Professional Documents
Culture Documents
This Following BMS Interview Questions and Answer Purely Focused On Testing and Commissioning Engineer
Uploaded by
jahangir sami0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views16 pagese
Original Title
This following BMS interview questions and answer purely focused on testing and commissioning engineer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documente
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views16 pagesThis Following BMS Interview Questions and Answer Purely Focused On Testing and Commissioning Engineer
Uploaded by
jahangir samie
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
This following BMS interview questions and answer purely
focused on testing and commissioning engineer, or related to
field works positions.
For other roles like designing, Estimations, Project engineer; In
addition to the below questions, the technical expectation will
be different.
What is the BMS System?
BMS otherwise called as BAS or building automation. It is a
computer-based control system which reduces the manpower,
automate the system, and saving the energy consumption in
buildings by monitoring and controlling the mechanical and
electrical equipment in modern-day buildings or any industrial
plants.
What is the main component of the BMS System?
Hardware
DDC-Direct digital controller
Sensors
Actuators
Cables to connect sensors, actuators to DDC.
HMI display-Human machine interface.
PC Workstation
Server to save the large database.
Software
Programming or configuration tools.
Graphics or User interface.
Networking protocols
TCP/IP– Transfer control protocols/Internet Protocol.
BACnet– Building automation controller network-
ASHRAE
Modbus
LONworks
CANbus
and numerous protocols available.
What is the purpose of the BMS System?
Monitoring and controlling the field equipment.
To reduce manpower in the building.
To provide comfort and healthcare for the building
the tenants.
To maintain the mechanical and electrical equipment
in the buildings.
Record all the events occurs in building machines and
raise alarm if any malfunction happens.
What are the basic features of BMS Software?
Log the events
Alarms.
Reporting
Scheduling.
Graphics.
Block diagram of BMS Architecture
Management Level: This is the front end for operator and
engineer used to visualise the graphics for controlling and
monitoring the systems which have computer workstation,
server, web browser, printers.
Automation Level: BMS Router and other main controllers
connected in building network integrate the third-party system
and connect BMS devices.
Field devices Level: this is Level where BMS controllers
connect to field systems sensors, actuators, and other panel
circuits to monitor and control.
What is Trend log?
Trend log records and displays the behaviour of an input or
output associated with BMS.
Trend logs help you troubleshoot problem areas and identify
critical operating trends in your system. For example, log the
temperature in a room to see if the system is keeping it within
desired set points.
What is the Alarm?
Alarms monitor equipment or environments in a building and
alert someone when conditions are outside the defined normal
range.
What is Report?
We can generate a report for any type of alarm, Trend log or
events in the required format for over a period of time
What is Scheduling?
Schedules are a type of object in BMS Controllers and it can be
configured to start and stop the machines pre-defined time.
Schedules enable you to plan system operations based on time
of day, special events, and holidays. The combination of a
standard, holiday, and event schedule is called a schedule set.
What are the optimum Starts?
Optimum start adjusts the heating or cooling start time in an
attempt to bring zone temperatures to the appropriate setpoint
for occupancy. For example, you want the classrooms in your
school to be at a comfortable temperature (their individual set
points) before class begins. You can do this by first setting up
each classroom as a zone and linking a schedule to each zone.
Then, you set up an optimum start for each zone (classroom).
Optimum start calculates when to start warming or cooling the
classrooms based on the settings you define.
What is Micro-controllers?
A microcontroller is an integrated circuit (IC) which is small,
low cost and self-contained computer designed to handle a
specific task in embedded systems. In simple words, a
microcontroller (MCU or Microcontroller Unit) is a small
computer integrated into a single chip.
What is Resistors?
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component
that implements electrical resistance as a circuit
element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce
current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active
elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses.
What is Ohms law?
Ohm’s law states that the current through
a conductor between two points is directly proportional to
the voltage across the two points. Introducing the constant of
proportionality, the resistance, one arrives at the usual
mathematical equation that describes this relationship
What is Relay?
Relays are the switches which aim at closing and opening the
circuits electronically as well as electromechanically. It controls
the opening and closing of the circuit contacts of an electronic
circuit. When the relay contact is open (NO), the relay isn’t
energized with the open contact. However, if it is closed (NC),
the relay isn’t energize given the closed contact. However,
when energy (electricity or charge) is supplied, the states are
prone to change
What is DDC Controllers?
