Professional Documents
Culture Documents
JHS Science Recovery Plan A.Y. 2022-2024
Uploaded by
Aiza CabatinganOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
JHS Science Recovery Plan A.Y. 2022-2024
Uploaded by
Aiza CabatinganCopyright:
Available Formats
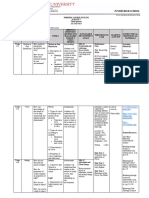
JHS SCIENCE RECOVERY PLAN
SAN BEDA SCIENCE CURRICULUM AUDIT
A.Y. 2023-2024
UNIVERSITY
Integrated Basic Education Department
www.sanbeda.edu.ph
GRADE 1ST QUARTER 2ND QUARTER 3RD QUARTER 4TH QUARTER
LEVEL
7 Matter Living Things and Their Forces and Motion Earth and Space
Environment
I. Nature of Science I. Forces and Motion I. Earth and Its Processes
A. Scientific Investigation I. Structure and Functions a. Motion in One Dimension a. Earthquakes and Faults
B. Measurement A. Cells i. Description of Motion i. Types of Fault
II. The Particle Nature of Matter a. History a. Meaning of Acceleration ii. Active and inactive faults
A. Properties of Solid, Liquid and b. The Cell Theory b. Graphical representations of iii. Movement along faults
Gas c. Parts of Cell acceleration iv. Earthquake focus and epicenter
B. Effects of Heat on the Particle d. Prokaryotic and II. Energy v. Seismic waves
Nature of Matter Eukaryotic cell a. Waves vi. Magnitude and intensity of
III.Diversity of Materials in the e. Transport Mechanisms in i. Types of waves according to the earthquake
environment Cells motion of the particles vii. Earthquake and tsunami
A. Pure Substances B. Biomolecules a. Transverse wave b. Volcanoes
a. Elements II. Heredity: Inheritance and b. Longitudinal wave i. Types of volcanic eruption
i. Metals, Metalloids and Variation ii. Types of waves according to ii. Energy from volcanoes
Non-metals A. Sexual and Asexual medium II. Weather and Climate
b. Compounds Reproduction a. Mechanical wave a. Layers of the Atmosphere
i. Organic and Inorganic B. Chromosomes b. Electromagnetic waves b. Land and Sea Breeze
Compounds C. Cell Cycle and Division iii. Characteristics of waves c. Monsoons
ii. Acids and Bases and Salts D. Chromosomal Aberrations iv. Properties of waves (reflection d. Intertropical Convergence Zone
B. Mixtures III. Biodiversity and Evolution and refraction) III. Solar System and the Universe
a. Solutions (solute and solvent) A. Levels of Biological a. Seasons
b. Factors affecting solubility Organization III. Sound i. Relation of seasons to the position
(stirring, particle size, IV. Ecosystem a. Subjective and Objective of the sun in the sky
temperature) A. Flow of Energy and Matter characteristics of sound b. Constellations
c. Saturation of solutions in Ecosystems IV. Light i. Circumpolar
d. Concentration of solutions a. Trophic levels a. Characteristics of Light (intensity and ii. Seasonal
i. Percent by mass b. Cycling of Materials color) iii. Zodiacal
RECOVERY PLAN | Science | A.Y. 2023 – 2024 | Page 1 of 6
ii. Percent by volume i. Water cycle V. Heat Transfer iv. Motions of the Earth and the
e. Naturally occurring and process ii. Oxygen-carbon cycle a. conduction Constellations
solutions iii. Nitrogen cycle b. convection
c. radiation
VI. Electricity
a. static electricity
b. charges
c. charging process
8 Forces and Motion Earth and Space Living Things and Their Environment Matter
I. Force and Motion I. Earth and Its Processes I. Structure and Function I. Atomic Structure
b. Laws of Motion a. Plate Tectonics A. Processes in the Human Digestive a. Development of the Atomic Theory
i. Law of Inertia i. Global distribution of System i. Dalton’s Atomic Model
ii. Law of Acceleration volcanoes, earthquake i. Digestion ii. J.J. Thompson’s Plum Pudding
iii. Law of Interaction and epicenters and ii. Excretion Model
II. Energy mountain ranges II. Heredity: Inheritance and Variation of iii. Rutherford’s Nuclear Model
