Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LeanIX Business-Capability-Map Default
LeanIX Business-Capability-Map Default
Uploaded by
IgnacioOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LeanIX Business-Capability-Map Default
LeanIX Business-Capability-Map Default
Uploaded by
IgnacioCopyright:
Available Formats
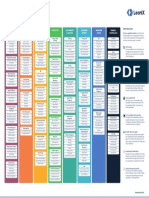
BEST PRACTICES TO DEFINE
Business Capability Map LeanIX
CUSTOMER ENTERPRISE FINANCE MARKETING & SALES PROCUREMENT & PRODUCT & SERVICE PRODUCTION STRATEGIC
BEST PRACTICES
RELATIONSHIP SUPPORT LOGISTICS DEVELOPMENT MANAGEMENT Business capability modeling is a technique for
the representation of an organization’s business
Contact Management Enterprise Effectiveness & Project Accounting Customer Success Management Logistics Management Engineering Change Management Business Concept anchor model, independent of the organization’s
Management
Classify Demand Cost Accounting Avoid Customer Churn Manage Demand Forecast Conceptualization Access Deviations Concept Establishment structure, processes, people, or domains.
Develop Projects
Contact Interaction Enterprise Consolidation Define Plans for Customer Upsell Manage Logistic Order Construction Analyze Deviations External Assessment
Manage Portfolio
Inbound Contact External Reporting Increase Customer Lifetime Value Manage Returns Design Products Manage Deviation Allowance Internal Analysis
Manage Programs Don’t overlap
Manage Interaction Inventory Valuation Manage Customer Onboarding Manage Transportation Manage Requirements Plan & Execute Deviations Market Surveys
Good capabilities do not overlap; they are
Outbound Contact Investor Relations Manage Upsells Trace Deviations Restructure Organization
Enterprise Risk Management
Purchasing Marketing Testing mutually exclusive. A good test is to check
Route Contact Manage General Ledger Terminate Contracts
Business Continuity
Approve & Transmit Order Analyse Customer Intelligence Infrastructure Management Externals Management whether you can assign Level 2 capabilities
Performance Reporting
Contract Management
Manage Compliance
Demand & Offer Management Decide On Sourcing Establish Measures Build Site Infrastructure Evaluate & Select without ambiguity.
Manage Fraud
Manage Contract Asset Management Identify Customer Define Sourcing Requirements Evaluate Market Opportunities Manage Location Restrictions Maintain Contracts
Manage Insurance
Manage Frame-Contract Asset Performance Mgmt Identify New Channels Define Sourcing Strategy Market Survey Operate Site Infrastructure Manage Payments Define “What”; not “How”
Manage Security
Manage Product Usage Decommissioning Manage Community Manage Category Plan & Control Construction Monitor Performance Business capabilities encapsulate what a
Method Development
Negotiate Contract Investment Planning Manage Customer Manage Purchase Catalogue Terminate Contracts business is doing right now and what it must
Human Resources Management
Define Method Machine Management
Manage Asset Lifecycle Manage Customer Hierarchy Manage Purchase Order be doing to meet current and future
HR Policies & Processes
Customer Management Innovation & Technology
Manage Customer Profile Manage Purchase Procedure
Execute Method Build Machine
challenges.
Manage Employee Management
Identify Customer Financial Planning & Analysis Refine Method Calibrate Machine
Manage Org. Context Manage Purchase Requirements
Manage Payroll Manage External Innovation
Manage Community Business Planning Validate Method Manage Machine Information
Manage Talents
Manage Purchase Requisition
Manage Innovation Process Long-term stability
Manage Customer Cost Accounting Marketing & Sales Development Operate Machine
Recruiting
Manage Sourcing Tender Process
Product & Service Delivery Manage Internal Innovation Properly defined business capabilities are
Manage Customer Hierarchy Forecasting Define Customer Value Proposition Optimize Machine
Tendering
Manage Product Traceability Scout Trends
fairly stable over time, persisting throughout
Manage Org. Context Define M&S Requirements
Information Management
Payroll Manage Production Maintenance Track Innovation
any organizational changes. Only major
Define Marketing Budget
Customer Scoring
Define Reports and KPIs
Manage Payment Sourcing Schedule Production Handle Spare Parts
model updates should affect them.
Develop M&S Channels
Gather Data Manage Core Business
Check Credit-Worthiness Process Taxes Test Quality Performance Manage Maintenance Plan
Develop M&S Messages
Define Customer Risks
Govern Data
Time Stamp Report Supplier Contact Management Recognize & Recover Failure
Coordinate Projects
Cross-organizational
Monitor Channels
Manage Customer Risks
Illustrate Data
Enact Supplier Contract
Product Preparation Evaluate Existing Products
Don’t focus too much on business units.