DDC is a controller which use the analogue or digital signals
from various devices of a field sensor and actuators and then
process and control the system based on the program written
inside the controllers and has the capability to sends the
information to another controller or DDC.
Digital Input – DI
Digital inputs are binary inputs (0 or 1) that are applied to the
DDC. Binary inputs are basically voltages, varying from 5V to
230V depending upon the type of card used. In simple words,
any push-button, switches or sensors produces digital inputs to
a DDC. Digital inputs are used to check the status of any
devices whether it is ON or OFF. For an Input module of 24Vdc,
0Vdc acts as OFF state (Binary 0) and 24Vdc acts as ON state
(Binary 1).
Digital Output – DO
Digital outputs are binary outputs (0 or 1) from the DDC. It is a
processed control output from the DDC to the field. It is used
to ON or OFF any piece of field equipment. DO is like a contact
of a relay when the preprogrammed conditions are satisfied the
contacts are closed. DO can be used to operate solenoid valves,
relays, indicating lamps or as a command to any other devices.
Analog Input – AI
Analog input is a continuous input from the field to the DDC.
Unlike digital signals, is not a constant voltage signal. It can
vary depending on the field conditions. The commonly used
analogue signals are 4-20mA signal and 0-10Vdc Signal.
Depending on the field conditions the input signal can vary
between 4-20mA or 0-10Vdc. For Example, if you are
monitoring a pressure of water flowing through a pipe using a
pressure transmitter of range 0-10 Bar, the transmitter will
give a signal between 0 and 10V proportional to the pressure in
the pipe.
Analog Output – AO
Analogue output is a continuous output from DDC to the field
devices. For example, if you have a variable frequency drive
and you want to give a speed reference signal to it you can use
analogue output. Otherwise, if you are measuring the pressure
using analogue input as explained above and you would like to
display it on an analogue meter you can use an analogue
output of DDC.
Read more on https://www.electricalclassroom.com/digital-i-o-
and-analog-i-o/
What is meant by Frequency?
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event
per unit of time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency,
which emphasizes the contrast to spatial frequency and
angular frequency. Frequency is measured in units of hertz
(Hz) which is equal to one occurrence of a repeating event per
second.
what is Pulse width modulation?
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) uses digital signals to control
power applications, as well as being fairly easy to convert back
to analogue with a minimum of hardware.
One of the parameters of any square wave is duty cycle. Most
square waves are 50%, this is the norm when discussing them,
but they don’t have to be symmetrical. The ON time can be
varied completely between the signal being off to being fully
on, 0% to 100%, and all ranges between.
Shown below are examples of a 10%, 50%, and 90% duty
cycle. While the frequency is the same for each, this is not a
requirement.
Image
Credit:https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/textbook/semiconduct
ors/chpt-11/pulse-width-modulation/
What are Open-loop and closed-loop control system?
Open Loop Control System
In the open-loop control system, the output does not affect the
control action of the system. In other words, the system whose
working depends on time is known as the open-loop control
system. The open-loop system is free from the feedback. Let’s
understand this with the help of the few examples.
Example 1: Consider the clothes dryer whose control action is
done manually by the operator. Depending on the wetness of
the clothes suppose the operator set the timer for 30 minutes.
After 30 minutes the timer will stop even after the clothes are
wet.
The dryer stops working even if the desired output is not
obtained. This shows that the system has no feedback. Here
clothes dryer is the example of the open-loop system and the
timer is the controller of the system.
Example 2: The automatic washing machine is an example of
the open-loop system. The operator manually sets the
operating time of the machine. The machine stops operating
after the set time, even the desire cleanliness of clothes are not
obtained. This happens because the machine has no feedback
system which signals the control action of the system for the
desired output.
The open-loop system is simple, require less maintenance.
Also, it is fast in operation and very economical. But the
accuracy of the system is less, and it is less reliable.
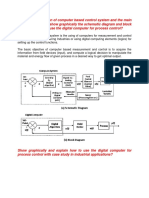
Closed-Loop Control System
The closed-loop control system means the output of the system
depends on their input. The system has one or more feedback
loops between its output and input. The closed-loop system
design in such a way that they automatically provide the
desired output by comparing it with the actual input. The
closed-loop system generates the error signal which is the
difference between the input and output.
Image/content Credit : https://circuitglobe.com/difference-
between-open-loop-and-closed-loop-system.html
What is PID?
