Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology 2
Uploaded by
bygbird10Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology 2
Uploaded by
bygbird10Copyright:
Available Formats
The Advantages of Sexual Reproduction
The sexual reproduction has many advantages over asexual reproduction. Much genetic variation
is not possible in asexual reproduction.
This is a disadvantage of asexual reproduction because it inhibits the further evolution of the
organism.
In sexual reproduction the offsprings, although similar to their parents, are not identical to them or
to one another. This is because of the mixing of genes of mother and father in various different
combinations, all the offsprings have genetic variations.
From the above discussion we conclude that sexual reproduction promotes diversity of characters
in the offsprings by providing genetic variation. Sexual reproduction plays an important role in
the origin of new species having different characteristics.
Why the Amount of DNA Does Not Get Doubled During Sexual
Reproduction
The gametes are special type of cells called reproductive cells which contain only half the
amount of DNA (or half the number of chromosomes) as compared to the normal body cells
of an organism. So, when a male gamete combines with a female gamete during sexual
reproduction, then the new cell ‘zygote’ will have the normal amount of DNA.
For example, the human sperm has 23 chromosomes and the human egg (or ovum) has also 23
chromosomes. So, when a sperm and an egg fuse together during fertilisation, then the zygote
formed will have 23 + 23 = 46 chromosomes, which is the normal number of chromosomes.
How Sexual Reproduction in Animals Takes Place
Sexual reproduction is the most common method of reproduction in animals (including human
beings). The sexual reproduction in animals takes place in the following steps :
1. The male parent produces male gametes (male sex cells) called sperms. The sperm is a small cell
with a long tail (flagellum) for movement.
2. The female parent produces female gametes (female sex cells) called ova (or eggs). The ovum
(or egg) is a much bigger cell than the sperm, having a lot of cytoplasm.
3. The sperm enters into the ovum (or egg) and fuses with it to form a new cell called ‘zygote’.This
process is called fertilisation. So, the zygote is a fertilised ovum (or fertilized egg).
4. The zygote then divides again and again to form a large number of cells (all of which remain
together). And ultimately zygote grows and develops to become a new baby.
PEAK POINT CLASSES 1
Address ; Adharshila Near Awadhpuri Police Station Bhopal(462022) Contact Numbers 9302186687,7987647505
The whole process of sexual reproduction in animals involves the formation of sperms and
eggs; joining together of sperm and egg to form a zygote; and then the growth and
development of zygote to form a baby animal.
Puberty
The age at which the sex hormones (or gametes) begin to be produced and the boy and girl
become sexually mature (able to reproduce) is called puberty.
Puberty tends to start earlier in females (girls) than in males (boys). Generally boys attain puberty
at the age of 13 to 14 years while girls reach puberty at a comparatively lower age of 10 to 12 years.
On attaining puberty, the male gonads called testes start producing male gametes called sperms
and the female gonads called ovaries start producing female gametes called ova (or eggs).
The testes produce the male sex hormone called testosterone, and the ovaries produce two
female sex hormones, oestrogen and progesterone. Puberty is the age at which the reproductive
organs reach maturity and secondary sexual characteristics develop.
The various changes which occur in boys at puberty are: Hair grow under armpits and in pubic
regions (genital area) between the thighs. Hair also grow on other parts of the body like chest and
face (moustache, beard, etc.). Body becomes more muscular due to the development of muscles.
The voice deepens (or cracks). Chest and shoulders broaden. The penis and testes become larger.
The testes start to make sperms. Feelings and sexual drives associated with adulthood begin to
develop.
The various changes which occur in girls at puberty are: Hair grow under armpits and pubic
region (This change is the same as in boys). Mammary glands (or breasts) develop and enlarge. The
hips broaden. Extra fat is deposited in various parts of the body like hips and thighs. Fallopian
tubes, uterus and vagina enlarge. Ovaries start to release eggs. Menstruation (monthly periods)
start. Feelings and sexual drives associated with adulthood begin to develop. All these changes in
girls are brought about by the female sex hormones ‘oestrogen’ and ‘progesterone’ made in ovaries.
