Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nutrition in Human
Uploaded by
cyxCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nutrition in Human
Uploaded by
cyxCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter test
7 Nutrition in humans
Name: ( ) Class: Date:
Total marks: 40 marks
Time allowed: 40 minutes Score: / 40
Answer ALL questions.
A. Concept checking (10 marks, 1 mark each)
1. The process of nutrition does not include the
A. intake of food.
B. use of food molecules for metabolism.
C. removal of metabolic wastes.
D. breakdown of food substances into simple molecules. □
2. Which of the following structure does not produce digestive juice?
A. Pancreas
B. Small intestine
C. Gall bladder
D. Stomach □
2 1 2 2
3. The dental formula of an animal is i 2 , c 1 , pm 2 , p 2 . How many teeth does this
animal have?
A. 7
B. 14
C. 28
D. 32 □
4. Which of the following statements about physical digestion and chemical digestion is correct?
A. Bile involves in both physical and chemical digestion.
B. In the mouth cavity, carbohydrates undergo physical digestion only.
C. In both types of digestion, food substances are broken down into simpler molecules.
D. Physical digestion can enhance the efficiency of chemical digestion. □
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 7-1
Chapter test 7 Nutrition in humans
Direction: Questions 5 to 7 refer to the graph below, which shows the percentage of undigested
molecules (P, Q and R) present along the alimentary canal.
100
10 Q R
Percentage of
undigested
50
molecules
(%)
0
Mouth Oesophagus Stomach Small Colon
cavity intestine
5. Which of the following statements correctly interprets the graph above?
A. No digestion occurs in the mouth cavity.
B. The rate of digestion is the fastest in the stomach.
C. The digestion of R is completed in the small intestine.
D. All molecules are absorbed in colon. □
6. Which of the following correctly identifies the three food substances?
P Q R
A. starch protein lipid
B. protein lipid starch
C. lipid starch protein
D. starch lipid protein □
7. Most water is absorbed in the small intestine. Based on the graph above, this is because
A. the small intestine has many villi to increase the surface area for water absorption.
B. most of the food substances are absorbed in the small intestine, the water potential of
blood in the small intestine decreases.
C. the alkaline intestinal juice favours the absorption of water in the small intestine.
D. the rate of digestion is the highest in the small intestine. □
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 7-2
Chapter test 7 Nutrition in humans
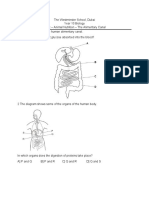
8. The diagram below shows a part of the alimentary canal. Blood vessel X connects the small
intestine and the liver.
liver
blood vessel X
small intestine
Which of the following descriptions about blood vessel X is correct?
A. It carries oxygenated blood to the liver.
B. The water potential of the blood inside blood vessel X is low.
C. It is an artery because the blood inside flows towards an organ.
D. It transports vitamin A to the liver. □
9. Lipids absorbed in the small intestine are first transported to the
A. liver.
B. gall bladder.
C. large intestine.
D. heart. □
10. Which of the following is not an excretory waste produced by the liver?
A. carbon dioxide
B. urea
C. bile pigment
D. bile salt □
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Related
7.1 7.5 7.2 7.5 7.5 7.5 7.5 7.7 7.7 7.7
section
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 7-3
Chapter test 7 Nutrition in humans
B. Problem solving (18 marks)
11. Peter has obesity. His doctor suggested him to take drug X to treat obesity. Drug X is effective
in inhibiting the action of pancreatic lipase.
lipase
lipids fatty acids + glycerol
The diagrams below show the shapes of a lipid molecule and the active part of drug X.
the shape of a lipid molecule active part of drug X
(a) After taking drug X, Peter found that his faeces became oily. Based on the diagrams
above, suggest the mechanism of drug X, which lead to the egestion of oily faeces.
(3 marks)
(b) Peter’s doctor suggested him to take vitamin supplements during the treatment. Suggest
what type of vitamins he should take and explain why. (2 marks)
(Total: 5 marks)
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 7-4
Chapter test 7 Nutrition in humans
12. A student studied the digestion of proteins in humans. He added some hydrochloric acid into
milk and stirred it with a glass rod. The milk became coagulated.