As the name suggests, this article is going to give a precise
idea about the structure and working of the PID controller.
However going into details, let us get an introduction about PID
controllers.
PID controllers are found in a wide range of applications for
industrial process control. Approximately 95% of the closed-
loop operations of industrial automation sector use PID
controllers. PID stands for Proportional-Integral-Derivative.
These three controllers are combined in such a way that it
produces a control signal
What is Database?
A database is an organized collection of data, generally stored
and accessed electronically from a computer system. Where
databases are more complex they are often developed using
formal design and modeling techniques.
The database management system (DBMS) is the software that
interacts with end-users, applications, and the database itself
to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS software
additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to
administer the database. The total of the database, the DBMS
and the associated applications can be referred to as a
“database system”. Often the term “database” is also used to
loosely refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an
application associated with the database.
What is SQL Database?
SQL is the standard language for dealing with Relational
Databases. SQL can be used to insert, search, update, and
delete database records. SQL can do lots of other operations,
including optimizing and maintenance of databases. SQL stands
for Structured Query language, pronounced as “S-Q-L” or
sometimes as “See-Quel”… Relational databases like MySQL
Database, Oracle, MS SQL Server, Sybase, etc. use ANSI SQL.
Read more on https://www.guru99.com/introduction-to-
database-sql.html
What is the BACnet protocol?
The protocol is supported and maintained by ASHRAE Standing
Standard Project Committee 135. Products are certified for
compliance and interoperability through BACnet International
via the BACnet Testing Laboratories (BTL). BTL Certification is
available from several testing facilities, including all WSPLabs,
MNB in Germany, and SoftDEL Systems headquartered in Pune,
India. Applications BACnet supports most building operations,
including HVAC, lighting, fire protection, and physical security
(access control, intrusion) devices.
What is Integration in BMS System?
BMS System main purpose for controlling the HVAC system by
its own DDC Controller whereas other connected equipment’s in
the building can be monitored.
Apart from that other ELV system like Lighting control system,
Fire alarm, UPS, Metering, etc can be integrated through over
Communication network instead of the hardwiring cable by
building network protocols like BACnet, Modbus, Lonworks,
OPC and more
Read more on https://methodstatementhq.com/integration-
interface-of-bms-system-with-other-services.html
What is HVAC?
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC)[1] is the
technology of indoor and vehicular environmental comfort. Its
goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air
quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical
engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid
mechanics and heat transfer. “Refrigeration” is sometimes
added to the field’s abbreviation, as HVAC&R or HVACR or
“ventilation” is dropped, as in HACR (as in the designation of
HACR-rated circuit breakers).
What is AHU?
Air handling units’ condition and distribute air within a building.
They take fresh ambient air from outside, clean it, heat it or
cool it, maybe humidify it and then force it through some
ductwork around to the designed areas within a building. Most
units will have an additional duct run to then pull the used dirty
air out of the rooms, back to the AHU, where a fan will
discharge it back to the atmosphere. Some of this return air
might be recirculated back into the fresh air supply to save
energy, we’ll have a look at that later in the article. Otherwise,
where that isn’t possible, thermal energy can be extracted and
fed into the fresh air intake. Again we’ll look at that later in
more detail.
Read more on https://theengineeringmindset.com/air-
handling-units-explained/
What is FCU?
CU stands for fan coil unit but often engineers will just call
them a fan coil, to save time. Fan coil units are very common
in all types of buildings, from offices, bars, canteens, even
some homes and apartments will have a fan coil unit in them.
Fan coil units are used to condition the local air to suit the
temperature requirements of the immediate space.
Read more on https://theengineeringmindset.com/fan-coil-
units-hvac/
https://youtu.be/MqM-U8bftCI
What is VAV?
Variable air volume is a type of heating, ventilating, and/or air-
conditioning system. Unlike constant air volume systems, which
supply a constant airflow at a variable temperature, VAV
systems vary the airflow at a constant temperature. Wikipedia
What is VFD?
A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is a type of motor controller
that drives an electric motor by varying the frequency and
voltage supplied to the electric motor. Other names for a VFD
are variable speed drive, adjustable speed
drive, adjustable frequency drive, AC drive, microdrive,
and inverter.
