Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cie 096 Assessment
Uploaded by
Kevin Abenojar NamayaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cie 096 Assessment
Uploaded by
Kevin Abenojar NamayaCopyright:
Available Formats
PHINMA EDUCATION – ARAULLO UNIVERSITY
CIE 096 – PROFESSIONAL INTEGRATION 4 (SEC)
ASSESSMENT
SET
NAME : SCORE :
SECTION : DATE :
INSTRUCTION: Answer the following questions. Provide a clear and neat solution.
Final answers with incorrect or no solutions shall not be considered. Round off
your final answer in 3 decimal places.
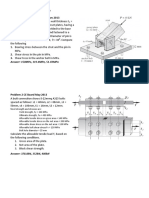
SITUATION NO. 1
The bracket shown is attached with 3-19 mm bolts arranged in an
equilateral triangle layout. A force is applied with a moment are 500
mm measured to the centroid of the bolt group. The maximum shear stress
in the bolts is limited to 100 MPa.
1. Determine the polar moment of inertia of a bolt about the centroid.
2. Determine the maximum force P that the connection can support.
3. Determine the torsional shear stress of each bolt.
SITUATION NO. 2
A 76mm x 76mm x 6mm angular section is welded to a gusset plate having
a thickness of 8mm. The length L1 = 125mm and L2 = 65mm.The angular
section has a cross sectional area of 929mm2. Fy = 248 MPa, Fu = 400
Mpa.
Allowable stresses:
Allowable tensile stress (gross area) = 0.60 Fy
Allowable tensile stress (net area) = 0.50 Fu
Allowable shear stress (net area) = 0.30 Fu
4. Determine the value of the tensile force P based on gross area.
5. Determine the value of tensile force P based on net area, if the
strength reduction coefficient is 0.85.
6. Determine the value of tensile force P based on block shear in
gusset plate along the weld.
PREPARED BY: ENGR. DOMINIC FLORES
PHINMA EDUCATION – ARAULLO UNIVERSITY
CIE 096 – PROFESSIONAL INTEGRATION 4 (SEC)
ASSESSMENT
SET
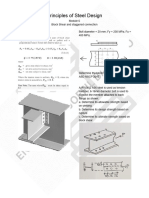
SITUATION NO. 3
A square hollow steel strut with wall thickness, t1 = 10 mm, is pin
connected to two gusset plates, t2 = 12 mm, which are welded to the base
plate, t3 = 12 mm, and fastened to a concrete base by 4 - 16 mm diameter
anchor bolts. Pin diameter = 16 mm. Compressive load, P = 48 kN. Angle
Ø = 30 degrees.
7. Calculate the bearing stress (MPa) between the strut and the pin.
8. Calculate the shear stress (MPa) in the pin.
9. Calculate the shear stress (MPa) in the anchor bolts.
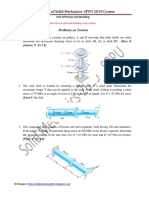
SITUATION NO. 4
The beam, W410 mm × 67 kg/m, with 9 mm web thickness subjects the girder,
W530 mm × 109 kg/m with 12 mm web thickness to a shear load, P (kN). 2L
– 90 mm × 90 mm × 6 mm with bolts frame the beam to the girder. Diameter
of hole is 3mm larger than the bolt diameter. All steel are A36 with Fy
= 248 MPa, Fu = 400 MPa
Given:
S1 = 40 mm S4 = 110 mm
S2 = 40 mm S5 = 40mm
S3 = 80 mm
Allowable Stresses are as follows:
Bolt shear stress, Fv = 120 MPa
Bolt bearing stress, Fp = 480 MPa
10. Determine the allowable load, P (kN), based on the shear capacity
of the 4 – 22 mm diameter bolts (4 – d1).
11. Calculate the allowable load, P (kN), based on bolt bearing stress
on the web of the beam.
12. Determine the allowable load P, based on the block shear failure
on the web of the beam.