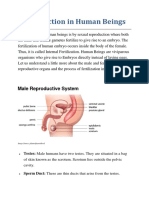
THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
The human male reproductive system consists of the following organs : Testes, Scrotum,
Epididymis, Vas deferens (or Sperm duct), Seminal vesicles, Prostrate gland and Penis.
Testes are the oval shaped organs which lie outside the abdominal cavity of a man. A man has two
testes (singular of testes is testis).
Testes are the primary reproductive organs in
man (or males).
The function of testes is to make the male sex cells
(or male gametes) called sperms and also to make
the male sex hormone called testosterone. The
testes of a man make the sex gametes (or sperms)
from puberty onwards, throughout his life.
The testes of a man lie in small muscular pouch
called scrotum, outside the abdominal cavity of the
body because the sperm formation requires a lower
temperature than the normal body temperature.
Being outside the abdominal cavity, the temperature of scrotum is about 3°C lower than the
temperature inside the body.
The sperms formed in testes come out and go into a coiled tube called epididymis. The sperms get
stored temporarily in epididymis.
PEAK POINT CLASSES 2
Address ; Adharshila Near Awadhpuri Police Station Bhopal(462022) Contact Numbers 9302186687,7987647505
From epididymis, the sperms are carried by a long tube called vas deferens (or sperm duct) which
joins with another tube called urethra coming from the bladder. Along the path of vas deferens, the
glands called seminal vesicles and prostrate gland add their secretions to sperms so that the
sperms are now in a liquid. This liquid plus the sperms it contains is called semen (which is a thick
liquid).
The secretions of seminal vesicles and prostrate gland provide nutrition to the sperms and
also make their further transport easier.
Urethra forms a common passage for sperms and urine. Urethra carries the sperms to an organ
called penis which opens outside the body.
The penis passes the sperms from the man’s body into vagina in the woman’s body during mating
for the purpose of reproduction.
NOTE; in man (or human male) there is only one opening for the urine and sperms to pass out of
the body.
THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
The human female reproductive system consists of the following organs: Ovaries, Oviducts (which
are also called Fallopian tubes), Uterus, and Vagina. A woman has two ovaries. Ovaries are the
primary reproductive organs in a woman (or female).
The function of ovaries is to make mature female sex cells
called ‘ova’ or ‘eggs’, and also to make the female sex
hormones (called oestrogen and progesterone). Each ovary is
composed of several thousand follicles (which are a kind of
unripe eggs or unripe ova).
At puberty these follicles mature to form the ripe eggs or ripe
ova. Just above the ovaries are the tubes called oviducts. The
oviducts are not directly connected to ovaries but have funnel
shaped openings which almost cover the ovaries. The ovum
released by an ovary goes into the oviduct through its funnel-
shaped opening. The fertilisation of egg (or ovum) by a sperm takes place in the oviduct.
The two oviducts connect to a bag like organ called uterus (or womb) at their other ends. The
growth and development of a fertilized ovum (or fertilised egg) into a baby takes place in the
uterus.
The uterus is connected through a narrow opening called cervix to another tube called vagina
which opens to the outside of the body. Vagina receives the penis for putting sperms into the
woman’s body.
Vagina is a tubular structure. Vagina is also called ‘birth canal’ because it is through this passage
that the baby is born after the completion of development inside the uterus of the mother.
NOTE: - in woman (or human female) the opening for passing out urine (called urethra) and the
vaginal opening are separate.
Fertilisation
In human beings, internal fertilisation takes place.
The sperms made in the testes of man are
introduced into the vagina of the woman through
penis during copulation (or mating).
In this way, millions of sperms are released into
the vagina at one time. The sperms are highly
active and mobile (moving). The sperms move up
through cervix into the uterus.
