Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Skeletal Functions
Uploaded by
Chriza Mae Dela Pe�a0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageThis document lists and describes the functions of various bones and structures in the human body. It discusses bones in the skull such as the maxilla, zygomatic, temporal, frontal, parietal, and occipital bones. It also describes bones in the vertebral column like the sacrum and coccyx as well as the ribs, shoulder blade, arm bones, wrist bones, leg bones, and pelvic bones. For each structure, it provides a brief explanation of its functional role, such as supporting muscles, protecting organs, or allowing movement.
Original Description:
Human Anatomy
Original Title
SKELETAL-FUNCTIONS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document lists and describes the functions of various bones and structures in the human body. It discusses bones in the skull such as the maxilla, zygomatic, temporal, frontal, parietal, and occipital bones. It also describes bones in the vertebral column like the sacrum and coccyx as well as the ribs, shoulder blade, arm bones, wrist bones, leg bones, and pelvic bones. For each structure, it provides a brief explanation of its functional role, such as supporting muscles, protecting organs, or allowing movement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageSkeletal Functions
Uploaded by
Chriza Mae Dela Pe�aThis document lists and describes the functions of various bones and structures in the human body. It discusses bones in the skull such as the maxilla, zygomatic, temporal, frontal, parietal, and occipital bones. It also describes bones in the vertebral column like the sacrum and coccyx as well as the ribs, shoulder blade, arm bones, wrist bones, leg bones, and pelvic bones. For each structure, it provides a brief explanation of its functional role, such as supporting muscles, protecting organs, or allowing movement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
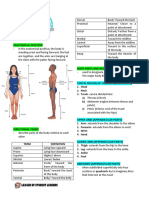
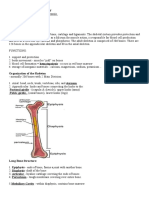
FUNCTIONS: attachment points for muscles that move
the spine and ribs.
Maxilla, also known as the upper jawbone, spinal cord transmits signals between the
is a bone that forms the upper jaw, brain and the rest of the body.
supports the upper teeth, and plays a role vertebral column protects the spinal cord,
in chewing, speaking, and smiling. supports the body, and allows for
Incisive fossa is a depression in the upper movement.
jawbone that supports the upper incisors, sacrum forms the base of the pelvis and
provides a passageway for the provides attachment points for muscles
nasopalatine ducts, and drains saliva from and ligaments.
the oral cavity. Ala is to support the shape of the nose and
Zygomtic bone, also known as the filter the air that we breathe.
cheekbone, forms the prominence of the coccyx is to provide support for the pelvic
cheek, supports the lower eyelid, and plays floor and anus.
a role in facial expressions. sacral hiatus is to allow for the passage of
Temporal bone houses the organs of nerves, blood vessels, and the filum
hearing and balance, and helps to protect terminale.
the brain. sternal is to protect the heart and lungs
Frontal bone forms the forehead, protects from injury and to provide a connection
the brain, and provides attachment points point for other bones and muscles.
for facial muscles. clavicle is to connect the sternum to the
Parietal bone forms the roof and sides of scapula and provide support for the
the skull, protects the brain, and plays a shoulder joint.
role in spatial awareness. scapula, or shoulder blade, is to provide a
occipital bone forms the back of the skull, stable base for the shoulder joint and to
protects the brain, and plays a role in allow for a wide range of motion.
vision. acromion is to provide a stable attachment
mastoid process houses the mastoid air point for the deltoid muscle and to help
cells, which are air-filled spaces that help protect the shoulder joint.
to amplify sound and reduce the weight of humerus is to connect the shoulder and
the skull. elbow joints and to allow for a wide range
nasal bone forms the bridge of the nose of arm movement.
and protects the nasal cavity. radius in anatomy is to allow for pronation
mandible, also known as the lower and supination of the forearm and wrist.
jawbone, forms the lower jaw, supports the ulna is to provide stability for the forearm
lower teeth, and plays a role in chewing, and wrist, and to allow for pronation and
speaking, and smiling. supination.
coronal suture connects the frontal bone carpals is to form the wrist joint and allow
to the parietal bones of the skull. for a wide range of wrist movement.