a. Work and Energy ii. Internal structure of the Traits iv. Bohr’s Orbital Model
i. Definition of work Earth A. The Cell b. Sub-atomic Particles
ii. Mechanical energy iii. Plate boundaries i. Chromosomes i. Protons
(Potential and Kinetic iv. Processes and ii. Cell Cycle ii. Neurons
Energy) landforms along plate iii. Cell Division iii. Electrons
iii. Law of Conservation of boundaries B. Mendelian Genetics c. Isotopes
Energy v. Mechanisms that drive C. Non-Mendelian Genetics d. Electron Configuration (Aufbau
b. Sound plate movement i. Incomplete dominance Principle)
i. Speed of sound and vi. Evidence of plate ii. Codominance i. Ground state electron
temperature movement iii. Multiple alleles ii. Noble Gas electron configuration
c. Light II. Weather and Climate iv. Polygenic inheritance e. Orbital Diagram (Pauli’s Exclusion
viii. Reflection of Light a. Understanding Typhoons III. Biodiversity and Evolution Principle and Hund’s Rule)
a. Law of reflection i. Formation of Typhoon A. Taxonomic Classification f. Valence Electrons
ix. Refraction of Light in ii.Location of the i. Domains (Bacteria, Archaea, II. Periodic Table of Elements
different media Philippines and the Eukarya) a. Development of the Periodic Table
x. Characteristics of visible occurrence of typhoons ii. Six-kingdom scheme b. Arrangement of Elements in the
light iii. Landforms and bodies (Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Periodic Table
d. Heat and temperature of water affecting Protista, Fungi, Plantae, c. Trends in the Periodic Table
i. Thermal Equilibrium typhoons within the Animalia)
ii. Effects of heat Philippine Area of B. Binomial Nomenclature
RECOVERY PLAN | Science | A.Y. 2023 – 2024 | Page 2 of 6
a. Change in temperature responsibility (PAR) IV. Ecosystem
b. Thermal Expansion III. Solar System and the A. Flow of Energy and Matter in
Universe Ecosystems
a. Other Members of the i. Photosynthesis
solar system ii. Cellular Respiration
i. Comets
ii. Meteoroids
iii. Asteroids
iv. Dwarf Planets
9 Living Things and Their Environment Matter Earth and Space Forces and Motion
I. Structure and Function I. Atomic Structure I. Earth and Its Processes I. Forces and Motion
a. Process in the Human Body a. Electron Configuration a. History of the Earth a. Free Fall
i. Respiration (Aufbau Principles) i. Geologic Time i. Kinematic equations for
ii. Circulation (circulation of i. Ground state electron ii. Absolute and relative dating Free-fall
materials such as food, configuration II. Weather and Climate ii. Graphical representation of
wastes, gases, electrolytes) ii. Noble gas electron a. Factors that affect climate Free-fall motions
II. Heredity: Inheritance and Variation configuration iii. Applications/examples of
i. Latitude
of Traits b. Orbital Diagram (Pauli’s free-fall motion
ii. Elevation
a. Mendelian Genetics Exclusion Principle and
iii. Distance from the ocean b. Momentum and Impulse
b. DNA Hund’s Rule)
iv. Topography c. Conservation of Linear Momentum
c. Central Dogma c. Valence Electrons
i. DNA Replication v. Ocean current
ii. Protein synthesis II. Chemical Bonding vi. Human Activities II. Energy
d. Mutations a. Lewis Electron Dot b. Global Climate Phenomena a. Light
III. Biodiversity and Evolution Structures (LEDS) i. Greenhouse Effect i. Diffraction
a. Levels of Biodiversity (genetics, b. Formation of Ionic bonds ii. Carbon footprint ii. Interference
species, and ecosystem) c. Naming and Writing Ionic iii. El Niño and La Niña iii. Polarization of Light
b. Species diversity compounds iv. Ozone Depletion b. Heat and Work
i. Threatened Species d. Formation of covalent III. Solar system and the Universe i. Heat Engine
Categories (critically bonding a. Stars ii. Efficiency of heat