Process Data Settlements & Payments
Sales Manage Supplier Contract
Align Resources Materials Management Manage Bus. Performance & Ops Capabilities should remain the same and be
Order Management Account Payables
Advise Client Manage Supplier Frame Contract
Master Production Schedule Fetch Material Manage Projects independent of the current structure of the
IT Management
Bundle Order Billing
Create ERP Negotiate Supplier Contract
Procure Materials & Services Handle Dangerous Goods organization.
Application Management Mergers & Acquisitions
Cancel Order Revenue Cycle Management Select Suppliers & Developers Manage Containers
Create Specific Offer
EA Management Manage M&A
Steer Order Travel & Expense Management Manage Incoming Materials
IT Project Management
Manage Client Warehouse Management
Quality Management Manage M&A Integration
7 to 10 capabilities at the top level
Track Order Manage Material Requirements
IT Service Management Tax Management
Manage Trials Commissioning
Manage Debugging Manage M&A Strategy
The highest level capabilities should be a
Validate Order
Negotiate Offer Goods Receipt & Service Entry complete description of your business. Aim
IT Strategy Management Handle Trading Manage Product Document Product Design & Planning Track Acquisitions
Qualify Opportunity Manage Claims to make your categories reflect key aspects
SLA Management Technology Management Manage Tax Questionnarie Test Initial Quality Define Production Process
Manage Inventory Organization Development of what the business actually does.
Manage SLA Violations Tax Determination Track Quality Define Production Site
Knowledge & Research Material Disposition Coordinate Process Strategy
Track & Report SLA Breaches Tax Planning Strategies Manage Production Requirements
Management Packaging
Tax Returns Mgmt.
R&D
Manage Waste Disposal
Develop Organization Goals Breadth rather than depth
Manage Knowledge Restocking
Tax Settlements
Manage Innovation
Plan Material Requirements
Plan Long Term Don’t go too deep. Illustrate the breadth of
Manage Research Shipping Manage Patent Strategize Business Units your organization’s business capabilities by
Manage Tech Scanning
Treasury Manage Product Portfolio Production Order Management going no more than three levels down. This
Strategic Business Initiatives
Legal
Cash Management Manage R&D Process Manage Order Validity will be enough to represent IT landscape of
Develop Strategic Initiatives
Corporate Governance Policies
Financial Risk Management Plan Production Orders your enterprise.
Requirements Definition Establish High-Level Measures
Foreign Exchange Management Plan Production Program
Ensure Compliance
Evaluate Existing Products Evaluate Strategic Initiatives
Preventive Law Program Dev.
Plan Supply Quantity
Accepted by all stakeholders
Manage Materials Select Strategy
Pre-production Planning The goal of business capabilities is that they
Require Distribution
Workforce Management
Strategy Development become a common basis for discussion and
Review Demand Production Steering
Deploy Workforce
Adapt Strategy planning. Take every opportunity to anchor
Bill of Material Management
Manage Work Order
Define Strategy
your organization's processes to the model.
Deliver Product
Workforce Planning
Develop Vision/Mission
Localize Product
Monitor Production Process
Manage Strategy Linking strategy and execution
Track Strategy Involve those who define the strategies
Retrieve Product Information
when creating your map. Consider strategy
as one input when defining your business
capabilities on the highest level.
www.leanix.net
You might also like
- Poster Finance-Business-Capabilities EN PDFDocument1 pagePoster Finance-Business-Capabilities EN PDFCarlos CardenasNo ratings yet
- 2020 LeanIX WhitePaper - Definitive Guide To Business CapabilitiesDocument14 pages2020 LeanIX WhitePaper - Definitive Guide To Business CapabilitiesCarlosBritoVonBodenburgNo ratings yet
- Investment Banking Capability ModelDocument8 pagesInvestment Banking Capability ModelCapability ModelNo ratings yet
- GNB Enterprise Architecture Roadmap - OverviewDocument1 pageGNB Enterprise Architecture Roadmap - OverviewHarumNo ratings yet
- Capability Based Planning PDFDocument65 pagesCapability Based Planning PDFdante981No ratings yet
- Operating Models PDFDocument12 pagesOperating Models PDFDhanysha Putri100% (2)
- KPMG - Target Operating ModelDocument2 pagesKPMG - Target Operating ModelSudip Dasgupta100% (1)