jugular foramen allows the passage of the metacarpals is to connect the carpals to
internal jugular vein, the glossopharyngeal the phalanges and form the knuckles.
nerve, the vagus nerve, and the accessory tarsals is to form the ankle and midfoot
nerve. joints and allow for a wide range of ankle
foramen magnum allows the passage of movement.
the spinal cord, the vertebral arteries, and metatarsals is to connect the tarsals to the
the accessory nerve. phalanges and form the knuckles.
sphenoid bone forms the base of the tibia is to support the body's weight and
skull, supports the pituitary gland, and allow for movement at the knee joint.
provides passageways for nerves and fibula is to provide stability for the ankle
blood vessels. joint and allow for movement at the knee
foramen ovale is an opening between the joint.
right and left atria of the heart that allows femur is to support the body's weight and
blood to bypass the lungs in the developing allow for movement at the knee joint.
fetus. pelvic bones is to support the upper body,
ethmoid bone forms the roof of the nasal protect the internal organs, and provide
cavity, supports the olfactory bulbs, and attachment points for muscles and
provides passageways for nerves and ligaments.
blood vessels. ilium is to support the weight of the upper
occipital condyle is a bony knob on the body, protect the internal organs, and
occipital bone that articulates with the atlas provide a stable base for the spine and
vertebra to allow for head movement. legs.
vertebral foramen is an opening in each pubis is to protect the internal organs and
vertebra that allows the passage of the provide a stable base for the spine and
spinal cord and the meninges. legs.
spinous process is a bony projection on ischium is to support the body's weight,
the back of each vertebra that provides a protect the internal organs, and provide
lever arm for muscles that move the spine. attachment points for muscles and
transverse process is a bony projection ligaments.
on the side of each vertebra that provides
You might also like
- Ranger Drifter Repair Manual F161!10!99aDocument676 pagesRanger Drifter Repair Manual F161!10!99aKatu201083% (6)
- Skeletal System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument29 pagesSkeletal System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD100% (1)
- Bates Chapter 1 Flashcards - QuizletDocument6 pagesBates Chapter 1 Flashcards - Quizletaznknight323No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System Lecture NotesDocument169 pagesMusculoskeletal System Lecture Noteszygote0711578796% (28)
- Chiropractic ICD-10 Code ListDocument5 pagesChiropractic ICD-10 Code ListDale100% (1)
- Directional Terms, PlanesDocument6 pagesDirectional Terms, PlanesRuby Jane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesSkeletal SystemJovi Floresca AberinNo ratings yet
- THE FIFTH KINGDOM Romantic SuspenseDocument10 pagesTHE FIFTH KINGDOM Romantic SuspenseCaridad PineiroNo ratings yet
- 6 Week Training Junior Program TennisDocument11 pages6 Week Training Junior Program TennisCiprianTeleaga0% (1)
- Office ErgonomicsDocument28 pagesOffice ErgonomicsAnonymous iI88Lt100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Facial BonesDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Facial BonesAubrey Unique Evangelista100% (2)
- ABA ABLS-Manual 08112023Document95 pagesABA ABLS-Manual 08112023chepebetosm100% (1)
- Veterinary OsteologyDocument279 pagesVeterinary OsteologyTatenda Mageja100% (2)
- Skeletal System of FrogsDocument3 pagesSkeletal System of Frogsallelie marieNo ratings yet
- Functions BonesDocument1 pageFunctions BonesLathea Daiser TheaNise TesalunaNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, Emmanuel Andrew M. BSN 3A NCM 116: Orthopedic Nursing Cranial BoneDocument3 pagesDela Cruz, Emmanuel Andrew M. BSN 3A NCM 116: Orthopedic Nursing Cranial BoneEmmanuel Andrew Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Midterms MedgloDocument13 pagesMidterms MedgloCorpuz, Jaylord L.No ratings yet