Frequency (or hertz) is directly related to the motor’s speed
(RPMs). In other words, the faster the frequency, the faster the
RPMs go. If an application does not require an electric motor to
run at full speed, the VFD can be used to ramp down the
frequency and voltage to meet the requirements of the electric
motor’s load. As the application’s motor speed requirements
change, the VFD can simply turn up or down the motor speed
to meet the speed requirement.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g7jFGOn6xfU
What is Chiller system?
Chilled Water System Basics – Chilled water systems in
residential HVAC systems are extremely rare. A typical chiller
uses the process of refrigeration to chill water in a chiller
barrel. This water is pumped through chilled water piping
throughout the building where it will pass through a coil. Air is
passed over this coil and the heat exchange process takes
place. The heat in the air is absorbed into the coils and then
into the water. The water is pumped back to the chiller to have
the heat removed. It then makes the trip back through the
building and the coils all over again.
Read more on https://highperformancehvac.com/chilled-water-
system-basics/
What is DDC?
DDC is a controller which use the analogue or digital signals
from various devices of a field sensor and actuators and then
process and control the system based on the programme
written inside the controllers and has the capability to sends
the information to another controller or DDC
Read more on https://bms-system.com/what-is-ddc-or-direct-
digital-controller-in-bms-system/
What is Ambient Temperature?
Ambient temperature is the air temperature of any object or
environment where equipment is stored. The
adjective ambient means “relating to the immediate
surroundings.” Also sometimes referred to as the ordinary
temperature or the baseline temperature, this value is
important for system design and thermal analysis.
In a computing context, maintaining an appropriate ambient
temperature is crucial to the proper functioning and longevity
of computer equipment. In general, a safe range is between 60
and 75 degrees Fahrenheit or 15 and 25 degrees Celsius,
although the cooler end of that range is better. Ambient
temperatures above those ranges make it difficult for a
computer’s cooling system to keep it at a safe operating
temperature.
What is Dry Bulb, Wet Bulb, and Dew Point Temperature?
The Dry Bulb, Wet Bulb and Dew Point temperatures are
important to determine the state of humid air. The knowledge
of only two of these values is enough to determine the state of
the moist air – including the content of water vapour and the
sensible and latent energy (enthalpy) in the air.
https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/dry-wet-bulb-dew-point-
air-d_682.html
The Dry Bulb temperature usually referred to as “air
temperature”, is the air property that is most commonly used.
When people refer to the temperature of the air they are
normally referring to the dry-bulb temperature.
The Dry Bulb Temperature refers basically to the ambient air
temperature. It is called “Dry Bulb” because the
air temperature is indicated by a thermometer not affected by
the moisture of the air.
The Wet Bulb temperature is the adiabatic saturation
temperature.
Wet Bulb temperature can be measured by using a
thermometer with the bulb wrapped in wet muslin. The
adiabatic evaporation of water from the thermometer bulb and
the cooling effect is indicated by a “wet-bulb temperature”
lower than the “dry bulb temperature” in the air.
The rate of evaporation from the wet bandage on the bulb, and
the temperature difference between the dry bulb and wet bulb,
depends on the humidity of the air. The evaporation from the
wet muslin is reduced when the air contains more water
vapour.
he Dew Point is the temperature where water vapour starts to
condense out of the air (the temperature at which air becomes
completely saturated). Above this temperature, the moisture
stays in the air.
if the dew-point temperature is close to the dry air
temperature – the relative humidity is high
if the dew point is well below the dry air temperature
– the relative humidity is low
If moisture condenses on a cold bottle taken from the
refrigerator the dew-point temperature of the air is above the
temperature in the refrigerator.
What is Humidity?
Humidity is the presence of water vapour in the atmosphere.
The more water evaporates in a given area, the more water
vapour rises into the air, and the higher the humidity of that
area is. Hot places tend to be more humid than cool places
because heat causes water to evaporate faster.
Read more on https://www.goblueox.com/blog/what-is-
humidity-and-why-does-it-matter/
What is Relativity Humidity?
Relative humidity (RH) is the ratio between the amount of
water vapour (moisture) in the air at a given temperature to
the maximum amount of water vapour the air can hold at that
temperature. RH is expressed as a percentage (%). A
rudimentary way to calculate it is by using a psychrometer to
measure the dry and wet bulb temperature.
For example, 50% RH at a warm temperature has more water
vapour than 50% RH at a colder temperature
Read more
on https://www.idt.com/us/en/blogs/understanding-relative-
humidity-and-dew-point
What are temperature and humidity sensors?