(a) What action of the stomach is simulated by the stirring action of the glass rod? (1 mark)
(b) Suggest why the digestion of milk protein can be facilitated by coagulation. (2 marks)
(c) The student then added some proteases into the coagulated milk. However, he mistakenly
added pancreatic proteases instead of proteases secreted by the stomach. He found that no
digestion occurs. Suggest why. (2 marks)
(Total: 5 marks)
13. The table below shows the relative amount of fatty acids and amino acids along the alimentary
canal after a meal.
Region of the
Fatty acids Amino acids
alimentary canal
oesophagus low low
stomach low increase
duodenum ___________________ ___________________
ileum ___________________ ___________________
colon low low
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 7-5
Chapter test 7 Nutrition in humans
(a) Name the action that helps moving food along the alimentary canal. (1 mark)
(b) Complete the table to show the changes in the amounts of fatty acids and amino acids
(increase or decrease) in the duodenum and the ileum. (2 marks)
(c) Explain the changes in the amounts of fatty acids in the
(i) duodenum. (2 marks)
(ii) ileum. (2 marks)
(d) Explain why a high-protein diet will lead to a high concentration of urea in the blood in
the hepatic vein? (1 mark)
(Total: 8 marks)
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 7-6
Chapter test 7 Nutrition in humans
C. Exam challenge (12 marks)
14. An investigation was carried out to study the effect of bile salt on the digestion of lipids. The
experiment was carried out at 37 oC. The diagram below shows the set-up.
Tube A Tube B Tube C
3
5 cm full-cream milk + 3
5 cm full-cream milk + 5 cm3 full-cream milk +
3
2 cm 3% lipase solution + 2 cm3 3% lipase solution + 2 cm3 3% boiled lipase solution +
phenolphthalein 2 cm3 bile salt + 2 cm3 bile salt +
phenolphthalein phenolphthalein
Phenolphthalein is a pH indicator. The table below shows the colour change of phenolphthalein
solution:
pH > 10 pH < 8
Colour of phenolphthalein pink colourless
The results of the investigation are shown below.
Tube A Tube B Tube C
Initial colour pink pink pink
Colour of indicator after 5 minutes pink colourless pink
Colour of indicator after 10 minutes pink colourless pink
Colour of indicator after 15 minutes colourless colourless pink
(a) (i) Explain the result of Tube A. (2 marks)
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 7-7
Chapter test 7 Nutrition in humans
(ii) Explain the differences in the results of Tube A and Tube B. (3 marks)
(iii) Explain the result of Tube C. (2 marks)
(b) Based on the result of the above experiment and your biological knowledge, predict how
the digestion of lipids would be affected if a person has high-fat meals after his gall
bladder is removed. (3 marks)
(c) Draw a flow chart to show how the digested lipid molecules are transported from the
small intestine to other parts of the body (including the organs and vessels involved).
(2 marks)
(Total: 12 marks)
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 7-8
Chapter test 7 Nutrition in humans
Marking scheme
A. Concept checking (10 marks, 1 mark each)
1. C 2. C 3. C 4. D 5. C
6. A 7. B 8. B 9. D 10. D
(1 mark each)
B. Problem solving (18 marks)
11. (a) The shape of drug X is similar to the shape of a lipid molecule. (1)
Drug X occupies the active site of pancreatic lipase and prevents lipids from binding to
the enzyme. (1)
The digestion of lipids is hindered and the undigested lipids are egested in faeces. (1)
(b) Fat-soluble vitamins (1)
Fat-soluble vitamins have to dissolve in lipids before absorption. (1)
Less fat-soluble vitamin can be absorbed together with lipids when taking drug X.
