebrations like weddings. Visayan Region.
Most Filipina are said to be described as karinyosa.
The term "folk dance" is simply defined as a dance that has This is introduced in the Philippines by the
a particular set of steps or figures that repeat in time to Spaniards in the 16th century.
music. There are also usually partners in folk dancing, where In honor of Maria Clara, a main character of Dr.
everyone from one couple to many couples can dance at Jose Rizal’s novel called “Noli Me Tangere”.
one time.
Costume:
TYPES OF FOLK DANCE:
Girl: Girls wear a Balintawak or a patadyong and
NATIONAL – traditional dances of a given country camisa. Girls has fan hanging at the right side of
(Cariῆosa, Tinikling) the waist.
REGIONAL – dance found in a certain localities or Boy: Boys wear a barong tagalog and any color of
regions (Sayaw sa Obando) trousers, usually black. Boys has a handkerchief in
their pocket.
CHARACTERISTICS OF PHILIPPINE DANCE
Dance figures:
As a rule, our dances begin and end with a
“saludo”. A SALUDO is a three-step-turn in place • The dance has eight figures. The music shows a great
and bow to either partner or audience. Spanish influence to the Filipinos. It is in ¾ time signatures.
A distance between 6 to 8 feet from each other.
o Three steps and point
Most of the dances are done in pairs or couple.
o Pointing
There is a little, if any bodily contact. Holding of the
hands are very common. o Back-to-back
Hand movements play an important part. o Hide-and-seek with a fan
War dances are found among non-Christians tribes. o Kneeling and fanning
It is traditional and expressive behavior. o Hide and seek with handkerchief
o Flirting with handkerchief
FUNDAMENTAL STEPS IN FOLK DANCE o Flirting
1. Arm: Raised arms to a circle in front of the chest. Reminder: This flirtation dance is known throughout the
Feet: Bring heels close to touch, toes apart. Philippines. Carinosa means affectionate, lovable, or
2. Arm: Open up arms side ward, raised below amiable. With a fan and a handkerchief, the dances go
Shoulder level with a graceful curve. through hideand-seek movements and other flirting acts
Feet: Bring feet apart side ward. expressing tender feelings for one another. There are many
3. Arm: Raise one arm overhead while another arm versions of this dance, but the Hide-and-seek movements
remains in 2nd position. are common in all.
Feet: Bring the heel of foot to touch the instep of the
other foot.
4. Arm: Raise one arm in front of chest in a half circle,
while one arm remains overhead.
Feet: Bring one foot in front of the other foot to walk
strike.
PHED (Prelims)
PHILIPPINE FOLK DANCE MUSLIM DANCES
DANCE: Influenced by Malay, Javanese and Middle Eastern Traders
(Islam)
- A form of expression of oneself through rhythmic
movement. Mysticism, royalty and beauty.
Uses intricate hand and arm movement.
FOLK DANCE
the fingers express feelings and emotions
-oldest form of dance and the earliest form of Uses shimmering costumes.
communication.
the traditional dance of a given country which
evolved naturally and spontaneously with everyday
activities. E.g: occupations, customs, festivals,
rituals.
It is handed down from generation to generation.
It has more or less a fixed movement in their
TRIBAL DANCES
pattern, but may differ in various areas or
provinces. Also known as Ethnic Dances; Ethnic minorities found in
different parts of the Philippines (T’boli, Bilaan, Manobo,
5 MAJOR CLASSIFICATIONS OF PHILIPPINE FOLK
Bagobo etc.)
DANCES
Intricate craftsmanship in metal, clothing and
CORDILLERA DANCES
jewelry.
dances reflect rituals which celebrate their daily lives – a Reflects rituals and animals, beliefs in “spirits” and
good harvest, health, peace, war, and other symbols of shamans, nature – “anito,”
living. animal sounds, human singing, indigenous
materials.
Bontoc, Ifugao, Benguet, Apayo, and Kalinga Tribes
A people whose way of life existed long before any
Spaniard or other foreigners stepped foot in the
Philippines.
Gongs, ganza.
RURAL DANCES
reflects the simple life of the people in the barrio.
depicts common work, daily activities of the
peasants.
SPANISH INFLUENCED DANCES shows gaiety and laughter, festivities
Performed in fiestas to honor patron saints.