Temperature sensors are components that directly translate
physical temperature into digital information. Likewise,
humidity sensors can measure atmospheric moisture levels and
translate that into digital information
check some of the temperature sensors
in https://www.tyrrellproducts.com/bms-controls-peripherals-
temperature/
humidity
sensors https://buildingcontrols.honeywell.com/subcategory/Se
nsors/Humidity-Sensors
What is damper actuators?
Actuators in HVAC systems control the dampers. By utilizing
a low voltage signal, the actuator places the damper at any
point between fully open and fully closed. A critical element of
an HVAC system, proper actuators ensure that
zone dampers function properly – without them,
the dampers won’t function at all.
https://www.thomasnet.com/insights/the-significance-of-
dampers-and-actuators-in-your-hvac-system/
What is PICV?
Pressure Independent Control Valves (PICV) can help reduce
energy costs and increase occupant comfort in heating and
cooling coil applications in buildings. A PICV is best described
as two valves in one: a standard 2-way control valve and a
balancing valve. PICV obtain optimal results because only the
necessary amount of hot water (in GPM) and chilled water (in
GPM) is delivered to the heating and cooling coils. Standard 2-
way control valves allow for overflow and underflow especially
if the CV is oversized or undersized. This generates excess
water to the pump to compensate for their inaccuracy, which
increases pumping cost. The actuators on PICV valves do not
cycle as often as standard 2-way valves to compensate for
pressure changes in the system that impact the flow, which
results in energy savings.
Read more
on https://www.neptronic.com/TechTime/20161207/PDFs/Tech
Time_November_2016_HVAC_Controls.pdf
What is Pre-Commissioning?
Pre-Commissioning is the activity of ensuring the
correctness of the following things
Cables termination between controller and field side.
Configuring the Sensors and actuators as per
requirement.
Checking the internal wiring of the BMS DDC
Controllers and power it up.
What is the role of Testing and commissioning?
BMS Testing and commissioning Engineer is responsible for
followings which are a key role to test from the installation of
the system to handover the system to the client
Installation and termination
Installing sensors and actuators as product manual
given by respective vendors is a vital factor of
performance for the operation of the BMS System.
Identify the best location in the equipment based on
which is recommended in the product manual and
considering the availability of providers in the site.
Based on the sensors and actuators, BMS internal
Networking, you need to install right cables from
devices to DDC Controllers and terminate it in both
sides.
Pre-commissioning
Good Pre-commissioning will reduce the most of
testing time in the site.
Pre-Commissioning is the activity of ensuring the
correctness of the following things
Cables termination between controller and field side.
Configuring the Sensors and actuators as per
requirement.
Checking the internal wiring of the BMS DDC
Controllers and power it up.
Programming Engineer
Should understand the sequence of operation of
various equipment’s in BMS mainly HVAC related like
chiller system, Air handling unit, Fan coil unit,
Variable air Volume etc.
Should write the program in Functional block(various
method available for different vendors)based on the
sequence of operation and given point list.
Should know to write a flowchart for a given
sequence of operation.
Graphics
Graphics is nothing but to show connected equipment
in BMS PC in graphical software provided by
respective vendors.
It needs only the necessary experience of using
computer tools.
Creating equipment’s graphics and adding/respective
mapping points to images to animate.
Testing and Commissioning
Testing Equipment
The program should be downloaded to the DDC
Controller and check the sequence of operation.
Should co-ordinate with respective equipment’s
technicians while testing system from BMS DDC
Controller.
Inspection
Once the system is ready to control and monitor from
BMS PC. Then Checklist should be submitted to the
contractor/consultant to raise inspection.
The consultant will check every point from BMS PC to
ensure the working of sensors and sequence of
operation.
Training and Handover
Once testing and inspection finished, we need to
handover the system to end-user by providing
operational & manual and training.
Training is the process of teaching end-user how to
operate the system.
How to check alarms, trend log, reports and
scheduling.