(Total: 5 marks)
12. (a) (i) Churning (1)
(ii) Milk proteins become semi-solid and therefore they stay in the stomach for a longer
time (1)
and to be digested by proteases. (1)
(b) Pancreatic proteases work best in alkaline medium. (1)
Pancreatic proteases are denatured in acidic medium. (1)
(Total: 5 marks)
13. (a) Peristalsis (1)
(b)
Region of the
Fatty acids Amino acids
alimentary canal
Duodenum increase increase
Ileum decrease decrease
(0.5 mark for each correct answer)
(c) (i) Any two of the following: (2)
receive bile (1)
lipids are emulsified by bile salts (1)
receive lipases from the pancreas / intestinal cells (1)
lipases digest lipids (1)
lipids are digested to form fatty acids (1)
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 7-M1
Chapter test 7 Nutrition in humans
(ii) Any two of the following: (2)
absorption / diffusion of fatty acids (1)
into lacteals of villi (1)
into lymph / lymph vessels (1)
(d) Liver breaks down excess amino acids to urea which is transported away through hepatic
vein. (1)
(Total: 8 marks)
C. Exam challenge (12 marks)
14. (a) (i) Any two of the following: (2)
hydrolysis of lipids (1)
produces fatty acids (1)
leads to a decrease in pH value (1)
(ii) Any two of the following: (3)
tube B has bile salts while tube A does not (1)
bile salts emulsify the lipids in the full-cream milk (1)
to increase the surface area for the action of lipase (1)
fatty acids are produced at a faster rate (1)
(iii) Lipase is denatured after boiling. (1)
No hydrolysis of lipids / production of fatty acids occur. (1)
(b) Gall bladder temporarily stores bile. It can regulate the amount of bile released. (1)
After the gall bladder is removed, the liver continues to produce bile, however the amount
of release cannot be regulated. (1)
The rate of the lipid digestion decreases as the amount of bile available is not enough to
emulsify all the fat. (1)
(c) Name 4 correct organs and vessel (1); link all the organs and vessels (1)
small intestine lacteal lymph vessel vena cava heart
aorta various parts of the body (2)
(Total: 12 marks)
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 7-M2
You might also like
- Healthy Pancreas, Healthy You. Part II. Healing Foods in the Digestive (Pancreatic) DisordersFrom EverandHealthy Pancreas, Healthy You. Part II. Healing Foods in the Digestive (Pancreatic) DisordersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Healthy Pancreas, Healthy You. Part 1: Structure, Function, and Disorders of the PancreasFrom EverandHealthy Pancreas, Healthy You. Part 1: Structure, Function, and Disorders of the PancreasRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Healthy Pancreas, Healthy You. Part 3. How to Improve the Exocrine Pancreatic Function, Postpone Pancreatic Deterioration, and Heal Digestive (Pancreatic) DisordersFrom EverandHealthy Pancreas, Healthy You. Part 3. How to Improve the Exocrine Pancreatic Function, Postpone Pancreatic Deterioration, and Heal Digestive (Pancreatic) DisordersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- (GR) COMPLETE - Multiple Choice Quiz Questions - BiologyDocument21 pages(GR) COMPLETE - Multiple Choice Quiz Questions - Biologyzoha shahzadNo ratings yet
- Ix Biology Worksheet Nutrition in Mammals 1Document7 pagesIx Biology Worksheet Nutrition in Mammals 1muneeza duevesh100% (1)
- Chap 02 - Set 2Document7 pagesChap 02 - Set 2Khor Han YiNo ratings yet
- 9 Regions of AbdomenDocument4 pages9 Regions of AbdomenKryza Dale Bunado Batican100% (1)
- Tanveer Notes - CPSP Imortant PointsDocument103 pagesTanveer Notes - CPSP Imortant PointsAyisha NazNo ratings yet
- Human Nutrition (Multiple Choice) QPDocument17 pagesHuman Nutrition (Multiple Choice) QPkeenNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive System ExplainedDocument3 pagesHuman Digestive System ExplainedSana Shakeel100% (8)
- Digestion 2 MCQDocument6 pagesDigestion 2 MCQgopod50% (4)
- The Digestive System Summative Test - Q3 - M1Document2 pagesThe Digestive System Summative Test - Q3 - M1Metchel100% (1)
- Digestive System TestDocument4 pagesDigestive System TestDaniel Walsh100% (1)
- Digestion Test BiologyDocument3 pagesDigestion Test BiologyKatrīna SimanovskaNo ratings yet
- Exploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008Document2 pagesExploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008shazia imamNo ratings yet
- Pathology Slides in English (Little Bit Bulgarian Too:)Document89 pagesPathology Slides in English (Little Bit Bulgarian Too:)Fırat Güllü94% (16)