Dances reflects Christianity, and European art and culture.
give homage to the barrio’s namesake for a good
Philippine aristocrats crewated Filipino adaptations harvest, health and perseverance.
of European dances. Indigenous materials, clapping, rondalla, percussion
Jotas, fandangos, mazurkas, waltzes. instruments.
dances by young socialites to the stringed music of
the rondalla.
CLASSIFICATION OF FOLKDANCES IN THE PHILIPPINES
PHED (Prelims)
OCCUPATIONAL DANCE The dancers used fan and handkerchief as their props. The
- depicting action of certain occupation, industry or female dancers use the fan to hide their face while dancing
human labor. and they move it with the rhythm of the music. When using
RELIGIOUS/ CEREMONIAL DANCE handkerchief, the female and male dancers hold the corners
- performed in connection with religious vows and of the handkerchief. They used it as their shield to each
ceremonies. other and they peek on each side as the music play.
COMIC DANCE Basically, the dance shows a courtship of the couple.
- depicting funny movements for entertainment. CARIŃOSA DANCE MECHANICS
GAME DANCE
- with play elements In this dance, performers should refrain from touching each
WEDDING DANCE other, but the steps shows the guy’s interest to the female
- performed during wedding feast. while the latter is shy and wants to be chased.
COURTSHIP DANCE Female dancer uses fan. She will be using it to fan herself
- depicting love making. with the beat while dancing.
FESTIVAL DANCE
- suitable for special occasion or any social They glance at each other from a handkerchief as if they
gatherings. were playing hide-and-seek, where each partners hold the
corners of the handkerchief while blocking each other’s face.
CARINOSA
Partners swap flirtatious waves and gestures, and then the
Is a Spanish word pronounced as [kaɾiˈɲosa], meaning the girl will kneel down with one knee and fans herself while the
loving or affectionate one. guy dances around the other and then vice versa.
It is a Philippine dance of Hispanic origin from the Maria BASIC CARIŃOSA STEPS
Clara suite of Philippine folk dances, where the fan or
handkerchief plays an instrumental role as it places the The step of Cariῆosa is similar to waltz and music is ¾
couple in romance scenario. signature. When the music starts, the female holds her skirt
with one or both hands, swaying the fabric of her skirt at the
It is closely associate with the island of Panay and side while moving around the floor by swaying to the side
the Visayas region in general. with a left foot by stepping your right next to the left.
Most Filipina women can be described as
karinyosa. STEP 1. 3 step turn and bow facing each other.
This is a courtship dance that portrays acts of flirtation STEP 2. 3 step and point Right-Left direction in 16 counts
between a man and a woman. The dancers perform steps
STEP 3. Touch step- 3 step forward in 2 counts. 4 touch
resembling hide-and-seek movements. The woman holds a
step, change position then repeat.
handkerchief or sometimes a fan.
STEP 4. 3 step forward and back to back 4 Touch step
More than the tinikling, the cariñosa is considered the
Change position and repeat the first two on step 4 above
national dance of the Philippines. It is introduced in the
Philippines by the Spaniards in the 16th century. STEP 5. 3 step forward. Girl opens her fan and will start
fanning herself 4 touch step Change position and the first
In honor of Maria Clara, a main character of Dr. Jose Rizal's
three on step 5 above
novel called “Noli Me Tangere" when translated in English
means "Touch Me Not". STEP 6. 3 step forward Boy move forward then kneel Girl
taps the boy with her fan and she will do 4 touch steps
The first ever published notation of the Cariñosa dance
Change position Girl will kneel as they look each other and
steps was from the book Philippine Folk Dances and Games
the boy will do 4 touch step
by Francisca Reyes-Tolentino (later became an Aquino).
Mrs. Tolentino's master's thesis which has the same title was STEP 7. 3 step forward Girl gets the handkerchief from the
revised and was later published in 1927 boy Both will move the handkerchief up and down four times
Change position then repeat the first three in step 7.
However, the most common of the many Cariñosa found in
the country is the one from the book "Philippine Folk Dances
v1" by Francisca Reyes Aquino, published sometime in
1940. The version integrated all the common dance figures
among the many versions throughout the land.
