Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PROBABLITY
Uploaded by
kkoolwal17Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PROBABLITY
Uploaded by
kkoolwal17Copyright:
Available Formats
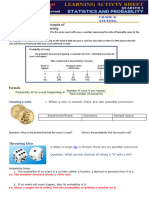
PROBABLITY
Probablity is the likelihood that the event will occur.
Two Conditions
Value is between 0 and 1
Sum of the probabilities all event must be 1
Basic terminologies
Experiment: An experiment is like a test or a trial where you do something
to see what happens. For example, flipping a coin to see if it lands heads or
tails is an experiment.
Trial: A trial is just one attempt or one time you do the experiment. If you
flip a coin five times, each flip is a trial.
Event (outcomes): An event is what you're looking for or what you want to
happen during the experiment. For example, in rolling a dice, getting a 6 is
an event.
Sample Space (set of all possible values): The sample space is like a list of all
the things that could possibly happen in your experiment. If you roll a dice,
the sample space includes the numbers 1 through 6 because those are all
the possible outcomes.
Mutually Exclusive Event: When events are mutually exclusive, it means
they can't happen at the same time. For example, in a game of chance, you
can't win and lose at the same time.
Equally Likely Event: Equally likely events are those where each outcome in
the sample space has the same chance of happening. In a fair coin toss,
getting heads or tails is equally likely because each has a 50% chance.
Independent Event: Independent events are like trials that don't affect each
other. For example, if you flip a coin and then roll a dice, the outcome of the
coin flip doesn't change what happens when you roll the dice.
Dependent Event: Dependent events are like trials that do affect each other.
For instance, if you draw a card from a deck and don't put it back, the
chances of drawing a certain card change because one card has already
been taken out.
You might also like
- Probability with Permutations: An Introduction To Probability And CombinationsFrom EverandProbability with Permutations: An Introduction To Probability And CombinationsNo ratings yet
- Probability: Probability Is A Branch of Mathematics That Deals With Calculating The Likelihood of A Given Event'sDocument4 pagesProbability: Probability Is A Branch of Mathematics That Deals With Calculating The Likelihood of A Given Event'sjhanelleNo ratings yet
- Basic Terminology in ProbabilityDocument4 pagesBasic Terminology in ProbabilityKashaf Amjad100% (1)
- ProbabilityDocument23 pagesProbabilityMusicNo ratings yet
- Probability: Tossing A CoinDocument4 pagesProbability: Tossing A Coinxanga007No ratings yet
- Probability-Math Is FunDocument5 pagesProbability-Math Is Funapi-233663523No ratings yet
- Random Experiment - Types of EventsDocument2 pagesRandom Experiment - Types of EventsRidwan MohsinNo ratings yet
- 8401 Assignment No 1Document12 pages8401 Assignment No 1Urooj KhanNo ratings yet
- Probability, Types and RulesDocument6 pagesProbability, Types and RulesNutukurthi Venkat RamjiNo ratings yet
- Probability DistributionDocument88 pagesProbability DistributionJay KumarNo ratings yet
- Stat & Prob - Learning Activity Sheets - 3rd - Basic Concepts of ProbabilityDocument3 pagesStat & Prob - Learning Activity Sheets - 3rd - Basic Concepts of ProbabilityQueeny CabasonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Probability and Normal DistributionDocument12 pagesLesson 1 Probability and Normal DistributionJOHN ALIDONNo ratings yet
- Slides CohenDocument27 pagesSlides CohenMudasserAliKhanNo ratings yet
- Week 8 (Prob & Prob Dist)Document26 pagesWeek 8 (Prob & Prob Dist)Sucklaj ShahidNo ratings yet
- Maths Probability Investigatory ProjectDocument15 pagesMaths Probability Investigatory ProjectPalash KurkuteNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Division of Mandaue CityDocument15 pagesDepartment of Education: Division of Mandaue CityEugen AgbayNo ratings yet
- Probability in Everyday LifeDocument11 pagesProbability in Everyday LifeMwendalubi Chiholyonga0% (1)
- Probability 120904030152 Phpapp01Document25 pagesProbability 120904030152 Phpapp01gioluisreyes1No ratings yet
- Probability: Examples of EventsDocument6 pagesProbability: Examples of EventsALINo ratings yet
- Basics of ProbabilityDocument19 pagesBasics of ProbabilityanamiyababyNo ratings yet