PREPARED BY: ENGR. DOMINIC FLORES
PHINMA EDUCATION – ARAULLO UNIVERSITY
CIE 096 – PROFESSIONAL INTEGRATION 4 (SEC)
ASSESSMENT
SET
SITUATION NO. 5
Refer to figure. The butt connection shows 8 – 22 mm diameter A325 bolts
spaced as follows:
S1 = 40 mm; S2 = 80 mm, S3 = 50 mm; S4 = 100 mm
Thickness of plates (top and bottom): t1 = 12 mm
Thickness of plates (middle): t2 = 16 mm
Steel strength and stresses are:
Yield strength, Fy = 248 MPa
Ultimate strength, Fu = 400 MPa
Nominal bolt shear stress, Fv = 120 MPa
Use LRFD.
13. Calculate the design tensile load, T (kN) based on tension on the
net area of the middle plate. Assume the hole diameter is 3 mm
more than the bolt diameter. Use = 0.75.
14. Calculate the design tensile load, T (kN) based on bolt shear.
Use = 0.75.
SITUATION NO. 6
15. Determine if the structure given below is determinate,
indeterminate or unstable.
PREPARED BY: ENGR. DOMINIC FLORES
You might also like
- HydraulicsDocument12 pagesHydraulicsMugiwara Sparrow0% (1)
- Stress-Strain Examples PDFDocument5 pagesStress-Strain Examples PDFGachirb BratNo ratings yet
- Steel Design 6 April 2023 PDFDocument2 pagesSteel Design 6 April 2023 PDFTristan CatapangNo ratings yet
- PS Steel - Set 1Document4 pagesPS Steel - Set 1Jovanie CabanigNo ratings yet
- Problem 1 Ce Board Nov 2011, Nov 2013: Answer: 150mpa, 119.4mpa, 51.69mpaDocument4 pagesProblem 1 Ce Board Nov 2011, Nov 2013: Answer: 150mpa, 119.4mpa, 51.69mpaLester John Precillas100% (1)
- Limit, Fits and TolerancesDocument85 pagesLimit, Fits and TolerancesdankuNo ratings yet
- Shear Reinforcement: Torrico - Reinforcedconcrete - ShearreinforcementDocument4 pagesShear Reinforcement: Torrico - Reinforcedconcrete - ShearreinforcementMarvin Carl GranadaNo ratings yet
- May 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 5: Eview NnovationsDocument4 pagesMay 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 5: Eview NnovationsKian Inductivo100% (1)
- ExamsDocument8 pagesExamsJoy CeeNo ratings yet
- Review Module 40 Steel4 Part2 Nov2021Document1 pageReview Module 40 Steel4 Part2 Nov2021Dream CatcherNo ratings yet
- Module 30 - Stress-Strain RIDocument3 pagesModule 30 - Stress-Strain RIClark Sibi100% (1)
- Polytechnic University of The Philippines: T C 1 P UDocument11 pagesPolytechnic University of The Philippines: T C 1 P Uacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Steel Design Module 6Document2 pagesSteel Design Module 6Anonymous KaiNo ratings yet
- MODULAR QUIZ - 57 - Steel DesignDocument9 pagesMODULAR QUIZ - 57 - Steel DesignCornelio J. FernandezNo ratings yet
- B. Tech. EXAMINATION, May 2017: No. of Printed Pages: 05 Roll No. ......................Document3 pagesB. Tech. EXAMINATION, May 2017: No. of Printed Pages: 05 Roll No. ......................Rahul SainiNo ratings yet
- "No Copying and Sharing of Answers ": Finals ExaminationDocument5 pages"No Copying and Sharing of Answers ": Finals ExaminationArvin LopezNo ratings yet
- 07 r05310305 Design of Machine Members IDocument8 pages07 r05310305 Design of Machine Members IandhracollegesNo ratings yet
- Review Module 40 - Steel 4 - Part 1Document2 pagesReview Module 40 - Steel 4 - Part 1Andrea MagtutoNo ratings yet
- Steel QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesSteel QuestionnaireenggNo ratings yet
- Nehru Institute of Engineering and TechnologyDocument3 pagesNehru Institute of Engineering and TechnologykousikkumaarNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Strength of Materials August 2014Document87 pagesLecture On Strength of Materials August 2014Cha Castillo100% (1)
- RCD 108 SitsDocument46 pagesRCD 108 Sitsmike reyesNo ratings yet
- MECH 314 Unit 1Document34 pagesMECH 314 Unit 1Tomas Otero IIINo ratings yet