You might also like
- Phed213 PrelimDocument1 pagePhed213 PrelimKaye OrtegaNo ratings yet
- 3rd FigureDocument2 pages3rd FigureElixa HernandezNo ratings yet
- Physical Fitness EducationDocument8 pagesPhysical Fitness EducationJayze MonroyNo ratings yet
- Handout PE03Document2 pagesHandout PE03Erlindss Ilustrisimo GadainganNo ratings yet
- Philippine Folk DanceDocument7 pagesPhilippine Folk DanceNatalie Enriquez100% (1)
- Philippine Folk DanceDocument7 pagesPhilippine Folk DanceAl SalasNo ratings yet
- Pe3: Reviewer: Panay and The Visayas Region inDocument4 pagesPe3: Reviewer: Panay and The Visayas Region inlonely ylenolNo ratings yet
- PE 2nd QRTR ReviewerDocument3 pagesPE 2nd QRTR Reviewerm97998668No ratings yet
- HOPE Reviewer MidtermDocument3 pagesHOPE Reviewer MidtermVinz AlilingNo ratings yet
- Pe 3 - Prelim ReviewerDocument3 pagesPe 3 - Prelim ReviewerNikoruNo ratings yet
- Folk Dance College ClassDocument35 pagesFolk Dance College Classaaron danyliukNo ratings yet
- Folk DanceDocument23 pagesFolk DanceAngilene BaruadoNo ratings yet
- Cot2 Pe q4 P.E. Week 1Document64 pagesCot2 Pe q4 P.E. Week 1Michael Dela Cruz RiveraNo ratings yet
- Prefinals ReviewerDocument2 pagesPrefinals ReviewerNix De La RosaNo ratings yet
- PE ReviewerDocument2 pagesPE ReviewerJeny Babe BuenavistaNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii: Dance Positions/Dance Steps and Philippine Folk DancesDocument11 pagesUnit Ii: Dance Positions/Dance Steps and Philippine Folk DancesCarl CesNo ratings yet
- Fabillar, Jan Jasmin E. Bs-Biology 2 Year Pe 3 (Women) - Q: Philippine Folk DanceDocument4 pagesFabillar, Jan Jasmin E. Bs-Biology 2 Year Pe 3 (Women) - Q: Philippine Folk DancedndqdqNo ratings yet
- PHED113Document5 pagesPHED113Mushy_ayaNo ratings yet
- Module 3-Week 3Document16 pagesModule 3-Week 3Naddie ParkNo ratings yet
- HANDOUTDocument22 pagesHANDOUTJarhis TabiosNo ratings yet
- Rhythmic ActivitiesDocument5 pagesRhythmic ActivitiesCristine ObialNo ratings yet
- Q1 W8-W9 Mod5 Physical-Education 12 FoklDancesDocument8 pagesQ1 W8-W9 Mod5 Physical-Education 12 FoklDancesClareen June DagoyNo ratings yet
- Local and Indigenous Philippine Folk DanceDocument3 pagesLocal and Indigenous Philippine Folk DanceShaira PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Physical EducationDocument7 pagesPhysical EducationAshantiNo ratings yet
- Folk DanceDocument5 pagesFolk DanceAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Hope 1Document7 pagesHope 1Alecel May PacardoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PE PDFDocument39 pagesReviewer in PE PDFLouise RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Pe 3 ReviewDocument3 pagesPe 3 ReviewBryan BerdinNo ratings yet
- PE2 Module 3Document6 pagesPE2 Module 3Winnie ToribioNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheets Q2 - W1 - W2Document15 pagesLearning Activity Sheets Q2 - W1 - W2Kier BayucaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Folk DanceDocument15 pagesPhilippine Folk Dancekyla_batallones100% (1)
- Physical Education and Health 1-4Document18 pagesPhysical Education and Health 1-4Annielese PorrasNo ratings yet
- Pe Reviewer Dance - FolkdanceDocument5 pagesPe Reviewer Dance - FolkdanceEreiya TuazonNo ratings yet
- Module For Quarter 1Document7 pagesModule For Quarter 1Mae BalacanaoNo ratings yet
- LESSON-4-Philippine FOLKDANCESDocument49 pagesLESSON-4-Philippine FOLKDANCESKian BabanggaNo ratings yet
- Dance Forms/ Genre and Its RelationshipsDocument20 pagesDance Forms/ Genre and Its RelationshipsMae FrtNo ratings yet
- HOPE 3 Philipine Folk DanceDocument35 pagesHOPE 3 Philipine Folk DanceSJ BatallerNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Dance and Rhythm IntroducDocument4 pagesUNIT 1 Dance and Rhythm IntroducheatherNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledKyla RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Introduction To Folk DanceDocument26 pages4.1 Introduction To Folk Danceangelty143No ratings yet
