Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pigmented Lesions
Pigmented Lesions
Uploaded by
basitcontentOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pigmented Lesions
Pigmented Lesions
Uploaded by
basitcontentCopyright:
Available Formats
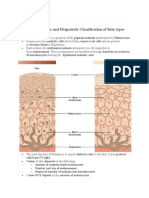
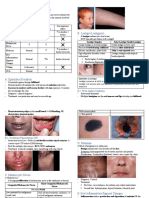
Pigmented lesions
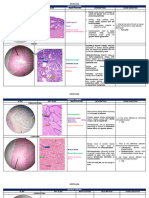
Melanocytic Clinical features Histopathology DD Treatment
lesion
Physiologic —---- Increased melanin —------- —-----
pigmentation production by melanocytes
Smoking 9 cigarettes cause Increased melanin —--------- Smoking cessation
associated melanosis production by melanocytes
melanosis Anterior labial gingiva
Brown color
Oral melanotic
macule
( focal melanosis )
Cafe au lait Small melanin spots with Increase melanin —---------------- No treatment
macule irregular margins production
6 or more cafe au lait Melanophages
Neurofibromatos represent
is neurofibromatosis
NF1 Size >0.5 cm before
Chromosome puberty
17q 11.2 >1.5 cm after puberty
NF2 Axillary spot ( crowe's
Chromosome sign )
22q 12
Mutations
Pigmented Darkly pigmented mass Alveolar pattern ( nest of —--------------------- Surgical excision
neuroectodermal Childrens cells
tumor of infancy ( Maxilla mandible brain Round oval shaped cells
skull ) are present in connective
tissue
Melanocytic nevus Nevus = mole Junctional nevus ; at —----------- Surgical excision
Size <0.5 cm junction of epithelium and
Skin common connective tissue
Intraoral rare Intradermal nevus ; (most
common )cells are located
in connective tissue
Compound nevus ; cells
are located in epithelium
and connective tissue
Blue nevus ; cells are
spindle shaped and in
connective tissue
Melanoacanthoma —--------- proliferation of —------------ —------
keratinocytes and
melanocytes localized to
the epidermis.
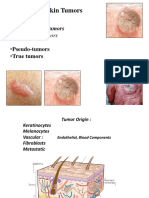
Melanoma Cutaneous melanoma
Types
Nodular melanoma
Superficial spreading
melanoma
Acral lentiginous
melanoma
Lentigo maligna
melanoma
Two types of growth
Horizontal
Vertical
Oral melanoma
Invasive melanoma ;
vertical growth
In Situ melanoma ;
horizontal growth
Atypical melanocytic
proliferation ; increased
melanocytes with
abnormal morphology
You might also like
- Final Coaching - Criminalistics '15Document31 pagesFinal Coaching - Criminalistics '15hamlet Danuco100% (2)
- Describing Skin LesionsDocument3 pagesDescribing Skin LesionsShuhada HamidNo ratings yet
- Bioengineered Skin SubstitutesDocument31 pagesBioengineered Skin Substitutesduverney.gaviriaNo ratings yet
- Parchment TreatmentsDocument144 pagesParchment Treatmentsmarbue100% (1)
- 04.the Cleveland Clinic Intensive Review of Pediatrics 2nd EdDocument513 pages04.the Cleveland Clinic Intensive Review of Pediatrics 2nd EdSav GaNo ratings yet
- TUMOR MATA FX TranslateDocument34 pagesTUMOR MATA FX TranslateAisyahNo ratings yet
- 23 SkinDocument11 pages23 SkinBalaji DNo ratings yet
- Pnle 2023 Notes - OncologyDocument9 pagesPnle 2023 Notes - OncologyJoya Jimenea GenzolaNo ratings yet
- Genital Nevus PresentationDocument18 pagesGenital Nevus PresentationdaveNo ratings yet
- OM Lecture 1Document12 pagesOM Lecture 1abood kofahiNo ratings yet
- Nev PigDocument11 pagesNev PigYeni PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Y1.6 Neoplasia - Malignant Tumors 2022 PDFDocument41 pagesY1.6 Neoplasia - Malignant Tumors 2022 PDFlina hossamNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology Dent1411Document7 pagesOral Pathology Dent1411api-663458841No ratings yet
- Melanocytic TumorsDocument11 pagesMelanocytic TumorsalfonsoNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument16 pagesSkinChristinePagsisihanNo ratings yet
- 6 - Disorders of MelanocytesDocument5 pages6 - Disorders of MelanocytesAbdul FatahNo ratings yet
- Biology of Melanocytes: Done By: Mohammed Abduljabbar Done By: Mohammed Abduljabbar KauhDocument66 pagesBiology of Melanocytes: Done By: Mohammed Abduljabbar Done By: Mohammed Abduljabbar Kauhmoon1312No ratings yet
- Electron MicrosDocument3 pagesElectron MicrosIm MiNo ratings yet
- Fits Patrick Chap 20Document8 pagesFits Patrick Chap 20FIT ChannelNo ratings yet
- Malignant Skin TumorsDocument18 pagesMalignant Skin TumorsGhaiidaa khhNo ratings yet
