Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Defintion 4
Defintion 4
Uploaded by
shue0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThis document defines key terms related to acids, bases, and salts. It explains that acids ionize in water to produce hydrogen ions and the basicity of an acid refers to the number of hydrogen ions produced. Acids are classified as monoprotic, diprotic, or triprotic depending on if they can produce one, two, or three hydrogen ions. Bases react with acids to produce salts and water. The pH scale measures the concentration of hydrogen ions and ranges from 0 to 14. Strong acids and bases ionize completely while weak ones only ionize partially. Concentration refers to the amount of solute dissolved in a given volume of solution.
Original Description:
Original Title
DEFINTION 4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines key terms related to acids, bases, and salts. It explains that acids ionize in water to produce hydrogen ions and the basicity of an acid refers to the number of hydrogen ions produced. Acids are classified as monoprotic, diprotic, or triprotic depending on if they can produce one, two, or three hydrogen ions. Bases react with acids to produce salts and water. The pH scale measures the concentration of hydrogen ions and ranges from 0 to 14. Strong acids and bases ionize completely while weak ones only ionize partially. Concentration refers to the amount of solute dissolved in a given volume of solution.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesDefintion 4
Defintion 4
Uploaded by
shueThis document defines key terms related to acids, bases, and salts. It explains that acids ionize in water to produce hydrogen ions and the basicity of an acid refers to the number of hydrogen ions produced. Acids are classified as monoprotic, diprotic, or triprotic depending on if they can produce one, two, or three hydrogen ions. Bases react with acids to produce salts and water. The pH scale measures the concentration of hydrogen ions and ranges from 0 to 14. Strong acids and bases ionize completely while weak ones only ionize partially. Concentration refers to the amount of solute dissolved in a given volume of solution.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
CHAPTER 6 : ACID, BASE AND SALT
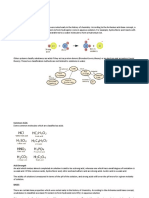
Acid Chemical substances ionise in water to produce hydrogen ions, H+.
Basicity of acids Basicity of acids refers to the number of hydrogen ions, H+ that can be
produced by an acid molecule that ionises in water.
Monoprotic acid Monoprotic acid because it can produce one hydrogen ion, H+ per acid
molecule.
Diprotic acid Diprotic acid because it can produce two hydrogen ion, H+ per acid molecule.
Triprotic acid Triprotic acid because it can produce three hydrogen ion, H+ per acid
molecule.
Base Base is a substance that reacts with acids to produce salt and water only.
Alkali Chemical substances that ionise in water to produce hydroxide ions, OH–.
pH pH is a logarithmic measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in an
aqueous solution.
pH scale pH scale which ranges from 0 to 14 is used to show the acidity and alkalinity
of an aqueous solution.
Strong acid A strong acid is an acid that ionises completely in water to produce a high
concentration of hydrogen ions, H+.
Weak acid A weak acid is an acid that ionises partially in water to produce low
concentration of hydrogen ions, H+.
Strong alkali A strong alkali is an alkali that ionises completely in water to produce a high
concentration of hydroxide ions, OH–.
Weak alkali A weak alkali is an alkali that ionises partially in water to produce a low
concentration of hydroxide ions, OH–.
Concentration Concentration of a solution is a measurement that shows the quantity of
solute dissolved in a unit volume of solution, normally in 1 dm3 solution.
Concentration in unit g dm–3, is the mass of solute found in 1 dm3 solution.
CHAPTER 6 : ACID, BASE AND SALT
Acid Chemical substances ionise in water to produce hydrogen ions, H+.
Basicity of acids Basicity of acids refers to the number of hydrogen ions, H+ that can be
produced by an acid molecule that ionises in water.
Monoprotic acid Monoprotic acid because it can produce one hydrogen ion, H+ per acid
molecule.
Diprotic acid Diprotic acid because it can produce two hydrogen ion, H+ per acid molecule.
Triprotic acid Triprotic acid because it can produce three hydrogen ion, H+ per acid
molecule.