endangered, endangered, e. Naming and writing i. Characteristics (luminosity, engines
vulnerable, other threatened covalent compounds surface, temperature, mass) c. Electricity
species) f. Determining ionic or ii. Stellar Evolution i. Current, voltage, and
c. Threats to Biodiversity covalent of Ionic bonds resistance
(pollution, climate change, g. Metallic Bonding ii. Ohm’s Law
RECOVERY PLAN | Science | A.Y. 2023 – 2024 | Page 3 of 6
overexploitation, invasive -Measurement of current
species, and habitat lass) III.Chemical Reaction and voltage
d. Protection and conservation of a. Evidences of Chemical iii. Variations of voltage,
endangered and economically Reactions current, and
important species b. Chemical Equation resistance in series
IV. Ecosystem c. Balancing Chemical and parallel
a. Types of Ecosystems in the Equations connections
Philippines d. Law of Conservation of d. Electricity and Magnetism
i. Tropical rainforests Mass i. Electromagnetic induction
ii. Swamps e. Types of Chemical
ii. Electric motor and generator
iii. Estuaries Reactions (combination,
iv. Mangrove forests decompositions, single-
v. coral reefs replacement, double-
b. Impact of human activities in an replacement, combustion)
(loss of habitat, decrease in f. Factors Affecting the Rates
biodiversity, etc.) of Chemical Reactions
10 Earth and Space Forces and Motion Matter Living Things and Their Environment
I. Earth and Its Processes I. Energy I. Mole Concept I. Structures and Functions
a. Sustainable management of a. Light a. Mass a. Processes in the Human Body
resources i. Mirror (plane and b. Moles i. Coordination (nervous and
curved) c. Avogadro’s Number endocrine system-hormones)
II. Weather and Climate ii. Lenses d. Percentage composition of a ii. Body Regulation (Homeostasis-all
a. Mitigation and Adaptation iii. Ray compound body systems)
using Green Technology diagramming II. Gas Law II. Heredity: Inheritance and Variation of
b. Electricity a. Kinetic Molecular Theory Traits
b. Volume, pressure, temperature and a. Biotechnology
III. Solar System and the Universe i. Static electricity
number of moles relationship i. Traditional
a. Theories on the formation of ii. Charges
i. Boyle’s Law ii. Modern
the Solar System iii. Charging
ii. Charles’ Law III.Biodiversity and Evolution
i. Nebular hypothesis process
iii. Gay-Lussac’s Law a. Theories of Evolution
ii. Accretion theory iv. Current, voltage,
iv. Avogadro’s Law i. Lamarck’s Theory of Evolution
iii. Protoplanet theory and resistance
v. Ideal Gas Laws ii. Darwin’s Theory of Evolution
iv. Capture Theory v. Ohm’s Law
III.The variety of Carbon Compounds b. Lines of Evidence of Evolution
-Measurement of
a. Carbon Atom’s (fossils, biography, comparative
current and
b. Types of Hydrocarbons morphology, patterns of development)
voltage
RECOVERY PLAN | Science | A.Y. 2023 – 2024 | Page 4 of 6
vi. Variations of IV. Ecosystems
voltage, current, and a. Photosynthesis
resistance in series b. Cell respiration
and parallel c. Carrying capacity of an ecosystem
connections d. Population Growth
c. Heat, Work, and
Efficiency (G9)
i. Generation,
Transmission, and
distribution of
electrical energy
from power plants
and geothermal
energy
d. Electromagnetic Waves
i. Relative
wavelength,
frequency, and
energy
ii. Practical
applications of EM
waves
iii. Effects of
radiation on living
things
e. Nuclear Energy
i. Nucleus of the
Atom
ii. Types of
radiation
iii. Nuclear fusion
and fission
RECOVERY PLAN | Science | A.Y. 2023 – 2024 | Page 5 of 6
Prepared by:
Ms. Rechel T. Avenido Ms. Toni Yzabelle B. Bilo Ms. Ma. Janina Joy F. Fernandez Mr. Gregorio C. Simangan
RECOVERY PLAN | Science | A.Y. 2023 – 2024 | Page 6 of 6
You might also like
