Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Skeletal System of Frogs
Uploaded by
allelie marieOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Skeletal System of Frogs
Uploaded by
allelie marieCopyright:
Available Formats
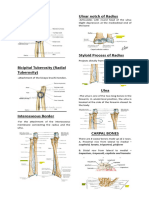
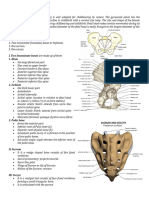
Metatarsal Tibiofibula
Metatarsals are convex in shape (arch upward), are Located between the femur and the tarsal, the tibia
long bones, and give the foot its arch. They work and the fibula fuse to form one long bone.
with connective tissues, ligaments and tendons, to
provide movement in the foot Femur
The femur supports its upper leg, and the bones of
the lower leg
Tarsal
The tarsal forms part of the plantar arch,
particularly the heel, and supports the whole body.
Ischium
Forms the posterolateral portion of the hip bone. It
Sternum supports the body.
It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the Urostyle
front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the
heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury Long bone of the posterior portion of the central
bony axis; it is formed by several fused vertebrae.
Phalanges
Ilium
The phalanges of the fingers help to manipulate
things in the environment while the phalanges of Large flat bone articulating backward with the
the foot helps to balance, walk, and run sacral vertebra; the juncture of the ilium and the
ischium is where the hind limb is attached.
Clavicle
Sacral vertebra
It supports the shoulder, encourages a full range of
motion. The sacral vertebrae is to articulate securely with
the pelvic girdle, and they are usually fused to
form a single bone (the sacrum) to provide a firm
Metacarpal support.
The basic function of the metacarpals is to act as Vertebrae
the bridge between the wrist and fingers, forming
the framework of the hand. Together as the carpus, Short bony parts of the dorsal area of the body
it is the vital part of the skeleton that holds forming the central bony axis.
together the small and large bones in the human
hand, stabilizing its dorsal and palmar sides Scapula
Radio-ulna Large flat back bone and it stabilizes the arm and
a single bone in the forelimb of an amphibian neck
(such as a frog) that represents fusion of the
separate radius Coracoid
Ventral bone articulating with the sternum; the
Humerus juncture of the scapula, clavicle and coracoid is the
The humerus is the long bone in the upper arm. It point where the hind limb is attached.
is located between the elbow joint and the
shoulder. At the elbow, it connects primarily to the Atlas
ulna, as the forearm's radial bone connects to the
wrist First cervical vertebra supporting the head and
supported by the axis.
Frontoparietal Talus: bone jointed with the leg bones.
Phalanges: each of the bones forming the toes.
Large flat bone of the upper anterior portion of the
cranial box. Metatarsus: each of the bones forming the part of
the foot between the toes and the heel.
Sacrum
Tarsus: each of the bones forming the heel.
acts as an additional limb to give more power to its
leaps. Femur: thigh bone.
Mandible Tibiofibula: leg bone.
Smooth curved movable bone comprising the Sacral vertebra: vertebra of the sacrum.
lower jaw.
Vertebra: each of the bones forming the spinal
The premaxilla is one of a pair of small cranial column.
bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many
animals, usually bearing teeth. Humerus: arm bone.
The function of each nasal bone is to bind together Radio-ulna: forearm bone.
the cartilage that forms individual nose contours
and shapes Scapular: shoulder bone.
The maxilla in animals is the upper fixed bone of Pterygoid: one of the bones of the palate, forming
the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary the root of the mouth.
bones
Skull: bony case of the brain
Maxillary: bony part of the jaw.
skull is the bony structure that forms the head in
Orbital cavity: skull cavity that contains the eye. the. It supports the structures of the face and forms
a cavity for the brain. Like the skulls of other
Quadratojugal: cheek bone. vertebrates, it protects the brain from injury.
