Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bones of The Body
Uploaded by
storm kit0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageThe document lists and describes various bones in the human body, including the phalanges in the fingers, femur in the thigh, radius and ulna in the forearm, scapula in the shoulder, mandible in the jaw, stapes in the ear, humerus in the upper arm, cranium in the skull, vertebrae in the spine, pelvis at the base of the spine, carpals in the wrist, patella as the kneecap, metacarpals between the wrist and fingers, tarsals in the ankle, ribs around the chest cavity, fibula and tibia in the lower leg, and clavicle as the collarbone.
Original Description:
Original Title
Bones of the Body (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document lists and describes various bones in the human body, including the phalanges in the fingers, femur in the thigh, radius and ulna in the forearm, scapula in the shoulder, mandible in the jaw, stapes in the ear, humerus in the upper arm, cranium in the skull, vertebrae in the spine, pelvis at the base of the spine, carpals in the wrist, patella as the kneecap, metacarpals between the wrist and fingers, tarsals in the ankle, ribs around the chest cavity, fibula and tibia in the lower leg, and clavicle as the collarbone.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageBones of The Body
Uploaded by
storm kitThe document lists and describes various bones in the human body, including the phalanges in the fingers, femur in the thigh, radius and ulna in the forearm, scapula in the shoulder, mandible in the jaw, stapes in the ear, humerus in the upper arm, cranium in the skull, vertebrae in the spine, pelvis at the base of the spine, carpals in the wrist, patella as the kneecap, metacarpals between the wrist and fingers, tarsals in the ankle, ribs around the chest cavity, fibula and tibia in the lower leg, and clavicle as the collarbone.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
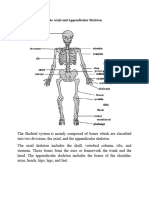
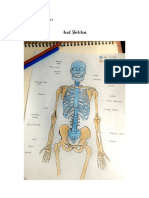
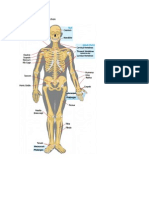
BONES OF THE BODY
Phalanges: any of the bones of the fingers.
Femur: the thighbone; the longest and strongest bone in the body.
Radius: lateral, shorter bone of the forearm.
Scapula: also called the shoulder blade; provides a foundation for joint function.
Mandible: the jawbone; holds the lower teeth in place; it is the strongest bone in
the face.
Stapes: located in the middle ear; the smallest bone in the body.
Humerus: upper arm bone; supports arm functions, such as lifting.
Cranium: the skull; encloses/ protects the brain.
Vertebrae: any of the 33 bones of the spinal column.
Pelvis: located near the base of the spine where the hind limbs/legs are attached;
this bone is separated in children and fused together in adults.
Ulna: inner, larger bone of the forearm.
Carpals: any of the 8 bones of the carpus/ wrist.
Patella: the kneecap; allows for knee extension
Metacarpals: the five bones of the metacarpus, located between the wrist and the
fingers.
Tarsals: the seven bones of the ankle joint.
Ribs: act as a protective cage for the heart, lungs, and liver; there are 12 pairs of
ribs.
Fibula: the outer, smaller bone located between the knee and the ankle.
Metatarsals: any of the bones located between the ankle and the toes.
Clavicle: also called the collarbone; allows your arms to hang freely.
Tibia: the inner, larger bone of the lower leg.
You might also like
- Skeletal SystemDocument28 pagesSkeletal SystemExequielNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesSkeletal SystemJovi Floresca AberinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Skeletal SystemDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Human Skeletal SystemKristine DomacenaNo ratings yet
- Jason Printable SkeletonDocument2 pagesJason Printable SkeletonAinhoaBjNo ratings yet
- Why The Skeleton System Is Important?: Pd4 December 8, 2015 Mr. WilliamsDocument2 pagesWhy The Skeleton System Is Important?: Pd4 December 8, 2015 Mr. Williamsapi-302705867No ratings yet
- What Is The Skeletal System?: Axial Skeleton AnatomyDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Skeletal System?: Axial Skeleton AnatomyJared RodriguezNo ratings yet
- The Parts Skeletal SystemDocument16 pagesThe Parts Skeletal SystemKathleenJoyGalAlmasinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Parts of The Skeletal SystemDocument29 pagesLesson 3 Parts of The Skeletal SystemReynaBaquillerNo ratings yet
- 12 The Need To Provide Bodily Shape and Support For Internal OrgansDocument2 pages12 The Need To Provide Bodily Shape and Support For Internal OrgansGrace Ann MeronNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Group 2Document2 pagesSkeletal System Group 2Joan Hilbero BermudoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System LessonDocument3 pagesSkeletal System LessonLiwayway De AsisNo ratings yet
- Choose From The Word Bank Below To Identify This Silly Skeleton's BonesDocument2 pagesChoose From The Word Bank Below To Identify This Silly Skeleton's Bonesbjy525No ratings yet
- Identifying Bones! PDFDocument2 pagesIdentifying Bones! PDFbjy525No ratings yet
