Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical Wires & Cables
Uploaded by
Joshua CarlCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Wires & Cables
Uploaded by
Joshua CarlCopyright:
Available Formats
Size of Wires wire and the cable installed is 25%
more than the load required.
Each application requires a certain
wire size for installation, and the Panel Feed Wires
right size for a specific application is
determined by the wire gauge. Panel feed cables are generally black
American wire gauge system. insulated THHN wire. These are
Common wire sizes are 10, 12 and used to power the main junction box
14 and the circuit breaker panels.
Wire Lettering Non-Metallic Sheathed Wires
The letters THHN, THWN, THW Non-metallic sheath wire, or Romex,
and XHHN represent the main is used in most homes and has 2-3
insulation types of individual wires. conductors, each with plastic
insulation, and a bare ground wire.
These letters depict the following NEC
requirements: Single Strand Wires
T – Thermoplastic insulation Single strand wire also uses THHN
H – Heat resistance wire, though there are other variants.
HH – High heat resistance (up to Each wire is separate and multiple
194°F) wires can be drawn together through
W – Water resistance suitable for a pipe easily.
wet locations
N – Nylon coating, resistant to Color Codes
damage by oil or gas
X – Synthetic polymer that is flame- Black : Hot wire, for switches or
resistant outlets.
Red : Hot wire, for switch legs. Also
Types of Electrical Wire for connecting wire between 2
hardwired smoke detectors.
Triplex Wires Blue and Yellow : Hot wires, pulled
in conduit. Blue for 3-4 way switch
Triplex wires are usually used in application, and yellow for switch
single-phase service drop legs to control fan, lights etc.
conductors, between the power pole White : Always neutral.
and weather heads. Green and Bare Copper : Only for
grounding.
Main Feeder Wires
Wire Gauge, Ampacity and
Main power feeder wires are the
wires that connect the service
Wattage Load
weather head to the house. They’re
made with stranded or solid THHN To determine the correct wire, it is
important to understand what
ampacity and wattage a wire can which is further surrounded by a
carry per gauge. tubular conducting shield, and might
also feature an outer sheath for extra
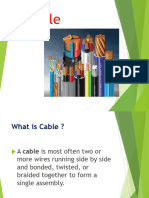
Types of Electrical Cables insulation.
Non-Metallic Sheathed Cable Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable
These cables are also known as non- Like the name suggests, this type
metallic building wire or NM cables. consists of two wires that are twisted
They feature a flexible plastic jacket together. The individual wires are
with two to four wires (TECK cables not insulated, which makes this cable
are covered with thermoplastic perfect for signal transmission and
insulation) and a bare wire for video applications.
grounding.
Ribbon Cable
Underground Feeder Cable
Ribbon cables are often used in
These cables are quite similar to NM computers and peripherals, with
cables, but instead of each wire various conducting wires that run
being individually wrapped in parallel to each other on a flat plane,
thermoplastic, wires are grouped leading to a visual resemblance to
together and embedded in the flat ribbons.
flexible material.
Direct-Buried Cable
Metallic Sheathed Cable
Also known as DBCs, these cables
Also known as armored or BX are specially-designed coaxial or
cables, metal-sheathed cables are bundled fiber-optic cables, which do
often used to supply mains electricity not require any added sheathing,
or for large appliances. insulation or piping before being
buried underground.
Multi-Conductor Cable
Twin-Lead Cable
This is a cable type that is commonly
used in homes, since it is simple to These are flat two-wire cables that
use and well-insulated. Multi- are used for transmission between an
conductor or multi-core (MC) cables antenna and receiver, like TV and
feature more than one conductor, radio.
each of which is insulated
individually. Twinaxial Cable
Coaxial Cable This is a variant of coaxial cables,
which features two inner conductors
A coaxial (sometimes heliax) cable instead of one and is used for very-
features a tubular insulating layer short-range high-speed signals.
that protects an inner conductor
Paired Cable
With two individually insulated
conductors, this cable is normally
used in DC or low-frequency AC
applications.
Twisted Pair
This cable is similar to paired cables,
but the inner insulated wires are
twisted or intertwined.