Prootic: bones forming the auditory region. The major function of the vertebral column is
protection of the spinal cord; it also provides
Phalange: each of the small bones forming the stiffening for the body and attachment for the
fingers. pectoral and pelvic girdles and many muscles
Occipital lateral: occipital lateral bone. Skull Pterygoid Scapular Radio-ulna
Humerus Vertebra Sacral Vertebra Tibio
Carpus: each of the bones forming the wrist. fibula Femur
Tarsus Metatarsus Phalanges Maxillary
Metacarpus: each of the bones forming the part of Orbital Quadratojugal Prootic Phalange
the hand between the fingers and the wrist.
Occiptal lateral
Urostyle: adaptation of one or several vertebrae,
Carpus Metacarpus Urostyle Illium
stretching the hindquarters. Ischium Calcanium Talus Premaxilla
Nasal Exoccipital
Ilium: projecting hip bone. Nuptal tuber Cleithrium Frontoparietal
Squamosal Metacarpals Carpals Ulna
Ischium: one of three bones forming the ilium. Radius Sacrum
Metatarsals Tibia fibula Fibulare Tibiale
Calcaneum: projecting heel bone. Prehallux Coracoid Mandible
You might also like
- Lecture 3Document39 pagesLecture 3Anne XxNo ratings yet
- Axial SkeletonDocument10 pagesAxial SkeletonFrancisco LeaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Skeletal SystemDocument26 pagesAnatomy - Skeletal SystemShereen AlobinayNo ratings yet
- Upper and Lower Extremity Bones Ribs Vertebral Column OkDocument30 pagesUpper and Lower Extremity Bones Ribs Vertebral Column OkXazar NuriyevNo ratings yet
- Frog Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesFrog Skeletal SystemMhikailah Louise MahoneNo ratings yet
- Why The Skeleton System Is Important?: Pd4 December 8, 2015 Mr. WilliamsDocument2 pagesWhy The Skeleton System Is Important?: Pd4 December 8, 2015 Mr. Williamsapi-302705867No ratings yet
- Skeletal FunctionsDocument1 pageSkeletal FunctionsChriza Mae Dela Pe�aNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesSkeletal SystemEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Vii. Laboratory/Diagnostic FindingsDocument29 pagesVii. Laboratory/Diagnostic Findingsgryph0nNo ratings yet
- Midterms MedgloDocument13 pagesMidterms MedgloCorpuz, Jaylord L.No ratings yet
- Understanding the Appendicular SkeletonDocument23 pagesUnderstanding the Appendicular SkeletonFachriza Effendi100% (1)
- Functions BonesDocument1 pageFunctions BonesLathea Daiser TheaNise TesalunaNo ratings yet
- Frog SkeletonDocument1 pageFrog SkeletonPonchoi PintacasiNo ratings yet
- Osteocytes - Bone Cells Classifications of Bones According To SizeDocument17 pagesOsteocytes - Bone Cells Classifications of Bones According To SizeA CNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke 7Document3 pagesPertemuan Ke 7Sukma WulandariNo ratings yet
- The Lower Limb - Boundless Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument15 pagesThe Lower Limb - Boundless Anatomy and PhysiologyHurulaeniNo ratings yet
- What is the Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesWhat is the Skeletal SystemJared RodriguezNo ratings yet
- What Is The Importance of The Skeletal System To Your BodyDocument11 pagesWhat Is The Importance of The Skeletal System To Your BodyKenny James CuberoNo ratings yet
- Axial SkeletonDocument65 pagesAxial Skeletonfatimamuzammil406No ratings yet
- Skripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogDocument15 pagesSkripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogElizabetaNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 Chapter 2:locomotion and Support: To: Mrs AnnamalDocument25 pagesBiology Form 5 Chapter 2:locomotion and Support: To: Mrs AnnamalAnnamal ArulnathanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3.1: Luminang, John Chris Bsmls 1B Anaphy Nov. 18, 2021Document13 pagesAssignment 3.1: Luminang, John Chris Bsmls 1B Anaphy Nov. 18, 2021John Chris LuminangNo ratings yet