Base Base is a substance that reacts with acids to produce salt and water only.
Alkali Chemical substances that ionise in water to produce hydroxide ions, OH–.
pH pH is a logarithmic measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in an
aqueous solution.
pH scale pH scale which ranges from 0 to 14 is used to show the acidity and alkalinity
of an aqueous solution.
ALWAYS LIKE A PROTON & STAY POSITIVE
4S1 2023/2024
Strong acid A strong acid is an acid that ionises completely in water to produce a high
concentration of hydrogen ions, H+.
Weak acid A weak acid is an acid that ionises partially in water to produce low
concentration of hydrogen ions, H+.
Strong alkali A strong alkali is an alkali that ionises completely in water to produce a high
concentration of hydroxide ions, OH–.
Weak alkali A weak alkali is an alkali that ionises partially in water to produce a low
concentration of hydroxide ions, OH–.
Concentration Concentration of a solution is a measurement that shows the quantity of
solute dissolved in a unit volume of solution, normally in 1 dm3 solution.
Concentration in unit g dm–3, is the mass of solute found in 1 dm3 solution.
ALWAYS LIKE A PROTON & STAY POSITIVE
4S1 2023/2024
You might also like
- Acid, Base, and SaltDocument12 pagesAcid, Base, and SaltTamoghna DeyNo ratings yet
- How To Save Energy in Refrigeration PDFDocument67 pagesHow To Save Energy in Refrigeration PDFcyclon2010100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry NotesDocument8 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry NotesZaheer Uddin100% (1)
- Non-Aqueous Acid Base TitrationDocument35 pagesNon-Aqueous Acid Base TitrationApurba Sarker Apu100% (9)
- BOILER OPERATION ENGINEEINEERING Ar Malick PDFDocument203 pagesBOILER OPERATION ENGINEEINEERING Ar Malick PDFAnupNandi88% (8)
- Beggs and Brill MethodDocument26 pagesBeggs and Brill MethodHassanKMNo ratings yet
- Insulation Thickness Chart PDFDocument9 pagesInsulation Thickness Chart PDFPartha Pratim GhoshNo ratings yet
- ICH 2101 Mass Transfer 1 ModulesDocument79 pagesICH 2101 Mass Transfer 1 ModulesGrace Lukogho MbafumojaNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases IGCSE NotesDocument15 pagesAcids and Bases IGCSE NotesMisbah KamranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document45 pagesChapter 4Lalita A/P AnbarasenNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases and SaltsDocument1 pageAcid Bases and SaltsSherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- PH and pOH ReviewerDocument7 pagesPH and pOH ReviewerFaller, Fiona Luie C.No ratings yet
- Acids, Bases, and pH2 PDFDocument20 pagesAcids, Bases, and pH2 PDFaprilia nur hidayahNo ratings yet
- 3 Chemical ChangesDocument5 pages3 Chemical ChangessophiederryNo ratings yet
- 7.1 &7.2Document43 pages7.1 &7.2Jajilah LatipNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases in Solution: Chapter 3, Section 3Document8 pagesAcids and Bases in Solution: Chapter 3, Section 3Kelli McDaniel MarchbanksNo ratings yet
- Acids 2Document4 pagesAcids 2Syed AyaanNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Acids Bases and SaltsDocument12 pagesChapter One: Acids Bases and Saltssubeer ismailNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form4 Chapter6 SPMDocument27 pagesChemistry Form4 Chapter6 SPMkaiqianNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases, and PH2Document20 pagesAcids, Bases, and PH2Ohm PawatNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases Lecture NotesDocument11 pagesAcids and Bases Lecture NotesmdonohueHGHSNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 3 Revision NotesDocument5 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Chapter 3 Revision NotesAnn Maria ThomasNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases, and pH2Document20 pagesAcids, Bases, and pH2Arihant JainNo ratings yet
- Chemisty - Lecture 9 Acid-Base Reactions - Power PointDocument25 pagesChemisty - Lecture 9 Acid-Base Reactions - Power PointjaninaD100% (1)