PEAK POINT CLASSES 3
Address ; Adharshila Near Awadhpuri Police Station Bhopal(462022) Contact Numbers 9302186687,7987647505
From uterus, the sperms pass into the oviducts
One of the oviducts contains an ovum released by the ovary during ovulation. Only one sperm fuses
with the ovum (or egg) in the oviduct to form a zygote. This is called fertilisation. Thus, the
fertilisation of the ovum (or egg) takes place in the oviduct.
Development of Embryo
The zygote divides rapidly by mitosis as it moves down
slowly in the oviduct and forms a hollow ball of
hundreds of cells. This hollow ball of cells, now called
an embryo, sinks into the soft and thick lining of the
uterus and gets embedded in it.
The embedding of embryo in the thick lining of the
uterus is called implantation.
After implantation, a disc-like special tissue develops between
the uterus wall and the embryo (or foetus), which is called
placenta (The foetus is connected to placenta in mother’s body
through umbilical cord).
It is through the placenta that all the requirements of the
developing foetus like nutrition, respiration, and excretion, etc.,
are met from the mother's body.
The time period from the
fertilisation up to the birth of
the baby is called gestation.
The average gestation period in humans is about nine months (or
about 38 weeks).
During the gestation period, the foetus grows to become a baby.
Birth begins when the strong muscles in the walls of the uterus
start to contract rhythmically. The rhythmic contraction of uterus
muscles gradually pushes the baby out of the mother’s body
through vagina. This is how a baby is born. All of us were born
from our mother in this way.
Sexual Cycle in Females: Menstruation
When a girl child is born, her ovaries already contain many thousands of immature ova (or eggs)
which are contained in immature follicles.
When a girl reaches the age of puberty, then one follicle develops at a time to form a mature ovum.
On maturing, the follicle bursts and the ovum (or egg) shoots out of the ovary. This is called
ovulation.
Thus, the release of an ovum (or egg) from an ovary is called ovulation.
In a normal, healthy girl (or woman), ovulation takes place on the 14th day of the beginning of
menstrual cycle of 28 days. This means that ovulation takes place in the middle of the menstrual
cycle (because 14th day is the middle of 28 days).
Before every ovulation, the inner lining of the uterus becomes thick and soft with lot of blood
capillaries (or blood vessels) in it. These changes in the uterus are necessary because in case the
ovum (or egg) released by the ovary gets fertilised by the sperm, then the uterus has to keep this
fertilised ovum (or egg) for further development and supply it with food and oxygen, etc., so that it
may grow into a baby in due course of time.
PEAK POINT CLASSES 4
Address ; Adharshila Near Awadhpuri Police Station Bhopal(462022) Contact Numbers 9302186687,7987647505
If, however, a sperm is not available at the time of ovulation, Thus, the unfertilized ovum (or egg)
dies within a day and the uterus lining also breaks down. Since the thick and soft uterus lining
contains a lot of blood vessels, so the breaking (or disintegration) of the uterus lining produces
blood along with other tissues. This blood and other tissues come out of the vagina in the form of
‘bleeding’.
The breakdown and removal of the inner, thick and soft lining of the uterus alongwith its
blood vessels in the form of vaginal bleeding is called menstrual flow or menstruation.
The menstrual cycle is controlled by hormones. Menstruation stops temporarily when the ovum (or
egg) gets fertilised and the woman gets pregnant.
This is because in this case the thick and soft lining of the uterus containing lot of blood vessels is
needed for the growth and development of the fertilised ovum (or fertilised egg cell) to form a baby.
Menstruation restarts after the birth of the baby.
Menarche and Menopause
The first occurrence of menstruation (or periods) at puberty is called menarche.
The permanent stoppage of menstruation (or periods) in a woman is called menopause.
Menopause occurs in women at the age of about 45 to 50 years.
the reproductive life of a woman starts at menarche and ends at menopause.