- Konsep Dasar MuskuloskeletalDocument42 pagesKonsep Dasar Muskuloskeletalkhayree100% (2)
- 1Document2 pages1Alien 35No ratings yet
- Bones that Make Up the Human Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesBones that Make Up the Human Skeletal Systemhannah peloniaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesSkeletal SystemJovi Floresca AberinNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Group 2Document2 pagesSkeletal System Group 2Joan Hilbero BermudoNo ratings yet
- Upper and Lower EkstremityDocument4 pagesUpper and Lower EkstremitySusantimarilalanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: Study of the Human BodyDocument37 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: Study of the Human BodyIndu GNo ratings yet
- 3 Musculoskeletal System-2020-10132Document11 pages3 Musculoskeletal System-2020-10132Горькое ДноNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesSkeletal SystemmelendezramesesjosephNo ratings yet
- Group 6 - Low BodyDocument8 pagesGroup 6 - Low BodyGusminandarNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageSkeletal SystemAlaysa Marie A. AzotesNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesThe Skeletal SystemBea GualbertoNo ratings yet
- College of Human Sciences & Psychology Department: ClavicleDocument17 pagesCollege of Human Sciences & Psychology Department: ClavicleJohn Patrick LagmayNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Skeletal SystemDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Human Skeletal SystemKristine DomacenaNo ratings yet
- Bio 统一小考-chapter 14Document10 pagesBio 统一小考-chapter 1422 Lee Xin Yong 李芯瑢No ratings yet
- BONEDocument27 pagesBONEVIJAYA KUMAR YNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document26 pagesUnit 4sivexgamingNo ratings yet
- Skeleton & LocomotionDocument10 pagesSkeleton & Locomotionali mtNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer PT 1Document9 pagesAnaphy Reviewer PT 1Keith MimisNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lower Part of The BodyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lower Part of The BodyHikmah khanza PutriNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument8 pagesDefinitionJamesNo ratings yet
- Maglaqui - Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesMaglaqui - Skeletal SystemNICOLE MAGLAQUINo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System ExplainedDocument6 pagesThe Skeletal System Explainedstar fireNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY I 23.03.20 I The Pectoral Girdle and Upper LimbDocument25 pagesANATOMY I 23.03.20 I The Pectoral Girdle and Upper LimbArianna RomanoNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: Bones, Structure and FunctionsDocument29 pagesThe Skeletal System: Bones, Structure and FunctionsReynaBaquillerNo ratings yet
- Human Skeleton F3 NoradinDocument5 pagesHuman Skeleton F3 NoradinIbnu RaxaabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument66 pagesChapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology21- VARNIKA DALALNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Parts and FunctionsDocument16 pagesSkeletal System Parts and FunctionsKathleenJoyGalAlmasinNo ratings yet
- 206 Bones that Support the Human BodyDocument6 pages206 Bones that Support the Human BodyRicky UchihaNo ratings yet
- Bones of The BodyDocument1 pageBones of The Bodystorm kitNo ratings yet
- Foot anatomy and structure overviewDocument9 pagesFoot anatomy and structure overviewToday NewsNo ratings yet
- Skeletal and Facial Bone AnatomyDocument12 pagesSkeletal and Facial Bone AnatomyAubrey Unique Evangelista100% (2)
- Avian Skeletal DifferencesDocument16 pagesAvian Skeletal DifferencesJohn MillerNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System AnatomyDocument6 pagesSkeletal System AnatomymanuelaristotleNo ratings yet
- Bones of The FootDocument23 pagesBones of The FootZaid AbdulqadirNo ratings yet
