Professional Documents
Culture Documents
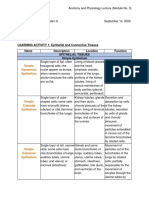
01 Tissues Key
Uploaded by
Britney NguyenOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
01 Tissues Key
Uploaded by
Britney NguyenCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Anatomy Name
Yes No Epithelial tissue is comprised of cells packed together tightly.
A tract is a body space that connects to the external environment.
The lumen is the inner part of a tract, duct, or space.
Yes No Epithelial tissue can form protective barriers.
Absorption is movement of materials into the body across an epithelial surface.
Yes No Epithelial tissue may be found in glands and specialized for secretion.
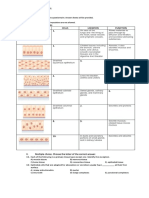
Has cilia and microvilli B A. basal surface of cell
Faces lumen of duct or tube B B. apical surface of cell
Typically supported by basement membrane A
Yes No Epithelial tissue tends to be highly vascularized with capillaries running between cells.
Yes No Epithelial cells are regularly regenerated.
A Basal lamina A. Layer of basement membrane produced by epithelial cells
B Reticular lamina B. Layer of basement membrane produced by connective tissue
Squamous D A. cells change shape
Cuboidal C B. cells are long and narrow
Columnar B C. cells are box-shaped
Transitional A D. cells are flat and scale-like
A Simple A. Single layer of cells
B Stratified B. Multiple layers of cells
Small ducts in kidneys C A. Stratified squamous
Air sacs in lungs B B. Simple squamous
Walls of capillaries B C. Simple cuboidal
Lining of small intestine D D. Simple columnar
Lining of urinary bladder E E. Transitional
Outer layers of skin A
Lining inside mouth A
Endocrine gland B A. secretions are released to external environment or space that
connects to external environment
Exocrine gland A B. secretions are released into blood
Cylindrical exocrine gland C A. acinar
Sac-like exocrine gland B B. alveolar
Rounded exocrine gland A C. tubular
Some glands have myoepithelial cells which contract to move secretions
out of the glands.
Endothelium is the inner epithelial lining of blood vessels.
Mesothelium is the epithelial lining of the walls of body cavities and outer surface of organs.
Cutaneous membrane B A. epithelial membrane lining tracts
Mucous membrane C B. epithelial membrane in skin
Serosal membrane D C. epithelial membrane lining body cavities and around organs;
secretes lubricating fluid
Parietal pleura C A. serosal membrane lining walls of abdominopelvic cavity
Visceral pleura D B. serosal membrane on surface of organs in abdominopelvic cavity
Parietal peritoneum A C. serosal membrane lining walls of chest cavity
Visceral peritoneum B D. serosal membrane on surface of lungs
Yes No Connective tissue is comprised primarily of extracellular material with few cells.
Yes No Fibers are typically elongated proteins.
Collagen fibers C A. form a network or framework
Elastic fibers B B. can stretch or compress and return to original shape
Reticular fibers A C. strong but flexible
Fibroblasts A A. lay down extracellular matrix in loose and dense connective tissue
Chondroblasts C B. lay down extracellular matrix in bone
Osteoblasts B C. lay down extracellular matrix in cartilage
Yes No Connective tissue can have defense cells such as macrophages, mast cells, and
plasma cells.
Thick collagen fibers interwoven together B A. Dense regular
Thick collagen fibers arranged in parallel A B. Dense irregular
Found in respiratory airways C C. Elastic
Found in joint capsules; resists forces in multiple directions B
Found in tendons and ligaments; resists forces in one main direction A
A. Areolar B. Adipose C. Reticular
A Thin collagen and elastic fibers which are not abundant
C Network of fibers in gelatinous matrix
B Stores energy; provides cushioning and insulation
C Found around and within organs; holds cells in place
A Found in loose fascia holding structures together
Yes No Blood, lymph, bone, and cartilage are types of connective tissue.