- Human Digestive System WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Digestive System WorksheetEvgeni Genev60% (5)
- Human Digestive System WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Digestive System WorksheetSumi Vj100% (1)
- DC Bio Assignment 2Document14 pagesDC Bio Assignment 2api-491445567No ratings yet
- Human Nutrition Classified Past Paper 2 Solved IGCSE Biology 0610 GCSE O LevelDocument38 pagesHuman Nutrition Classified Past Paper 2 Solved IGCSE Biology 0610 GCSE O LevelIGCSE Physics & Chemistry100% (1)
- Final Exam in ScienceDocument2 pagesFinal Exam in ScienceMarilou VirtudazoNo ratings yet
- Basic Abdominal Ultrasound - BestDocument36 pagesBasic Abdominal Ultrasound - Bestifeanyi100% (2)
- Biology Assignment 2Document18 pagesBiology Assignment 2api-491537689No ratings yet
- Digestion System Science Form 2Document3 pagesDigestion System Science Form 2SCNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesDigestive SystemWisdiyan Hadi HastomoNo ratings yet
- Digestion Quiz MraDocument4 pagesDigestion Quiz Mraapi-353447897No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Nutrition & Digestion WorksheetDocument2 pagesGrade 9 Nutrition & Digestion WorksheetthanunovaisnoNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition DigestionDocument26 pagesAnimal Nutrition Digestionabdulrehman mughalNo ratings yet
- Bio More PracticeDocument6 pagesBio More PracticemeromoNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument22 pagesDigestionNaphtali MwansaNo ratings yet
- S3Biology Exercise 2 (Food)Document6 pagesS3Biology Exercise 2 (Food)廖陞民(LEFT-2021) LIU SING MANNo ratings yet
- Biology 2nd Term ExamDocument10 pagesBiology 2nd Term ExamJohny CashNo ratings yet
- Digestive System.Document3 pagesDigestive System.Andri MulyaniNo ratings yet
- 2021 Hyss Sr2 S2e Sci Sect A (QP)Document14 pages2021 Hyss Sr2 S2e Sci Sect A (QP)MUMARNo ratings yet
- The Alimentary Canal W.S.Document3 pagesThe Alimentary Canal W.S.Hiba WasimNo ratings yet
- Digestive System. Paper. 1. Name-Nikol Surname - Kokhiya /14 1Document7 pagesDigestive System. Paper. 1. Name-Nikol Surname - Kokhiya /14 1Giorgi JincharadzeNo ratings yet
- Tissues and Organs - Digestive SystemDocument8 pagesTissues and Organs - Digestive SystemAbijah ClarkeNo ratings yet
- Biology Weekly Exercise g7 s2 PB Nutrition in HumansDocument2 pagesBiology Weekly Exercise g7 s2 PB Nutrition in HumansD'ferti AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Absorption, Assimilasion and Defecation SCIENCE FORM 2Document2 pages3.4 Absorption, Assimilasion and Defecation SCIENCE FORM 2SCNo ratings yet
- Bio Assignment - Danika Wilson BrownDocument16 pagesBio Assignment - Danika Wilson Brownapi-491784406No ratings yet
- Digestion and EnzymesDocument8 pagesDigestion and Enzymesanusha051142No ratings yet
- ANNUAL REVISION TEST SYSTEM FOR BIOLOGY CLASSDocument2 pagesANNUAL REVISION TEST SYSTEM FOR BIOLOGY CLASSFaAriiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Life Processes MCQ Practice QuestionsDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 10 Life Processes MCQ Practice QuestionsBasavarajNo ratings yet
- final-test-for-4th-quarter-scienceDocument1 pagefinal-test-for-4th-quarter-scienceLeah DumdumNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Digestive System Test BankDocument8 pagesUnit 5: Digestive System Test Bankjv peridoNo ratings yet
- B g8 Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesB g8 Digestive SystemnoorlailyNo ratings yet
- Digestion: Section A: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument11 pagesDigestion: Section A: Multiple-Choice QuestionsSoniaAlexNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive System WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Digestive System WorksheetMoath AlsaidNo ratings yet
- Grade 10mDocument5 pagesGrade 10mSameh NoorNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Biol1700 Mar Covid-19 Brandon WrightDocument16 pagesAssignment 2 Biol1700 Mar Covid-19 Brandon Wrightapi-508331036No ratings yet
- Science PT3 Form 2 Chapter 3 NutritionDocument5 pagesScience PT3 Form 2 Chapter 3 NutritionSCNo ratings yet
- Class-10 Revision Test - NutritionDocument4 pagesClass-10 Revision Test - NutritionVarshini PeraNo ratings yet