- Epithelium IIDocument44 pagesEpithelium IIRanjit DanielNo ratings yet
- I. Reactive Lesions: Stacey MendozaDocument11 pagesI. Reactive Lesions: Stacey MendozaRianNo ratings yet
- 10-4 Melanocytic LesionsDocument40 pages10-4 Melanocytic LesionsSorin DeacuNo ratings yet
- Clinical Stomatology Conference Pigmented Lesions: DNSC D9910.00Document9 pagesClinical Stomatology Conference Pigmented Lesions: DNSC D9910.00Mira AnggrianiNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman TumorDocument31 pagesRangkuman TumorraishapiNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document31 pagesPresentation 1Nice YouNo ratings yet
- وسام عوض Benign Skin Tumor-5 (Muhadharaty)Document6 pagesوسام عوض Benign Skin Tumor-5 (Muhadharaty)Alaa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Histopathological Spectrum of Benign MelanocyticDocument5 pagesHistopathological Spectrum of Benign Melanocyticmuhammad rizqi romadlonNo ratings yet
- Skin CancerDocument7 pagesSkin Cancerعبدالعزيز احمد علي عتشNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue Lesions: CINCO, Gerardo, Guerra, Harder, OrtegaDocument131 pagesConnective Tissue Lesions: CINCO, Gerardo, Guerra, Harder, Ortegator torNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Disorders: Chapter OutlineDocument43 pagesEpithelial Disorders: Chapter Outlineitza andradeNo ratings yet
- Dermatology For Plastic Surgeon I - Skin Care and Benign Dermatologic ConditionsDocument10 pagesDermatology For Plastic Surgeon I - Skin Care and Benign Dermatologic ConditionsNabil MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Melanoma: Meku Damtie (M.D.) July 18, 2006Document38 pagesMelanoma: Meku Damtie (M.D.) July 18, 2006Worku KifleNo ratings yet
- Dermatology RR CerebellumDocument80 pagesDermatology RR Cerebellumभईया भोसडिकाNo ratings yet
- Skin PathologyDocument1 pageSkin PathologySean KeenanNo ratings yet
- Eye Pathology: Dr. Jusuf FantoniDocument8 pagesEye Pathology: Dr. Jusuf Fantonitutor tujuhNo ratings yet
- An Update On Cutaneous Tumours With Neural DifferentiationDocument24 pagesAn Update On Cutaneous Tumours With Neural DifferentiationAdriana Gabriela Ugarte MacíasNo ratings yet
- Melanoma & IHCDocument23 pagesMelanoma & IHCkarimahihdaNo ratings yet
- Salivary Gland TumorsDocument25 pagesSalivary Gland TumorsdrpnnreddyNo ratings yet
- Open Access Textbook of General Surgery: Melanoma Jej KrigeDocument6 pagesOpen Access Textbook of General Surgery: Melanoma Jej KrigeZakkiyah PatelNo ratings yet
- Signaling Pathways in Melanogenesis: Molecular SciencesDocument18 pagesSignaling Pathways in Melanogenesis: Molecular SciencesEllen FernandaNo ratings yet
- Skin Cancer ShowDocument57 pagesSkin Cancer ShowNice YouNo ratings yet
- Dermatoscopy The Basics With ExercisesDocument130 pagesDermatoscopy The Basics With Exerciseslaszlo_mihalyimre2100% (3)
- Pearls: 1889. Colour of Skin and Fitzpatrick Classification of Skin TypesDocument118 pagesPearls: 1889. Colour of Skin and Fitzpatrick Classification of Skin TypesswastikNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Pigmentation and Melanocytes 1Document18 pagesDisorders of Pigmentation and Melanocytes 1Jas GandingcoNo ratings yet
- Skin Tumors: .Benign Tumors .Precancerous TumorsDocument38 pagesSkin Tumors: .Benign Tumors .Precancerous TumorsanandafirstyNo ratings yet
- 9p Salivary Gland - 2Document58 pages9p Salivary Gland - 2sara.madkour99No ratings yet
- Lab - Benign and MalignantDocument9 pagesLab - Benign and Malignantkimkaigel6No ratings yet
- Pigmentary DisordersDocument6 pagesPigmentary DisordersMinh ChâuNo ratings yet
- Moles: Nevus (Or Naevus, Plural Nevi or Naevi, From NævusDocument4 pagesMoles: Nevus (Or Naevus, Plural Nevi or Naevi, From NævusAphrie SusantieNo ratings yet
- Skin and Endo 2022Document10 pagesSkin and Endo 2022Sure NavyasriNo ratings yet
- dlt1109 1334 1336 PDFDocument3 pagesdlt1109 1334 1336 PDFmona abdoNo ratings yet
- BENIGN & MALIGNANT LESIONS OF THE SKIN by AlbraaDocument7 pagesBENIGN & MALIGNANT LESIONS OF THE SKIN by AlbraaZoi PapadatouNo ratings yet
- Online Learning ModuleDocument49 pagesOnline Learning ModuleLaura ElenaNo ratings yet