BIRTH CONTROL
The population of our country is increasing rapidly day by day. Though our country has sufficient
food resources but still many people do not get sufficient food for their large families (having many
children) due to poverty. Family planning enables a couple to decide on the number of children it
wants to have and when to have them. If a couple has less number of children, it can provide good
food, good clothes, and good education to each child. This will make the parents as well as the
children happy. So, a small family is a happy family
Family planning can be done by practising birth control measures. Birth control can be done by
preventing pregnancy in females (or women). And pregnancy can be prevented by adopting a
method or procedure by which sperms produced during copulation between man and his wife can
be prevented from meeting the ovum (or egg) and fertilising it. It is possible to prevent fertilisation
(and hence prevent pregnancy) because the ovum is available for fertilisation only for a short
period.
BIRTH CONTROL METHODS
The prevention of pregnancy in women (by preventing fertilisation) is called contraception.
And any device or chemical (drug) which prevents pregnancy in woman is called a contraceptive.
All the birth control methods can be broadly divided into three categories :
1. Barrier methods, 2. Chemical methods, and 3. Surgical methods.
PEAK POINT CLASSES 5
Address ; Adharshila Near Awadhpuri Police Station Bhopal(462022) Contact Numbers 9302186687,7987647505
1. Barrier Methods
In the barrier methods of preventing pregnancy, the physical devices such as condoms and
diaphragm (or cap) are used. Condoms are used by males (by putting them as a covering on the
penis).Diaphragm (or cap) is used by females (by putting it in the vagina to cover the cervix).
An important benefit in the use of condom is that it protects a person from the sexually
transmitted diseases such as gonorrhoea, syphilis and AIDS.
NOTE:- No other method of contraception provides protection against sexually transmitted
diseases.
2. Chemical Methods
In the chemical methods of preventing pregnancy, the females use two types of pills: oral pills and
vaginal pills, which are made of specific drugs.
The oral pills contain hormones which stop the ovaries from releasing ovum (or eggs) into the
oviduct. Oral pills are also called Oral Contraceptives. This is a very effective method of preventing
pregnancy so long as the pills are taken at the right time.
Some women, however, do experience unpleasant side effects on taking oral pills because they change
the hormonal balance in the body. So, it is important that the women on pills have regular check-ups
with their doctor.
The vaginal pills contain the chemicals called spermicides which kill the sperms.
3. Intra-Uterine Contraceptive Device (IUCD)
The use of intrauterine contraceptive device called Copper-T is also very effective in preventing
pregnancy. A Copper-T is placed inside the uterus by a doctor or a trained nurse.
The IUCD or Copper-T prevents the implantation of fertilised egg in the uterus. If a woman uses a
Copper-T as a method of contraception for avoiding unwanted pregnancies, then Copper-T cannot
protect her from acquiring sexually transmitted diseases (if her partner has such a disease).
4. Surgical Methods
In males, a small portion of the sperm duct (or vas deferens) is removed by surgical operation and
both the cut ends are ligated (or tied) properly. This prevents the sperms from coming out. The
surgical procedure carried out in males is called ‘vasectomy’.
In females, a small portion of the oviducts is removed by surgical operation and the cut ends are
ligated (or tied). This prevents the ovum (or egg) from entering into the oviducts. The surgical
procedure carried out in females is called tubectomy.
Stop Female Feticide!
Surgical operations can also be used for the termination of pregnancies in women particulary after
eight weeks of conception. Such surgical termination of pregnancy (or abortion) is allowed by law
only in certain circumstances where the doctors decide that continuance of pregnancy can affect
the health of mother or of unborn child gravely.
Some people, however, misuse the technique of surgical termination of pregnancy for ulterior
motive to get rid of female foetus (or unborn girl child). In order to have a male child (son), some
misguided people in our country get the sex of their unborn child determined by ultrasound
technique (though it is illegal to do so), and if it is a female foetus, they get it removed by surgery.
This killing of the unborn girl child is called female foeticide.