- Summative Test 1 - Physical ScienceDocument4 pagesSummative Test 1 - Physical ScienceKennedy Fieldad Vagay100% (3)
- Diagnostic Test in Physical ScienceDocument5 pagesDiagnostic Test in Physical ScienceLAURENCE CASILDONo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy Class Notes Chemical SciencesDocument173 pagesSpectroscopy Class Notes Chemical SciencesSwashy Yadav100% (1)
- Integrated Science 8: Governor Cuenco Avenue, Banilad, Cebu City 6000 PhilippinesDocument3 pagesIntegrated Science 8: Governor Cuenco Avenue, Banilad, Cebu City 6000 PhilippinesKirsten LopezNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Science 5 (Personal)Document2 pagesCourse Outline Science 5 (Personal)Tessie Rose ColasNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Science 5Document2 pagesCourse Outline Science 5Tessie Rose ColasNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Guide in Science Grade X S.Y. 2020-2021: St. Scholastica'S Academy Tabunok, Talisay City, CebuDocument15 pagesCurriculum Guide in Science Grade X S.Y. 2020-2021: St. Scholastica'S Academy Tabunok, Talisay City, CebuWarley JabelNo ratings yet
- Course Outline S11 2nd SemDocument2 pagesCourse Outline S11 2nd SemrachellejulianoNo ratings yet
- F.Y.B.a.-geographyDocument6 pagesF.Y.B.a.-geographyom handeNo ratings yet
- 4 Months JAMB Study PlanDocument4 pages4 Months JAMB Study PlanOMILABU DOYINNo ratings yet
- Arandia College, Inc.: Date Topic / Content ActivitiesDocument3 pagesArandia College, Inc.: Date Topic / Content Activitiesgian gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Earth Science TopicsDocument1 pageEarth Science TopicsDyoley Pearl ZantuaNo ratings yet
- Zero GravityDocument31 pagesZero Gravityudefavour447No ratings yet
- Bicol State College Astronomy Course OutlineDocument1 pageBicol State College Astronomy Course OutlineDyoley Pearl ZantuaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Summative TestDocument4 pagesGrade 8 Summative TestHarold Nalla Husayan100% (1)
- Physical Science ReviewerDocument4 pagesPhysical Science ReviewerjehonieeeNo ratings yet
- For Mam Virgie Topics IsDocument2 pagesFor Mam Virgie Topics IsamsiNo ratings yet
- PRETESTDocument2 pagesPRETESTTan QuimNo ratings yet
- Stem Engine: College Entrance Test Review Preparation (Science)Document4 pagesStem Engine: College Entrance Test Review Preparation (Science)Anonymous rHn7ormVlNo ratings yet
- Pre Test in Earth and Life Science Answer KeydocxDocument2 pagesPre Test in Earth and Life Science Answer KeydocxJake UrbiNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Multiple Choice Questions on Planets, Minerals, Rocks and Earth's SpheresDocument2 pagesEarth Science Multiple Choice Questions on Planets, Minerals, Rocks and Earth's SpheresClaudene GellaNo ratings yet
- Science Olympiad Study Guide 2023-24Document6 pagesScience Olympiad Study Guide 2023-24musunuru.nikhilNo ratings yet
- History of Life Chapter QuestionsDocument43 pagesHistory of Life Chapter QuestionsUltramixNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Exam in Earth Science (2023-2024)Document2 pagesFirst Quarter Exam in Earth Science (2023-2024)Marvin Earl O. RabinoNo ratings yet
- F.Y.B.A. Geography PDFDocument3 pagesF.Y.B.A. Geography PDFKrupasagar majhi100% (1)
- Ocn 750 - Benthic Biological Oceanography Reading CourseDocument2 pagesOcn 750 - Benthic Biological Oceanography Reading CourseAnonymous QlJjisdlLINo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument4 pagesEarth and Life ScienceANNA CLARISSA AVESNo ratings yet
- June Exam 2fDocument2 pagesJune Exam 2fmariazuNo ratings yet
- Course Outline in Science 7Document4 pagesCourse Outline in Science 7Connie Joy CalawagNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test ELSDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Test ELSLorie Mae ViloriaNo ratings yet