- Nursing AnaPhy-Skeletal System Axial SkeletonDocument29 pagesNursing AnaPhy-Skeletal System Axial SkeletonGail Chantel Spring PerlasNo ratings yet
- Skeleton & LocomotionDocument10 pagesSkeleton & Locomotionali mtNo ratings yet
- Skripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogDocument15 pagesSkripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogElizabetaNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System IyahDocument55 pagesThe Skeletal System IyahAnna R. DionisioNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Skeletal System TopicDocument21 pagesFunctions of The Skeletal System TopicTUNGCALING ACNo ratings yet
- Maglaqui - Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesMaglaqui - Skeletal SystemNICOLE MAGLAQUINo ratings yet
- Vii. Laboratory/Diagnostic FindingsDocument29 pagesVii. Laboratory/Diagnostic Findingsgryph0nNo ratings yet
- Bones & JointsDocument18 pagesBones & Jointsroychanchal562No ratings yet
- L1 Skeletal SystemDocument40 pagesL1 Skeletal SystemMalibay ES (R III - Bulacan)No ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Body Systems and Related Medical Terminology - Part 2 PDFDocument166 pagesIntroduction To Human Body Systems and Related Medical Terminology - Part 2 PDFAnne StudiesNo ratings yet
- Why The Skeleton System Is Important?: Pd4 December 8, 2015 Mr. WilliamsDocument2 pagesWhy The Skeleton System Is Important?: Pd4 December 8, 2015 Mr. Williamsapi-302705867No ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument8 pagesSkeletal SystemJules ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReportingDocument17 pagesAnaphy ReportingKIA KHYTE FLORESNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 Chapter 2:locomotion and Support: To: Mrs AnnamalDocument25 pagesBiology Form 5 Chapter 2:locomotion and Support: To: Mrs AnnamalAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- The Parts Skeletal SystemDocument16 pagesThe Parts Skeletal SystemKathleenJoyGalAlmasinNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual DownloadDocument9 pagesHuman Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual DownloadArturo Thomas100% (29)
- Osteocytes - Bone Cells Classifications of Bones According To SizeDocument17 pagesOsteocytes - Bone Cells Classifications of Bones According To SizeA CNo ratings yet
- HumanskelotonDocument11 pagesHumanskelotoneboigbeeghosa7No ratings yet
- CH - Pptxaxial Skeleton 2 2Document33 pagesCH - Pptxaxial Skeleton 2 2a_waldenNo ratings yet
- Bones and Muscle 1Document4 pagesBones and Muscle 1Luciely Castro YatesNo ratings yet
- The SkeletonDocument29 pagesThe SkeletonCatherine Joy delos SantosNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesThe Skeletal SystemBea GualbertoNo ratings yet
- 206 BonesDocument4 pages206 BonesCedrick John Gabbac DalagNo ratings yet
- Hip JointDocument1 pageHip JointSeco AhmadNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Berasrama Penuh Integrasi Gopeng Prepared By:Muhd Fazli Bin DollahDocument60 pagesSekolah Berasrama Penuh Integrasi Gopeng Prepared By:Muhd Fazli Bin DollahrameshkasinathanNo ratings yet
- Axial SkeletonDocument65 pagesAxial Skeletonfatimamuzammil406No ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document39 pagesLecture 3Anne XxNo ratings yet
- Spine AnatomyDocument8 pagesSpine Anatomyvishramki2009No ratings yet
- Anatomy Chapter3Document29 pagesAnatomy Chapter3jules BlasabasNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesSkeletal SystemEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 - MSKDocument3 pagesChapter 24 - MSKannoja selvaNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System Human Body (206) Axial Skeleton (80) Skull (28) A. Paired Bones (11x2 22)Document17 pagesThe Skeletal System Human Body (206) Axial Skeleton (80) Skull (28) A. Paired Bones (11x2 22)Leo Cordel Jr.No ratings yet
- Axial Skeleton ScriptDocument4 pagesAxial Skeleton ScriptMichaelVincentLimNo ratings yet
- 8 SkeletonDocument3 pages8 SkeletonMichelleAquinoSuzukiNo ratings yet
- A. Definition of SkeletonDocument6 pagesA. Definition of SkeletonNEIRA LENE SALONGANo ratings yet
- Laboratory 3 SkeletalDocument9 pagesLaboratory 3 SkeletalKyla InoferioNo ratings yet