- Skeletal System of FrogsDocument3 pagesSkeletal System of Frogsallelie marieNo ratings yet
- Vii. Laboratory/Diagnostic FindingsDocument29 pagesVii. Laboratory/Diagnostic Findingsgryph0nNo ratings yet
- Chapter VII - Human AnatomyDocument6 pagesChapter VII - Human AnatomyIndranil SinhaNo ratings yet
- The Human Skeleton: DifferentDocument5 pagesThe Human Skeleton: DifferentChae Mie Hnin EainNo ratings yet
- Choose From The Word Bank Below To Identify This Silly Skeleton's BonesDocument2 pagesChoose From The Word Bank Below To Identify This Silly Skeleton's BonesAinhoaBjNo ratings yet
- The Appendicular Skeleton and JointsDocument3 pagesThe Appendicular Skeleton and JointsNguyên HoàngNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesThe Skeletal SystemJessa Mae BanquirigNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Report PDFDocument86 pagesSkeletal System Report PDFMarian Elaine RufilaNo ratings yet
- Exp-4, To Study The General Features of Axial and Appendicular Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesExp-4, To Study The General Features of Axial and Appendicular Skeletal SystemKeshab KapoorNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageSkeletal SystemAlaysa Marie A. AzotesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lower Part of The BodyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lower Part of The BodyHikmah khanza PutriNo ratings yet
- Human Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesHuman Skeletal SystemDrexel DalaygonNo ratings yet
- английскийDocument2 pagesанглийскийВікторія СвєтлозароваNo ratings yet
- Organ System of GrasshopperDocument4 pagesOrgan System of GrasshopperPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Skeletal and Integumentary SystemDocument20 pagesSkeletal and Integumentary SystemAbby Gaile LopezNo ratings yet
- BPE211Document6 pagesBPE211Sayrah TahilNo ratings yet
- Skeleton Bones SongDocument3 pagesSkeleton Bones Songامنة العقيلNo ratings yet
- RJ SkeletonDocument19 pagesRJ Skeletonkimberly vasquezNo ratings yet
- Osteocytes - Bone Cells Classifications of Bones According To SizeDocument17 pagesOsteocytes - Bone Cells Classifications of Bones According To SizeA CNo ratings yet
- SkeletonprojectDocument4 pagesSkeletonprojectapi-299654825No ratings yet
- Clase 2 - Human Skeleton 2023Document6 pagesClase 2 - Human Skeleton 2023Tady BenavidesNo ratings yet
- L1 Skeletal SystemDocument40 pagesL1 Skeletal SystemMalibay ES (R III - Bulacan)No ratings yet
- L7 - Locomotion and Movement - Oct 8, 2019 PDFDocument47 pagesL7 - Locomotion and Movement - Oct 8, 2019 PDFKent WellsNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System AnatomyDocument6 pagesSkeletal System AnatomymanuelaristotleNo ratings yet
- What Is The Importance of The Skeletal System To Your BodyDocument11 pagesWhat Is The Importance of The Skeletal System To Your BodyKenny James CuberoNo ratings yet
- Midterm TopicDocument5 pagesMidterm Topicjamesbaguia315No ratings yet
- Frog SkeletonDocument1 pageFrog SkeletonPonchoi PintacasiNo ratings yet
- Osseous SystemDocument101 pagesOsseous Systemarpitsonone16No ratings yet
- The Human Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesThe Human Skeletal System201090178No ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Skull Vertebral Column/spinal Cord Thoracic CageDocument7 pagesSkeletal System: Skull Vertebral Column/spinal Cord Thoracic Cagehannah peloniaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Anatomy: Skull Mandible Temporal BoneDocument5 pagesSkeletal System Anatomy: Skull Mandible Temporal BoneMichael Villamor100% (1)
- DefinitionDocument8 pagesDefinitionJamesNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Week 1 3Document51 pagesSkeletal System Week 1 3Nichole Balao-asNo ratings yet
- The Appendicular SkeletonDocument12 pagesThe Appendicular SkeletonWani SweetnessmilkyteaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Anatomy: Excerpt From A LectureDocument4 pagesUnit 7: Anatomy: Excerpt From A LectureAnonymous Wfl201YbYoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReportingDocument17 pagesAnaphy ReportingKIA KHYTE FLORESNo ratings yet
- The Human Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesThe Human Skeletal Systemdplsss1No ratings yet
- The HandDocument4 pagesThe HandRoland Garcia Pelagio Jr.No ratings yet
- Materi Human SkeletonDocument6 pagesMateri Human SkeletonRicky UchihaNo ratings yet
- Maglaqui - Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesMaglaqui - Skeletal SystemNICOLE MAGLAQUINo ratings yet
- Skripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogDocument15 pagesSkripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogElizabetaNo ratings yet
- INGLES MEDICO I - Clase 1 - Human Body 2023Document26 pagesINGLES MEDICO I - Clase 1 - Human Body 2023alinelucioalvesNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument28 pagesSkeletal SystemAivee SumulongNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of The Skelital SystemDocument6 pagesStructure and Functions of The Skelital SystemLucshaan GaneshadasanNo ratings yet
- The Human Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesThe Human Skeletal System201090182No ratings yet