- ALS Science Review TestDocument2 pagesALS Science Review TestLan Calungsod100% (1)
- Earth Science Module 1Document37 pagesEarth Science Module 1Joksian TrapelaNo ratings yet
- 1Document3 pages1Roceline AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Mock TestDocument7 pagesEarth and Life Science Mock TestFederico Bautista Vacal Jr.No ratings yet
- Midterm Exam in Earth and Life ScienceDocument3 pagesMidterm Exam in Earth and Life ScienceRene John Bulalaque EscalNo ratings yet
- 1stQ Earth and Life ScienceDocument3 pages1stQ Earth and Life ScienceCarmelito Nuque Jr0% (1)
- Diagnostic Test in Science 9Document3 pagesDiagnostic Test in Science 9Pepito Rosario Baniqued, JrNo ratings yet
- FC - GenscienceDocument8 pagesFC - GenscienceReden OriolaNo ratings yet
- I. Multiple Chice. Circle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument2 pagesI. Multiple Chice. Circle The Letter of The Correct Answernardo saladoresNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test ElsDocument5 pagesDiagnostic Test ElsLAURENCE CASILDONo ratings yet
- Physci Reviewer ExamDocument2 pagesPhysci Reviewer ExamJasper DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Name: Subject: Grade/Section: Subj. Teacher: Week: 5 of Quarter IIDocument9 pagesName: Subject: Grade/Section: Subj. Teacher: Week: 5 of Quarter IIIrene AmansecNo ratings yet
- B. Cell B. HeredityDocument6 pagesB. Cell B. HeredityCHARLES GODWIN CAASNo ratings yet
- Readings of Bio and Earth SciDocument2 pagesReadings of Bio and Earth SciStephanie GenosaNo ratings yet
- Week 03 - QuizDocument1 pageWeek 03 - QuizMarian Joy RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test in Earth and Life Science 60 ItemsDocument6 pagesDiagnostic Test in Earth and Life Science 60 ItemsBeianne Jaef AlmindrasNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer 4Document84 pagesLET Reviewer 4jovan amihanNo ratings yet
- Summative Tes 1 & 2 (1ST SEM)Document4 pagesSummative Tes 1 & 2 (1ST SEM)Keyam NielNo ratings yet
- 2Document3 pages2Roceline AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Geology305 GeologicDatingHomework Summer 2018Document7 pagesGeology305 GeologicDatingHomework Summer 2018Kimberly Sheen YamsonNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test G8 ScienceDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Test G8 ScienceCirille AgpaoaNo ratings yet
- Junior High School Science Topics - PhilippinesDocument13 pagesJunior High School Science Topics - PhilippinesFrancis Neil Jarical100% (1)
- First Quiz in Earth & Life ScienceDocument4 pagesFirst Quiz in Earth & Life ScienceRenz FerrerNo ratings yet
- Science Proficiency - Simulation Exam I 2020 PDFDocument15 pagesScience Proficiency - Simulation Exam I 2020 PDFLyndon Allen Sales100% (1)
- DIAGNOSTIC TEST EARTH SCIENCE KEYDocument8 pagesDIAGNOSTIC TEST EARTH SCIENCE KEYForshia Antonette BañaciaNo ratings yet
- N A T ReviewerDocument15 pagesN A T ReviewerJundon Ivo De BorjaNo ratings yet
- Physics Model Exam Grade .8@ethiostudenteDocument14 pagesPhysics Model Exam Grade .8@ethiostudenteBahar AbdurahmanNo ratings yet
- Microstructures of Irradiated Materials: Treatise on Materials Science and Technology, Vol. 7From EverandMicrostructures of Irradiated Materials: Treatise on Materials Science and Technology, Vol. 7No ratings yet