- Wrist and Hand AnatomyDocument10 pagesWrist and Hand Anatomyarold bodoNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesThe Skeletal SystemJessa Mae BanquirigNo ratings yet
- Familiarization With Body Points of AnimalsDocument5 pagesFamiliarization With Body Points of AnimalsvijayNo ratings yet
- Terra Rosa Emag #20Document61 pagesTerra Rosa Emag #20Terra Rosa100% (1)
- OsteologiDocument37 pagesOsteologiNasrul NasehatiNo ratings yet
- Fetal Skull and Maternal PelvisDocument28 pagesFetal Skull and Maternal PelvisJawed HakeemNo ratings yet
- OSCE On 14/3/2008: Describe Gynaecoid PelvisDocument82 pagesOSCE On 14/3/2008: Describe Gynaecoid PelvisKahing LiNo ratings yet
- CarcinomarectumDocument45 pagesCarcinomarectumHuzefa MemonNo ratings yet
- Maternal Anatomy of the Anterior Abdominal Wall and External GenitaliaDocument9 pagesMaternal Anatomy of the Anterior Abdominal Wall and External GenitaliaRem AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Fracturile de Bazin (R)Document51 pagesFracturile de Bazin (R)Cozma IonutNo ratings yet
- Articulo Publicado 3 Karina PortilloDocument4 pagesArticulo Publicado 3 Karina PortilloKarina PortilloNo ratings yet
- History of Spine Biomechanics from Antiquity to RenaissanceDocument10 pagesHistory of Spine Biomechanics from Antiquity to RenaissancemarceloNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Planes Dimensions and ContractionTITLEDocument12 pagesPelvic Planes Dimensions and ContractionTITLEDavid Eka PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 16th Edition Charles Welsh Cynthia Prentice Craver DownloadDocument33 pagesTest Bank For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 16th Edition Charles Welsh Cynthia Prentice Craver Downloadaliciarodriguezswrtpyjemk100% (23)
- Back Care ChecklistDocument2 pagesBack Care ChecklistSumi100% (1)
- Anatomy of Female PelvisDocument16 pagesAnatomy of Female PelvisChristineAlaNo ratings yet
- Material Mini NetterDocument11 pagesMaterial Mini NetterVALENTINA ALBORNOZ BASTÍASNo ratings yet
- STM ManualDocument95 pagesSTM ManualKyle DavisNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Journal Explores Physicochemical Analysis of Purified and Processed Mercury OreDocument32 pagesAyurvedic Journal Explores Physicochemical Analysis of Purified and Processed Mercury OreHinduism EbooksNo ratings yet
- List of Bones of The Human SkeletonDocument3 pagesList of Bones of The Human SkeletonLoise ChristineNo ratings yet
- Procedure Manual For Obstetrics and Gynecological Nursing: Government College of Nursing Somajiguda, Hyderabad, T.SDocument119 pagesProcedure Manual For Obstetrics and Gynecological Nursing: Government College of Nursing Somajiguda, Hyderabad, T.SBlessy Madhuri100% (5)
- Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 9Th Edition Martini Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument56 pagesFundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 9Th Edition Martini Test Bank Full Chapter PDFgillanolympia4091253100% (9)
- Interpretation of MriDocument12 pagesInterpretation of Mrijimitkapadia100% (1)
- Jrsocmed00158 0011 PDFDocument6 pagesJrsocmed00158 0011 PDFWahyu SutrisnaNo ratings yet
- Homeo TipsDocument124 pagesHomeo TipsAditya uniyal100% (2)
- Chapter 9: The Biomechanics of The Human SpineDocument6 pagesChapter 9: The Biomechanics of The Human SpineHiraNo ratings yet
- Assessment For Massage TherapistDocument656 pagesAssessment For Massage Therapistbb_ul100% (6)
- Teach Yourself Pelvis and PerineumDocument22 pagesTeach Yourself Pelvis and PerineumSambili Tonny100% (1)
- Anatomy For FRCADocument38 pagesAnatomy For FRCAdrbartakke100% (3)
- Protocol For Symptoms HomeopathyDocument17 pagesProtocol For Symptoms HomeopathyUmer Shahzad ANSERNo ratings yet
- Co PDFDocument4 pagesCo PDFReginaJacobNo ratings yet
- Female Pelvis Anatomy and ChildbirthDocument4 pagesFemale Pelvis Anatomy and Childbirthvarshasharma05100% (1)