- Pe 4 ReviewerDocument5 pagesPe 4 ReviewerRaffy Superales MarquezNo ratings yet
- ShaneDocument7 pagesShaneAlvin Jay Anatalio100% (1)
- Fundamental Dance PositionsDocument5 pagesFundamental Dance PositionsRizaldy Ventura TanNo ratings yet
- Hand Outs in Physical Education and Health 3Document5 pagesHand Outs in Physical Education and Health 3Bea PiñonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document9 pagesLesson 3RAGUDO, ELEAZAR O.No ratings yet
- Philippine Folkdance 1Document44 pagesPhilippine Folkdance 1Anne HawtawayNo ratings yet
- We Transform Lives Senior High School Department: Mary The Queen College (Pampanga)Document5 pagesWe Transform Lives Senior High School Department: Mary The Queen College (Pampanga)Limmuel GiganteNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Lesson 1-4Document22 pagesModule 2 Lesson 1-4Rysal YapitNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Pe and HealthDocument11 pagesReviewer in Pe and HealthHchNo ratings yet
- Philippine Folk DancesDocument25 pagesPhilippine Folk DancesMARIZ VLOGNo ratings yet
- PE112-Rhythmic Activities-MIDTERMSDocument16 pagesPE112-Rhythmic Activities-MIDTERMSJunnil MondingNo ratings yet
- Folk DanceDocument2 pagesFolk DanceSideTrip SideKickNo ratings yet
- DanceDocument20 pagesDanceJayno Labajo LamosaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Philippine Folk DancesDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Philippine Folk DancesMark Ian Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Pe ReviewerDocument2 pagesPe ReviewerDyvineNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Pe2 FinalDocument6 pagesModule 4 Pe2 FinalAiyah Khite Jumamoy SocajelNo ratings yet
- RhythmDocument7 pagesRhythmMarjon Villanueva0% (1)
- Pe ReviewerDocument5 pagesPe ReviewerDexcyrille Fhaye GacutanNo ratings yet
- Oriental Dance: Discovering the Art of Belly DancingFrom EverandOriental Dance: Discovering the Art of Belly DancingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Vrts112 PrelimDocument2 pagesVrts112 Prelimeli pascualNo ratings yet
- NCMA217 SL RUBRICS LEOPOLDs MANEUVERDocument2 pagesNCMA217 SL RUBRICS LEOPOLDs MANEUVEReli pascual100% (1)
- Ncma216: BSN 2Nd Year 1St Semester Prelim 2021: Bachelor of Science in Nursing 2YADocument32 pagesNcma216: BSN 2Nd Year 1St Semester Prelim 2021: Bachelor of Science in Nursing 2YAMARIA STEPHANY DELA CRUZ100% (1)
- Human SexualityDocument20 pagesHuman SexualityLeo Santos MagnoNo ratings yet
- Case Study LayoutDocument5 pagesCase Study Layouteli pascualNo ratings yet
- Etic111 PrelimDocument6 pagesEtic111 PrelimNiacinth LoredoNo ratings yet
- Normal Changes During Pregnancy 1Document60 pagesNormal Changes During Pregnancy 1eli pascualNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Science in Nursing: Care of Mother, Child and ADOLESCENT (Well Clients)Document8 pagesBachelor of Science in Nursing: Care of Mother, Child and ADOLESCENT (Well Clients)Big DaddyNo ratings yet
- Etic111 PrelimDocument6 pagesEtic111 PrelimNiacinth LoredoNo ratings yet
- Brgy. Pob. West BSN Level2 2 1Document90 pagesBrgy. Pob. West BSN Level2 2 1eli pascualNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Infant Mortality RateDocument7 pagesMaternal and Infant Mortality Rateeli pascualNo ratings yet
- Framework For Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument9 pagesFramework For Maternal and Child Health Nursingeli pascualNo ratings yet
- CM3 - Cu12 Assessment of Heart & Neck VesselsDocument15 pagesCM3 - Cu12 Assessment of Heart & Neck Vesselseli pascualNo ratings yet