- 3Q Science 7 PCO AY 2023-2024 V1Document3 pages3Q Science 7 PCO AY 2023-2024 V1Aiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Final PT - Innovative Green Technology Prototype PresentationDocument2 pagesFinal PT - Innovative Green Technology Prototype PresentationAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Mini Task 3 - Design Sketch IIDocument3 pagesMini Task 3 - Design Sketch IIAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- 2Q - Worksheet #3 - Ohm's Law.fDocument2 pages2Q - Worksheet #3 - Ohm's Law.fAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- 1ST Trimestral Exam Math 4Document5 pages1ST Trimestral Exam Math 4Aiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Mini Task 2 - Design Sketch IDocument2 pagesMini Task 2 - Design Sketch IAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Mini Task 2 - Design Sketch IDocument2 pagesMini Task 2 - Design Sketch IAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Science project peer assessmentDocument2 pagesScience project peer assessmentAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Place Value-Put To PracticeDocument1 pagePlace Value-Put To PracticeAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Fraction Pizza Recipe-WorksheetDocument1 pageFraction Pizza Recipe-WorksheetAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Quiz-Comparing and Ordering NumbersDocument4 pagesQuiz-Comparing and Ordering NumbersAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Factor Tree-WorksheetDocument1 pageFactor Tree-WorksheetAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Seatwork #2 Science - Golf Ball Projectile MotionDocument1 pageSeatwork #2 Science - Golf Ball Projectile MotionAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Projectile Launched at An AngleDocument47 pagesProjectile Launched at An AngleAiza Cabatingan100% (1)
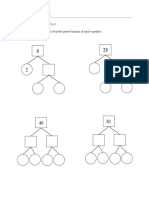
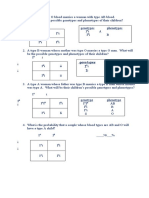
- Blood type inheritance probabilitiesDocument1 pageBlood type inheritance probabilitiesAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Take Photos of Triangles and Quadrilaterals in Your HomeDocument1 pageTake Photos of Triangles and Quadrilaterals in Your HomeAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Cloud in A Bottle - Exp 1 - EarthsciDocument2 pagesCloud in A Bottle - Exp 1 - EarthsciAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- OLSPS Junior High Science Worksheet on Newton's LawsDocument2 pagesOLSPS Junior High Science Worksheet on Newton's LawsAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Identification Mukbang ExperimentDocument1 pageNutrient Identification Mukbang ExperimentAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Junior High Science Grade 10 First Trimester Instructional PlanDocument23 pagesJunior High Science Grade 10 First Trimester Instructional PlanAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- 5 - ElectromagnetismDocument6 pages5 - ElectromagnetismAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Multiple Allele QuestionaireDocument1 pageMultiple Allele QuestionaireAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 3.1. Quantum Mechanical ModelDocument2 pagesACTIVITY 3.1. Quantum Mechanical ModelAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- ST Grade 8 Bio Lesson 6Document10 pagesST Grade 8 Bio Lesson 6Aiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- ST Grade 8 Bio Lesson 4Document6 pagesST Grade 8 Bio Lesson 4Aiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- The Right Family-MechanicsDocument1 pageThe Right Family-MechanicsAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Checklist - What's Your Carbon FootprintDocument1 pageChecklist - What's Your Carbon FootprintAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Activity 2.5Document2 pagesActivity 2.5Aiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Activity 2.4Document2 pagesActivity 2.4Aiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Numerical study of transient friction factors in gas pipeline flow ramp-up and ramp-down conditionsDocument153 pagesNumerical study of transient friction factors in gas pipeline flow ramp-up and ramp-down conditionshjxyNo ratings yet