Female foeticide is reducing the number of girls drastically in some societies of our country.
Our Government has already enacted laws to ban prenatal (before-birth) determination of sex of
foetuses. These laws must be enforced strictly to save our society from the grave dangers of female
foeticide in the long run.
PEAK POINT CLASSES 6
Address ; Adharshila Near Awadhpuri Police Station Bhopal(462022) Contact Numbers 9302186687,7987647505
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
The diseases which are spread by sexual contact with an infected person are called sexually
transmitted diseases (or STD). Thus, a healthy person can get STD by making sexual contact with
an infected person. Some of the common sexually transmitted diseases are :
(i) Gonorrhoea,
(ii) Syphilis, and
(iii) AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome).
Gonorrhoea and syphilis are caused by bacteria. The bacteria which cause these diseases spread
through sexual contact with an infected person.
The most common symptoms of the these sexually transmitted diseases are burning sensation at
urination, passing of urethral discharge (containing pus) and sores in the genitals. Gonorrhoea and
syphilis are curable diseases.
AIDS disease is caused by a virus called HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus). AIDS damages the
body’s immune system so that the body becomes weak and cannot protect itself against infection.
So, AIDS is a very dangerous disease which leads to death. No definite cure has been found for the
AIDS disease so far.
PEAK POINT CLASSES 7
Address ; Adharshila Near Awadhpuri Police Station Bhopal(462022) Contact Numbers 9302186687,7987647505
You might also like
- Human Reproduction: Male and Female Systems ComparedDocument34 pagesHuman Reproduction: Male and Female Systems ComparedBimal DasNo ratings yet
- The Male and Female Reproductive Systems ExplainedDocument53 pagesThe Male and Female Reproductive Systems ExplainedKâmê KêlâhNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive BiologyDocument8 pagesHuman Reproductive BiologyEda, Haidee Gennie Anne R.No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction - Class 10Document7 pagesHuman Reproduction - Class 10faizalNo ratings yet
- 8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesDocument13 pages8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesAndre KachigambaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Is The Process by Which Organisms Make More Organisms Like ThemselvesDocument4 pagesReproduction Is The Process by Which Organisms Make More Organisms Like ThemselvesjohnNo ratings yet
- Project On Reproduction: By: Aaron FreyDocument27 pagesProject On Reproduction: By: Aaron FreyLaurinda Asiedu DavisNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument17 pagesHuman Reproductionmyisha dailyNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction in 12 WordsDocument16 pagesHuman Reproduction in 12 Wordsprince matamboNo ratings yet
- All living things reproduceDocument4 pagesAll living things reproduceMelinde BarluadoNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals, Humans and PlantsDocument18 pagesSexual Reproduction in Animals, Humans and PlantsRacma Saranga MaluagNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemJoseph CristianNo ratings yet
- S.A. U2 - 3.describe The Process of Sexual Reproduction in HumansDocument12 pagesS.A. U2 - 3.describe The Process of Sexual Reproduction in Humansbahadur.kerwynusNo ratings yet
- Quiz 9 - Reproductive System - ORLINA, M.A.Document3 pagesQuiz 9 - Reproductive System - ORLINA, M.A.Mae Antonette OrlinaNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesThe Reproductive Systemdevgod729No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction-1Document21 pagesHuman Reproduction-1Coni Espinoza YupanquiNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesReproductive SystemJohn Matthew ViañaNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesThe Reproductive SystemAndri SusantoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction System Explained: Male and Female OrgansDocument31 pagesReproduction System Explained: Male and Female OrgansYu HasNo ratings yet
- Female ReproductiveDocument3 pagesFemale ReproductiveBolos, Kate Hampshire L.No ratings yet