- CM3 - Cu13 Assessment of Peripheral Vascular SystemDocument12 pagesCM3 - Cu13 Assessment of Peripheral Vascular Systemeli pascualNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Subcellular ComponentsDocument31 pagesAnalysis of Subcellular Componentseli pascualNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Setting Goals For SuccessDocument2 pagesChapter 13 - Setting Goals For Successeli pascualNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAditya ShanbhagNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect and Present Perfect ProgressiveDocument5 pagesPresent Perfect and Present Perfect ProgressiveKiara Fajardo matusNo ratings yet
- Monster Hunter: World - Canteen IngredientsDocument5 pagesMonster Hunter: World - Canteen IngredientsSong HoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Strategy Analysis and Choice: Strategic Management: A Competitive Advantage Approach, 16e (David)Document27 pagesChapter 6 Strategy Analysis and Choice: Strategic Management: A Competitive Advantage Approach, 16e (David)Masum ZamanNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument32 pagesProjectroshan jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Sips 1328Document64 pagesSips 1328Jean Claude De AldánNo ratings yet
- 8 Adam AmuraroDocument28 pages8 Adam Amurarokmeena73No ratings yet
- UserProvisioningLabKit 200330 093526Document10 pagesUserProvisioningLabKit 200330 093526Vivian BiryomumaishoNo ratings yet
- Project Report For Tunnel ExcavationDocument19 pagesProject Report For Tunnel ExcavationAbhishek Sarkar50% (2)
- General Return Service Agreement (RSA) GuidelinesDocument2 pagesGeneral Return Service Agreement (RSA) GuidelinesJune Francis AngNo ratings yet
- Industrial Motor Control Part IDocument38 pagesIndustrial Motor Control Part Ikibrom atsbha100% (2)
- Aman Singh Rathore Prelms Strategy For UPSCDocument26 pagesAman Singh Rathore Prelms Strategy For UPSCNanju NNo ratings yet
- Icc Esr-2302 Kb3 ConcreteDocument11 pagesIcc Esr-2302 Kb3 ConcretexpertsteelNo ratings yet
- Chrysler CDS System - Bulletin2Document6 pagesChrysler CDS System - Bulletin2Martin Boiani100% (1)
- Science9 Q4 Week2Document16 pagesScience9 Q4 Week2Maria Josie Lopez TumlosNo ratings yet
- GST RATE LIST - pdf-3Document6 pagesGST RATE LIST - pdf-3Niteesh KumarNo ratings yet
- PedagogicalDocument94 pagesPedagogicalEdson MorenoNo ratings yet
- Dress Code19sepDocument36 pagesDress Code19sepapi-100323454No ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance Manual Compressor Models: P105WJD, P130DWJD, P160DWJD, P175DWJDDocument70 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual Compressor Models: P105WJD, P130DWJD, P160DWJD, P175DWJDManuel ParreñoNo ratings yet
- SRS For Travel AgencyDocument5 pagesSRS For Travel AgencyHardik SawalsaNo ratings yet
- The Sandbox Approach and Its Potential For Use inDocument13 pagesThe Sandbox Approach and Its Potential For Use invalentina sekarNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document51 pagesLab 1aliNo ratings yet
- The Ethics of Peacebuilding PDFDocument201 pagesThe Ethics of Peacebuilding PDFTomas Kvedaras100% (2)
- (Schottel) Aspects of The Design Procedure For Propellers Providing Max Bollard PullDocument10 pages(Schottel) Aspects of The Design Procedure For Propellers Providing Max Bollard Pulldevu2chodankarNo ratings yet
- Rare Watches (Christie's) 16. 05. 2016.Document236 pagesRare Watches (Christie's) 16. 05. 2016.Simon LászlóNo ratings yet
- Review Course 2 (Review On Professional Education Courses)Document8 pagesReview Course 2 (Review On Professional Education Courses)Regie MarcosNo ratings yet
- Speaking RubricDocument1 pageSpeaking RubricxespejoNo ratings yet
- Economics - Economics - Cheat - SheetDocument1 pageEconomics - Economics - Cheat - SheetranaurNo ratings yet
- 835 (Health Care Claim PaymentAdvice) - HIPAA TR3 GuideDocument306 pages835 (Health Care Claim PaymentAdvice) - HIPAA TR3 Guideअरूण शर्माNo ratings yet