- Simple Stresses From MathalinoDocument58 pagesSimple Stresses From MathalinoGien Lim100% (5)
- EngDocument11 pagesEngMugiwara SparrowNo ratings yet
- RC Lec01 Dec2019-2020Document8 pagesRC Lec01 Dec2019-2020king koyNo ratings yet
- Worked Calculations Non Permanent Fasteners With Naration - PPSXDocument28 pagesWorked Calculations Non Permanent Fasteners With Naration - PPSXTeeNo ratings yet
- Enhancement Program TIMBER DESIGNDocument7 pagesEnhancement Program TIMBER DESIGNChristian VillenaNo ratings yet
- Stress Calculation (WSD)Document18 pagesStress Calculation (WSD)Alexes DomingoNo ratings yet
- Review Module - SMAT 3 - Part 2Document1 pageReview Module - SMAT 3 - Part 2Jessa Mae BesingNo ratings yet
- MOM Mod4@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument15 pagesMOM Mod4@AzDOCUMENTS - inMahadev MetriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Simple StressesDocument27 pagesChapter 1 Simple StressesLalaine RamosNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 AssignmentsDocument5 pagesUnit 4 AssignmentsbattuarunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Part II STDDocument35 pagesChapter 8 Part II STDBelkacem AchourNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 (Allowable Stress)Document5 pagesTugas 1 (Allowable Stress)WAHYU DWI LESTARINo ratings yet
- Assignment 01Document3 pagesAssignment 01RamNocturnalNo ratings yet
- Stress: Normal Stress Shearing Stress Bearing StressDocument79 pagesStress: Normal Stress Shearing Stress Bearing StressMelanie Samsona100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Simple StressesDocument39 pagesChapter 1 - Simple StressesJovy Notorio100% (2)
- Steel Design Regular Review Apr 2023Document2 pagesSteel Design Regular Review Apr 2023Carlo Magno Olano JrNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument8 pagesLab ReportHenrique PradoNo ratings yet
- Stress: Normal Stress Shearing Stress Bearing StressDocument23 pagesStress: Normal Stress Shearing Stress Bearing StressMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Beam Deflection If Minimum Thickness Is Not Satisfied, Check Beam DeflectionDocument7 pagesBeam Deflection If Minimum Thickness Is Not Satisfied, Check Beam DeflectionLester John PrecillasNo ratings yet
- Simple Stress PDFDocument20 pagesSimple Stress PDFJullian Paul GregorioNo ratings yet
- Bolted ConnectionsDocument16 pagesBolted ConnectionsCharizza Montarin CENo ratings yet
- Dme Home Assignment 2019-20Document4 pagesDme Home Assignment 2019-20VenkateshNo ratings yet
- B616-212.002 PP 3-9 Smit BRKT Strength CalcsDocument7 pagesB616-212.002 PP 3-9 Smit BRKT Strength Calcsnavalzero910100% (1)
- Torrico ReinforcedConcrete 01 PDFDocument8 pagesTorrico ReinforcedConcrete 01 PDFNajib A. CasanNo ratings yet
- May 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 4: Eview NnovationsDocument3 pagesMay 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 4: Eview NnovationsKian Inductivo100% (1)
- Prestressed Concrete - 1 IntroductionDocument21 pagesPrestressed Concrete - 1 Introduction4493464No ratings yet
- Point Load Strength Index Test of RockDocument5 pagesPoint Load Strength Index Test of RockRasydanRais50% (4)
- Problem SetDocument3 pagesProblem SetChristian RigonNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET NO. 1 Singly Reinforced BeamsDocument1 pagePROBLEM SET NO. 1 Singly Reinforced BeamsJorgieCaraigNo ratings yet
- Question For IcDocument4 pagesQuestion For IcPrem MNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Fuad AhmedinNo ratings yet
- ENSC 13 Problem Set 1Document4 pagesENSC 13 Problem Set 1Roxanne de RoxasNo ratings yet
- Design 2Document29 pagesDesign 2cielo_cetd3670No ratings yet