- Chapter III SkeletalDocument26 pagesChapter III SkeletalTitoMacoyTVNo ratings yet
- SkeletonprojectDocument4 pagesSkeletonprojectapi-299654825No ratings yet
- The Functions of The Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesThe Functions of The Muscular SystemJOSHUA ABELLANOSANo ratings yet
- I. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Document6 pagesI. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Aria IsipNo ratings yet
- I. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Document6 pagesI. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Aria IsipNo ratings yet
- Osteology: Dr. Gloria S. ValenciaDocument67 pagesOsteology: Dr. Gloria S. ValenciaChen Romaquin Jimenez ThesisNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The SpineDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The SpineKinahZildredBibitNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy,: Chapter 7 Lecture Outline: Axial SkeletonDocument55 pagesHuman Anatomy,: Chapter 7 Lecture Outline: Axial Skeletonmuhammad lutfiNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy,: Chapter 7 Lecture Outline: Axial SkeletonDocument55 pagesHuman Anatomy,: Chapter 7 Lecture Outline: Axial Skeletonmuhammad lutfiNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesThe Skeletal Systemstar fireNo ratings yet
- CC CCC C C C CCCCCCC CCCCCCC CCCCCC CCCCCCCC CCC CDocument12 pagesCC CCC C C C CCCCCCC CCCCCCC CCCCCC CCCCCCCC CCC CBrian GenesisNo ratings yet
- Interaction of Skeletal and Muscular SystemDocument43 pagesInteraction of Skeletal and Muscular SystemJezebel MolinoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document26 pagesUnit 4sivexgamingNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesThe Skeletal SystemDaisuke InoueNo ratings yet
- Hot Spots (Wet Eczema, Pyotraumatic Dermatitis)Document2 pagesHot Spots (Wet Eczema, Pyotraumatic Dermatitis)Donnie DityaNo ratings yet
- Sci Asia Scale PPT (Final)Document29 pagesSci Asia Scale PPT (Final)palNo ratings yet
- Yoga PosesDocument29 pagesYoga PosesthippliNo ratings yet
- Tle 10Document49 pagesTle 10peepee poopooNo ratings yet
- Naruto Sage Mode - Strengh TheoryDocument3 pagesNaruto Sage Mode - Strengh TheoryEmersonNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Eccrine Sweat Glands and SweatingDocument8 pagesDisorders of The Eccrine Sweat Glands and SweatingAnnisa Chaerani BurhanuddinNo ratings yet
- CSS Efusi PleuraDocument21 pagesCSS Efusi PleuraRahadian Nugi SutrisnoNo ratings yet
- Dewalt Power Washer 4000 PsiDocument52 pagesDewalt Power Washer 4000 PsiTiftenNo ratings yet
- Latihan Teori DominoDocument1 pageLatihan Teori DominoJulian JuliNo ratings yet
- Combination Skeletal LatestDocument21 pagesCombination Skeletal LatestSyarifah Nur NadhilahNo ratings yet
- Legmed DoctrinesDocument7 pagesLegmed DoctrinesPrincess Sarah PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Pattern of Injuries in Fall From Height PDFDocument4 pagesPattern of Injuries in Fall From Height PDFRetno SawitriNo ratings yet
- One Lung VentilationDocument24 pagesOne Lung Ventilationapi-254759511No ratings yet
- Fumedica Bringing Hope To The Under Privileged Citizens of CartagenaDocument23 pagesFumedica Bringing Hope To The Under Privileged Citizens of CartagenaAditya MuchayatsyahNo ratings yet
- Skeleton Printable GameDocument5 pagesSkeleton Printable GameRizki AmaliyahNo ratings yet
- Purvatana 3Document9 pagesPurvatana 3garratemucoNo ratings yet
- Neuro Sensory AssessmentDocument46 pagesNeuro Sensory AssessmentPrecious SantayanaNo ratings yet
- A1 Rhinoplasty Cosmetic Nose SurgeryDocument3 pagesA1 Rhinoplasty Cosmetic Nose SurgerymadmaxpsuNo ratings yet
- PF PulmoDocument5 pagesPF PulmoNaja Hasnanda100% (1)
- Muscle System BrochureDocument2 pagesMuscle System Brochureapi-482100632No ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesThe Skeletal SystemTRISHA NICOLE LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Gullivers Travels in LilliputDocument5 pagesGullivers Travels in LilliputPASTOBRAS MEXICO SA DE CVNo ratings yet