You might also like
- Industrial Automation - Technical Interview QuestionsDocument27 pagesIndustrial Automation - Technical Interview QuestionsAnjali Sharma79% (19)
- Introduction To AutomationDocument20 pagesIntroduction To AutomationGourav Solanki100% (1)
- Introduction to Process Control SystemsDocument59 pagesIntroduction to Process Control SystemsUdit Upreti100% (1)
- Full Opcodes Tables of CPUs: Z80A, Z80180 (HD64180)Document9 pagesFull Opcodes Tables of CPUs: Z80A, Z80180 (HD64180)Eugene LisovyNo ratings yet
- What Is A BMS or Building Management System?Document21 pagesWhat Is A BMS or Building Management System?hane zawNo ratings yet
- Professional Cloud Architect Exam - Free Actual Q&as, Mar 32pageDocument335 pagesProfessional Cloud Architect Exam - Free Actual Q&as, Mar 32pageTharun PanditiNo ratings yet
- What Is A BMS or Building Management SystemDocument27 pagesWhat Is A BMS or Building Management SystemMr. JC NiloNo ratings yet
- PLC QuestionsDocument17 pagesPLC QuestionsbahyNo ratings yet
- Digital PID ControllersDocument21 pagesDigital PID Controllerssopan saNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Controller BasicsDocument28 pagesProgrammable Logic Controller BasicsMOHAMMED RAHEELNo ratings yet
- Control System: Types of Industrial Control SystemsDocument19 pagesControl System: Types of Industrial Control SystemsAdnan Nawaz100% (2)
- Programmable Logic ControllerDocument36 pagesProgrammable Logic ControllerAnjireddy Thatiparthy100% (1)
- Sick Format-1-1 - PDFDocument7 pagesSick Format-1-1 - PDFNoah Esho100% (1)
- Dcs Vs ScadaDocument44 pagesDcs Vs ScadaSAYED QAISAR SHAH100% (1)
- Building Automation by Prabhu Kumar SurarapuDocument29 pagesBuilding Automation by Prabhu Kumar Surarapuprabhu4scribd100% (1)
- Industrial Automation Guide: Costs, Benefits & ApplicationsDocument153 pagesIndustrial Automation Guide: Costs, Benefits & ApplicationsTanvir KhanNo ratings yet
- DCS and SCADA Systems ExplainedDocument44 pagesDCS and SCADA Systems ExplainedMuntaha Daudpota100% (1)
- Fsc1 Sample Eng Obe QP v2 FinalDocument5 pagesFsc1 Sample Eng Obe QP v2 FinalAsu AsuNo ratings yet
- PLCDocument14 pagesPLCPrateek S VirdiNo ratings yet
- BMS KNXDocument8 pagesBMS KNXMohamed MaherNo ratings yet
- Scada Study MaterialDocument9 pagesScada Study MaterialSaravanakumar KNo ratings yet
- How SCADA Systems Work?Document8 pagesHow SCADA Systems Work?jessa realyn unlayaoNo ratings yet
- Direct Digital Control: Om Prakash BhartiDocument5 pagesDirect Digital Control: Om Prakash Bhartivictor alfonso campechano venturaNo ratings yet
- Abstract of DCSDocument13 pagesAbstract of DCSEngMohamedReyadHelesyNo ratings yet
- Iaa Unit 04Document19 pagesIaa Unit 04SurajNo ratings yet
- Iaa Unit 04Document19 pagesIaa Unit 04SurajNo ratings yet
- Priyadarshini Inst of Tech & SciencesDocument5 pagesPriyadarshini Inst of Tech & SciencesSuneetha SmileyNo ratings yet
- What Is SCADA System:SCADA Hardware, Software Architecture and WorkingDocument11 pagesWhat Is SCADA System:SCADA Hardware, Software Architecture and Workingldnladiesman217100% (1)
- Introduction To SCadaDocument18 pagesIntroduction To SCadaDip PatelNo ratings yet
- Final Eb MeterDocument49 pagesFinal Eb MeterSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) BasicsDocument5 pagesProgrammable Logic Controller (PLC) BasicsShah JayNo ratings yet
- PID & PLC Controllers ExplainedDocument4 pagesPID & PLC Controllers ExplainedRadab HameedNo ratings yet
- IasalumnoDocument36 pagesIasalumnoFernando Leyva VegaNo ratings yet
- SCADA Systems ExplainedDocument24 pagesSCADA Systems ExplainedPrabhat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ion & Control Eng'gDocument106 pagesIon & Control Eng'gMark de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Field Monitoring and Automation Using Iot in AgricultureDocument114 pagesField Monitoring and Automation Using Iot in AgriculturedileeppatraNo ratings yet