You might also like
- Annex A Sample Training Plan Electrical Installation and Maintenance NC IiDocument5 pagesAnnex A Sample Training Plan Electrical Installation and Maintenance NC IiNer Mangaron100% (1)
- Home Electrical WiringDocument51 pagesHome Electrical Wiringsmanmugen100% (2)
- Electrical Load ComputationDocument4 pagesElectrical Load ComputationAllen Velasquez Mangaoil87% (15)
- 18th BS7671 Practice Paper 1 PDFDocument6 pages18th BS7671 Practice Paper 1 PDFdvt2365No ratings yet
- Activity 01 - San Pedro CJBDocument48 pagesActivity 01 - San Pedro CJBColeen Jonah San PedroNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Wires and CablesDocument69 pagesGrade 10 Wires and Cablesedmondimalanta34No ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.2-1Document4 pagesInformation Sheet 1.2-1Gen FuNo ratings yet
- Wires and CablesDocument5 pagesWires and Cablesbolt sparkNo ratings yet
- 11Document3 pages11Kurimaw SyNo ratings yet
- Electrical Wires and Cables TypesDocument10 pagesElectrical Wires and Cables TypesMarlo AristorenasNo ratings yet
- Market Survey On ElectricalsDocument16 pagesMarket Survey On ElectricalsGurbaksh SinghNo ratings yet
- Services CabelesssssDocument14 pagesServices Cabelessssssaransh yadavNo ratings yet
- Types of Electrical Wires and CablesDocument27 pagesTypes of Electrical Wires and CablesTaguno ChrisNo ratings yet
- Unit-VIII (Electrical Wiring) : Different Types of Conductors Used For Electrical WiringDocument26 pagesUnit-VIII (Electrical Wiring) : Different Types of Conductors Used For Electrical WiringMonte CarloNo ratings yet
- Electrical Conduits & Fittings: Protect Electrical Cables and WiresDocument18 pagesElectrical Conduits & Fittings: Protect Electrical Cables and WiresA Ma RaahNo ratings yet
- Wires and CablesDocument47 pagesWires and CablesMadhushree RNo ratings yet
- Assigntment No.2 - Types of Wires and CablesDocument5 pagesAssigntment No.2 - Types of Wires and CablesCiara MaryNo ratings yet
- 26 Type of Electrical Cables LT, HT, ST, EHT, PVC, XLPE, Oil, FlatDocument7 pages26 Type of Electrical Cables LT, HT, ST, EHT, PVC, XLPE, Oil, FlatSubbuNo ratings yet
- Electrical CABLE AND WIRINGDocument24 pagesElectrical CABLE AND WIRINGArchitects Of BIT MesraNo ratings yet
- Wires & CablesDocument23 pagesWires & CablesJohn E. T.No ratings yet
- Rohini 69038786578Document4 pagesRohini 69038786578Avinash SinghNo ratings yet
- Date: Page No.: Miracle Educational Society Group of InstitutionsDocument20 pagesDate: Page No.: Miracle Educational Society Group of InstitutionsVLSS Phani REDDYNo ratings yet
- Multitester: Computer System ServicingDocument8 pagesMultitester: Computer System ServicingArthur CapawingNo ratings yet
- Cabling and Cable JoinDocument24 pagesCabling and Cable JoinGopi AravindNo ratings yet
- Electrical Wires CablesDocument17 pagesElectrical Wires Cablesspoti fyiaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Electrical Wires and Cables: Student NameDocument11 pagesDifferent Types of Electrical Wires and Cables: Student NameKiller AviNo ratings yet
- Types of Cables-3Document16 pagesTypes of Cables-3Grace ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- Ballast Ch12 ElectricalDocument19 pagesBallast Ch12 ElectricalSk Abdul RavoofNo ratings yet
- Review 2 ElectricalWiringDocument11 pagesReview 2 ElectricalWiringPogii AkooNo ratings yet
- Types of Electrical SystemDocument72 pagesTypes of Electrical SystemLauro CanceranNo ratings yet
- Electrical Wire LabelingDocument2 pagesElectrical Wire LabelingAlliver SapitulaNo ratings yet