- Acids - NotesDocument16 pagesAcids - Notesvarun puriNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument2 pagesAcids and Basesaimeejoy brosolaNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument34 pagesAcids, Bases and SaltsV de VendettaNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases SaltsDocument13 pagesAcids Bases SaltsChito JarciaNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases&Salts NotesDocument12 pagesAcids Bases&Salts NotesAngelic Shine100% (1)
- Chapter 7: Acid and Bases: Chemistry A+ Agathum, U Can DO IT!!!!Document42 pagesChapter 7: Acid and Bases: Chemistry A+ Agathum, U Can DO IT!!!!NurNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases IGCSE NotesDocument15 pagesAcids and Bases IGCSE Notessaowanee toonchueNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases (Topic 7) : Designed, Prepared and Edited By: Chemistry Unit Mara Junior Science College Jasin Sept 2005Document13 pagesAcids and Bases (Topic 7) : Designed, Prepared and Edited By: Chemistry Unit Mara Junior Science College Jasin Sept 2005ajakazNo ratings yet
- C5-Acid Base and SaltDocument14 pagesC5-Acid Base and SaltHarshaWakodkarNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument63 pagesAcids and Basesgarnettdalagan.bascNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument7 pagesAcids and BasesM.zuhair asifNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases & OxidesDocument22 pagesAcids, Bases & OxidesMustafa ghazanfarNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmaceutical Chemistry 15Document108 pagesBasic Pharmaceutical Chemistry 15Gideon AntwiNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts For Students To StickDocument4 pagesAcids Bases and Salts For Students To StickARSHAD JAMILNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Topic 8 Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument1 pageDefinitions - Topic 8 Acids, Bases and SaltsMohammad Abdur Rahman Yousha ,usableNo ratings yet
- Acid & BaseDocument70 pagesAcid & BaseQistina RafeziNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Inorganic ChemDocument27 pagesChapter 4-Inorganic ChemMark Harold GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project Chemistry PH in Everyday LifeDocument23 pagesInvestigatory Project Chemistry PH in Everyday LifeHarshita Jain67% (3)
- 5.5 Acids Alkali and NutralisationDocument13 pages5.5 Acids Alkali and NutralisationDayangNo ratings yet
- Arrhenius Definition of An AcidDocument27 pagesArrhenius Definition of An AcidnelsonNo ratings yet
- Tut-Acids and BasesDocument30 pagesTut-Acids and BasesThabelo NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Science Notes: DilutionDocument5 pagesScience Notes: DilutionKylie smithNo ratings yet
- YT Acid Base and Salt 1Document77 pagesYT Acid Base and Salt 1reyanshNo ratings yet
- Acidsbasesgr 220731024722 Ba34e4dcDocument25 pagesAcidsbasesgr 220731024722 Ba34e4dcTaylors VersionNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Acids and BasesDocument5 pagesComparison of Acids and BasesSANDEEP SINGH100% (1)
- What Is The Difference Between Acid and BaseDocument8 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Acid and BaseFSG ChillNo ratings yet
- Acid Base PH NotesDocument10 pagesAcid Base PH NotesCyrus Flores,No ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument25 pagesAcid BaseMuhammad Yaser RayyanNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument11 pagesAcids and Basesgregory128414No ratings yet
- Introduction To Acids, Bases and Salts: Classification of MatterDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Acids, Bases and Salts: Classification of MatterSumit JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Kliping KimiaDocument6 pagesKliping KimiaSitti SolehaNo ratings yet