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- Oceanography For General Studies UPSC Civil Services Exam: Short Notes PDFDocument71 pagesOceanography For General Studies UPSC Civil Services Exam: Short Notes PDFHari ShankarNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Computer Aided Analysis and Design ofDocument7 pagesComparison of Computer Aided Analysis and Design ofPacha Khan KhogyaniNo ratings yet
- VRF Application DAIKIN PDFDocument256 pagesVRF Application DAIKIN PDFMohamed Yassine LahianiNo ratings yet
- Square Wave SimulinkDocument10 pagesSquare Wave SimulinkEysha qureshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 McmurryDocument23 pagesChapter 5 McmurryCarolina XavierNo ratings yet
- Face Prep Wipro NTH Slot Analysis 25th Sep 2021 Slot 2Document22 pagesFace Prep Wipro NTH Slot Analysis 25th Sep 2021 Slot 2Viyyapu SaradaNo ratings yet
- Innovative Push Launching Technique For Long Span BridgeDocument8 pagesInnovative Push Launching Technique For Long Span BridgeAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Nov 21st 2014 Friday: Products DetailsDocument1 pageNov 21st 2014 Friday: Products DetailsXuân Giang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- ME 4131 Notes 4Document2 pagesME 4131 Notes 4jaz squaredNo ratings yet
- Pamphlet 121 - Explosive Properties - Ed. 3 - 01-2009Document37 pagesPamphlet 121 - Explosive Properties - Ed. 3 - 01-2009sangoi87No ratings yet
- F07 Hw11a PDFDocument12 pagesF07 Hw11a PDFLuis ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Highway Pavement-1Document60 pagesIntroduction To Highway Pavement-1Sagni Oo ChambNo ratings yet
- Spare Part List - LJ 320P - 20110316Document54 pagesSpare Part List - LJ 320P - 20110316Henrique J. AntunesNo ratings yet
- Pelton WheelDocument5 pagesPelton WheelMuhammedShafiNo ratings yet
- Spread Footing Verification Input Data: Ef Ef 3 Su 3Document8 pagesSpread Footing Verification Input Data: Ef Ef 3 Su 3asrdjanovNo ratings yet
- Alia APT3000 Pressure TransmitterDocument2 pagesAlia APT3000 Pressure TransmitterRexCrazyMindNo ratings yet
- Preventive MaintenanceDocument46 pagesPreventive MaintenanceNandhakumarNo ratings yet
- An Interceu Busbar Topology To Improve Resilience To Anomalies of Copper Electrorefining ProcessDocument6 pagesAn Interceu Busbar Topology To Improve Resilience To Anomalies of Copper Electrorefining ProcessPablo ParraguezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Catalytic ReactionsDocument33 pagesChapter 7. Catalytic ReactionsAbhinav AnandNo ratings yet
- BiCMOS FabricationDocument7 pagesBiCMOS FabricationMahabub Hossain100% (1)
- Generic TWS600S Service ManualDocument113 pagesGeneric TWS600S Service ManualWise So100% (2)
- Spray-Type Deaerating Heaters: TABLE 12.2Document2 pagesSpray-Type Deaerating Heaters: TABLE 12.2Yanuar KrisnahadiNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Test Pressure CalculationDocument1 pageHydrostatic Test Pressure Calculationmarclkm93% (15)
- CMAA MovementDocument9 pagesCMAA MovementalbertoxinaNo ratings yet
- ECE 2416 JKUAT 2021 - Lecture NotesDocument52 pagesECE 2416 JKUAT 2021 - Lecture NotesThomasNo ratings yet
- Almansoori Inspection Services: Travelling Block AssemblyDocument2 pagesAlmansoori Inspection Services: Travelling Block AssemblyRanjithNo ratings yet
- Seplat Energy PLC: Ohaji South Flare Out ProjectDocument6 pagesSeplat Energy PLC: Ohaji South Flare Out ProjectELIJAH OKONNo ratings yet
- Nex Flow: Frigid-X Panel CoolerDocument17 pagesNex Flow: Frigid-X Panel CoolerrehanNo ratings yet
- Question For Homi Bhabha PDFDocument3 pagesQuestion For Homi Bhabha PDFPRASHNo ratings yet
- Astm F 519-97 E98Document12 pagesAstm F 519-97 E98Jorge ToribioNo ratings yet