- LE - Wires and CablesDocument8 pagesLE - Wires and CablesMailee CañeteNo ratings yet
- Types of Electrical SystemDocument72 pagesTypes of Electrical SystemJade NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Cable Types, Sizes, and Installation - TopcableDocument13 pagesElectrical Cable Types, Sizes, and Installation - TopcableNathan NiuNo ratings yet
- Questions: 1) Write A Short Research Paper On The FollowingDocument13 pagesQuestions: 1) Write A Short Research Paper On The FollowingClifford Eli AfedohNo ratings yet
- Electrical - CT111L - LEARNING-MODULEDocument45 pagesElectrical - CT111L - LEARNING-MODULEmaling malinglingNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Electrical Wires and Cables: Student NameDocument11 pagesDifferent Types of Electrical Wires and Cables: Student NameKiller AviNo ratings yet
- 05 18 Jones DEDocument14 pages05 18 Jones DEDe AbstruseNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log 2Document8 pagesDaily Lesson Log 2Emmanuel GallidoNo ratings yet
- Types of CablesDocument19 pagesTypes of CablesJimmy Makiling PamugasNo ratings yet
- Determine Best Fit Topology LO1 Part-IIDocument49 pagesDetermine Best Fit Topology LO1 Part-IIBekaNo ratings yet
- Communication 3 MidtermDocument12 pagesCommunication 3 MidtermSumangil, Maria Margarita P.No ratings yet
- The Complete Guide To WiringDocument52 pagesThe Complete Guide To WiringEhab SaberNo ratings yet
- EIM 4 Lesson 6 Conductors For General WiringDocument65 pagesEIM 4 Lesson 6 Conductors For General WiringVictor RosalesNo ratings yet
- Cable (Sizing and Calculation)Document31 pagesCable (Sizing and Calculation)Ajaysingh SolankiNo ratings yet
- InstallationDocument180 pagesInstallationtilahuntenaye4No ratings yet
- Cabling: Presented by Wisdom, Patsika, GreenDocument31 pagesCabling: Presented by Wisdom, Patsika, GreenShione T MundawararaNo ratings yet
- Overhead and Underground Distribution Lines: April Rose D. Herrera EE-5ADocument40 pagesOverhead and Underground Distribution Lines: April Rose D. Herrera EE-5AisraeljumboNo ratings yet
- Covered Conductor 3 PPT 1Document29 pagesCovered Conductor 3 PPT 1Gaurav Agarwal100% (1)
- Electrical Cable Types, Sizes, and Installation: Electric Cables Voltage Índice de ContenidosDocument8 pagesElectrical Cable Types, Sizes, and Installation: Electric Cables Voltage Índice de ContenidosEmre DalgicNo ratings yet
- 1armoured CableDocument23 pages1armoured CableScala PinkerNo ratings yet
- Conductor, Insulator and Other Wiring DevicesDocument38 pagesConductor, Insulator and Other Wiring DevicesBoxtrolls MushroomNo ratings yet
- Engineering Workshop Practices Lecture 6Document44 pagesEngineering Workshop Practices Lecture 6Mueen FaisalNo ratings yet
- Electrical System - Part2Document23 pagesElectrical System - Part2LARA JOANNE DORIANo ratings yet
- Twisted Pair Cable: ExplanationDocument14 pagesTwisted Pair Cable: Explanationarslangul7No ratings yet
- 5 Cables and Cable JointsDocument14 pages5 Cables and Cable JointsCOLLINS KIPRUTONo ratings yet
- Electrical Wiring WorkbookDocument40 pagesElectrical Wiring Workbookrob yeley100% (3)
- Cable: Electrical System TN-S Grand Coulee Dam Fire Test Sweden FireDocument7 pagesCable: Electrical System TN-S Grand Coulee Dam Fire Test Sweden FireSanjeev GuptaNo ratings yet
- Types of CableDocument28 pagesTypes of Cabletin mg mgNo ratings yet
- Power Cable: Distribution, Sizing and MergingDocument59 pagesPower Cable: Distribution, Sizing and MergingM.AbbasNo ratings yet