- Teachers Education Program: Inorganic Chemistry (Sci Ac5)Document4 pagesTeachers Education Program: Inorganic Chemistry (Sci Ac5)Franklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument10 pagesAcids and BasesFrancis EssilfieNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Acids, Alkalis, and NeutralisationDocument21 pagesLesson - Acids, Alkalis, and NeutralisationĐỗ NguyênNo ratings yet
- S H A N: Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument14 pagesS H A N: Acids, Bases and SaltsVino AldrinNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and PHDocument8 pagesAcids, Bases and PHSaisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument16 pagesChemistry ProjectAhmed fatahNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases SaltsDocument74 pagesAcids Bases SaltshaloNo ratings yet
- Acids & Bases OL NotesDocument5 pagesAcids & Bases OL NotesHooria AminNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Acids, Bases & Salts NotesDocument10 pagesChapter-2 Acids, Bases & Salts NotesMohammed RamzanNo ratings yet
- 4206 PS 70526 Concentrator and Trap Columns Product SpecificationsDocument13 pages4206 PS 70526 Concentrator and Trap Columns Product SpecificationsMondommeg SohanemNo ratings yet
- Answers & Solutions JEE - (Advanced) - 2021 Paper-1Document39 pagesAnswers & Solutions JEE - (Advanced) - 2021 Paper-1Akshay KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Solved With COMSOL Multiphysics 5.1 JoulDocument10 pagesSolved With COMSOL Multiphysics 5.1 JoulKarthik RaoNo ratings yet
- M.E LAB 3 Experiment 4 Heat Losses From PipesDocument14 pagesM.E LAB 3 Experiment 4 Heat Losses From PipesDrw ArcyNo ratings yet
- Initial Analysis of PCM Integrated Solar CollectorsDocument5 pagesInitial Analysis of PCM Integrated Solar CollectorsTushar Kant SwainNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base TitrationDocument18 pagesAcid-Base Titrationmasya marchelinaNo ratings yet
- Fire PPT CompilationDocument9 pagesFire PPT CompilationDonna Mae MartinezNo ratings yet
- Stability Constant of A Complex by SpectrophotometryDocument11 pagesStability Constant of A Complex by SpectrophotometryDa Prince80% (5)
- MCAT Physics Review NotesDocument7 pagesMCAT Physics Review Notesmina minaNo ratings yet
- Titration Lab Report 1Document28 pagesTitration Lab Report 1api-607048551No ratings yet
- Science - 2nd Quarter Periodical Exam ReviewerDocument3 pagesScience - 2nd Quarter Periodical Exam ReviewerJann Nicole BautistaNo ratings yet
- Unknown - Unknown - Solubility and Common Ion Effect PDFDocument7 pagesUnknown - Unknown - Solubility and Common Ion Effect PDF_dreyyaaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24: Fiber Optics: Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pagesChapter 24: Fiber Optics: Multiple ChoiceAntonio AntonioNo ratings yet
- Prerana 2017 IDECDocument53 pagesPrerana 2017 IDECabmopalhvacNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab Manual 10 Icse Rachna SagarDocument14 pagesChem Lab Manual 10 Icse Rachna SagarSarahNo ratings yet
- Phyw 2Document42 pagesPhyw 2Sajjad FaisalNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Chemistry Experiment 6 Group 1Document12 pagesLab Report Chemistry Experiment 6 Group 1NUR RABIAHTUL NAZILLA BINTI MAPATANG FS21110430No ratings yet
- Test No-4 Hydrocarbon - Q.P PDFDocument1 pageTest No-4 Hydrocarbon - Q.P PDFNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology DelhiDocument5 pagesIndian Institute of Technology DelhiAchyut SalunkheNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project PhysicsDocument8 pagesInvestigatory Project PhysicsRonald100% (1)
- ORG LAB Recrystallization2009 PDFDocument12 pagesORG LAB Recrystallization2009 PDFAnnaReyesNo ratings yet
- HygrometerDocument5 pagesHygrometersbdmanNo ratings yet
- Studi Kinetika Reaksi Sintesis Bornyl Khlorida Dari Alpha-PineneDocument1 pageStudi Kinetika Reaksi Sintesis Bornyl Khlorida Dari Alpha-PineneDaniar RianawatiNo ratings yet
- SMPBufferDocument5 pagesSMPBufferALemayehu KifluNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Chemistry ProblemsDocument65 pagesTheoretical Chemistry Problemstun lykoungNo ratings yet