- Key For NatSci 2 Prefinal ExamDocument4 pagesKey For NatSci 2 Prefinal ExamManongdo AllanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ₪ Nutrition ₪ Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 ₪ Nutrition ₪ Multiple Choice QuestionsKhor Han YiNo ratings yet
- Teeth & Digestion Answered QueutionsDocument10 pagesTeeth & Digestion Answered QueutionsKeelah BennNo ratings yet
- 2022-23 F3 Biology Exam Mock Paper 1 1Document20 pages2022-23 F3 Biology Exam Mock Paper 1 1azuryicerobloxNo ratings yet
- Digestive System QuizDocument3 pagesDigestive System Quizapi-709247070No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Evaluation: Test ADocument12 pagesUnit 1 Evaluation: Test ADRIANA GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Biology Assignment 2 Atefah Razack 1Document15 pagesBiology Assignment 2 Atefah Razack 1api-491258706No ratings yet
- Activity-1_Parts-Functions-Process-of-Digestive-SystemDocument2 pagesActivity-1_Parts-Functions-Process-of-Digestive-SystemHezel MarieNo ratings yet
- Kallyssa Perry Assignment 2Document15 pagesKallyssa Perry Assignment 2api-491451675No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Natural Science Ls June Revision Questions 2015 CheckedDocument27 pagesGrade 9 Natural Science Ls June Revision Questions 2015 CheckedMfanafuthiNo ratings yet
- Section Quiz: Section: The Digestive SystemDocument1 pageSection Quiz: Section: The Digestive SystemDavid GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Biology Assignment 2 - Mock TestDocument9 pagesBiology Assignment 2 - Mock Testapi-439638108No ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Clients with Cirrhosis of the LiverDocument7 pagesNursing Care for Clients with Cirrhosis of the LiverNur Fadhillah Qurratul AinNo ratings yet
- Indian Childhood CirrhosisDocument28 pagesIndian Childhood CirrhosisBelbi MolNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology AscitesDocument2 pagesGastroenterology AscitesNour SamadNo ratings yet
- LIVER SlidesDocument144 pagesLIVER SlidesChiiraq EugeneNo ratings yet
- CC - DAY 4 - PRE-TEST RationalizationDocument21 pagesCC - DAY 4 - PRE-TEST RationalizationVincent AmitNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Paper A FINAL - txt000000000Document16 pagesIGCSE Biology Paper A FINAL - txt000000000fahdtheemperorNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Functions of the Gallbladder, Liver and Bile DuctDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Functions of the Gallbladder, Liver and Bile DuctLarisse de LeonNo ratings yet
- 874 Hepa Merz 1331899928 PDFDocument1 page874 Hepa Merz 1331899928 PDFSanjay NavaleNo ratings yet
- Non Viral HepatitisDocument40 pagesNon Viral Hepatitisostaz2000100% (1)
- Me and DR KhalidDocument29 pagesMe and DR KhalidUmer KhanNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Gallbladder Polyp Final OneDocument24 pagesCase Study of Gallbladder Polyp Final OneMayer AlsaberNo ratings yet
- September 2013Document88 pagesSeptember 2013Cleaner MagazineNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests SummaryDocument2 pagesLiver Function Tests SummaryAdrian CastroNo ratings yet
- ELSA 2019 Program Scientific ProgramDocument22 pagesELSA 2019 Program Scientific ProgramShinta DeboraNo ratings yet
- 7.digestive SystemDocument29 pages7.digestive SystemMai Z HaniyaNo ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary Pancreatic Radiology 1683072599120Document31 pagesHepatobiliary Pancreatic Radiology 1683072599120Shivank RastogiNo ratings yet
- Session #19 SAS - Nutrition (Lecture)Document15 pagesSession #19 SAS - Nutrition (Lecture)Charisse Arriane BelasotoNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument3 pagesJaundiceMony MstNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Liver Chemistry TestsDocument5 pagesInterpretation of Liver Chemistry TestsaveekumbharNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis - Case StudyDocument8 pagesHepatitis - Case Studynight24rushNo ratings yet
- Clinical Conditions of Hepatitis BDocument2 pagesClinical Conditions of Hepatitis BnurseNo ratings yet
- Liver TraumaDocument27 pagesLiver Traumamuhammad haryatman-No ratings yet
- Billy Ray A. Marcelo, BSN, RN Faculty Bataan Peninsula State UniversityDocument292 pagesBilly Ray A. Marcelo, BSN, RN Faculty Bataan Peninsula State UniversityDarell M. Book100% (1)
- Substance Use and Abuse For Students 2018-2019Document50 pagesSubstance Use and Abuse For Students 2018-2019ZauraNo ratings yet
- Pharma NotesDocument5 pagesPharma NotesyoojeongredNo ratings yet