- Industrial Automation PrimerDocument2 pagesIndustrial Automation Primersfire_87No ratings yet
- 1 Understand The Basic Concept of BMS System: What Is A BMS or Building Management System?Document12 pages1 Understand The Basic Concept of BMS System: What Is A BMS or Building Management System?Salahudheen anas TNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Embedded System DesignDocument57 pagesChapter 1 Embedded System DesignRakesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Computer Controlled Systems SyllabusDocument74 pagesComputer Controlled Systems SyllabusAravinthNo ratings yet
- SCADA PaperDocument15 pagesSCADA Paperprashantbgpatel1No ratings yet
- Introduction To Microprocessor-Based ControlDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Microprocessor-Based ControlAhdan FawwazNo ratings yet
- A SCADA System Performs Four FunctionsDocument14 pagesA SCADA System Performs Four FunctionsariefNo ratings yet
- Computer-Process Interface For Data Acquisition and ControlDocument8 pagesComputer-Process Interface For Data Acquisition and ControlVidisha JhaNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument32 pagesAcknowledgementIsmail Afridi100% (1)
- A Mini Project On, Ivrs Based Automation System With Voice AcknowledgementDocument46 pagesA Mini Project On, Ivrs Based Automation System With Voice Acknowledgementkis111No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Industrial AutomationDocument19 pagesChapter 4 Industrial AutomationMelkamu SimenehNo ratings yet
- Irjet V3i6175Document4 pagesIrjet V3i6175Alemu EshetuNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: 1.1 Introduction To Embedded SystemsDocument36 pagesChapter-1: 1.1 Introduction To Embedded SystemsphanibhargavNo ratings yet
- Iii B.Tech Ii Sem Eie (R18) : Unit - VDocument62 pagesIii B.Tech Ii Sem Eie (R18) : Unit - VSrinivas PapaniNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Project Report: Ihtisham Ul HaqDocument9 pagesDigital Signal Processing Project Report: Ihtisham Ul Haqihtishamul HaqNo ratings yet
- Scada (Supervisory Control & Data Acquisition) For Remote Industrial PlantDocument2 pagesScada (Supervisory Control & Data Acquisition) For Remote Industrial Plantmksamy2021No ratings yet
- CA Bmi SatyaDocument60 pagesCA Bmi SatyaMr. RAVI KUMAR INo ratings yet
- Microcomputer Application in Motion ControlDocument5 pagesMicrocomputer Application in Motion ControlInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Project Synopsis Digital Controller Using Matlab: Deptt. of Electronics and InstrumentationDocument9 pagesProject Synopsis Digital Controller Using Matlab: Deptt. of Electronics and InstrumentationSaumya TripathiNo ratings yet
- SCADA Applications in Power SystemsDocument5 pagesSCADA Applications in Power SystemsTeju NookalaNo ratings yet
- Mark Vi术语表Document9 pagesMark Vi术语表meirangongNo ratings yet
- 25.ACCESSIBLE DISPLAY DESIGN TO CONTROL HOME AREA NETWORKSDocumentDocument84 pages25.ACCESSIBLE DISPLAY DESIGN TO CONTROL HOME AREA NETWORKSDocumentdileeppatraNo ratings yet
- PSDLDocument22 pagesPSDLHarshal PatilNo ratings yet
- Industrial AutomationDocument107 pagesIndustrial AutomationArivukkarasan RajaNo ratings yet
- Real-Time Monitoring and Assessment of Circuit Breaker Operations For Diagnostics and Control Applications - EEEDocument11 pagesReal-Time Monitoring and Assessment of Circuit Breaker Operations For Diagnostics and Control Applications - EEEpradeep9007879No ratings yet
- Vehicle Speed Control System Using RF CommunicationDocument80 pagesVehicle Speed Control System Using RF CommunicationSaheb Amrinder100% (6)
- CISA - Special TopicsDocument18 pagesCISA - Special TopicszamanbdNo ratings yet
- FIREPLUS-LHD DIGITAL LINEAR HEAT DETECTION CABLE - Sales Leaflet - 2019Document4 pagesFIREPLUS-LHD DIGITAL LINEAR HEAT DETECTION CABLE - Sales Leaflet - 2019jahangir samiNo ratings yet