- Cables, Wire, Electrical Terminal Connectors & AccessoriesDocument33 pagesCables, Wire, Electrical Terminal Connectors & AccessoriesmentongNo ratings yet
- ASCO Series 300 D-Design 30-230A, Oper Manual, 381333-228Document20 pagesASCO Series 300 D-Design 30-230A, Oper Manual, 381333-228Kevin DampmanNo ratings yet
- Current Limiting Appen4Document7 pagesCurrent Limiting Appen4Sabri GunaydinNo ratings yet
- White Rodgers 1687 9 Refrigeration Temperature Controls Instruccion de InstalacionDocument6 pagesWhite Rodgers 1687 9 Refrigeration Temperature Controls Instruccion de InstalacionAbelNo ratings yet
- Dos and DontsDocument4 pagesDos and DontsAjayNo ratings yet
- Electrical Estimate & BOQDocument22 pagesElectrical Estimate & BOQkiran raghukiranNo ratings yet
- SATIP-P-116-02 Rev 7 FinalDocument3 pagesSATIP-P-116-02 Rev 7 FinalHatemS.MashaGbehNo ratings yet
- Nec ExplainDocument13 pagesNec ExplainHusam Al-BehadiliNo ratings yet
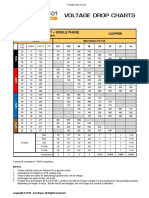
- Single Phase Voltage Drop ChartsDocument2 pagesSingle Phase Voltage Drop ChartsFranklinNo ratings yet
- 8118 28 Im WLANHandsetRackCharger 8AL90830ENAA 1 enDocument15 pages8118 28 Im WLANHandsetRackCharger 8AL90830ENAA 1 enSuporte [CS Telecom]No ratings yet
- GFCI BrochureDocument28 pagesGFCI Brochurewhitefang828100% (2)
- Change Order - Rev2 - 44873036-001Document5 pagesChange Order - Rev2 - 44873036-001Hugo MoralesNo ratings yet
- Schools Division of Parañaque City Technology and Livelihood Education Electrical Installation & Maintenance 9 Quarter 4 Week 1 - 2 Electrical Supplies and MaterialsDocument4 pagesSchools Division of Parañaque City Technology and Livelihood Education Electrical Installation & Maintenance 9 Quarter 4 Week 1 - 2 Electrical Supplies and MaterialsWinsher PitogoNo ratings yet
- Katalog MCB Schneider 2020Document12 pagesKatalog MCB Schneider 2020Fatmala Sumardianti100% (3)
- Lifts, Escalators and Similar EquipmentDocument9 pagesLifts, Escalators and Similar EquipmenttemamNo ratings yet
- Ar Material Requirement - Bhubaneshwar - Odisha - Large - ElectricalDocument92 pagesAr Material Requirement - Bhubaneshwar - Odisha - Large - ElectricalAryan DashNo ratings yet
- Trane MCV090-120 Electrical DiagramDocument1 pageTrane MCV090-120 Electrical DiagramcoronaqcNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent Coordination Setting Guidelines ConductorsDocument5 pagesOvercurrent Coordination Setting Guidelines ConductorsMrNo ratings yet
- Pumphouse Cables List: S.No Description RMT Drum NoDocument3 pagesPumphouse Cables List: S.No Description RMT Drum Noramkumar meilNo ratings yet
- Diagram PC3.3 For QSK60-P8Document20 pagesDiagram PC3.3 For QSK60-P8Trần Quang ToánNo ratings yet
- Draft Lembar PenilaianDocument6 pagesDraft Lembar PenilaianNunu NugrahaNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Monitoring Izin Kerja (Working Permit) : Laporan Bulanan K3Document89 pages2.8 Monitoring Izin Kerja (Working Permit) : Laporan Bulanan K3marchelinda ayuningtyasNo ratings yet
- FCE20 CompletoDocument6 pagesFCE20 CompletoRig 25 Sr. ElectricianNo ratings yet
- Umidificator PDFDocument3 pagesUmidificator PDFPC MediaPointNo ratings yet
- Schedule of LoadsDocument46 pagesSchedule of LoadsDel James LambongogNo ratings yet
- Conducting in Service Safety Testing of Electrical Cord ConnectedDocument82 pagesConducting in Service Safety Testing of Electrical Cord Connectedkassa mamo100% (1)
- Session Plan Core 1Document25 pagesSession Plan Core 1Jdeified Dimol100% (1)
- 11Document4 pages11reeNo ratings yet