- Target Operating Model Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandTarget Operating Model Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Map Business Architecture To Define Your StrategyDocument94 pagesMap Business Architecture To Define Your StrategyAndyMia100% (1)
- Application Rationalization Key Initiative Overview: AnalysisDocument4 pagesApplication Rationalization Key Initiative Overview: AnalysisOOPASANA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Architecture Body Of Knowledge A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionFrom EverandEnterprise Architecture Body Of Knowledge A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNo ratings yet
- Business Capability Model: Quick GuideDocument6 pagesBusiness Capability Model: Quick Guidekadeoye80% (5)
- An Education in Service Management: A guide to building a successful service management career and delivering organisational successFrom EverandAn Education in Service Management: A guide to building a successful service management career and delivering organisational successNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Architecture Tools A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionFrom EverandEnterprise Architecture Tools A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Delloitte TOMDocument27 pagesDelloitte TOMDJ100% (5)
- Business Technology Optimization Capability MapDocument2 pagesBusiness Technology Optimization Capability Mapvdimitrov100% (7)
- Business Capability Modeling Complete Self-Assessment GuideFrom EverandBusiness Capability Modeling Complete Self-Assessment GuideNo ratings yet
- Introducing The Next Gen Operating Model PDFDocument127 pagesIntroducing The Next Gen Operating Model PDFAnirban Dasgupta100% (4)
- Target Operating Model - V070809Document27 pagesTarget Operating Model - V070809bhsiung416100% (1)
- 1 1 IT-Metrics Metrics Storyboard SampleDocument13 pages1 1 IT-Metrics Metrics Storyboard SampleAshri AriffinNo ratings yet
- Lu Deloitte and Target Operating Model 122014Document1 pageLu Deloitte and Target Operating Model 122014Mudit Kapoor0% (1)
- Transform FrameworkDocument29 pagesTransform FrameworkVictor Ho100% (1)
- High-Level Target Operating Model TOM DevelopmentDocument4 pagesHigh-Level Target Operating Model TOM Developmentlaura_roman50% (4)
- D-G4-L4-050 Target Operating Model DesignDocument15 pagesD-G4-L4-050 Target Operating Model DesignDJ100% (1)
- Target Operating ModelDocument18 pagesTarget Operating ModelRohitNo ratings yet
- Designing Operating Models OVERVIEW SC - 2019Document2 pagesDesigning Operating Models OVERVIEW SC - 2019ميلاد نوروزي رهبرNo ratings yet
- Group IT Handbook - EN - 2019.02.25Document58 pagesGroup IT Handbook - EN - 2019.02.25Jose Luis100% (1)
- IT Operating ModelDocument2 pagesIT Operating ModelRene Corvo67% (3)
- BRM and Agile A Perfect Union PDFDocument7 pagesBRM and Agile A Perfect Union PDFsandeepm75No ratings yet
- Business Capability AnalysisDocument22 pagesBusiness Capability AnalysisStella-Jebas50% (2)
- Roland Berger Operating ModelDocument16 pagesRoland Berger Operating ModelBogdanIonescuNo ratings yet
- Target Operating Model PDFDocument1 pageTarget Operating Model PDFSabrina Sanchez100% (6)
- CEB IT-Building and Putting Your Business Capability Model To WorkDocument27 pagesCEB IT-Building and Putting Your Business Capability Model To WorkOleksandrNo ratings yet
- Gartner-Best Practices For Managing Enterprise InformationDocument10 pagesGartner-Best Practices For Managing Enterprise InformationJhonOmarVivasAvelinoNo ratings yet
- BIZBOK5 Part 1Document15 pagesBIZBOK5 Part 1John TorresNo ratings yet
- CEB Architecture High Impact CapabilityDocument12 pagesCEB Architecture High Impact CapabilityCody LeeNo ratings yet
- Enhance Your Roadmap For Data Analytics GovernanceDocument11 pagesEnhance Your Roadmap For Data Analytics GovernanceJorge WillemsenNo ratings yet
- Data Management Target Operating ModelDocument4 pagesData Management Target Operating ModelSamuel Dogbatse88% (8)
- Target Operating ModelDocument3 pagesTarget Operating ModelCege Wa Njoroge100% (1)
- GroupIT OpModel Redist v1Document20 pagesGroupIT OpModel Redist v1Juan MestasNo ratings yet
- Designing Operating Models DOM-Info-sheetDocument6 pagesDesigning Operating Models DOM-Info-sheetespinosafausto4764No ratings yet
- Bridging The Gap Between A Companys Strategy and Operating Model VFDocument5 pagesBridging The Gap Between A Companys Strategy and Operating Model VFRaviteja GogineniNo ratings yet
- PwC-Enterprise Architecture and Implementation DeckDocument1 pagePwC-Enterprise Architecture and Implementation DecksowmikchakravertyNo ratings yet