- Win-Pak 4.9.4 User GuideDocument1,220 pagesWin-Pak 4.9.4 User Guidejahangir samiNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric The Connected Room Solution SXWRCF16A10003Document4 pagesSchneider Electric The Connected Room Solution SXWRCF16A10003jahangir samiNo ratings yet
- Syed Jahangir Sami: Professional SkillsDocument3 pagesSyed Jahangir Sami: Professional Skillsjahangir samiNo ratings yet
- VSS-2 Rev01Document1 pageVSS-2 Rev01jahangir samiNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument1 pageProjectjahangir samiNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument1 pageProjectjahangir samiNo ratings yet
- FIREPLUS-LHD DIGITAL LINEAR HEAT DETECTION CABLE - Sales Leaflet - 2019Document4 pagesFIREPLUS-LHD DIGITAL LINEAR HEAT DETECTION CABLE - Sales Leaflet - 2019jahangir samiNo ratings yet
- MTM800增强型控制头Document308 pagesMTM800增强型控制头1012268087No ratings yet
- Evermotion Archinteriors 16 PDFDocument2 pagesEvermotion Archinteriors 16 PDFJulieNo ratings yet
- Free SEO Audit TemplateDocument3 pagesFree SEO Audit Templatepassivejournal74No ratings yet
- Zerust Flange Savers - WebDocument2 pagesZerust Flange Savers - WebFederico MoranNo ratings yet
- Learning Support G7 2023Document6 pagesLearning Support G7 2023Aiza SulemanNo ratings yet
- WIRING DIAGRAM Wifi VendoDocument5 pagesWIRING DIAGRAM Wifi VendoDikdik PribadiNo ratings yet
- As Test 04Document6 pagesAs Test 04LearnchemNo ratings yet
- Definite Integrals and Trigonometric FunctionsDocument4 pagesDefinite Integrals and Trigonometric Functionskartikey papnoiNo ratings yet
- Semrush-Backlinks Overview-Root Domain Https Ganknow Com - 11th Mar 2023Document3 pagesSemrush-Backlinks Overview-Root Domain Https Ganknow Com - 11th Mar 2023RrKartika RatnasariNo ratings yet
- Electric Application Solution ExpertDocument21 pagesElectric Application Solution ExpertChonticha ChobsonNo ratings yet
- No. Hotel Address City Star Number of Room Room Allocation PIC Phone EmailDocument27 pagesNo. Hotel Address City Star Number of Room Room Allocation PIC Phone Emailali71usmanNo ratings yet
- 8051 MaterialDocument198 pages8051 Materialsupreetp555No ratings yet
- File (SQL Tutorial)Document81 pagesFile (SQL Tutorial)imranbaiggeekNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Defining and Collecting Data Triệu Vi GửiDocument43 pagesChapter 1. Defining and Collecting Data Triệu Vi GửiDang Thuy Trang (K17 QN)No ratings yet
- Data Sheet Ultrastar DC Ha210Document2 pagesData Sheet Ultrastar DC Ha210Marian DiaconescuNo ratings yet
- Spring Boot & Micro Services Course ContentDocument4 pagesSpring Boot & Micro Services Course ContentRamakrishna PradhanNo ratings yet
- POTS telephone service and local subscriber loopDocument2 pagesPOTS telephone service and local subscriber loopjeevanNo ratings yet
- Microscope 101: How To Safely Use A Microscope: Preparing A Wet-Mount SlideDocument2 pagesMicroscope 101: How To Safely Use A Microscope: Preparing A Wet-Mount SlideClara AbegãoNo ratings yet
- Assigned Questions ListDocument4 pagesAssigned Questions ListDeepam AsnaniNo ratings yet
- Standardised Effect Size in Mixed ML ModelsDocument9 pagesStandardised Effect Size in Mixed ML ModelsSergio Enrique Mora MojicaNo ratings yet
- Productivity: IncreaseDocument2 pagesProductivity: IncreaseJose Corcega britoNo ratings yet
- Notes:: Brisbane City Council Standard DrawingDocument1 pageNotes:: Brisbane City Council Standard DrawingShaunitchi El GrecoNo ratings yet
- Haier Biomedical General Catalogue 2019 PDFDocument96 pagesHaier Biomedical General Catalogue 2019 PDFJean TorreblancaNo ratings yet
- DIADesigner User Guide - En-UsDocument797 pagesDIADesigner User Guide - En-Ushuertourbano27No ratings yet
- 2) N5, N6 and N7 (NPS2 - 300#) PDFDocument20 pages2) N5, N6 and N7 (NPS2 - 300#) PDFpraffulNo ratings yet
- Article Review 1Document24 pagesArticle Review 1limap5No ratings yet