- I.T.S Dental College, Greater NoidaDocument38 pagesI.T.S Dental College, Greater NoidaAMIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- Simplified Melanocytic Lesions of The SkinDocument1 pageSimplified Melanocytic Lesions of The SkinDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Histophysiology+of+the+Skin+for+Vula+ Dr+MowlaDocument28 pagesHistophysiology+of+the+Skin+for+Vula+ Dr+MowlaYaaseen GallantNo ratings yet
- Tumors of The Orbit by Dr. Jonathan Del Prado 082708Document3 pagesTumors of The Orbit by Dr. Jonathan Del Prado 082708CitrusNo ratings yet
- Common Diseases in Eye Lid & Its AnatomyDocument41 pagesCommon Diseases in Eye Lid & Its AnatomyTahmidur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Last Aid Dermatology SARPDocument7 pagesLast Aid Dermatology SARPskNo ratings yet
- Congenital Melanocytic Nevi: ReviewDocument7 pagesCongenital Melanocytic Nevi: ReviewSuzana SoozyNo ratings yet
- NeurologyDocument33 pagesNeurologyjhqmpzg7sjNo ratings yet
- Practical 19 HistoDocument12 pagesPractical 19 HistoarjunNo ratings yet
- Salivary Gland Cancer: From Diagnosis to Tailored TreatmentFrom EverandSalivary Gland Cancer: From Diagnosis to Tailored TreatmentLisa LicitraNo ratings yet
- AcuPulse Versatility SupplementDocument16 pagesAcuPulse Versatility SupplementSD DSNo ratings yet
- Science Unit Papers - Grade 8 Sri Lanka Local SylubusDocument5 pagesScience Unit Papers - Grade 8 Sri Lanka Local SylubusMallindu Perera83% (6)
- Introduction To Fitness TrainingDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Fitness TrainingShailendra Singh ChouhanNo ratings yet
- NCM 114 Unit 1 To 4 GeriaDocument85 pagesNCM 114 Unit 1 To 4 GeriaJohn Van Dave Taturo100% (1)
- Integumentary & Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary & Skeletal SystemMaisonette MichNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Patient With A Skin DisorderDocument2 pagesApproach To The Patient With A Skin DisorderElrey InocianNo ratings yet
- Comparative Evaluation of Efficacy and Tolerability ofDocument8 pagesComparative Evaluation of Efficacy and Tolerability ofMelanny CindyNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Body Coverings MinDocument1 pageDifferent Types of Body Coverings MinAbdullah AbdiNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletonintegument 63 PDFDocument71 pagesMusculoskeletonintegument 63 PDFOok ChayapornNo ratings yet
- Pompholyx EczemaDocument4 pagesPompholyx EczemaMariaNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Cosmetology - Clinical & AyurvedicDocument2 pagesDiploma in Cosmetology - Clinical & AyurvedicJdNo ratings yet
- Assessing The IntegumentaryDocument73 pagesAssessing The IntegumentaryHelena Meurial HilkiahNo ratings yet
- Module Cut Leather by Hands Footwear Leathergoods Level 1Document58 pagesModule Cut Leather by Hands Footwear Leathergoods Level 1Abu Bakr AtikuNo ratings yet
- 7 in 1 H2 O2 Hydra FacialDocument22 pages7 in 1 H2 O2 Hydra FacialAarifNo ratings yet
- Atopic Eczema: Dr. Wistiani, Spa, Msi. MedDocument16 pagesAtopic Eczema: Dr. Wistiani, Spa, Msi. MedhwelpNo ratings yet
- DLL Animal Body Coverings DemoDocument8 pagesDLL Animal Body Coverings DemoLyka ZorillaNo ratings yet
- Mcqs of Icthyosis With KeyDocument7 pagesMcqs of Icthyosis With KeysaleemNo ratings yet
- Surgery 8th Se Skin Subcu Compiled TransbooksnotestpreviewersDocument237 pagesSurgery 8th Se Skin Subcu Compiled TransbooksnotestpreviewersMildred DagaleaNo ratings yet
- Sylfirm BrochureDocument8 pagesSylfirm BrochureyousefdrahmedNo ratings yet
- Thomas H. Huxley Lessons in Elementary PhysiologyDocument481 pagesThomas H. Huxley Lessons in Elementary PhysiologyAMNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Human Skin Equivalents Developed at Body's Core and Surface TemperaturesDocument12 pagesCharacterization of Human Skin Equivalents Developed at Body's Core and Surface TemperaturesFitria Ayu LestariNo ratings yet
- Sportsdermatology: Skin Disease in AthletesDocument22 pagesSportsdermatology: Skin Disease in Athletesleticia floresNo ratings yet
- PiodermaDocument43 pagesPiodermaAnisaNo ratings yet
- Burns PresentationDocument34 pagesBurns PresentationMiriam ArchibongNo ratings yet
- CRC Princess 2 Mei 2022Document52 pagesCRC Princess 2 Mei 2022Maulfaya NoorNo ratings yet