- MudassirDocument26 pagesMudassirhussain aliNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction UPDATEDDocument16 pagesHuman Reproduction UPDATEDCandy OpsadNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument23 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemQuennie AceronNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Human Beings (Part 1)Document40 pagesSexual Reproduction in Human Beings (Part 1)puspita8967628No ratings yet
- What Is Reproduction?: Male Reproductive System GenesDocument4 pagesWhat Is Reproduction?: Male Reproductive System GenesPrada Maya AnggariNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 11 Revision NotesDocument8 pagesClass 10 Biology Chapter 11 Revision NotesShayon BeraNo ratings yet
- Plant: Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesPlant: Reproductive Systemchan_1016No ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemAltheaNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System: Development of The Reproductive OrgansDocument11 pagesHuman Reproductive System: Development of The Reproductive OrgansDhion Ardhian NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Resmen Bio PrimerospuntosDocument3 pagesResmen Bio PrimerospuntosNatividad Araújo SánchezNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageMale Reproductive SystemYug PanaraNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Animals Class 8 NotesDocument6 pagesReproduction in Animals Class 8 Notesthulasi narravulaNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System Yr 11 Biology 114629Document7 pagesHuman Reproductive System Yr 11 Biology 114629Zach ZaneNo ratings yet
- Task 4Document20 pagesTask 4maryamshahzad489No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 - Reproduction 1.2Document15 pagesCHAPTER 4 - Reproduction 1.2Halizah RamthanNo ratings yet
- MudassirDocument26 pagesMudassirhussain aliNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System: Reproductive Cells and GonadsDocument3 pagesReproductive System: Reproductive Cells and Gonadsisaack_mahlangu5999No ratings yet
- Repoductive SystemDocument14 pagesRepoductive SystemJhoanna Marie RebutNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: © Lisa MichalekDocument30 pagesHuman Reproduction: © Lisa MichalekMj Briones100% (2)
- UNIT 3. ReproductionDocument3 pagesUNIT 3. ReproductionParsel BlehNo ratings yet
- Female and Male Reproductive SystemsDocument5 pagesFemale and Male Reproductive SystemsPol HuelarNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System - Wikipedia PDFDocument4 pagesHuman Reproductive System - Wikipedia PDFAubrey EuropeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On The Parts and Functions of The Female Reproductive System by Madel May EgeraDocument5 pagesLecture Notes On The Parts and Functions of The Female Reproductive System by Madel May EgeraMadel May D EgeraNo ratings yet
- Learn about the male and female reproductive systemsDocument7 pagesLearn about the male and female reproductive systemsJumarie ypilNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document16 pagesLecture 3Smasher AustineNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument21 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemLuCky Tem LacToseNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction FullDocument46 pagesSexual Reproduction FullSharara YMNo ratings yet
- BiosiceDocument57 pagesBiosiceLJ. Lagaras vlogNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1. Reproductive SytemDocument21 pagesLesson 1. Reproductive Sytemseanbalangcod29No ratings yet
- Sexual EducationDocument14 pagesSexual EducationLaya ShrbagiNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: A Concise Guide to the Male and Female AnatomyDocument58 pagesHuman Reproduction: A Concise Guide to the Male and Female AnatomyFelix HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Human Reproduction New Vocabulary: English WordDocument9 pagesGrade 6 Human Reproduction New Vocabulary: English WordCRISTIAN RAFAEL MENDOZA MALDONADONo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Human Reproduction New Vocabulary: English WordDocument9 pagesGrade 6 Human Reproduction New Vocabulary: English WordSalome TamaraNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument39 pagesReproductive SystemCenando Bodanio100% (1)