List the three types of cartilage:
a. hyaline cartilage b. fibrocartilage c. elastic cartilage
List the three types of muscle tissue:
a. skeletal b. cardiac c. smooth
You might also like
- Test Bank For Histology and Cell Biology 2nd Edition Abraham L KierszenbaumDocument5 pagesTest Bank For Histology and Cell Biology 2nd Edition Abraham L KierszenbaumMarta Tronaas100% (38)
- Histology Question Bank-1Document55 pagesHistology Question Bank-1Abd El-Rahman Salah100% (5)
- MCQs in Connective Tissue and BloodDocument7 pagesMCQs in Connective Tissue and Bloodashour_abdelsalam632681% (27)
- Histology QuestionsDocument8 pagesHistology QuestionsRutendo Mutosvori100% (1)
- Histology Mock ExamDocument73 pagesHistology Mock ExamRozen GaiserNo ratings yet
- Histology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers For PDFDocument26 pagesHistology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers For PDFslinger1482% (96)
- Anatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology - ExamDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology - ExamQoppppNo ratings yet
- Socrative Quiz 1Document3 pagesSocrative Quiz 1Rachel HayonNo ratings yet
- Histology Seminar 3 MCQDocument31 pagesHistology Seminar 3 MCQNeo ShiriNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam Part IIIDocument8 pagesDiagnostic Exam Part IIIAkosi AbakadaNo ratings yet
- BBS - Finals Compilation - Project Coffee PDFDocument318 pagesBBS - Finals Compilation - Project Coffee PDFNoel JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Exam IIIDocument8 pagesAnatomy Exam IIIJonathanNo ratings yet
- Lab Technologist-7Document15 pagesLab Technologist-7AHAMED SHIFAAN100% (1)
- Ch. 3 Tissues Test: NameDocument5 pagesCh. 3 Tissues Test: Namestephanieyoung07No ratings yet
- Histology 2Document1 pageHistology 2zaydeeeeNo ratings yet
- GITDocument19 pagesGITPurple Ivy GuarraNo ratings yet
- Ana Lecture 1Document5 pagesAna Lecture 1Nureen Alizah OsbucanNo ratings yet
- Lab Technologist-6Document24 pagesLab Technologist-6AHAMED SHIFAANNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues Questions and AnswersDocument24 pagesCells and Tissues Questions and AnswersAJ Sagg. Cann.No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Exam 2 NotesDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Exam 2 NotesMissy Sanders100% (1)
- Module IV MCQ Exam (A)Document6 pagesModule IV MCQ Exam (A)Precious JuliusNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 TissuesDocument6 pagesLesson 2 TissuesRodefe AmitNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument16 pagesBiology ReviewerAngela Nicole ManasNo ratings yet
- CB - IX - Sci - CH 6 - Tissues - MCQsDocument3 pagesCB - IX - Sci - CH 6 - Tissues - MCQsHarshikaNo ratings yet
- General Biology Summative Test 2Document6 pagesGeneral Biology Summative Test 2Jean RubyNo ratings yet
- Classification of Epithelial TissueDocument2 pagesClassification of Epithelial TissueItzel HinojosNo ratings yet
- Structural OrganizationDocument18 pagesStructural OrganizationMSANITYNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue: D. Urinary BladderDocument3 pagesEpithelial Tissue: D. Urinary BladderNuhu SibaNo ratings yet
- Tissues MCQDocument3 pagesTissues MCQananthi rajasekarNo ratings yet
- A&P Chapter 4 Quiz 1Document3 pagesA&P Chapter 4 Quiz 1Nicole Dela Torre100% (1)
- Tissues 9thDocument3 pagesTissues 9thmaulikngandhiNo ratings yet
- Name This Section: A) Frontal B) Sagittal C) Lateral D) Transverse E) DistalDocument32 pagesName This Section: A) Frontal B) Sagittal C) Lateral D) Transverse E) DistalRachel GordonNo ratings yet
- Title: Tissues: Simple Squamous EpitheliumDocument12 pagesTitle: Tissues: Simple Squamous EpitheliumManelli Faten Buenaventura100% (1)
- Structural Organisation NewDocument10 pagesStructural Organisation NewRuthraNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PrelimDocument19 pagesReviewer PrelimALPEREZ, GRACE LYN C.No ratings yet
- F Module FADocument2 pagesF Module FAPiyo ThathsaraniNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes Ch07 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument6 pages11 Biology Notes Ch07 Structural Organisation in AnimalsSham PhadtareNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledPatricia DesireeNo ratings yet
- Histo ReviewerDocument21 pagesHisto ReviewerIan Iglesia100% (1)
- HIS-01 LAB Histology 1 (1/1) 01 FinalsDocument2 pagesHIS-01 LAB Histology 1 (1/1) 01 Finalsrenato renatoNo ratings yet
- Test 1 DPCDocument6 pagesTest 1 DPCNur Shahirah Nasir Faculty of Social Science and FoundationNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument19 pagesMCQMohamed Shaban faroukNo ratings yet
- Types of Tissue 13.01.2016Document18 pagesTypes of Tissue 13.01.2016Christian MontesNo ratings yet
- Test Questions: A. Cardiovascular System and LymphaticsDocument24 pagesTest Questions: A. Cardiovascular System and LymphaticsLunna Cruz100% (1)
- Tissue ReviewerDocument3 pagesTissue ReviewerFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- Identifying Parts of Respiratory System, As Level BioDocument10 pagesIdentifying Parts of Respiratory System, As Level BioFatima-KNo ratings yet
- Zoology QP 04-08-2023Document17 pagesZoology QP 04-08-2023sujathadevarakonda81No ratings yet
- PERIDA EMMALYN T. - BSci103-Lesson 2.1-Learning TaskDocument13 pagesPERIDA EMMALYN T. - BSci103-Lesson 2.1-Learning TaskEmmalyn PeridaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions June6 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument10 pagesNcert Solutions June6 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsdrathod4653No ratings yet
- Chapter 04Document78 pagesChapter 04aljh62002No ratings yet
- Revision - Cell and TissuesDocument18 pagesRevision - Cell and TissuesFifa MatchesNo ratings yet
- SMS..exam 1Document8 pagesSMS..exam 1Ozgan SüleymanNo ratings yet
- Bank of Questions 1 Solved Tema 1-6Document17 pagesBank of Questions 1 Solved Tema 1-6Valesska SánchezNo ratings yet
- Tissues: By: Ruth Abigail C. Valdez BSN, RNDocument62 pagesTissues: By: Ruth Abigail C. Valdez BSN, RNrJNo ratings yet
- Narayana Medical PG Coaching - Week-03 Test (28-09-2014) Anatomy (Histology & Genetics)Document5 pagesNarayana Medical PG Coaching - Week-03 Test (28-09-2014) Anatomy (Histology & Genetics)drpnnreddyNo ratings yet