- Virtual Live GAMSAT Preparation Course: Topic OutlineDocument4 pagesVirtual Live GAMSAT Preparation Course: Topic OutlineMegan Guerrero50% (2)
- Energy: Mehdi Mehrpooya, Mohammad Mehdi Moftakhari Sharifzadeh, Marc A. RosenDocument23 pagesEnergy: Mehdi Mehrpooya, Mohammad Mehdi Moftakhari Sharifzadeh, Marc A. Rosenkishna009No ratings yet
- Introduction To Qualitative Chemistry (Review On Chemical Concepts)Document6 pagesIntroduction To Qualitative Chemistry (Review On Chemical Concepts)Rosalinda Frias GarciaNo ratings yet
- Presentation: Thermal Properties of MatterDocument226 pagesPresentation: Thermal Properties of MatterSpartinNo ratings yet
- ApchemDocument89 pagesApchemqwertysummerloveNo ratings yet
- 2023 Y5 H2 Gaseous State Tutorial (Suggested Solutions)Document19 pages2023 Y5 H2 Gaseous State Tutorial (Suggested Solutions)liujiaming2006No ratings yet
- Horiba: Continuous Monitor For SO Model HORIBA APSA-370Document2 pagesHoriba: Continuous Monitor For SO Model HORIBA APSA-370ikarimzaiNo ratings yet
- CE 7002 AIR POLLUTION AND CONTROL ENGINEERING Syllabus UGDocument2 pagesCE 7002 AIR POLLUTION AND CONTROL ENGINEERING Syllabus UGKavinkumar RNo ratings yet
- Teknik Menjawab Kertas 2 FizikDocument41 pagesTeknik Menjawab Kertas 2 FizikCikgu Mohamad Esmandi HapniNo ratings yet
- HFID hydrocarbon analyzer calibration proceduresDocument3 pagesHFID hydrocarbon analyzer calibration proceduresSahil BiswasNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms-Focused Approach, 3rd Edition, Thomas R Gilbert, Rein V Kirss, Stacey Lowery Bretz, Natalie FosterDocument10 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms-Focused Approach, 3rd Edition, Thomas R Gilbert, Rein V Kirss, Stacey Lowery Bretz, Natalie Fosterloudly.nereisnai6100% (17)
- B.E. Gelfand - Blast Waves Attenuation in Two-Phase MediaDocument17 pagesB.E. Gelfand - Blast Waves Attenuation in Two-Phase MediaYamveaNo ratings yet
- Micro-DCI Micro-Mite 53SL6000 Single Loop Controllers: - 2-Year WarrantyDocument4 pagesMicro-DCI Micro-Mite 53SL6000 Single Loop Controllers: - 2-Year WarrantyMoiReyesNo ratings yet
- High-Pressure Steam Reformed Gas Waste Heat BoilersDocument1 pageHigh-Pressure Steam Reformed Gas Waste Heat BoilersDavid PierreNo ratings yet
- Popping Under Pressure: The Physics of PopcornDocument20 pagesPopping Under Pressure: The Physics of PopcornDelhi FreakNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science 2009 Paper 1 Level 5-7Document28 pagesKS3 Science 2009 Paper 1 Level 5-7Aryaveer Kumar100% (1)
- Che CHM QuestionsDocument82 pagesChe CHM QuestionsErik WeeksNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 6th Edition Kundu Solutions Manual - PDFDocument21 pagesFluid Mechanics 6th Edition Kundu Solutions Manual - PDFUma SinghNo ratings yet
- 10 35378-Gujs 948875-1810534Document18 pages10 35378-Gujs 948875-1810534jonyg01No ratings yet
- Course Outline - Grade 9: Igcse (Chemistry)Document5 pagesCourse Outline - Grade 9: Igcse (Chemistry)Bhawana SinghNo ratings yet
- Storm in A TeacupDocument224 pagesStorm in A TeacupChanKelvin100% (5)
- Valve Terminology GlossaryDocument33 pagesValve Terminology GlossaryJan JomwongNo ratings yet
- Fans and BlowersDocument11 pagesFans and BlowerskennnNo ratings yet
- Alat CSRDocument11 pagesAlat CSROperation TewehNo ratings yet
- Day1 From GeloDocument15 pagesDay1 From GeloEfrenE.GarciaJr.92% (12)
- SF6 Gas Sampling ProcedureDocument4 pagesSF6 Gas Sampling ProcedureMohsin YasinNo ratings yet
- Prospective ChemistryDocument10 pagesProspective ChemistryAdolfNo ratings yet
- Theoretical DeliverabilityDocument201 pagesTheoretical DeliverabilityJorge Cespedes De UgarteNo ratings yet