- Reproductive System LessonDocument3 pagesReproductive System LessonmargemunozNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument18 pagesThe Reproductive Systemcmillica1176No ratings yet
- Reproductive Science 10Document22 pagesReproductive Science 10palicpicbea50No ratings yet
- Lesson 6.3 Human ReproductionDocument39 pagesLesson 6.3 Human ReproductionJohn Victor MalupaNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument25 pagesThe Reproductive SystemCoran St Nicholi Beckford INo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument18 pagesMenstrual Cycle: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaZACHARIAH MANKIRNo ratings yet
- HahahaDocument16 pagesHahahaJohn BretanaNo ratings yet
- AHD - 121 AssignmentDocument11 pagesAHD - 121 AssignmentNikhilNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Biology Lesson on Menstrual CycleDocument5 pagesGrade 10 Biology Lesson on Menstrual CycleCheskaTelanNo ratings yet
- Rs Vita Insani Jl. Merdeka No.329, Pematangsiantar Tel. (0622) 22520, Fax. (0622) 24521 Laporan Register Pasien Poliklinik - Form Mode 1Document2 pagesRs Vita Insani Jl. Merdeka No.329, Pematangsiantar Tel. (0622) 22520, Fax. (0622) 24521 Laporan Register Pasien Poliklinik - Form Mode 1Reymon SihombingNo ratings yet
- GynaecologyDocument466 pagesGynaecologymyselfrakesh57No ratings yet
- Female reproductive system parts and functionsDocument2 pagesFemale reproductive system parts and functionsRaquel Cartera83% (24)
- OB FormDocument2 pagesOB FormJasuchineNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter Grade 10 Science Learning ModuleDocument25 pagesThird Quarter Grade 10 Science Learning ModuleJea Christine P. NoronioNo ratings yet
- So What Is A Vulva Anyway Final BookletDocument17 pagesSo What Is A Vulva Anyway Final BookletAdrianaVeraNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1FEMALE Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesMODULE 1FEMALE Reproductive SystemHoney Lou SemblanteNo ratings yet
- Below the Belt CareDocument7 pagesBelow the Belt CareRose WidantiNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical TestDocument4 pagesSecond Periodical TestRyan Zambrano RoaNo ratings yet
- 2011 Introduction To Maternity Pediatric Nursing Solution Manual 6th EditionDocument24 pages2011 Introduction To Maternity Pediatric Nursing Solution Manual 6th EditionAndrewFoleydegk100% (42)
- Quiz ReproductiveDocument78 pagesQuiz ReproductiveMedShare86% (7)
- Embryology GenitalDocument53 pagesEmbryology GenitalDhonat Flash100% (1)
- Oogenesis Oogenesis Is The Process Whereby Oogonia Differentiate Into Mature Oocytes. It Starts in TheDocument7 pagesOogenesis Oogenesis Is The Process Whereby Oogonia Differentiate Into Mature Oocytes. It Starts in ThebarbacumlaudeNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesReproductive SystemJasmin Jacob100% (3)
- Embryology Reviewer Chapter 1 and 2Document9 pagesEmbryology Reviewer Chapter 1 and 2Allison Eunice ServandoNo ratings yet
- Histology of Male Reproductive SystemDocument56 pagesHistology of Male Reproductive SystemMuhammad Irfan100% (2)
- Multiple Choice Questions: ReproductionDocument12 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: ReproductionJohn Osborne100% (1)
- Science 10 Q3 - M2Document14 pagesScience 10 Q3 - M2Avha CortesNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System 5esDocument10 pagesHuman Reproductive System 5esJoseph Joel AlmagroNo ratings yet
- 2.1.1 Reproductive Systems Teacher Answer SheetDocument3 pages2.1.1 Reproductive Systems Teacher Answer SheetFerdi Hasan100% (1)
- HANDOUTDocument7 pagesHANDOUTRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Tfu Dan LocheaDocument14 pagesTfu Dan LocheaP17331205036 OKVIASARI NURAZIZAHNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System DiagramsDocument9 pagesFemale Reproductive System DiagramselizabethNo ratings yet
- Growing Up OK!Document36 pagesGrowing Up OK!Derison MarsinovaNo ratings yet
- BIO202L+Lab+18+the Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesBIO202L+Lab+18+the Reproductive Systemmyra Thiong'oNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of DUBDocument18 pagesPathophysiology of DUBAnna San100% (2)