- Operating ModelDocument16 pagesOperating ModelOleksandr100% (5)
- Module 2 - Business Architecture PDFDocument26 pagesModule 2 - Business Architecture PDFfrom_ac5969100% (1)
- Exploring The Critical Success Factors of Different Types of FinTDocument10 pagesExploring The Critical Success Factors of Different Types of FinTSina FardiNo ratings yet
- Gartner sd08Document30 pagesGartner sd08Sina FardiNo ratings yet
- 46-Article Text-136-1-10-20201228Document18 pages46-Article Text-136-1-10-20201228Sina FardiNo ratings yet
- LeanIX Poster Best Practices To Define Business Capability Maps enDocument1 pageLeanIX Poster Best Practices To Define Business Capability Maps enSina FardiNo ratings yet
- LeanIX Poster Best Practices To Define Business Capability MapsDocument1 pageLeanIX Poster Best Practices To Define Business Capability MapsSina FardiNo ratings yet
- Controller Manufacturing ERP Lean in Seattle Bellingham WA Resume Rod MatthewsDocument4 pagesController Manufacturing ERP Lean in Seattle Bellingham WA Resume Rod MatthewsRodMatthewsNo ratings yet
- Newmont Annual Report 101 202Document102 pagesNewmont Annual Report 101 202David RvNo ratings yet
- Jegan Curriculum VitaeDocument4 pagesJegan Curriculum VitaeSree BalanNo ratings yet
- Slide 6 (MGT) - Project Cost ManagementDocument64 pagesSlide 6 (MGT) - Project Cost ManagementpramilaNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 3Document10 pagesIntermediate Accounting 3Hannaniah PabicoNo ratings yet
- Annual ReportDocument2 pagesAnnual ReportKishor Biswas100% (1)
- Audit McqsDocument9 pagesAudit Mcqssamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- AUE Study Guide 001 - 2020 - 4 - BDocument170 pagesAUE Study Guide 001 - 2020 - 4 - BLindelwe NeneNo ratings yet
- IC 46-General Insu. Accounts Preparation and Regulation of InvestmentDocument6 pagesIC 46-General Insu. Accounts Preparation and Regulation of InvestmentSurajit MisraNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument14 pagesResearchrichel sanchezNo ratings yet
- Pts SP Course, Hcopl 23 May 1989rb Issue I, Rev 5 May 2001Document30 pagesPts SP Course, Hcopl 23 May 1989rb Issue I, Rev 5 May 2001FlibberdygibberNo ratings yet
- Request For Action (Rfa) : Section 1: Details of Nonconformity / OFI (To Be Accomplished by Auditor / Initiator)Document3 pagesRequest For Action (Rfa) : Section 1: Details of Nonconformity / OFI (To Be Accomplished by Auditor / Initiator)Jeaneth Dela Pena CarnicerNo ratings yet
- RMC No 47-2019Document5 pagesRMC No 47-2019Renren QuiranteNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Vocabulary: AKT 9 OctDocument3 pagesUnit 1: Vocabulary: AKT 9 OctPecinta bobaNo ratings yet
- SOP Renuka WarehouseDocument4 pagesSOP Renuka WarehouseSagnik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Annisa CV - Updated 2020Document6 pagesAnnisa CV - Updated 2020Viriya ParamitaNo ratings yet
- 6-International Procurement ProceduresDocument1 page6-International Procurement ProceduresmohammedNo ratings yet
- RMP Everymonth Closing Activities: S.No. English Desciption Wave V SAPDocument11 pagesRMP Everymonth Closing Activities: S.No. English Desciption Wave V SAPSyed Zain Ul AbdinNo ratings yet
- COA - 98-002 - Prohibition Against Employment by Local Government Units of Private Lawyers ToDocument3 pagesCOA - 98-002 - Prohibition Against Employment by Local Government Units of Private Lawyers ToYan Rodriguez DasalNo ratings yet
- AAA CourseworkDocument4 pagesAAA Courseworkalvinmono.718No ratings yet
- Questionnaire For Peer Review 2022Document25 pagesQuestionnaire For Peer Review 2022Sanya Agrawal0% (1)
- Auditing Problems 2Document8 pagesAuditing Problems 2Luzviminda Maruzzo100% (2)
- Dyaryo Magdalo - Double-Compensation Racket at LandbankDocument2 pagesDyaryo Magdalo - Double-Compensation Racket at LandbankEmilio Suntay IIINo ratings yet
- Auditing Revision GuideDocument4 pagesAuditing Revision GuideBao NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-MCQDocument1 pageChapter 5-MCQHads LunaNo ratings yet
- Executive Order No 79Document9 pagesExecutive Order No 79Ivy KatrinaNo ratings yet
- T 1: M Hse-Ms: Able Inimum Expectations FORDocument21 pagesT 1: M Hse-Ms: Able Inimum Expectations FORbmkallarackalNo ratings yet
- MT JMO Syllabus PDFDocument5 pagesMT JMO Syllabus PDFMadhu SudhanNo ratings yet
- Submitted By:: Chanchal Dubey Varun Kohli Sumit Pandey Somaditya Banarjee Shakun Bansal Shubham Mishra Anil YadavDocument22 pagesSubmitted By:: Chanchal Dubey Varun Kohli Sumit Pandey Somaditya Banarjee Shakun Bansal Shubham Mishra Anil Yadavanil03No ratings yet