- Probability DefinitionsDocument8 pagesProbability DefinitionsMahtab UddinNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument126 pagesProbabilitydawit tesfaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document18 pagesChapter 13Pawan NayakNo ratings yet
- Different Types of ProbabilitiesDocument16 pagesDifferent Types of Probabilitieslunok mariitNo ratings yet
- Probability and SamplingDocument20 pagesProbability and SamplingTsitsi AbigailNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - ProbabilityDocument5 pagesGrade 10 - Probabilitygurusamyrenuga4No ratings yet
- Introduction To StatisticsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To StatisticsStephen John NicolasNo ratings yet
- Unit-8 Block 4 Statistics in PsychologyDocument32 pagesUnit-8 Block 4 Statistics in PsychologyRashmi NNo ratings yet
- Probability and Stochastic ProcessesDocument24 pagesProbability and Stochastic ProcessesAbdiasis Abdallah JamaNo ratings yet
- Combinatorics and ProbabilityDocument17 pagesCombinatorics and ProbabilityHedi mar NecorNo ratings yet
- TiMMS (Probability)Document14 pagesTiMMS (Probability)Ahmed AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Probability Notes EceDocument5 pagesProbability Notes EceArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Probability CalculationDocument12 pagesProbability CalculationAlishba KhanNo ratings yet
- Concepts of ProbabilityDocument32 pagesConcepts of ProbabilityRushina SinghiNo ratings yet
- New Probability PDFDocument14 pagesNew Probability PDFSunita SahooNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Literacy. Topic: Probability. Grade 11 Begin With TerminologyDocument2 pagesMathematics Literacy. Topic: Probability. Grade 11 Begin With TerminologyImtiyaazmoosaNo ratings yet
- Probability NotesDocument2 pagesProbability NotesRajesh Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Theory of ProbabilityDocument51 pagesTheory of ProbabilityVeronica Sanders57% (7)
- Probability: Sample SpaceDocument1 pageProbability: Sample SpaceIvan Kent Paga ParajesNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Tutorials Concepts of Probability in Real Life ScenariosDocument121 pagesUnit 3 Tutorials Concepts of Probability in Real Life Scenariosbt2q68txkbNo ratings yet
- AbshDocument8 pagesAbshabsharaliks82No ratings yet
- Probability: ExperienceDocument12 pagesProbability: Experiencevidyamane23No ratings yet
- Statistics For ManagementDocument15 pagesStatistics For ManagementSuresh PeguNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: ProbabilityDocument13 pagesChapter 2: ProbabilityMatthew MiradorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Concept of ProbabilityDocument30 pagesChapter 5. Concept of ProbabilityrahafNo ratings yet
- To Lecture On Probability & StatisticsDocument8 pagesTo Lecture On Probability & StatisticsAbhay KumarNo ratings yet
- Probability!: Notes Examples Sample ProblemsDocument12 pagesProbability!: Notes Examples Sample ProblemsIrfan BalochNo ratings yet
- Presented By, Name-Ankita Rath ROLL NO-17STAT008 P.G. Dept. of Statistics 2 YrDocument30 pagesPresented By, Name-Ankita Rath ROLL NO-17STAT008 P.G. Dept. of Statistics 2 YrSoumya Ranjan SatapathyNo ratings yet
- Probability and StatisticsDocument35 pagesProbability and Statisticsapi-20012397100% (1)
- On ProbabilityDocument13 pagesOn ProbabilitySridhar PantNo ratings yet
- 3rd Lecture BSCS-IDocument16 pages3rd Lecture BSCS-IHamza GamingNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument2 pagesProbabilityPranav ShindeNo ratings yet
- Name: Date: Grade & Section: Group #. - ScoreDocument2 pagesName: Date: Grade & Section: Group #. - ScoreWalter ManliguezNo ratings yet
- Concepts of ProbabilityDocument32 pagesConcepts of ProbabilityRushina SinghiNo ratings yet
- SRDS Lecture 1 Brief Introduction To ProbabilityDocument42 pagesSRDS Lecture 1 Brief Introduction To Probabilityprraaddeej chatelNo ratings yet
- Module 5 BCC ProbabilityDocument10 pagesModule 5 BCC ProbabilityJean Rose RamillaNo ratings yet
- Probability TheoryDocument221 pagesProbability TheoryJoy Hazel RomeroNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument55 pagesProbabilitypranayNo ratings yet
- Probability PDFDocument56 pagesProbability PDFRameshKumarMuraliNo ratings yet
- Percentage CHDocument3 pagesPercentage CHsani devNo ratings yet